Assessment of association between anthropometric indices and individuals’Mizaj
Hamid Reza Sheikh Roshandel,Fateme Ghadimi,Roksana Mirkazemi
1Research Institute of Nutritional Sciences and Traditional Medicine, Taamasrar Institute, Tehran 1461744366, Iran. 2Farzanegan Nik Andish Institute for the Development of Knowledge and Technology,Tehran 1471743893,Iran.
Abstract Objectives:The whole concept of diagnosis and treatment of diseases in Persian medicine is based on Mizaj; accurate identification of Mizaj is crucial in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases in this medicine. The objective of this study was to assess the association between anthropometric measures and individuals’ Mizaj. Methods: The study design was cross-sectional. The data collection tool included the Innate Nature Assessment Tool and Body analyzer (inbody model 570) for measuring anthropometric indices. The anthropometric indices included height, body mass index, total body protein, minerals, fat mass, intracellular water, extracellular water, bone mineral, cell mass level and mid-arm circumference. Statistical package for social sciences version 19.0 for windows (IBM Corporation, New York, NY, United States) was used for analysis. Settings: The setting of the study was Tehran, Iran.The study was conducted among 240 young individuals without any history of chronic or acute and congenital diseases working in an IT company during the year 2014-2015 in Tehran, Iran. Results: 39.2% (n = 94) of participants had sanguine Mizaj and a similar proportion had phlegmatic Mizaj. 5% (n = 12) had melancholic Mizaj and 12.9%(n=31)had choleric Mizaj.The rest has a combined Mizaj of sanguine-choleric.There was a significant association between all the anthropometric indices (Height, body mass index, total body protein, total body minerals, bone minerals, extracellular water and intracellular water and body cell mass) ( P = 0.000 for all the indices), except mid-arm circumference measure(P= 0.461). Conclusions: The study results showed that there was a significant association between almost all anthropometric measures and Mizaj of individuals, and the pattern of association was consistence with the literature of Persian medicine about characteristics of Mizaj of individuals.
Keywords:anthropometric; indices; Mizaj; temperament; association
Background
Persian medicine originated from Greek/Unani medicine and evolved during Arab civilization [1].
It is based on the four elements theory (everything is made up of fire, weather, water, and soil). These four elements combine together to produce unique qualities, which are called “Temperaments”(Mizaj).Mizajis the representation of the quality of each element[2-4]. The word temperament is the English translation ofMizaj,derived from the Latin word “Tempero”, meaning to mix together[5-8].
Mizajforms the basic concept of Persian medicine and determines for nutrition, growth, and metabolism of an organism, health maintenance, and disease prevention [2-11]. In this medicine, the etiology and pathology of most diseases and their diagnosis and treatment are based on theMizajof individuals [1, 12-14].
Mizajis a unique quality and the number ofMizajis equal to the number of living individuals in the world [2, 4]. However, for ease of assessment, all kinds ofMizajhave been divided into nine major groups based on different degrees of warmness and wetness and include one moderateMizajin the central equilibrium or medium region of the four spectra ofMizajand four simpleMizaj(warm, cold,moist, and dry) and four combinedMizaj(warm and moist,warm and dry, cold and moist, cold and dry) [15, 16].
Avicenna and other famous scholars of Persian medicine ascribed different characteristics to different types ofMizaj, including individuals’ face, appearance, and behavior, for example, the volume of muscle mass of the body,or the speed of growth of hair and nails in an individual or skin color,level of activities, rhetoric skill,defecation status, and even individual traits and personality like being wise or lazy, indecency, imagination and optimism [2, 8, 17, 18].
In ancient times, these characteristics were the basis for the identification ofMizajby physicians and even usual people. There are two types ofMizaj: innate instinctive and individuals are born with it,and acquired, which is affected through life due to nutrition,problems, complications, diseases and so on [2, 6, 7].
Recently, Roshandel et al. have developed an instrument for determiningMizajof individuals that can be used as the basis for the identification ofMizajat present [16]. Another study shows that this tool had a high level of consistency with the experts’ diagnosis ofMizajof individuals [17]. This questionnaire comprises 26 items for identifying innateMizajand 56 items for identifying acquiredMizajof individuals.
As accurate identification ofMizajof individuals is crucial in the detection and treatment of diseases in Persian Medicine, and morphology is one of the main characteristics ofMizajof individuals,which can be assessed easily without the need for a sophisticated instrument [18]. Therefore, this study was conducted in order to assess the association between anthropometric measures and individuals’Mizaj.
Methods
Study design
A cross-sectional study was conducted among 240 young, healthy individuals to assess the association between anthropometric measures and theirMizajduring 2014-2015, in Tehran, Iran.
Participants
The study participants included 240 individuals working in an IT company during 2014-2015 in Tehran, Iran. The inclusion criteria included not having a history of any congenital or identified chronic disease. The existence of any chronic illness or co-morbidity was identified based on the report of the participants.Those with a history of any identified chronic or acute disease and those who did not have consent to participate in the study were excluded from the study. As the IT company was developed recently, all the recruited individuals were young below 35 years of age. This sample was selected because of the convenience of the researchers.
Data collection tool
To identifyMizajof participants, Innate Nature Assessment Tool 16 and to collect the morphologic indices measures of individuals body analyzer (inbody model 570) was used.
Innate Nature Assessment Tool 16 is a standard tool for assessing the innateMizaj; the previous study 16 showed a content validity index and content validity ratio of one for both measures and a high level of reliability (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.912) for this tool. This tool was made of 26 items which assessed the color of skin (in the covered section of the body), the color of hair (at the time of adolescence or childhood), the structure of the face, the forehead size, the ratio of eyes to face,the color of the iris,color and status of the sclera,the size and shape of nose and nostril, shape and size of lips, mouth, and cheeks and their ratio to face, the shape of the chin, length of the tongue, length of neck, diameter of the neck, the status of vessels (at room temperature), the shape of muscles of arms, shape of hands,appears of shoulders, length of shoulders and its diameter before any cosmetic operation. Each question had four options related to one of the fourMizaj. Each question had a score of 1, and therefore there were a total of 26 scores. TheMizajwith the highest score among otherMizajhas been considered the dominantMizajof an individual(Figure 1).
The anthropometric indices included height, total body protein,total body minerals, total body fat, body mass index (BMI),intracellular water, extracellular water, complete body bone mineral,total body cell mass, and mid-arm circumference.
The anthropometric indices were measured by using the inbody composition analyzer (model 570). Inbody composition analyzer is one of the most precise, accurate, and convenient bioelectrical impedance analysis body composition analyzers. The measurement was done as per the developed guideline by the InBody company. The test was conducted before a meal.Subjects were advised not to do any exercise or take a shower or bath before the measurements, and stand still for about 5 minutes, do not take measures during the menstrual cycle.Also,the test was conducted at normal temperatures(20-25)℃.
Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed using statistical package for social sciences version 19.0 for windows (IBM Corporation, New York, NY,United States). Descriptive statistics like mean (standard deviation)and frequency (percentage) were used. The Chi-square and ANOVA tests were used to assess the association between different studied variables andMizajof individuals.
To assess the association between the anthropometric measures andMizajof the individuals, one-way ANOVA and Tukey Post hoc statistic test was used. The significant level was set atP< 0.05.
Results
Table 1 shows the characteristics of participants and theirMizaj. The mean age of participants was 33.6 ± 8.3; the mean BMI was 25.1 ±4.3. Around half of the participants, 50.8% (n = 122), were males.39.2% (n = 94) of participants had sanguineMizajand a similar proportion had phlegmaticMizaj. 5%(n =12) had melancholicMizajand 12.9%(n=31)had cholericMizaj.The rest has a combinedMizajof sanguine-choleric.
Table 2 shows an association between anthropometric measures andMizajof Individuals. There was a significant association between all the anthropometric indices (Height, BMI, total body protein, total body minerals, bone minerals, extracellular water and intracellular water, and body cell mass) (P= 0.000 for all the indices), except mid-arm circumference measure (P= 0.461).
Mean height was highest among individuals with SanguineMizaj(176.9 cm) and lowest among individuals with melancholicMizaj(159.6 cm). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between cholericMizajindividuals and phlegmatic and MelancholicMizajindividuals (P= 0.000), between sanguineMizajindividuals and phlegmaticMizajindividuals (P= 0.000), between phlegmaticMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals(P= 0.000), and between choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals and melancholicMizajindividuals (P= 0.000).

Figure 1 Actual innate nature assessment questionnair
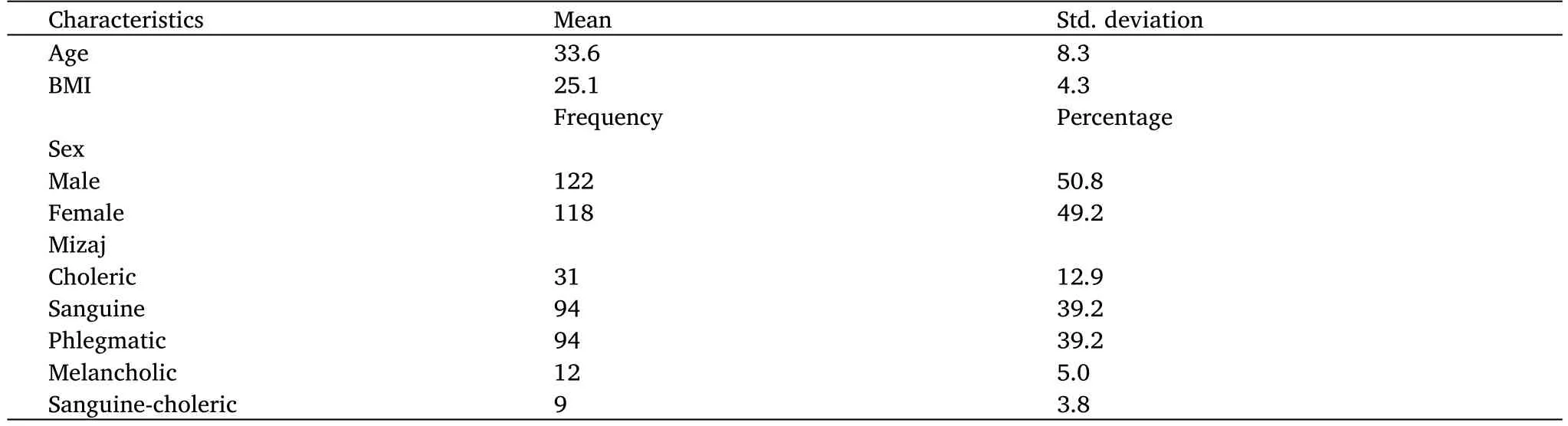
Table 1 Characteristics of participants
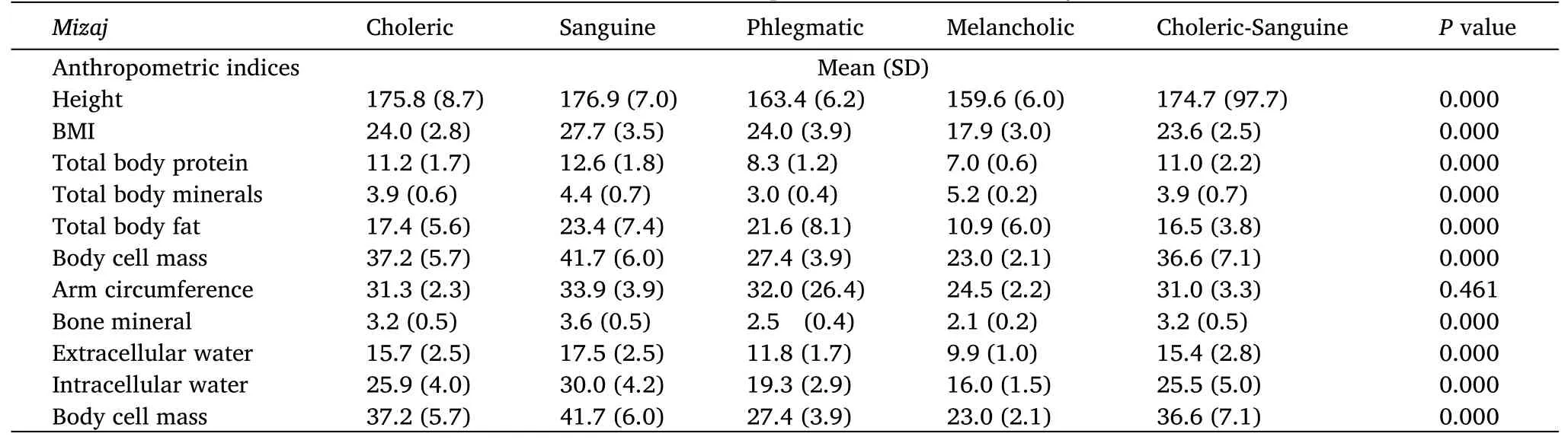
Table 2 Association between anthropometric indices and Mizaj of individual
Mean BMI was highest among individuals with sanguineMizaj(27.7 kg/m2) and lowest among individuals with melancholicMizaj(17.9 kg/m2). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between cholericMizajindividuals and sanguine and melancholicMizajindividuals (P= 0.000), between sanguineMizajindividuals and melancholicMizajindividuals all other types ofMizaj(P< 0.05).
Mean total body protein was highest among individuals with sanguineMizaj(12.6 kg) and lowest among individuals with melancholicMizaj(7.0 kg). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between all the groups (P< 0.05), except between cholericMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals (P= 0.999).
Mean total body minerals were highest among individuals with melancholicMizaj(5.2 kg) and lowest among individuals with phlegmaticMizaj(3.0 kg). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between all the groups (P< 0.05), except between cholericMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals (P= 1.000) and sanguineMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals (P= 0.067).
Mean body fat mass was highest among individuals with sanguineMizaj(23.4 kg) and lowest among individuals with melancholicMizaj(10.9 kg). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between all the groups(P<0.05),except between cholericMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals(P=1.000)and sanguineMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals (P= 0.067).
Mean intracellular water was highest among individuals with SanguineMizaj(30.0 kg) and lowest among individuals with MelancholicMizaj(16.0 kg). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between sanguineMizajindividuals and choleric and melancholicMizajindividuals (P= 0.000) and between phlegmaticMizajindividuals and choleric and melancholicMizajindividuals (P< 0.05).
Mean extracellular water was highest among individuals with SanguineMizaj(17.5 kg) and lowest among individuals with MelancholicMizaj(9.9 kg). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between all the groups (P< 0.05), except between cholericMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals(P=0.990).
Mean bone mineral was highest among individuals with sanguineMizaj(3.6 kg) and lowest among individuals with melancholicMizaj(2.1 kg). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between all the groups(P<0.05),except between cholericMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals(P=1.000)and sanguineMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals(P=0.072).
Mean body cell mass was highest among individuals with SanguineMizaj(41.7 kg) and lowest among individuals with melancholicMizaj(23.0 kg). Tukey test showed that between groups difference was significant between all the groups(P<0.05),except between cholericMizajindividuals and choleric-sanguineMizajindividuals (P=0.998).
Discussion
Traditional medicine has been essential in treating disease since long ago and recently has re-emerged and is gaining importance in treating illness, especially chronic diseases, in many countries, including Iran[9,10].As the whole concept of diagnosis and treatment of diseases in Persian Medicine is based onMizaj, therefore developing a simple method for accurate identification ofMizajis important. Recently,some attempts were made to develop questionnaires forMizajassessment [15,16].
However,the instruments used to identifyMizajwere sophisticated,subjective, and hard to apply. Therefore, this study attempted to assess the association betweenMizajand anthropometric measures in the hope of developing new indices for measuringMizajof individuals.The young (mean age 33.6) and healthy individuals with a BMI at normal/slightly overweight level (25.1) employees of an IT company were selected for the study.
This study showed that sanguineMizajwas associated with significantly higher height,weight,BMI,total body protein level,body fat level,intracellular water level,extracellular water level,total body bone mineral, and whole body cell mass compared to individuals with other types ofMizaj. SanguineMizajwas described as having warm and moist nature and in Persian medicine it was mentioned that a high level of muscles (protein content) is associated with warm nature [2].Also, sanguineMizajis moist; therefore, extra and intracellular water was more in thisMizaj.
PhlegmaticMizajwere associated with a high level of fat mass.Some contents in Persian medicine attribute the accumulation of fat in the human body to his/her cold and moist nature [2-16, 19, 20]. In Persian medicine, cold and moist nature has been attributed to bulky tissues (with low density), such as fat and warm nature to condensed tissues(with high density), such as muscles [7].
This study showed that melancholicMizajwas associated with the lowest level of height, weight, BMI, protein, fat mass, extracellular water,bone mineral,and body cell mass.Individuals with melancholicMizajhad the highest level of total mineral level. These findings show that individuals with melancholic nature have a smaller body size compared to other groups of individuals. Also, melancholy nature is associated with a high level of minerals in the body,which is why they have a cold and dry nature.
Some previous studies also showed an association betweenMizajof individuals and anthropometric measures [21]. Hassan Lari et al.study among 148 healthy subjects in the age group of 18-40 years,having melancholic and phlegmatic temperament,showed that among males (n = 82) and females (n = 66), the difference in the mean height between cholericMizajand phlegmaticMizajindividuals was insignificant.The mean weight,as well as the mean BMI of individuals with phlegmaticMizaj, was significantly higher than cholericMizajmales[22].
Dar et al. study on 52 healthy males showed that the mean BMI of phlegmaticMizajmales was significantly higher than sanguine and cholericMizaj[23].
Also, this study showed that sanguine and phlegmaticMizajwere the most prevalentMizajafter that cholericMizajand the least were melancholicMizaj, as was expected for people from Aryan and other Iranian races [2, 6-8].
Vahedi et al. study emphasized the importance of investigating the role of anthropometric dimensions of the human body in identifying temperament (Mizaj) in traditional Iranian medicine, and their study showed that the size of the chest is associated with warmMizajand the thinness of the body is a sign of dryness.Also,the predominance of muscle tissue is a sign of warmth,and the predominance of fat tissue is a sign of coldness [24].
Ahmer et al. Study investigated the total body water Damavi and SafraviMizajof healthy males. It indicated a relationship between total body water and theMizajof individuals[25].
Akhtar et al. study also reported a similar result by reviewing the original Persian medicine books [26].
However, a study by Mirtaheri et al. did not show any difference between the type ofMizajand body weight and BMI value of participant women [27].
Conclusions
Morphological characteristics have been attributed to differentMizajof individuals in traditional medicine literature as one of the main criteria in the detection ofMizajof individuals. This study showed a significant association betweenMizajof individuals and the morphology of their bodies. It confirmed the attributes in the literature of traditional medicine using scientific methods and instruments.
