扫描电子束能量峰值对表面温度场的影响规律
李新凯,王荣,胡露瑶,任旭隆,王喜社
扫描电子束能量峰值对表面温度场的影响规律
李新凯1,王荣1,胡露瑶2,任旭隆1,王喜社1
(1.桂林电子科技大学,广西 桂林 541004;2.桂林旅游学院,广西 桂林 541004)

扫描电子束;能量;温度场;热源;表面改性
近年来,电子束以其非接触、可控性强、真空无污染、能量利用率高等优点而广泛应用于材料表面改性领域中[1-2]。常见的电子束表面处理技术包括电子束表面合金化、表面淬火、表面非晶态、表面熔凝等,以上电子束技术均是对金属材料表层进行处理,需实现电子束大面域、均匀、稳定下束[3-4]。
目前,国内外学者已对强流脉冲电子束与大面域辐照两种电子束表面改性加工方法进行了深入研究,主要考察电子束类型[5]及工艺参数[6]、电子束能量分布规律[7]以及表面改性优化方法[8]等方面。研究发现脉冲电子束能量密度较大,适用于处理高熔点、大深宽比金属表面改性,但处理过程中表层金属会发生溅射产生“熔坑”缺陷,同时高能作用下表层经历骤热急冷过程,易造成内应力与组织应力集中,产生结构裂纹缺陷[9-11]。大面积电子束辐照是通过电子束散焦的方式实现最大面积为60 mm范围的改性,因下束面积大所以更适用于表面微熔处理,然而该方式对电子枪功率要求较高,较难实现电子束能量的均匀分布[12]。本团队在此基础上,针对电子束表面微熔处理能量密度均匀且稳定分布的需求,开发了一种新型连续扫描电子束技术(Continuous Scanning Electron Beam Technique Process,CSEBP),通过聚焦线圈与偏转线圈共同作用,实现电子束聚焦的同时以高频率旋转实现环状下束效果[13-15]。研究发现环状扫描下束下电子枪无需高功率即可实现较高能量密度的均匀分布。另外,CSEBP能量密度分布除了受到电子束束流以及加速电压等电子枪参数影响外,还受到能量分布特征参数影。因此,有必要对电子束下束过程中能量分布规律进行探索,以指导CSEBP在表面改性领域的应用。
本文以45钢为电子束表面改性为研究对象,通过数值求解、仿真计算与试验验证相结合的方式探究能量峰值系数对电子束能量分布的影响规律,详细探讨了多种峰值系数下45钢表层温度的变化规律,并通过电子束微熔试验进行验证,力图为电子束大面域扫描提供新的方法和理论依据。
1 扫描电子束微熔处理数学物理模型的建立
1.1 CSEBP下束方式原理
本课题组自主研发的扫描电子束下束方式如图1所示,其中,为工件移动速度,为扫描带半径,为扫描长度,扫描带纵向5个均分点为后续热循环曲线仿真取样点。其原理是将编辑好的电子束扫描轨迹及运动方式的控制程序输入信号发生器,用方程x+y=2来描述圆形的电子束扫描轨迹,其中方向的分量分别为cos,sin(0≤≤π),通过所产生的偏转磁场实现电子枪内部束流沿固定角度倾斜与高频旋转,从而实现环状扫描电子束轨迹。
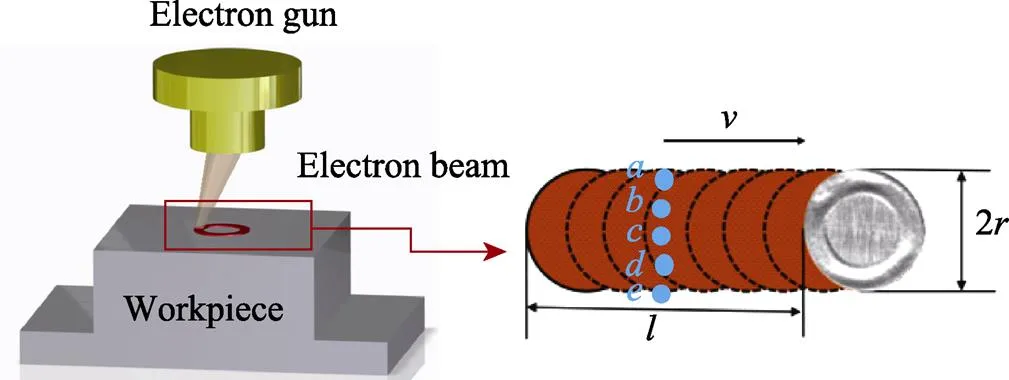
图1 连续扫描电子束(CSEBP)示意图
1.2 环状下束电子束能量分布数学模型
环状电子束热源与常用的高斯热源、双椭球热源有较大不同,其作用形式为高斯热源在环形区域的叠加。为此以高斯热源为基础搭建环状电子束能量密度函数,如图2和图3所示。

图2 电子束能量密度分布图
设表面中心处的热流密度()为:

式中:为任意一点的热流密度(W);m为最大热流密度(W/m2);为任意一点到加热中心的距离(m);为热源集中系数。
扫描电子束微熔处理时在扫描面的功率为:
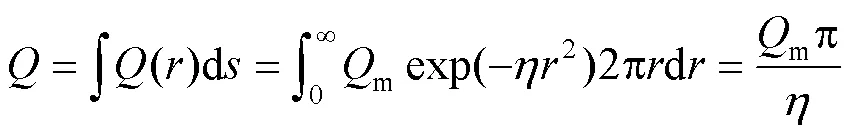
由式(2)得:
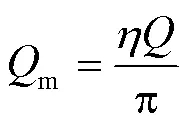
将式(3)代入(1)得:
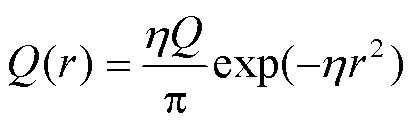
通常情况下扫描电子束处理时,一般取95%的有效能量范围[18]。

由此可得:

因电子束作用过程中,束斑内能量峰值可调,为此引入能量峰值位置参数,综合以上计算可将扫描电子束能量分布数学模型表征为:


式中:Rx为电子束下束环外径(mm);Rp为电子束能量峰值位置距离z轴的距离(mm);rx为圆环内径(mm);为束流偏转角(°);为能量峰位置系数,;z为离焦量(mm),R0为束斑宽度(mm)。
1.3 能量峰值对电子束热源模型的影响
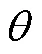
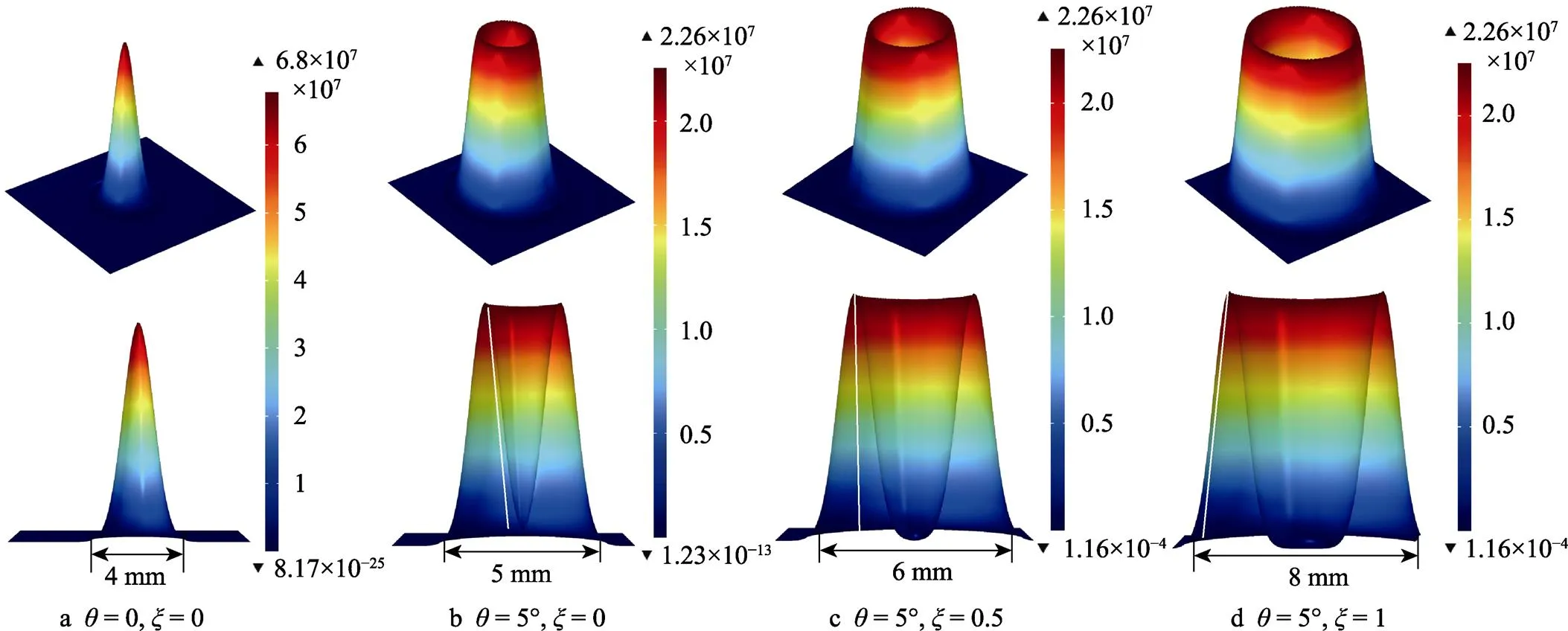
图4 不同入射角度和能量峰值系数下的电子束能量分布模拟图
上述所建立的电子束热源数学模型中引入能量峰位置系数,可对环形区域内的电子束能量分布状态作更加详细的定义,该系数对平衡环形束斑内外侧温度补偿与中心热传导有重要意义。
2 建立扫描电子束有限元模型
2.1 模型假设
电子束表面处理过程是一个骤热急冷的非稳态过程,表层的金属的熔融与凝固均在极短时间内完成,为简化模型、减少运算量,对模型作出以下假设:45钢的热物性参数为温度的函数;电子束扫描过程中热传导处于稳态;样为各向同性的均匀介质;试样被处理前的温度和所处的工作室温度均为300 K;不考虑热对流;忽略组织相变引起的塑性变形[19-20]。
2.2 几何建模与网格划分
采用COMSOL软件对45钢扫描电子束微熔过程进行模拟,模型尺寸与实际试样尺寸一致,为50 mm× 50 mm×50 mm,在工作面选取50 mm×8 mm区域作为电子束加工区域,并进行网格加密处理,电子束扫描区域采用六面体的单元类型进行较细的网格划分,其他区域采用四面体的单元类型进行智能网格划分,网格划分模型如图5所示[21-22]。模型内部为均匀介质,所以将试样中某处定义为微元控制体积ddd。
电子束扫描试样表面时,热传导会通过控制体积的各个面发生。利用泰勒公式展开控制表面的导热速度,直角坐标系中的热扩散方程为:
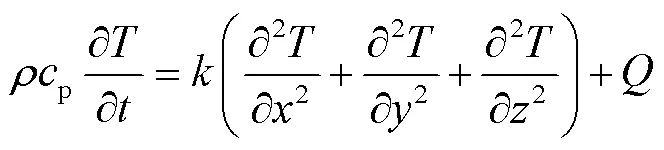
式中:为密度(kg/m3);为定压比热容(J·kg/K);k为导热系数(W/(m·K))。
2.3 电子束热源模型及边界条件
扫描电子束是以高能电子束轰击金属表面产生的高温为热源,并以指定速度平移实现大面域扫描,由上述搭建能量分布数学模型,其移动热源与时间的函数表达式为:

扫描电子束微熔处理是在真空环境中进行,真空度为10‒2Pa,故可忽略空气热对流造成的热量损失,而热辐射的传递不需借助任何介质[23]。因此可认为基体的导热与表面的热辐射是工件主要散热方式,电子束热源作用区域的传热方程为:

热辐射满足第三类边界条件,可由斯蒂芬–波尔兹曼方程来计算:
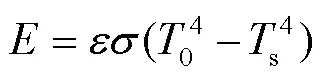
3 扫描电子束微熔处理温度场仿真分析
根据前期研究结果[24-25],温度场仿真工艺参数为:=60 kV,=5 mA,=3 mm/s,=230 mm,R+0/2=2 mm,=5°,=400 Hz,整个电子束加热时间为16.7 s。
3.1 电子束能量峰值对热循环过程的影响
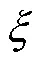

图6 扫描带上不同点热循环曲线

3.2 电子束能量峰值对温度场的影响
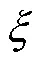
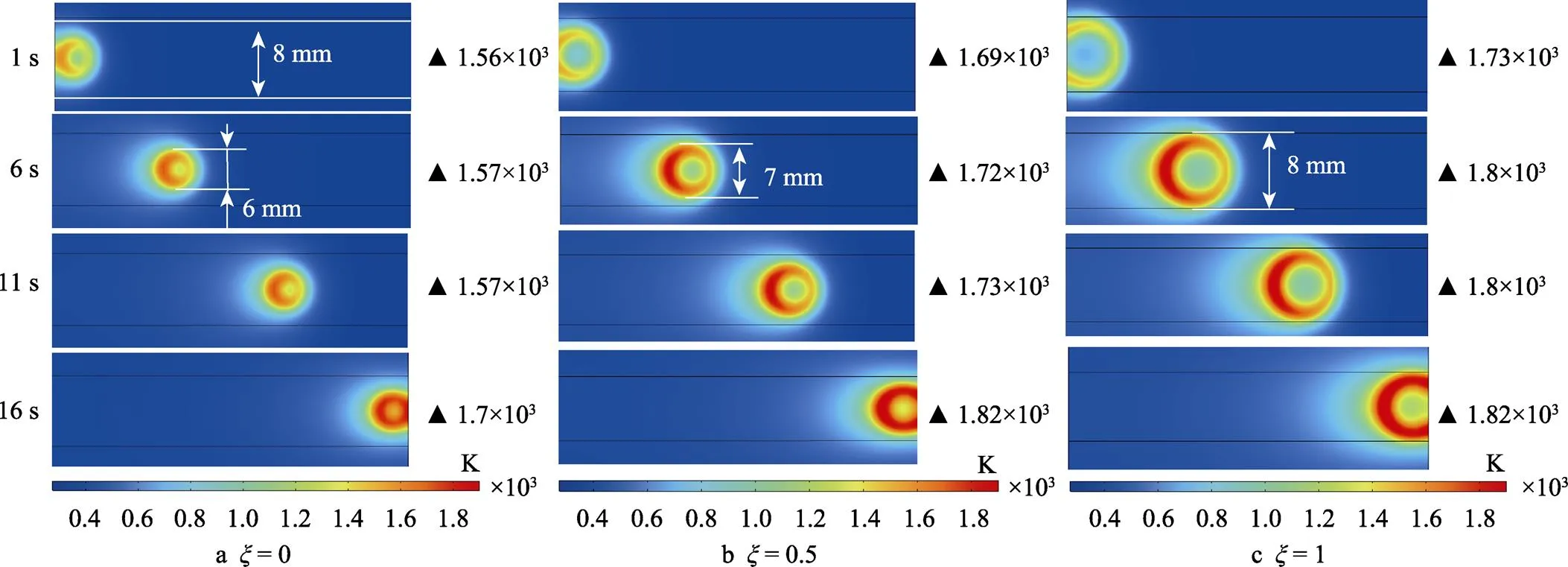
图7 扫描区温度云图

4 扫描电子束微熔处理试验
试验选用45钢作为实验用原材料,使用铣床将原材料加工成50 mm×50 mm×50 mm的立方体,加工过程中通过控制进刀量、铣削速度、主轴转速等参数恒定,将试样表面粗糙度控制在1.9~2.0 μm内,电子束加工前使用酒精擦拭表面并风干,去除表面油污。使用HDZ–6F型高压数控真空电子束机进行表面处理试验,实验参数与数值模拟参数一致。采用光学显微镜对熔融层进行观测,采用OLS4100激光显微镜测试处理后表面粗糙度。每个待测面均匀测量5次粗糙度,取其均值作为该面粗糙度值。


图8 不同峰值系数下的表面形貌
5 结论



[1] LEE T, BIAN Hua-kang, AOYAGI K, et al. Fabricating 9-12 Cr Ferritic/Martensitic Steels Using Selective Electron Beam Melting[J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 271: 127747.
[2] GUO Shun, ZHOU Qi, KONG Jian, et al. Effect of Beam Offset on the Characteristics of Copper/304stainless Steel Electron Beam Welding[J]. Vacuum, 2016, 128: 205-212.
[3] LI Xin-kai, WANG Rong, XIN Zhe, et al. Changes in Surface Roughness and Microstructure of 45 Steel after Irradiation by Electron Beam[J]. Materials Letters, 2021, 296: 129934.
[4] IVANOV Y F, ZAGULIAEV D V, GLEZER A M, et al. Changes in Surface Structure and Mechanical Characteristics of Al-5 wt%Si Alloy after Irradiation by Electron Beam[J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 275: 128105.
[5] LU Jian, SUI Xin-meng, YANG Bo-hang, et al. Ultrafast In-Situ Transformation of Graphite into Graphene Nanosheets by High Current Pulsed Electron Beam Direct Irradiation[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 572: 151498.
[6] LEI Shuang, LI Xian-feng, DENG Ya-qi, et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Electron Beam Freeform Fabricated TiB2/Al-Cu Composite[J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 277: 128273.
[7] LI Xin-kai, WANG Rong, WANG Qi-chao, et al. Scanning Electron Beam Polishing and Defect Analysis of 65 Steel[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms, 2021, 490: 34-38.
[8] 陈军, 李伟, 贺冬云, 等. 强流脉冲电子束表面改性FeCrAl涂层的显微组织及耐高温腐蚀性能研究[J]. 表面技术, 2020, 49(5): 200-206.
CHEN Jun, LI Wei, HE Dong-yun, et al. Surface Microstructure and High-Temperature Erosion Resistance of FeCrAl Coating after High Current Pulsed Electron Beam Treatment[J]. Surface Technology, 2020, 49(5): 200-206.
[9] LU Jian, WEI De-qiang, WANG Rong, et al. Surface Polishing and Modification of 3Cr2Mo Mold Steel by Electron Beam Irradiation[J]. Vacuum, 2017, 143: 283- 287.
[10] LV Peng, SUN Xiao, CAI Jie, et al. Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Nickel Based Alloy GH4169 Irradiated by High Current Pulsed Electron Beam[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 309: 401-409.
[11] HAO Sheng-zhi, WANG Hui-hui, ZHAO Li-min. Surface Modification of 40CrNiMo7Steel with High Current Pulsed Electron Beam Treatment[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms, 2016, 368: 81-85.
[12] FU Yu-lei, HU Jing, SHEN Xian-feng, et al. Surface Hardening of 30CrMnSiA Steel Using Continuous Electron Beam[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms, 2017, 410: 207-214.
[13] WEI De-qiang, WANG Xiao-bing, WANG Rong, et al. Surface Modification of 5CrMnMo Steel with Continuous Scanning Electron Beam Process[J]. Vacuum, 2018, 149: 118-123.
[14] CUI Hong-yang, WANG Rong, WEI De-qiang, et al. Surface Modification of the Carbon Tool Steel by Continuous Scanning Electron Beam Process[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms, 2019, 440: 156-162.
[15] LI Xin-kai, WANG Rong, DONG Yu-jian, et al. Surface Morphology and Grain Size of 45 Steel after Scanning by Electron Beam[J]. Materials Letters, 2021, 297: 129884.
[16] 李广琪, 王丽芳, 朱刚贤, 等. 扫描方式对中空环形激光熔覆层残余应力及基板变形的影响研究[J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(3): 158-170.
LI Guang-qi, WANG Li-fang, ZHU Gang-xian, et al. Influence of Scanning Patterns on Residual Stress of Cladding Layer and Substrate Deformation Produced by Hollow-Ring Laser Cladding[J]. Surface Technology, 2021, 50(3): 158-170.
[17] 胡兴, 彭昭成, 冯广杰, 等. SUS310S不锈钢局部真空电子束焊接接头残余应力及变形研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(21): 38-47.
HU Xing, PENG Zhao-cheng, FENG Guang-jie, et al. Numerical Simulation of Residual Stress and Deformation of SUS310S Stainless Steel Local Vacuum Electron Beam Welded Joint[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(21): 38-47.
[18] 魏德强, 李新凯, 王晓冰. 电子束抛光技术的研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2016, 45(4): 175-182.
WEI De-qiang, LI Xin-kai, WANG Xiao-bing. Research Progress of Electron Beam Polishing Technology[J]. Surface Technology, 2016, 45(4): 175-182.
[19] 郭顺, 罗添元, 彭勇, 等. Ti/Cu异种金属电子束焊接界面行为[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(8): 26-32, 162.
GUO Shun, LUO Tian-yuan, PENG Yong, et al. Interface Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Ti/Cu Dissimilar Metals Welding by Electron Beam[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(8): 26-32, 162.
[20] 房玉超, 杨子酉, 何景山. 电子束点焊熔池的液态金属冲刷效应作用规律[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(6): 137-142, 167.
FANG Yu-chao, YANG Zi-you, HE Jing-shan. Study on Liquid Metal Flushing Effect during Electron Beam Spot Welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(6): 137-142, 167.
[21] 赵桐, 唐振云, 刘巧沐, 等. GH4065A合金电子束焊接工艺及接头组织性能[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(22): 22105-22110.
ZHAO Tong, TANG Zhen-yun, LIU Qiao-mu, et al. Electron Beam Welding Process and Microstructure and Properties of Joint of GH4065A Alloy[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(22): 22105-22110.
[22] 郭超, 林峰, 葛文君. 电子束选区熔化成形316L不锈钢的工艺研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(21): 152-158.
GUO Chao, LIN Feng, GE Wen-jun. Study on the Fabrication Process of 316L Stainless Steel via Electron Beam Selective Melting[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(21): 152-158.
[23] REISGEN U, OLSCHOK S, KRICHEL T, et al. Determination of the Influence of Welding Parameters on the Efficiency of Electron Beam Welding by Measurement of Backscattered Electrons[J]. Vacuum, 2019, 159: 182-185.
[24] 李新凯, 王荣, 王启超, 等. 扫描电子束微熔抛光临界功率密度规律及实验研究[J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(7): 386-393.
LI Xin-kai, WANG Rong, WANG Qi-chao, et al. Research on Critical Power Density and Experiment of Scanning Electron Beam Micro-Melting Polishing[J]. Surface Technology, 2021, 50(7): 386-393.
[25] Lu Jian, Wei De-qiang, Wang Rong, et al. Surface Polishing and Modification of 3Cr2Mo Mold Steel by Electron Beam Irradiation[j]. Vacuum, 2017, 143: 283-287.
[26] NIU Shao-qiang, YOU Qi-fan, YOU Xiao-gang, et al. Mechanism of Impurities Reduction and Evaporation of Alloying Elements for a Multi-Elements Ni-Based Superalloy during Electron Beam Remelting[J]. Vacuum, 2018, 156: 345-350.
[27] WANG Rong, YU Jie, WEI De-qiang, et al. Surface Microstructures and Improved Mechanical Property of 40CrMn Steel Induced by Continuous Scanning Electron Beam Process[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms, 2019, 459: 130-136.
The Influence of the Peak Energy of Scanning Electron Beam on the Surface Temperature Field
1,1,2,1,1
(1. Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guangxi Guilin 541004, China; 2. Guilin Tourism University, Guangxi Guilin 541004, China)
The mathematical model of energy distribution in the circular downward beam mode of scanning electron beams is clearly defined. Obtain the influence law of energy crest factor on the surface temperature field of 45 steel. Based on the Gaussian heat source model, the energy peak position parameter is introduced to calculate the mathematical model of the energy distribution in the scanning electron beam downward beam mode. The COMSOL software was used to simulate the thermal cycle curve and temperature field of the scanning zone. Revised the electron beam heat source model in the ring-shaped downward beam mode. The results show that the electron beam energy distribution was symmetrically distributed along the center line. The surface energy distribution was related to the deflection angle and the energy peak parameter. When the energy peak parameter was within 0 to 1, the value becomes higher and higher, the larger the first and second energy peaks at point, the larger the difference between the two. When the parameter was 0, the maximum temperature difference at the sampling point was 1 065 K. The smaller the temperature difference between the longitudinal points of the scanning belt, the smaller the distance between the thermal cycle curves. At the same time, it can be seen from the heat source model that the energy peak has a greater impact on the beam diameter of the ring electron beam, and the maximum ring diameter can be up to 8 mm under the selected basic parameters. When the parameter was 1, the temperature curves of the sampling points are the closest, which indicates that the surface heat distribution under this parameter was uniform. It can be seen from the temperature field simulation diagram that the beam spot temperature varies greatly during the down and converging phases of the electron beam, while the temperature in the middle of the scan was relatively stable, and the temperature difference was basically stable within 20 K. The larger the energy peak parameter, the larger the radius of the high temperature area on the surface of 45 steel, and the maximum temperature will increase accordingly. After 45 steel was subjected to different energy peak coefficients, the width of the scanning zone and the sub-high temperature zone were different. Finally, based on the simulation parameters, the scanning electron beam micro-melting polishing experiment was carried out. It was found that the surface roughness of 45 steel was reduced under this scanning mode, and the surface showed a bright white scanning area relative to the substrate. The scanning area width increased with the increase of the energy peak parameter. This was in full agreement with the simulation results. The surface roughness after scanning electron beam treatment was as low as 0.36 μm relative to the substrate. In the end, the following conclusion can be drawn that the energy peak parameter has a great influence on the energy distribution of the ring electron beam. When= 1, the energy gradient of each position on the surface of the scanning area was the smallest, which was beneficial to the uniform energy distribution under the surface modification of the large area electron beam.
scanning electron beams; energy; temperature field; heat source; surface modification
V261.6
A
1001-3660(2022)07-0306-08
10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2022.07.030
2021–04–02;
2021–11–20
2021-04-02;
2021-11-20
广西自然科学基金项目(2020GXNSFBA297079,2022GXNSFAA035585);国家自然科学基金资助项目(52165057,51665009);桂林市重点研发计划(20211B032068)
Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Project (2020GXNSFBA297079, 2022GXNSFAA035585); National Natural Science Foundation of China (52165057, 51665009); Guilin City Key Research and Development Plan (20211B032068)
李新凯(1993—),男,博士研究生,主要研究方向为电子束表面改性。
LI Xin-kai (1993-), Male, Ph. D. candidate, Research focus: electron beam surface modification.
王喜社(1966—),女,高级实验师,主要研究方向为数控加工与工艺优化。
WANG Xi-she (1966-), Female, Senior experimenter, Research focus: CNC machining and process optimization.
李新凯, 王荣, 胡露瑶, 等. 扫描电子束能量峰值对表面温度场的影响规律[J]. 表面技术, 2022, 51(7): 306-313.
LI Xin-kai, WANG Rong, HU Lu-yao, et al. The Influence of the Peak Energy of Scanning Electron Beam on the Surface Temperature Field[J]. Surface Technology, 2022, 51(7): 306-313.
责任编辑:万长清

