Effects of Different Fertilization Measures on Chemical Composition and Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco
Zhongwen ZHANG, Linda LI, Cheng ZHANG, Weimin WANG, Tao ZHANG, Changhe CHENG, Dongkun WANG, Xiaoqiang WANG*
1. China Tobacco Zhejiang Industrial Co., Ltd., Hangzhou 310008, China; 2. Institute of Tobacco Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Qingdao 266101, China
Abstract [Objectives] The paper was to obtain fertilizer varieties and fertilization techniques that meet the special nutritional requirements of characteristic tobacco varieties in Mengyin tobacco area. [Methods] With the local main plant variety NC102 as the test material, the effects of combined application, dosage and application methods of different types of organic fertilizers, compound fertilizers and potassium fertilizers on chemical composition and quality of NC102 flue-cured tobacco leaves were studied. [Results] Under the premise of reducing the amount of fertilizer applied, the slow-release integrated fertilizer increased the sugar- alkali ratio and potassium-chloride ratio, and reduced the sulfur content of tobacco leaves, but it did not significantly improve the sensory quality of tobacco leaves. Increasing the application of organic fertilizer made the sugar-alkali ratio and potassium-chloride ratio more coordinated, reduced the sulfur content and improved the sensory quality of tobacco leaves. Microbial agents significantly increased the sugar-alkali ratio in tobacco leaves, and had obvious effects of increasing potassium and reducing chlorine. Different types and application methods of potassium fertilizers had obvious effects on sensory quality of tobacco leaves. Increasing the application amount of potassium fertilizer and later topdressing significantly improved the potassium content and sensory quality of tobacco leaves. [Conclusions] The study provides a basis for balanced fertilization in characteristic flue-cured tobacco production in Mengyin tobacco area.
Key words NC102; Organic fertilizer; Potassium fertilizer; Slow-release integrated fertilizer; Chemical composition; Quality
1 Introduction
Mengyin tobacco area is located in the hinterland of Yimeng mountain area, with a forest coverage rate of more than 80%. It has the typical characteristics of Yimeng mountain, with mild climate, four distinct seasons and a large temperature difference between day and night, and is one of the most suitable areas for flue-cured tobacco planting in China. Selection of appropriate fertilizers and rational application plays a vital role in improving the yield and quality of tobacco. On the one hand, it is beneficial to the accumulation of dry matter in tobacco leaves, the improvement of phosphorus and potassium nutrition in flue-cured tobacco leaves, and the promotion of the degradation of chlorophyll and mature yellowing in late period, making the chemical composition of tobacco leaves more coordinated. On the other hand, it increases the root volume of tobacco and the distribution ratio of nitrogen nutrition to roots, and reduces the distribution ratio of NPK in stem, thus improving the quality of cured tobacco leaves[1]. Therefore, it is of great significance to improve the quality and highlight the characteristics of tobacco varieties by studying different fertilization measures, including selection of appropriate fertilizer varieties and supporting fertilization techniques. Therefore, the study discussed the effects of different fertilizers and application methods on chemical composition and quality of flue-cured tobacco, in order to provide a basis for balancing fertilization in the production of characteristic flue-cured tobacco in Mengyin tobacco area.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Location and type of fertilizersThe test was conducted in Liancheng, Mengyin County, and representative plots suitable for irrigation and drainage with medium fertility and even land capability were selected. The flue-cured tobacco cultivar NC102 was used in the test. Fertilizers tested included conventional compound fertilizer (10-10-20), Dasanyuan integrated fertilizer, tobacco slow-release integrated fertilizer, microbial fertilizer, wormcast organic fertilizer, Yandashuai organic fertilizer, potassium nitrate, potassium sulfate, potassium humic acid, potassium fulvic acid, and mineral potassium.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1Field test. Contrast tests of three types of fertilizers were conducted, including tobacco conventional and slow-release integrated fertilizer contrast test, organic fertilizer contrast test and potassium fertilizer contrast test. Each treatment covered an area of 667 m2with 2 replicates, and the experimental land covered a total area of 1.47 hm2. The experimental design schemes are shown in Tables 1-3. The field management was carried out according to the local standardized operation, and three-stage five-step baking technology was adopted as the modulation method.

Table 1 Tobacco conventional and slow-release integrated fertilizer test
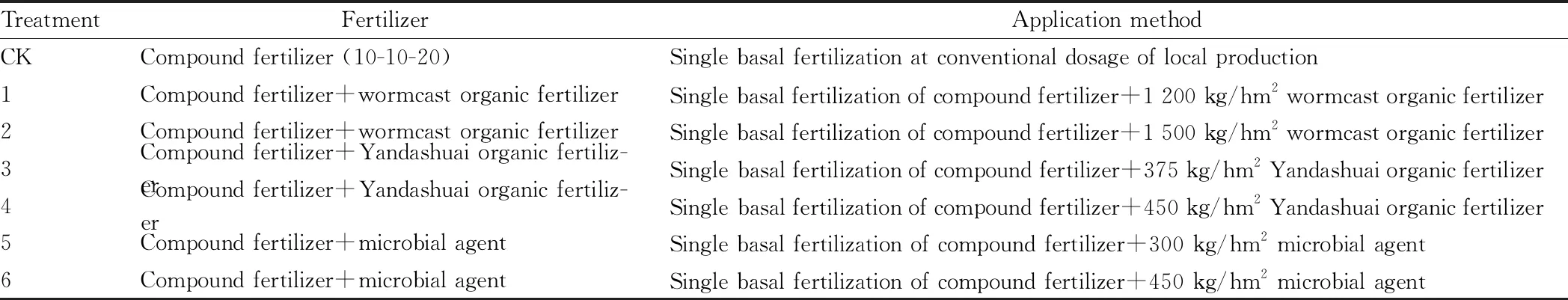
Table 2 Wormcast organic fertilizer test
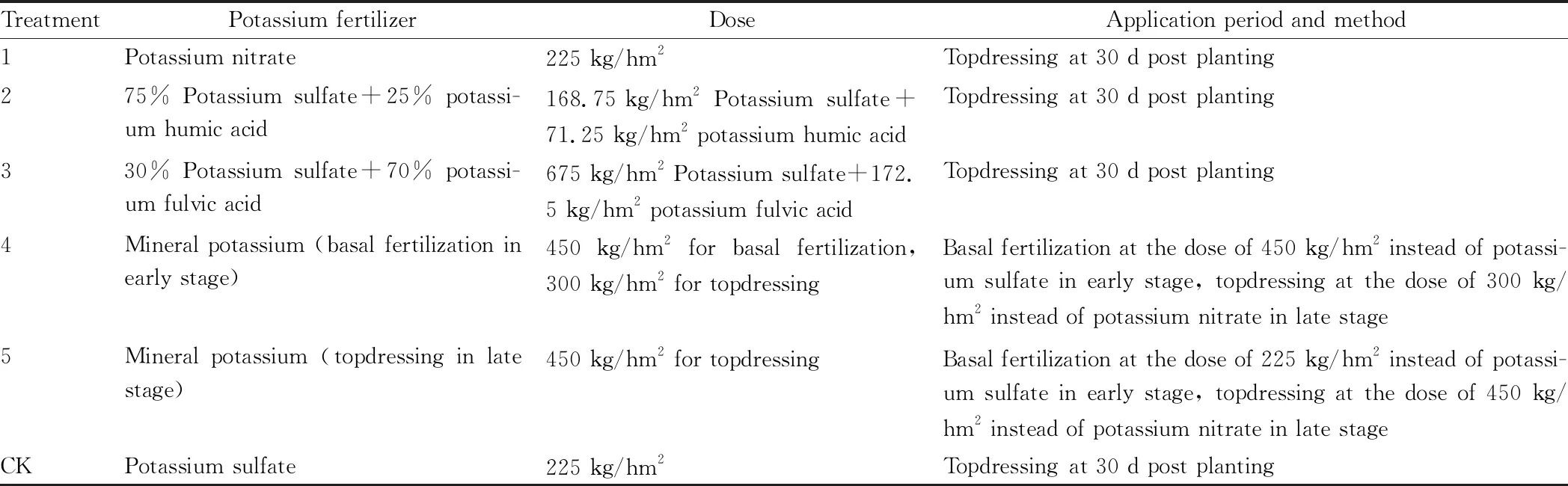
Table 3 Potassium fertilizer test
2.2.2Determination of chemical composition. The conventional chemical composition was determined according to the latestAnalysisMethodofChemicalQualityforTobacco[2].
2.2.3Sensory quality evaluation. The sensory quality was assessed by a panel composed of 10 people from the Quality Testing Center of Institute of Tobacco Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The 13 indexes, including quality of aroma, volume of aroma, permeability, offensive odor, exquisiteness, softness, roundness, irritation, dryness, after taste, flavor type, smoke concentration and physical strength, were scored, and the average of each score was the final score.
2.2.4Data analysis. All data were statistically analyzed by Excel 2007 software.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Tobacco conventional and slow-release integrated fertilizer contrast test
3.1.1Chemical composition analysis. The chemical composition analysis results of tobacco leaves treated with different compound fertilizers (Table 4) showed that different fertilizer treatments had certain effects on the chemical composition content of tobacco leaves. Basal fertilization of 60 kg tobacco slow-release integrated fertilizer slightly increased the sugar-alkali ratio and potassium-chloride ratio, and the sulfur content of tobacco leaves was significantly lower than that of conventional control treatment.
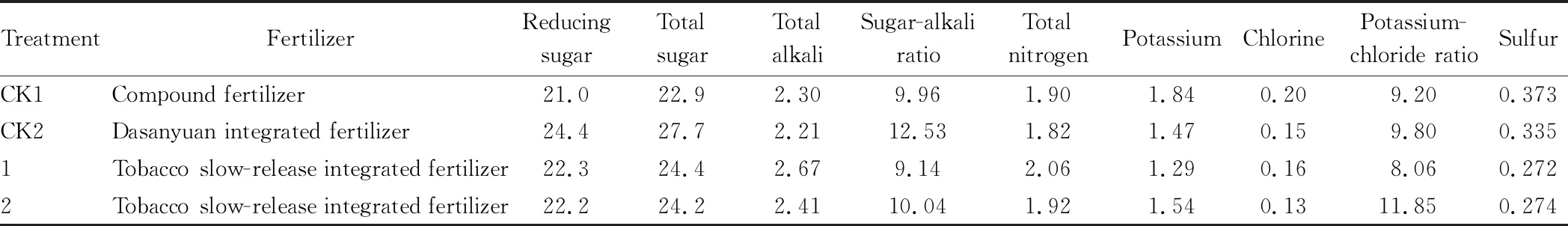
Table 4 Chemical composition of tobacco leaves treated with different compound fertilizers
3.1.2Sensory quality evaluation. The sensory evaluation results of tobacco leaves treated with different compound fertilizers (Table 5) showed that compared with the control, the application of slow-release integrated fertilizer did not significantly improve the sensory quality of tobacco leaves, and the overall comfort level of after taste was not good, with general clarity.
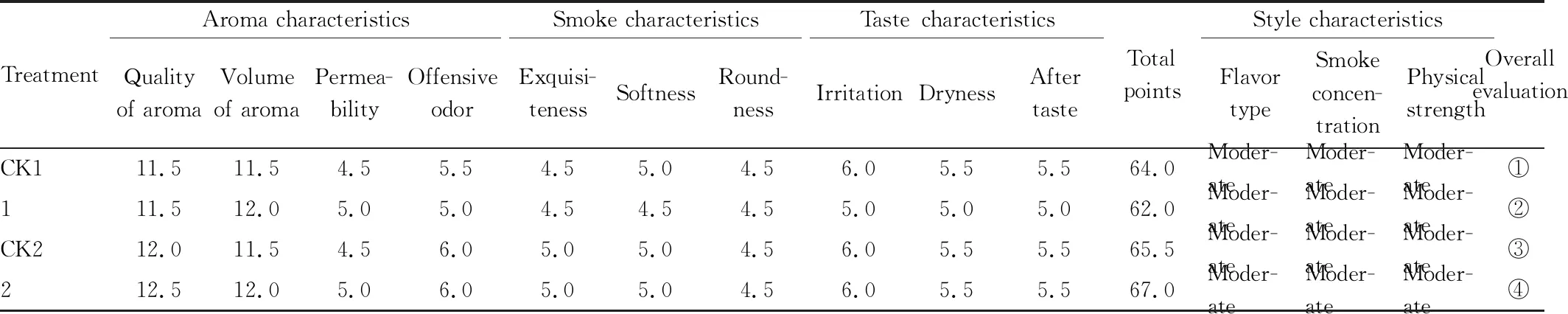
Table 5 Sensory quality evaluation of raw tobacco treated with different compound fertilizers
3.2 Organic fertilizer contrast test
3.2.1Chemical composition analysis. The chemical composition analysis results of tobacco leaves treated with different organic fertilizers (Table 6) showed that increased application of organic fertilizer and microbial agent significantly improved the sugar-alkali ratio of tobacco leaves, and also had certain effect on the potassium-chlorine ratio. The addition of microbial agent significantly increased potassium and decreased chlorine. With the increase of microbial agent, the sulfur content decreased obviously.
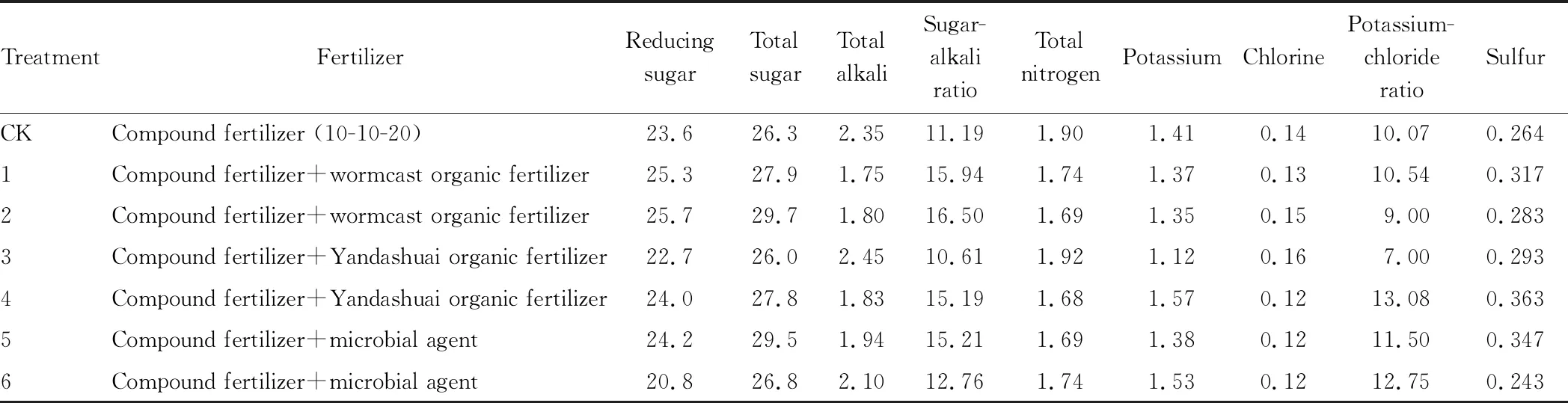
Table 6 Chemical composition of tobacco leaves treated with different organic fertilizers
3.2.2Sensory quality evaluation. The sensory evaluation results of tobacco leaves treated with different organic fertilizers (Table 7) showed that the sensory quality of tobacco leaves treated with compound fertilizer+1 500 kg/hm2wormcast organic fertilizer and compound fertilizer+625 kg/hm2Yandashuai organic fertilizer was improved compared with the tobacco leaves in the control. Compound fertilizer+microbial agent significantly increased the sugar-alkali ratio and had the effect of increasing potassium and decreasing chlorine in tobacco leaves, but the sensory quality was lower than that of the control.
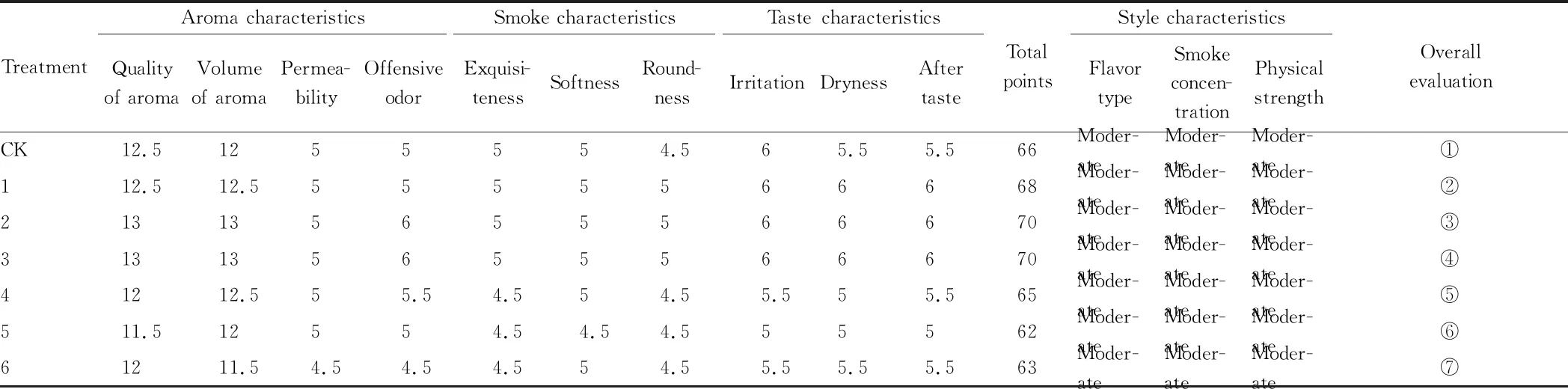
Table 7 Sensory quality evaluation of raw tobacco treated with different organic fertilizers
3.3 Potassium fertilizer contrast test
3.3.1Chemical composition analysis. The chemical components analysis results of tobacco leaves treated with different potassium fertilizers (Table 8) showed that different potassium fertilizers had certain influence on chemical composition of tobacco leaves, and application of potassium nitrate significantly improved the sugar-alkali ratio and potassium-chloride ratio. Potassium sulfate substitution significantly reduced the sulfur content in tobacco leaves, and topdressing of mineral potassium in late stage significantly increased the potassium content in tobacco leaves.
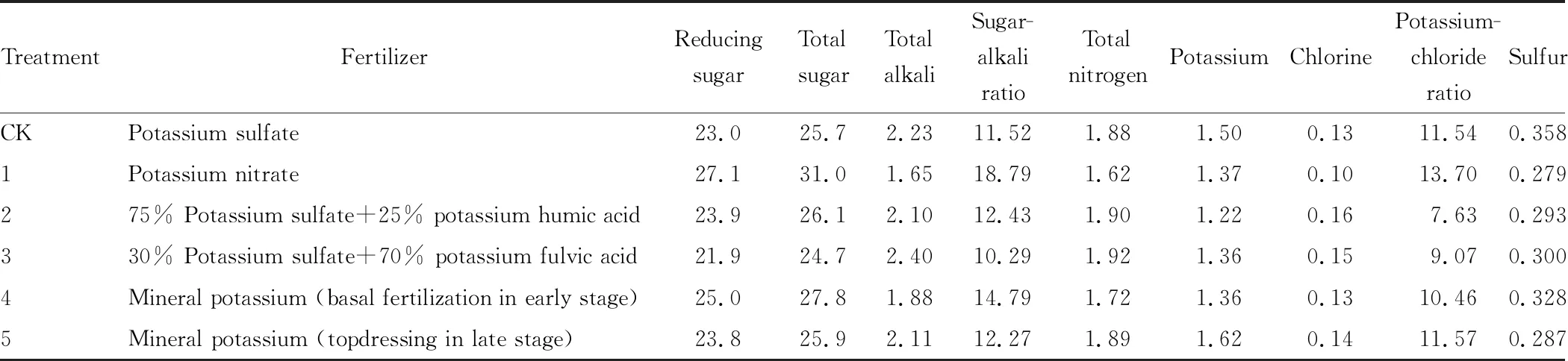
Table 8 Chemical composition of tobacco leaves treated with different potassium fertilizers
3.3.2Sensory quality evaluation. The sensory evaluation results of tobacco leaves treated with different potassium fertilizers(Table 9) showed that compared with the control, most potassium fertilizer treatments had positive effects on improving sensory quality of tobacco leaves, among which 30% potassium sulfate+70% potassium fulvic acid (topdressing), basal fertilization at the dose of 450 kg/hm2, and topdressing at the dose of 300 kg/hm2(mineral potassium) had the most significant improvement effect, especially in highlighting comfort level of after taste, sweetness and sweet aroma.

Table 9 Sensory quality evaluation of raw tobacco treated with different potassium fertilizers
4 Discussion
Rational selection and efficient application of fertilizers are very important for flue-cured tobacco production. Previous studies have shown that different types and doses of potassium fertilizer have different effects on the content of slowly available potassium and rapidly available potassium in soil, and also have certain effects on the root system and micro-ecological environment of tobacco plants, thus affecting the absorption, accumulation and distribution of potassium in tobacco plants as well as the absorption of other nutrient elements, and finally affecting the quality of tobacco leaves[3]. Zhaoetal.[4]and Yeetal.[5]showed that increasing potassium fertilizer within a certain range promoted root development and root dry weight accumulation of flue-cured tobacco plants, indicating that appropriate increase of potassium fertilizer was conducive to increasing root vitality and improving root absorption capacity of potassium. Our research results also demonstrated that different types and application methods of potassium fertilizer had obvious effects on chemical composition and sensory quality of tobacco. Increasing the application rate of potassium fertilizer and topdressing in late period could significantly improve the potassium content and sensory quality of tobacco leaves.
It plays an important role in reducing environmental pollution, increasing flue-cured tobacco yield and improving flue-cured tobacco quality by applying inorganic fertilizer together with organic fertilizer. Organic fertilizer has great influence on the quality of flue-cured tobacco. Bioorganic fertilizer forms complex intermediates in the decomposition process, which promotes the growth and metabolism of flue-cured tobacco, and is conducive to the accumulation of sugars and aromatic substances, and further affects the aroma, taste and appearance quality of cured tobacco leaves. Zhangetal.[6]showed that the application of appropriate compound bio-organic fertilizer could harmonize the chemical composition of tobacco leaves, enhance the intrinsic quality, and improve aroma, odor, irritation and other evaluation indicators of tobacco leaves. This study showed that the application of organic fertilizer could coordinate the sugar-alkali ratio and potassium-chloride ratio in tobacco leaves, decrease the sulfur content and improve the sensory quality of tobacco leaves. The microbial agent significantly improved the sugar-alkali ratio in tobacco leave, and had the obvious effects of increasing potassium and reducing chlorine.
Due to the differences in soil types, nutrient content and ecological environment in different regions, the appropriate levels of nutrient elements vary with regions, so it is necessary to select appropriate fertilizer types and application methods according to the local soil conditions. It is an important research topic in tobacco production in the future by choosing different fertilization measures according to the specific local production conditions to maximize the utilization rate of fertilizer and improve the quality of tobacco leaves.
- 植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Demonstration and Promotion of Integrated Management Technology of Wheat Sheath Blight and Wheat Crown Rot in Zibo City
- Status Analysis of Recycling and Disposal of Pesticide Packaging Waste in Western Zhejiang
- Identification and Control of Several Leaf Diseases of Poplar
- Life History and Control Measures of Dendrolimus sibiricus Tschetw. in Northeast China
- Control Measures against Main Pinus koraiensis Diseases in Liaoning Province
- Prevention and Control Test of Semiaphis heraclei in Spring

