基于多弛豫信号补偿的快速磁共振T1r散布成像
刘元元,杨育昕,2,朱庆永,崔卓须,程 静,刘聪聪,梁 栋,,朱燕杰*
基于多弛豫信号补偿的快速磁共振1散布成像
刘元元1,杨育昕1,2,朱庆永3,崔卓须3,程 静1,刘聪聪1,梁 栋1,3,朱燕杰1*
1. 保罗C.劳特伯生物医学成像研究中心,中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,广东 深圳 518055;2. 药学与生物工程学院,重庆理工大学,重庆 400054;3. 医学人工智能研究中心,中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,广东 深圳 518055
定量磁共振成像(MRI)可量化组织特性,是科学研究和临床研究的重要工具.旋转坐标系下的自旋-晶格弛豫时间(1)能反映水与大分子之间的低频交互作用,在3 T及以上的高场环境下,1受水和不稳定质子之间化学交换的影响较大,通过测量弛豫率随自旋锁定场强度的变化而得到其分布情况(1散布),可用于分析和量化质子的交换过程,因此1散布是一种重要的定量MRI技术.然而,获得不同自旋锁定场强下1加权图像的时间过长,限制了其应用范围.针对这一问题,本研究提出一种基于多弛豫信号补偿策略的快速1散布成像方法.该方法将不同锁定频率下的1加权图像补偿到同一信号强度水平,并结合低秩与稀疏建立重建模型.实验结果表明,该方法在加速倍数高达7倍时仍获得了较好的重建结果.
磁共振定量成像;1散布;信号补偿;低秩与稀疏
引 言
磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)具有无电离辐射、无创伤且对比度丰富等优势,是临床诊断及疗效评估的重要医学影像工具之一.磁共振定量成像是利用MRI技术量化组织的物理或生理参数的方法,相较于常规的结构成像,定量成像在组织间区分时具有更高的敏感度.定量成像测量的参数范围广泛,不仅包括反映组织物理特性的磁共振弛豫时间(如1、2)和质子密度等参数,还包括反映组织中水分子布朗运动、血流灌注等生理特性的扩散系数和灌注分数等[1-5].

1 基于多弛豫信号补偿的L+S重建原理
1.1 多弛豫信号补偿


1.2 L+S重建模型
基于L+S矩阵分解的重建方法已广泛应用于快速磁共振动态成像中,并取得了较大成功[24-28].该方法将动态图像序列组成的空间-时间矩阵分解为低秩分量矩阵和稀疏分量矩阵的叠加,并通过求解以下凸优化问题来进行图像重建:

1.3 基于多弛豫信号补偿的L+S模型
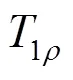

其中,为应用于稀疏分量S的全变分变换;为第n个锁定时间及自旋锁定频率下的加权图像;d为欠采样的k空间数据;执行逐像素的信号补偿;,为编码算子,其中A代表欠采样算子,F代表傅里叶变换算子,H代表线圈敏感度矩阵[27,29];代表图像矩阵的秩.图1为本文提出的-DISC方法的流程图.

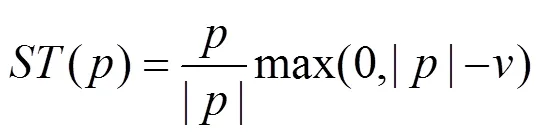
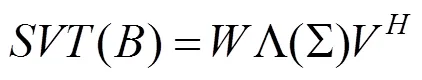

输入:d:欠采样的k空间数据 E:编码算子 :第n个锁定时间输出:X:重建图像1. 初始化和初始定量图2. 对于外部迭代,执行下述步骤直至收敛:[1] 计算[2] [3] 初始化[4] 对于内部迭代,执行下述步骤:a. 更新,b. 更新,c. 数据一致性[5] 内部迭代结束[6] [7] 利用更新[8] 外部迭代结束
1.4 T1r弛豫模型
在本研究中,我们采用单指数模型来测量弛豫率:
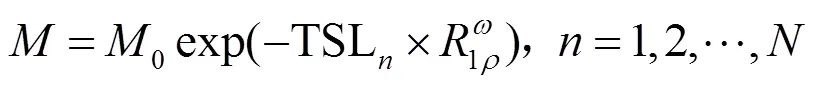
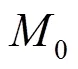
2 在体实验
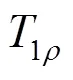


图2 加速倍数R分别为(a) 4和(b) 7时,相位编码-帧方向的欠采样模板
我们对比了不同方法的计算复杂度,并以归一化均方根误差(normalized root mean square error,nRMSE)、结构相似指数(structural similarity index,SSIM)[33]、峰值信噪比(peak signal-to-noise ratio,PSNR)[34]为指标,对不同加速倍数下各方法的重建图像进行了定量分析.nRMSE的定义如下:

3 结果与讨论
3.1 不同重建方法的重建性能对比
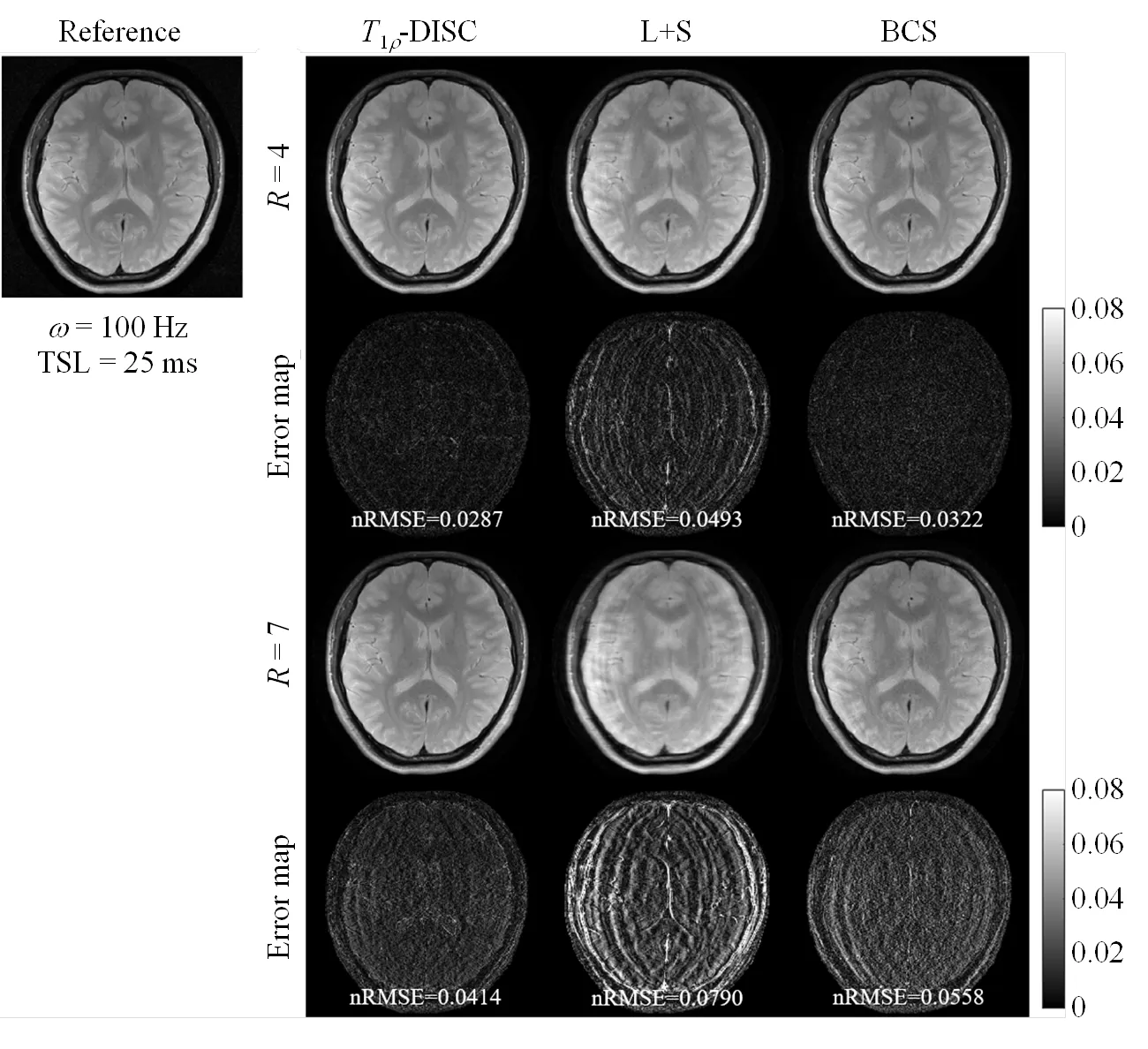
图3 R=4和7时,经T1r-DISC、L+S和BCS方法重建的T1r加权图像及误差图(ω=100 Hz,TSL=25 ms)
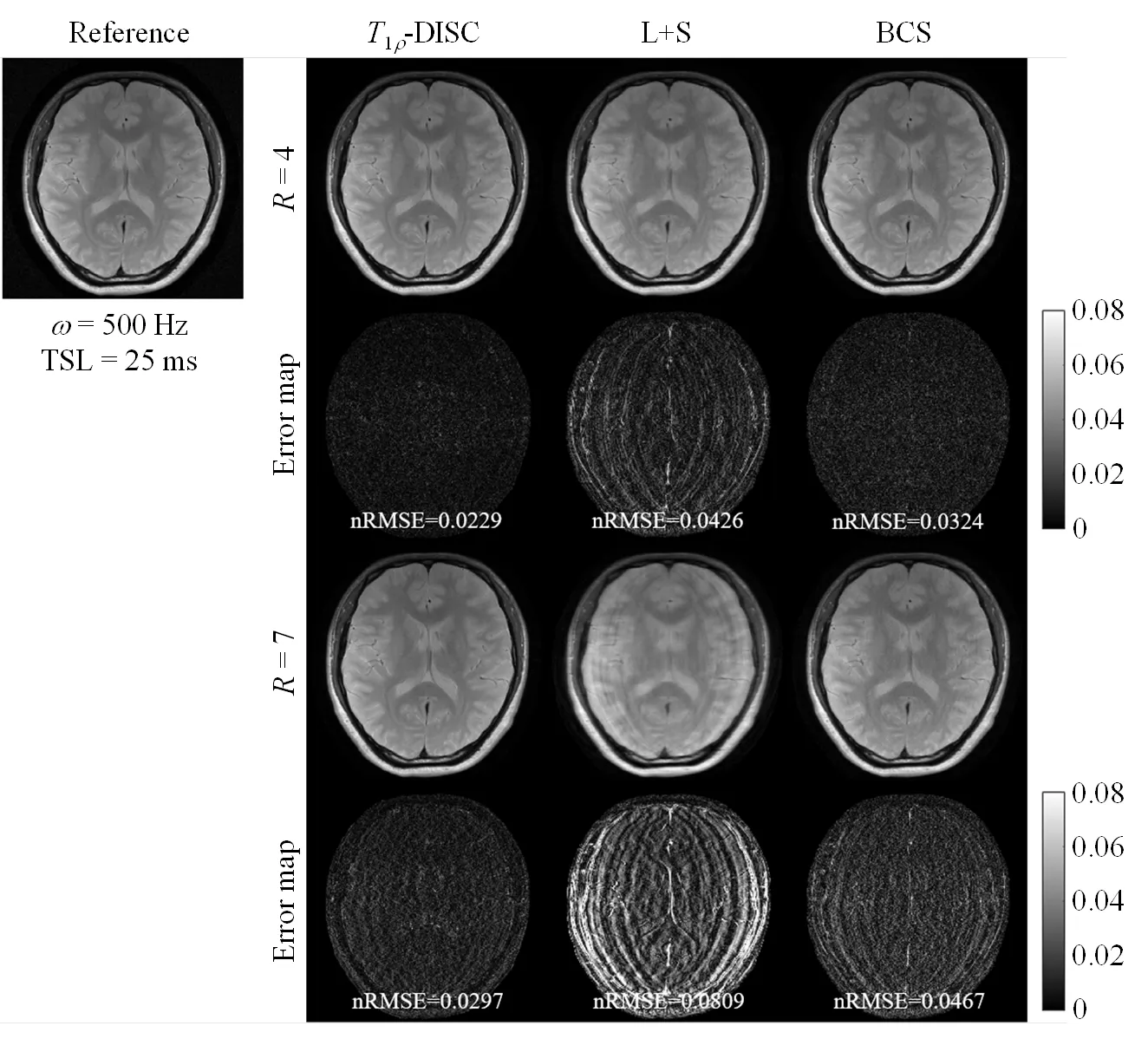
图4 R=4和7时,经T1r-DISC、L+S和BCS方法重建的T1r加权图像及误差图(ω=500 Hz,TSL=25 ms)

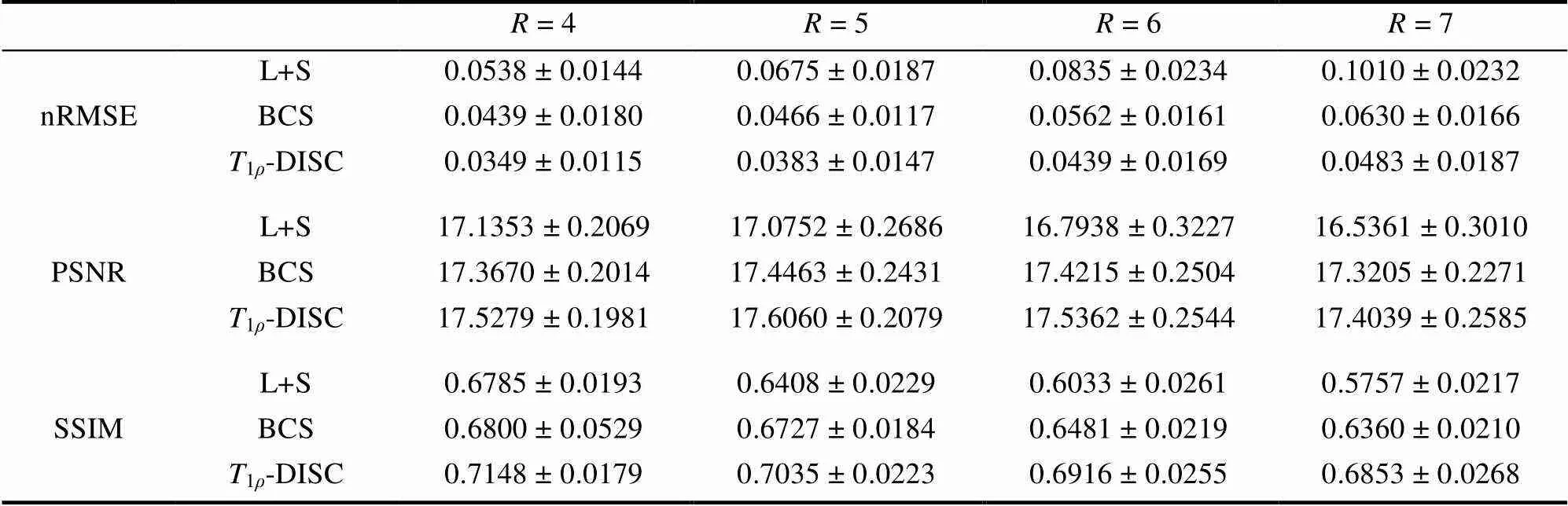
表1 各加速倍数下,各方法重建的所有自旋锁定频率下T1ρ加权图像的nRMSE、PSNR及SSIM的均值±标准差对比
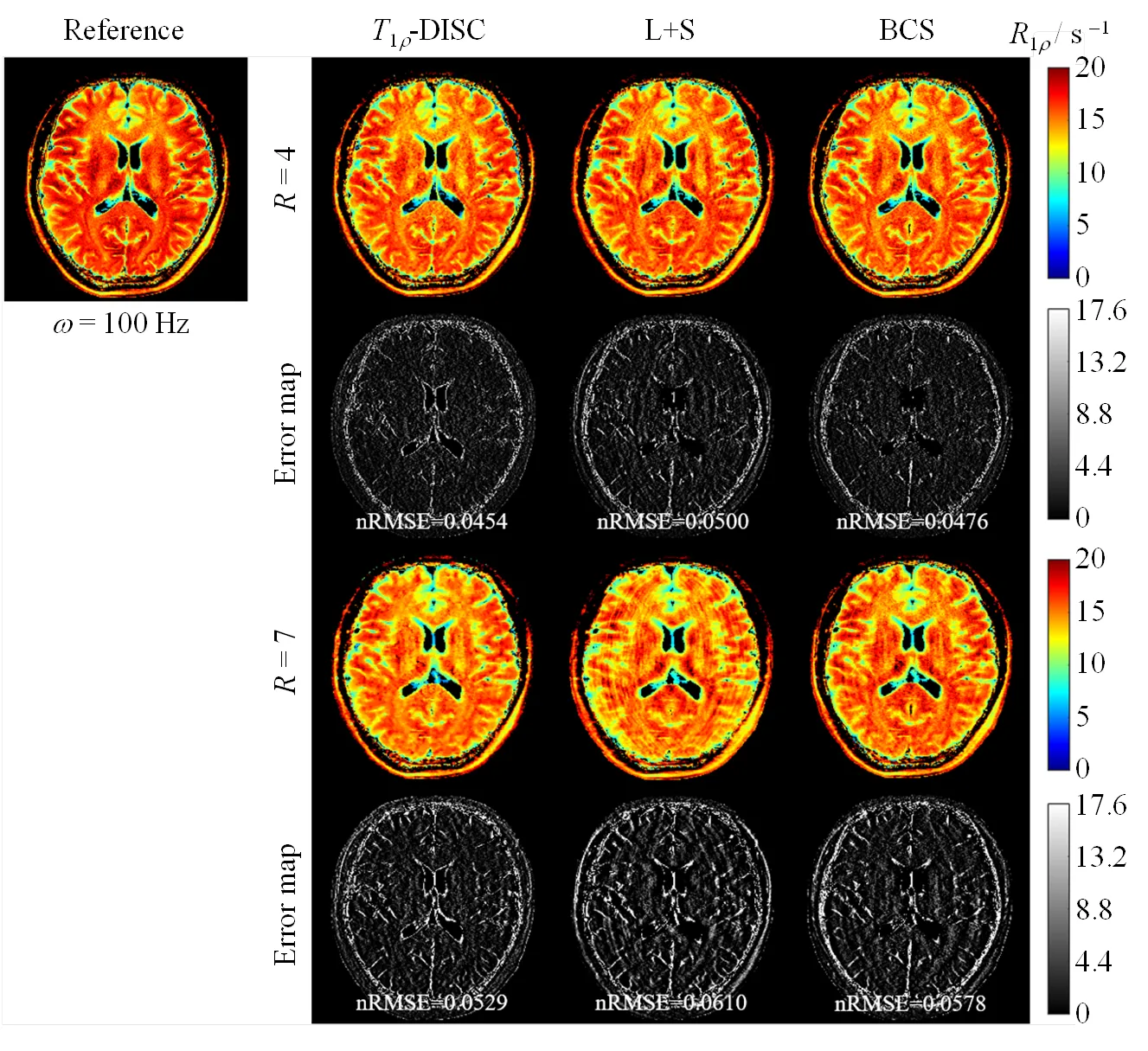
图5 R=4和R=7时,经T1r-DISC、L+S和BCS方法重建得到的R1r定量图及误差图(ω=100 Hz)

图6 R=4和7时,经T1r-DISC、L+S和BCS方法重建得到的R1r定量图及误差图(ω=500 Hz)
3.2 计算复杂度对比

表2 各算法的计算复杂度对比
3.3 不同自旋锁定频率下R1r的变化规律
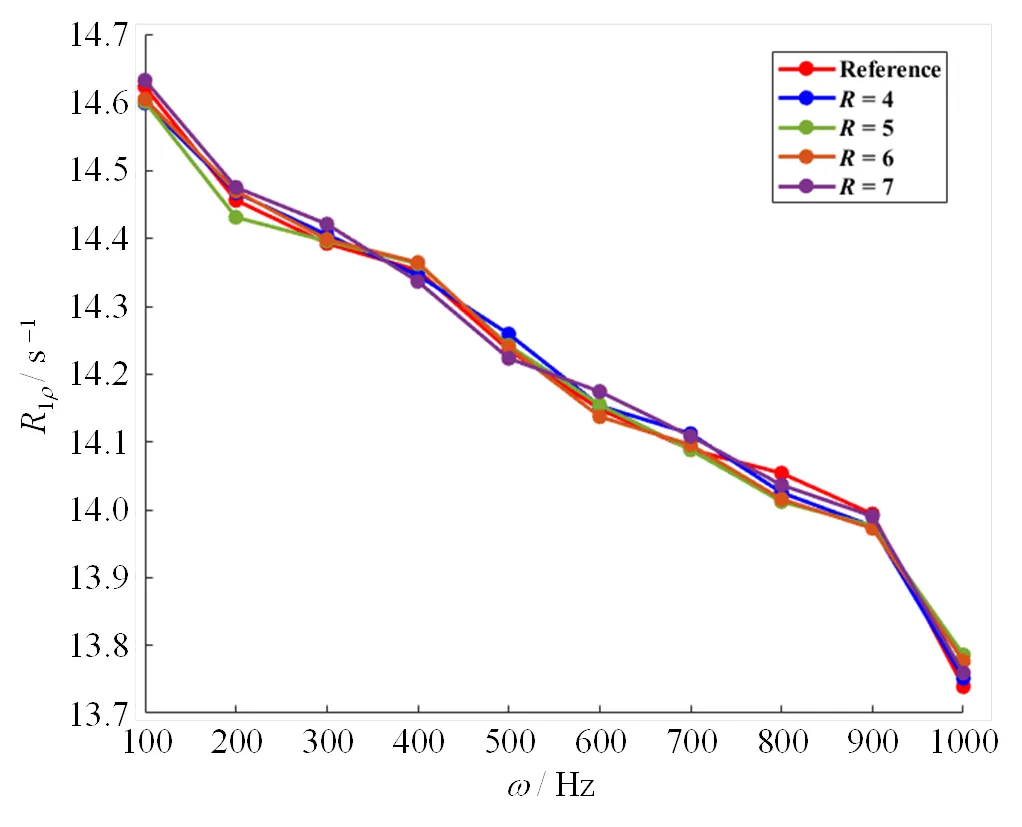
图7 R=4、5、6、7时,利用T1r-DISC方法的重建图像拟合计算得到的R1r随自旋锁定频率的变化曲线
3.4 讨论

此外,基于深度学习的快速MRI方法显示出巨大的应用潜力.基于深度学习数据驱动的特性,如果有足够多的数据,深度学习方法将显著提高重建图像的质量.神经网络还可以用于磁共振多层同时激发成像,提升重建质量[37].文献[26]提出了一种基于模型的L+S网络的动态磁共振图像重建方法,该网络使用交替线性化最小化方法来解决低秩和稀疏正则化的优化问题,并引入了学习奇异值阈值法来保证低秩分量与稀疏分量的分离,最后将迭代步骤展开成正则化参数可学习的网络.

图8 R=4和7时,利用T1r-DISC 方法在k空间中心全采样比例分别为0.05、0.10和0.12时重建的T1r加权图像及误差图(ω = 200 Hz,TSL = 25 ms)
4 结论
无
表S1 各方法重建图像评价指标的值结果
[1] DEONI S C, PETERS T M, RUTT B K. High-resolution1and2mapping of the brain in a clinically acceptable time with DESPOT1 and DESPOT2[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2005, 53(1): 237-241.
[2] GANZETTI M, WENDEROTH N, MANTINI D. Whole brain myelin mapping using1-and2-weighted MR imaging data[J]. Front Hum Neurosci, 2014, 8: 671.
[3] KNIGHT M J, MCCANN B, TSIVOS D, et al. Quantitative2mapping of white matter: applications for ageing and cognitive decline[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2016, 61(15): 5587-5605.
[4] SENER R N. Diffusion MRI: apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values in the normal brain and a classification of brain disorders based on ADC values[J]. Comput Med Imaging Graph, 2001, 25(4): 299-326.
[5] TAYLOR A J, SALERNO M, DHARMAKUMAR R, et al.1Mapping: basic techniques and clinical applications[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2016, 9(1): 67-81.
[6] ALI S O, FESSAS P, KAGGIE J D, et al. Evaluation of the sensitivity of1MRI to pH and macromolecular density[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 58: 156-161.
[7] WANG Y X, ZHANG Q, LI X, et al.1magnetic resonance: basic physics principles and applications in knee and intervertebral disc imaging[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2015, 5(6): 858-885.
[8] LI X, WYATT C, RIVOIRE J, et al. Simultaneous acquisition of1and2quantification in knee cartilage: repeatability and diurnal variation[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2014, 39(5): 1287-1293.
[9] WANG Y X, YUAN J. Evaluation of liver fibrosis with1MR imaging[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2014, 4(3): 152-155.
[10] HARIS M, SINGH A, CAI K, et al.1MRI in Alzheimer’s disease: detection of pathological changes in medial temporal lobe[J]. J Neuroimaging, 2011, 21(2): e86-90.
[11] COBB J G, XIE J, GORE J C. Contributions of chemical exchange to1dispersion in a tissue model[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2011, 66(6): 1563-1571.
[12] COBB J G, XIE J, GORE J C. Contributions of chemical and diffusive exchange to1dispersion[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 69(5): 1357-1366.
[13] LUSTIG M, DONOHO D, PAULY J M. Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2007, 58(6): 1182-1195.
[14] BHAVE S, LINGALA S G, JOHNSON C P, et al. Accelerated whole-brain multi-parameter mapping using blind compressed sensing[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 75(3): 1175-1186.
[15] PANDIT P, RIVOIRE J, KING K, et al. Accelerated1acquisition for knee cartilage quantification using compressed sensing and data-driven parallel imaging: a feasibility study[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 75(3): 1256-1261.
[16] KAMESH IYER S, MOON B, HWUANG E, et al. Accelerated free-breathing 3D1cardiovascular magnetic resonance using multicoil compressed sensing[J]. J Cardiovasc Magn R, 2019, 21: 5.
[17] LI Y Y, LI L, LI X S, et al. 3D dynamic MRI with homotopic0minimization rconstruction[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson , 2022, 39(1): 20-32.
李嫣嫣, 李律, 李雪松, 等. 基于同伦0范数最小化重建的三维动态磁共振成像[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(1): 20-32.
[18] ZHAN J Y, TU Z R, DU X F, et al. Progresses on low-rank reconstruction for non-uniformly sampled NMR spectra[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37(3): 255-272.
詹嘉莹, 涂章仁, 杜晓凤, 等. 基于低秩矩阵的非均匀采样NMR波谱重建进展[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(3): 255-272.
[19] HALDAR J P, LIANG Z P. Low-rank approximations for dynamic imaging[C]// 2011 8th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 2011: 1052-1055.
[20] JACOB M, MANI M P, YE J C. Structured low-rank algorithms: theory, magnetic resonance applications, and links to machine learning[J]. IEEE Signal Process Mag, 2020, 37(1): 54-68.
[21] ZIBETTI M V W, SHARAFI A, OTAZO R, et al. Accelerating 3D-1mapping of cartilage using compressed sensing with different sparse and low rank models[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 80(4): 1475-1491.
[22] PENG X, YING L, LIU Y Y, et al. Accelerated exponential parameterization of2relaxation with model-driven low rank and sparsity priors (MORASA)[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 76(6): 1865-1878.
[23] ZHU Y J, LIU Y Y, YING L, et al. SCOPE: signal compensation for low-rank plus sparse matrix decomposition for fast parameter mapping[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2018, 63(18): 185009.
[24] BOUWMANS T, SOBRAL A, JAVED S, et al. Decomposition into low-rank plus additive matrices for background/foreground separation: A review for a comparative evaluation with a large-scale dataset[J]. Comput Sci Rev, 2017, 23: 1-71.
[25] ONG F, LUSTIG M. Beyond low rank plus sparse: multiscale low rank matrix decomposition[J]. IEEE J Sel Topics Signal Process, 2016, 10(4): 672-687.
[26] HUANG W Q, KE Z W, CUI Z X, et al. Deep low-rank plus sparse network for dynamic MR imaging[J]. Med Image Anal, 2021, 73.
[27] OTAZO R, CANDES E, SODICKSON D K. Low-rank plus sparse matrix decomposition for accelerated dynamic MRI with separation of background and dynamic components[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015, 73(3): 1125-1136.
[28] PETROV A Y, HERBST M, STENGER V A. Improving temporal resolution in fMRI using a 3D spiral acquisition and low rank plus sparse (L plus S) reconstruction[J]. Neuroimage, 2017, 157: 660-674.
[29] PRUESSMANN K P, WEIGER M, BORNERT P, et al. Advances in sensitivity encoding with arbitrary-space trajectories[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2001, 46(4): 638-651.
[30] MORE J J. The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm: implementation and theory[J]. Numerical analysis, 1978, 105-116.
[31] MITREA B G, KRAFFT A J, SONG R, et al. Paired self-compensated spin-lock preparation for improved1quantification[J]. J Magn Reson, 2016, 268: 49-57.
[32] RICH A, GREGG M, JIN N, et al. Cartesian sampling with variable density and Adjustable temporal resolution (CAVA)[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2020, 83(6): 2015-2025.
[33] WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2004, 13(4): 600-612.
[34] MASON A, RIOUX J, CLARKE S. Comparison of objective image quality metrics to expert radiologists’ scoring of diagnostic quality of MR Images[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 39(4): 1064-1072.
[35] ZHU Y, LIU Y, YING L, et al. A 4-minute solution for submillimeter whole-brain1quantification[J]. Magn Reson Med , 2021, 85(6): 3299-3307.
[36] KORZHNEV D M, OREKHOV V Y, KAY L E. Off-resonance1NMR studies of exchange dynamics in proteins with low spin-lock fields: An application to a fyn SH3 domain[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127(2): 713-721.
[37] WANG W T, SU S, JIA S, et al. Reconstruction of simultaneous multi-slice MRI data by combining virtual conjugate coil technology and convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37(4): 407-421.
王婉婷, 苏适, 贾森, 等. 基于虚拟线圈和卷积神经网络的多层同时激发图像重建[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 407-421.
Accelerating1Dispersion Imaging with Multiple Relaxation Signal Compensation
1,1,2,3,3,1,1,1,3,1*
1. Paul C. Lauterbur Research Centre for Biomedical Imaging, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen 518055, China; 2. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Chongqing University of Technology, Chongqing 400054, China; 3.Research Center for Medical AI, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen 518055, China
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can quantify characteristic values of tissues, serving as an important tool for scientific and clinical research. Magnetic resonance1relaxation time reflects the low-frequency motional processes between water and macromolecules. At high fields of 3 T and above,1is greatly affected by the chemical exchange between water and exchangeable protons, and1dispersion measured with varying spin-lock fields can be utilized to analyze and quantify the proton exchange process. However, it is time-consuming to obtain1-weighted images with different spin-lock fields, which limits its application. To solve this problem, a fast1dispersion imaging method based on multiple relaxation signal compensation strategy is proposed in this work, which compensates the1-weighted images at different locking frequencies to the same signal strength level, and combines the low-rank plus sparse model in the reconstruction. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves good reconstruction results even when the acceleration factor is up to 7.
magnetic resonancequantitative imaging,1dispersion, signal compensation,low-rank plus sparse

O482.53
A
10.11938/cjmr20222976
2022-02-16;
2022-04-28
中国科学院磁共振技术联盟仪器设备功能开发技术创新项目(2020GZL006);国家重点研发计划课题(2020YFA0712200);广东省基础与应用基础研究基金项目(2021A1515110540);深圳市优秀科技创新人才培养项目(RCYX20210609104444089);中国博士后科学基金面上项目(2020M682990, 2021M69331, 2021M703390);广东省磁共振成像与多模系统重点实验室(2020B1212060051).
* Tel: 0755-86392243, E-mail: yj.zhu@siat.ac.cn.

