Students’ Feedback on Integrating Engineering Practice Cases into Lecture Task in Course of Built Environment
YANG Xuebin(杨学宾), ZHONG Ke(钟 珂), CHEN Linna(陈琳娜) , YANG Zili(杨自力), LIANG Zhen(梁 珍)
1 College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China 2 College of Continuing Education, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
Abstract: The improvement of students’ abilities is of great significance to discover the relevant scientific problems in daily life, to analyze and solve practical problems, to trigger scientific inspiration, and to encourage innovation and entrepreneurship. Taken the course entitled Built Environment(BE)as an example, this study introduces five lecture cases combining with engineering practices, and examines the evaluation of teaching and learning effect on student outcomes. The cases consider various problems to be solved urgently in an actual project, and evaluate the student outcomes by statistically analyzing the questionnaires. Most of the students actively participate in five cases and cheerfully share their achievements. More than 85% of students are satisfied with the engineering practice and the learning proposal, and convey a little or even significantly change in their understanding of the employment prospects.
Key words: student outcome; feedback; engineering practice; lecture task; Built Environment and Energy Application Engineering(BEEAE)
Introduction
As the core course of the national first-class discipline of Built Environment and Energy Application Engineering(BEEAE)in Donghua University, Built Environment(BE)is an important basic course which includes the contents of architecture, heat transfer, sound, light, material, physiology, and psychology.This course connects basic courses with professional courses, and expounds the connotation, professional field and knowledge direction of BEEAE.
An extensive evidence is the active learning works better than a completely passive lecture[1].As a logical and valuable teaching philosophy, the pragmatism centers on linking theories, researches, ideas and actions to multi-disciplinary practical applications[2].Härkkietal.[3]proposed a model of contextualized co-teaching that supported implementing and researching co-teaching as a part of second-order educational changes.Bereczki and Krpti[4]discussed six overarching technology-based creativity-fostering approaches such as igniting students’ creativity, supporting idea development, creating digital products, scaffolding students’ creative processes, augmenting creative collaboration among students, and facilitating the evaluation of creative student outcomes.Voermanetal.[5]described a theory-based trajectory for professional development called feedback-theory into practice that aimed to have an observable effect on teacher classroom behavior.
Romeroetal.[6]applied the quick and real-time quizzes and the tests with Moodle for a longer time scale to improve students’ motivation, engagement and self-efficacy.Effectively noticing, interpreting, and then responding to students’ mathematical ideas can be quite challenging for teachers as they try to balance multiple, competing goals in an authentic classroom setting[7].Olivieretal.[8]contrasted three hypotheses to determine the best configuration of teacher need-supporting practices in terms of classroom-level of behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement.Kiemeretal.[9]examined the video-based teacher professional development intervention on productive classroom discourse improved students’ learning motivation and interest development.Pehmeretal.[10]investigated the extent of two teacher professional development programs on classroom discourse.
Better problem-solving is associated with practice making expert-level decisions[11].There is a range of ways to link with industry when teaching risk and safety courses[12].The effective delivery of industry based modules has been through continuous communication and evaluation with relevant stakeholders: students, academic staff and industrialists[13].Analyzing students’ textual feedback is substantial as well as analyzing ratings, and students’ mood can be very informative for both administrators and teaching staff[14].Critical industry feedback affects learners’ self-beliefs, triggers metacognition, and creative outcomes[15].
The traditional teaching process of professional courses is usually based on multimedia lectures.The teaching method of compulsory indoctrination has certain advantages in the text examination of questions and answers.However, there are still some deficiencies in discovering the relevant scientific problems in daily life, analyzing and solving practical problem, stimulating scientific inspiration, and encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship.Students’ abilities in these aspects are obviously weak.Even for the students who are about to graduation, they could not clearly describe what they have learned in the past four years.
This study considers some various problems to be solved in practical engineering, combines these cases with professional teaching content, and explores the teaching reform and practice of integrating specialty and creativity.
(1)The extracted innovative and entrepreneurial projects are closely related to lecture tasks and practical engineering problems.
(2)The training of practical engineering cases is implemented in the fields of practical applications and service objects, market modes, economic benefits, business developments, contents, students’ initial entrepreneurial abilities, and other practical fields.
On the basis of statistical survey on students’ evaluation and outcomes, this study expounds five engineering practice cases.Section 2 introduces five cases combined with engineering practice, and section 3 investigates the evaluation of teaching and learning effect and survey on student outcomes.
1 Outline of Course of BE
The course of BE is a professional basic lesson for the BEEAE program, namely heating, ventilating and air conditioning(HVAC).It is the first professional course for students to really contact with the substantive content, and is also the core professional course of BEEAE.BE is a window for students to have a preliminary macro understanding of residential and industrial built environment.It is also the basis for the correct application of HVAC and other professional technical means.
As an interdisciplinary subject, BE has the characteristics of wide range of knowledge and diversified contents, involving the knowledge of heat, hydrodynamics, physics, psychology, physiology, labor hygiene, urban meteorology, housing architecture, and other fields.A lot of content can only be tasted in teaching, or can only be explained in more abstract theoretical and conceptual lecture.In addition, the lecture content includes the outdoor environment, the indoor hot and humid environment, human body’s response to hot and humid environment, the indoor air quality, the theoretical basis of indoor air environment construction, building sound environment, building light environment,etc.Most of lecture content is closely related to occupant daily life.For example, in the chapter of hot and humid environment in building environment as shown in Fig.1, the lectures related to human thermal comfort and indoor air quality are the human body’s objective experience and subjective response to the actual environment.Therefore, the popular science lectures should be avoided in teaching only, and should be closely combined with other courses and practical application.This is the key for students to understand and master the knowledge of this course.
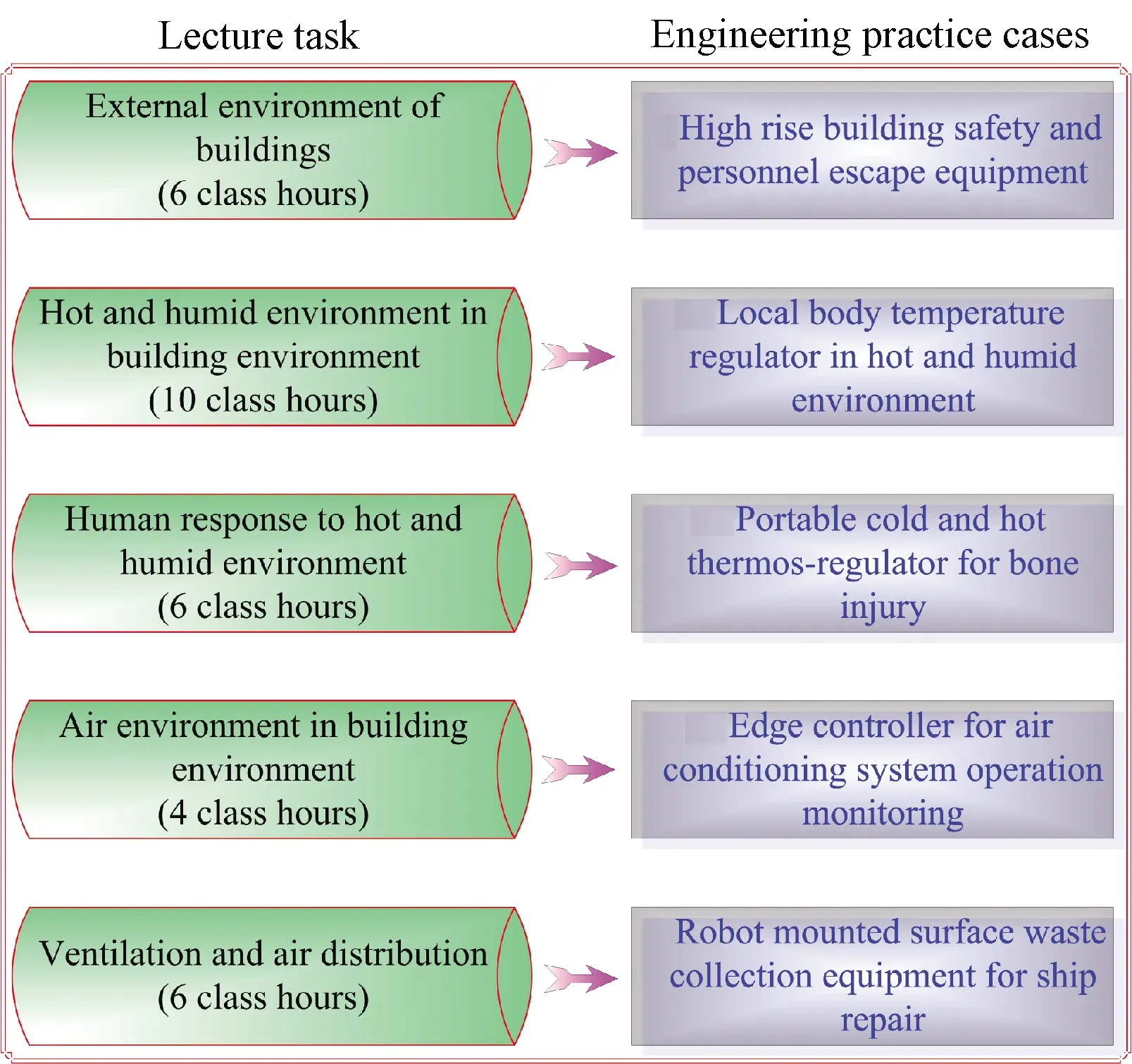
Fig.1 Combination of engineering practice cases with lecture task in course of BE
2 Combined Engineering Practice Cases
The output-based education focuses the attention and efforts on the desired results of education which are expressed in terms of individual student learning[16].In view of the problems that need to be solved urgently in the social development, the professional lecture attempts to take some practical engineering cases as examples to stimulate students’ free thinking and cross-curricular outcomes.This achievement orientation is helpful to carry out curriculum practice teaching design.Figure 1 illustrates the engineering practice cases combining with lecture task in the course of BE.
(1)External environment of building.As shown in Fig.2, an example is the personnel escape equipment for the occupants in high-rise buildings.Especially in case of fire and other accidents, the equipment needs to be developed to ensure the personnel to escape safely in the shortest time.
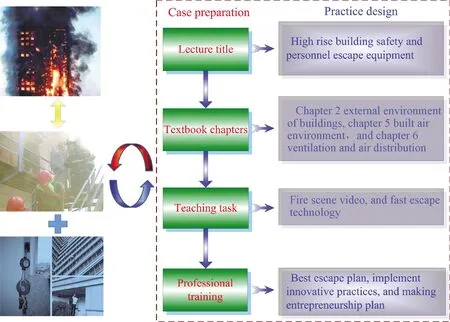
Fig.2 Case preparation and practice design of a lecture case example
(2)Hot and humid environment in building environment.An example is a temperature regulator for local cooling of human body which can avoid heatstroke and provide good comfort under extreme working conditions of high heat and humidity.
(3)Human body’s response to hot and humid environment.An example is a portable temperature regulator with cold and hot compress under special working conditions.
(4)Air environment in building environment.More and more air conditioning systems are transformed by Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence.An example is an edge controller to monitor the operation of air conditioning systems.
(5)Ventilation and air distribution.An example is a robot mounted waste collection equipment, which aims at capturing the waste residue such as the rust and paint residual produced on the surface of ship repair and paint mist produced by spraying.
The heuristic teaching method is adopted in the lecture of engineering practice cases, which enables students to think about and learn with problems, and appropriately quotes the latest scientific research achievements, so as to stimulate students’ desire for knowledge and expand their horizons.The structure of a lecture includes three flipped tasks.
(1)Before class.An engineering practice problem is put forward in the industrial process or national construction.The students are required to summarize some material and to list the solutions or schemes to solve such a problem.All students are divided into dozens of teams, and each team has three or four students.If each team has any questions, they can consult the teacher or other professionals.
(2)In class.Each team introduces the points to other teams one by one.A team shares some points such as how to deal with the problem, what means are used, what theories and techniques are used, and what results and conclusions are drawn.
(3)After class.Teachers can introduce some advanced methods adopted by researchers at home and abroad,e.g.,what problems can be solved, and what is the significance.All teams can improve or update their solutions or schemes.
3 Students’ Feedback
In order to evaluate the effect of integrating engineering practice cases into lecture task, the questionnaires were distributed to 47 students, including overall evaluation, evaluation of teaching and learning, and survey on student outcomes.Table 1 shows the students’ votes for a case example of local cooling technology of human body.The content of questionnaire on students’ feedback is illustrated in Fig.3.Twenty questions are designed to collect the students’ responses of overall evaluation, learning guide, lecture activity, and student outcomes.

Table 1 Students’ votes for local cooling technology of human body
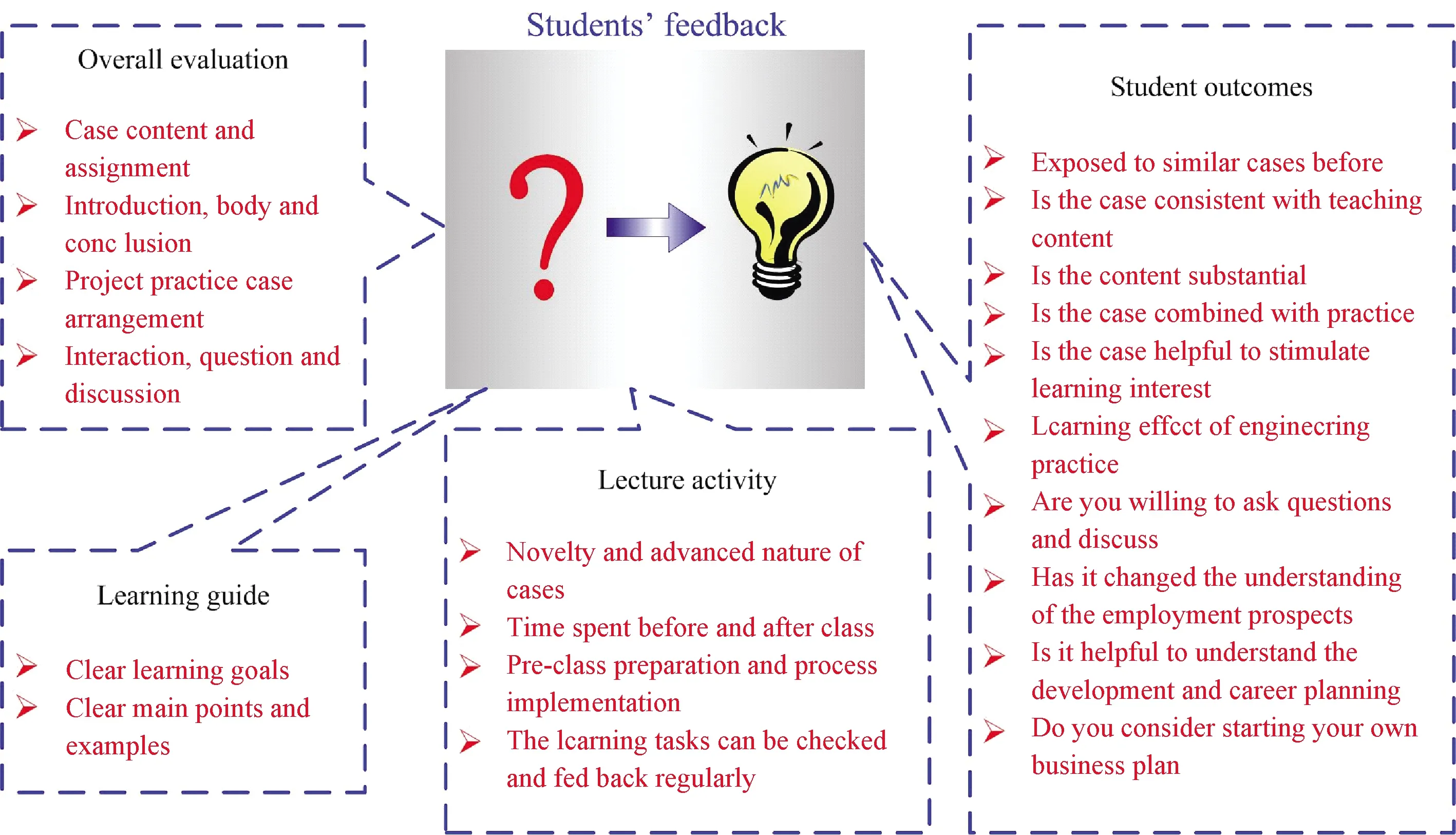
Fig.3 Content of questionnaire on students’ feedback
3.1 Overall evaluation
Table 2 lists four statements investigated for the overall evaluation of engineering practice and leaning proposal.More than 85% of the students are satisfied with the engineering practice cases, including overall evaluation, contents, classroom assignments, arrangements, and course learning proposals.The other students are generally or dissatisfied with the engineering practice and learning proposal.

Table 2 Overall evaluation of engineering practice cases and learning proposal
3.2 Evaluation of teaching and learning effect
Table 3 summarizes the evaluation of teaching and learning effect of engineering practice cases.More than 85% of the students show satisfaction with the substantial levels, contents, novelty and advanced nature, teaching schedules, relevance, spent time, pre-class preparations, class time, energy input, and interactions between teachers and students, and learning tasks of engineering practice cases.Nearly 6.39% to 14.90% of students are dissatisfied with these nine statements.In the future flipped class or lecture process, the goal and main points, the structure and language, and the practice and feedback should be paid more attention to the participation and learning activities of these students.
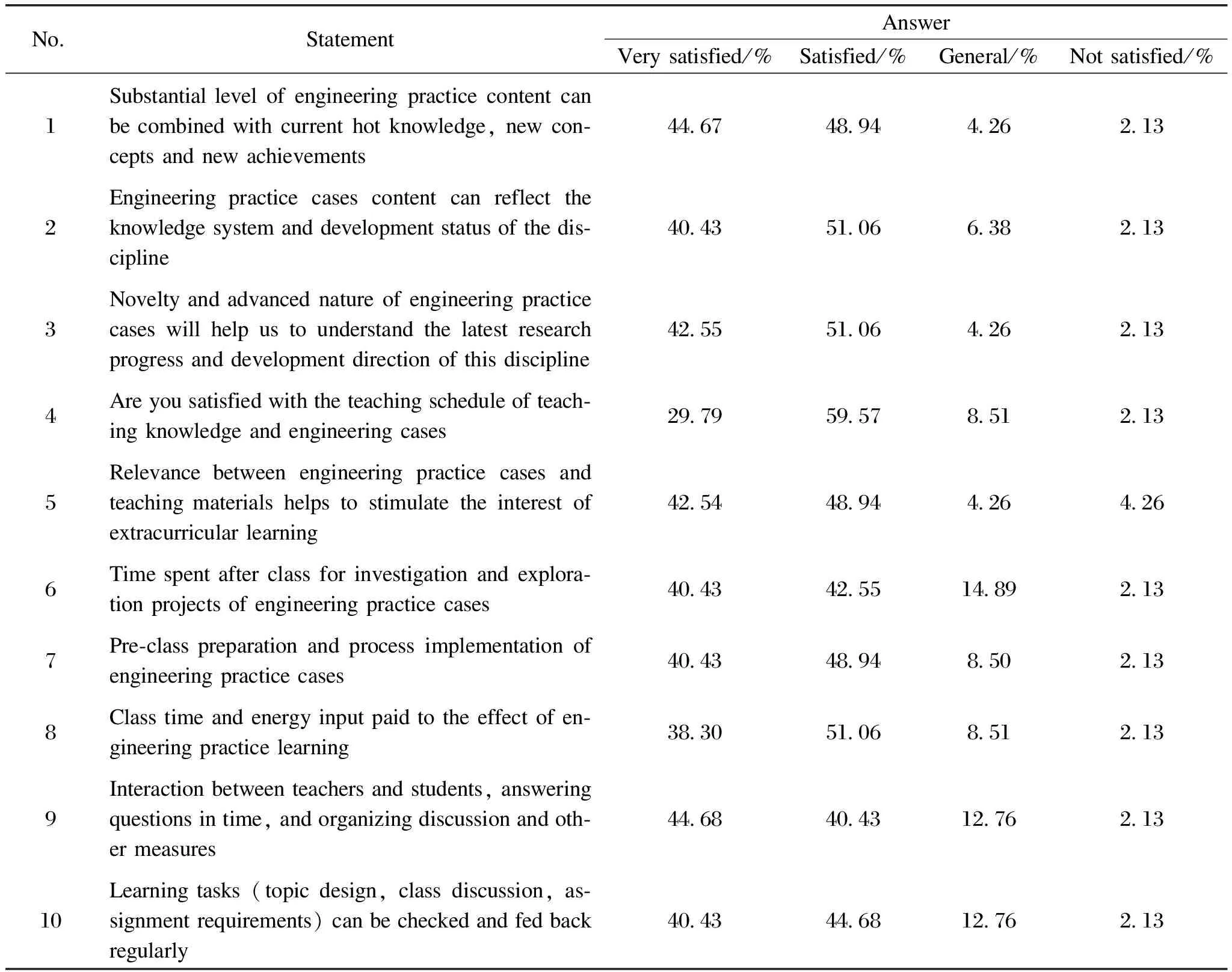
Table 3 Evaluation of teaching and learning effect of engineering practice cases
3.3 Survey on student outcomes
Figure 4 depicts the student survey results of engineering practice cases.Approximately 48.94% of students know a few of similar engineering practice cases before class, and 19.15% of students have never known any similar cases(shown in Fig.4(a)).About 42.55% of students hold that the engineering practice cases are consistent with the lecture task, and 46.81% of students consider that there is a little difference between them(shown in Fig.4(b)).Nearly 42.55% of students are willing to ask questions and discuss with colleagues or other students, and 46.81% of students exhibit a moderate attitude(shown in Fig.4(c)).About 34.04% of students significantly change their understanding of employment prospects of the major after learning the engineering practice cases, and 51.06% of students have a little change(shown in Fig.4(d)).Nearly 34.04% of students consider that the cases are helpful to understand the professional development and career planning, and 55.32% of students think that it is a little helpful(shown in Fig.4(e)).About 31.91% of students consider their own business planning through case training, and 29.79% of students will give a whirl if they have any opportunity(shown in Fig.4(f)).
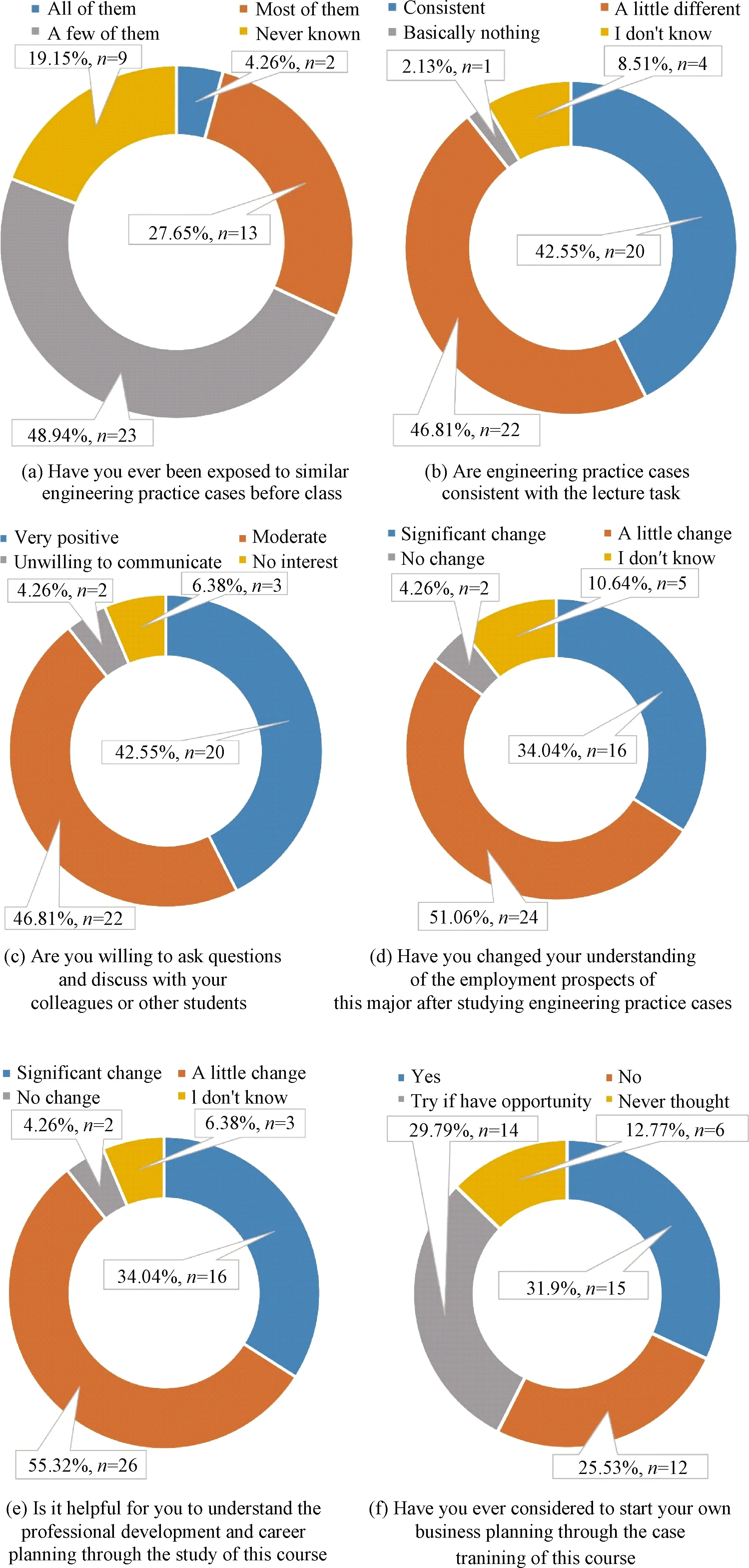
Fig.4 Survey on student outcomes of engineering practice cases
3.4 Acquisition and improvement
Some students left their message for the acquisition from the engineering practice cases and the improvement for the future lecture.The main four points are collected as follows.
(1)The lecture should focus on some key points and tell what knowledge points to be mastered, and what is the final assessment.The extra-curricular knowledge should be expanded on the basis of meeting these requirements, otherwise everything will be the castles in air.
(2)Some characteristics of built environment can be explained by the proposed engineering cases, it is suggested that much more cases could be prepared for other learning tasks.
(3)The language and rhythm in class can be slower, so that the students will have enough time to understand.
(4)Understanding these engineering cases is an important way to acquire advanced knowledge.The lecture is spoken with great passion and nothing needs to be improved.As for the students, it’s difficult to change the learning situation of college students.
According to the suggestions put forward by the students, the following three points should be paid much more attention to in the future teaching work.
(1)The key contents of each case should be further summarized to support the main knowledge points and to combine with the classroom teaching.
(2)Much more engineering practice cases should be collected to relate to the characteristics of BE and to meet with the learning tasks of lectures.
(3)The teaching language and rhythm in class should be slowed down and the students would be asked whether they have understood or not.
4 Conclusions
This study combines five engineering practice cases with the professional lecture in the course of BE.The students’ feedback and student outcomes are examined by statistically analyzing the questionnaires.
Some urgent technologies or programs in the social development are more interesting, attractive and beneficial for students to learn monotonous and dogmatic textbook knowledge.Most of the students actively participate in it, actively summarize literatures and other materials, cheerfully share their achievements, and enjoy the whole process.
The proposed engineering practice cases make comfortable for the vast majority of students.More than 85% of the students are satisfied with the engineering practice and learning proposal, and the teaching and learning effect of engineering practice cases.
The proposed engineering practice cases make sense to lecture task in the course of BE.More than 68% of the students have a little known or even unknown about the proposed five cases.And more than 85% of the students have a little or even significantly change in their understanding of the employment prospects.
 Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2022年3期
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2022年3期
- Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Effects of Concentration of(3-Aminopropyl)Triethoxysilane on Waterborne Polyurethane
- Design of Creative Incentive Contract of Cultural and Creative Industry Chain from Dual Perspective
- Design and Synthesis of Acceptor-Donor-Acceptor Type Non-Fullerene Acceptors Using Oxindole-Based Bridge for Polymer Solar Cells Applications
- PbI2/Pb5S2I6 van der Waals Heterojunction Photodetector
- Health Monitoring of Induction Motor Using Electrical Signature Analysis
- Acquisition, Pointing and Tracking System for Shipborne Space Laser Communication without Prior Information
