Phytochemicals targeting NF-κB signaling:Potential anti-cancer interventions
Aknsh Chuhn,Asim Ul Islm,Hridyesh Prksh,Sndhy Singh,*
aAmity Institute of Physiology&Allied Sciences,Amity University,Noida,Uttar Pradesh,India
bCentre for Interdisciplinary Research in Basic Sciences,Jamia Millia Islamia,New Delhi,India
cAmity Institute of Virology&Immunology,Amity University,Noida,Uttar Pradesh,India
ABSTRACT
Nuclear factor κB(NF-κB)is a ubiquitous regulator of the signalome and is indispensable for various biological cell functions.NF-κB consists of five transcription factors that execute both cytoplasmic and nuclear signaling processes in cells.NF-κB is the only signaling molecule that governs both pro-and antiapoptotic,and pro-and anti-inflammatory responses.This is due to the canonical and non-canonical components of the NF-κB signaling pathway.Together,these pathways orchestrate cancer-related inflammation,hyperplasia,neoplasia,and metastasis.Non-canonical NF-κB pathways are particularly involved in the chemoresistance of cancer cells.In view of its pivotal role in cancer progression,NF-κB represents a potentially significant therapeutic target for modifying tumor cell behavior.Several phytochemicals are known to modulate NF-κB pathways through the stabilization of its inhibitor,IκB,by inhibiting phosphorylation and ubiquitination thereof.Several natural pharmacophores are known to inhibit the nuclear translocation of NF-κB and associated pro-inflammatory responses and cell survival pathways.In view of this and the high degree of specificity exhibited by various phytochemicals for the NF-κB component,we herein present an in-depth overview of these phytochemicals and discuss their mode of interaction with the NF-κB signaling pathways for controlling the fate of tumor cells for cancerdirected interventions.
Keywords:
Cancer
Transcription factor
Phytochemicals
Inflammation
Chemoprevention
Peer review under responsibility of Xi'an Jiaotong University.
1.Introduction
Nuclear factor κB(NF-κB)is a master transcription factor with multiple roles in all mammalian cells,such as the production of cytokines,stimulation of DNA transcription,and cell survival.It is also intricately involved in cell responses to various stimuli,such as stress,heavy metals,free radicals,oxidized low-density lipoprotein(LDL),UV irradiation,and bacterial/viral antigens.NF-κB was discovered by Sen and Baltimore thirty years ago as a rapidly inducible transcription factor[1].NF-κB has been identified as a nuclear factor that selectively binds to the kappa(κ)light chain enhancer and is present in B cell tumors as well as in other types of cells.NF-κB exists in cells in an inhibited state[2],due to the action of inhibitor of κB(IκB).IκB forms a stoichiometric complex with NF-κB in the cytoplasm and prevents it from binding to DNA[2].NF-κB has gained enormous attention since its discovery owing to its comprehensive role in diverse biological processes.
The NF-κB protein family comprises two subfamilies of proteins,namely,the ‘NF-κB’proteins and the ‘Rel’proteins[3].The Rel family consists of three proteins:RelA(p65),RelB,and c-Rel.p105 and p100 are the two members of the NF-κB protein family[4].The NF-κB subfamily contains multiple copies of ankyrin repeats containing long C-terminal domains.Ankyrin repeats are involved in the inhibition of these proteins[5].The two NF-κB proteins transform into active shorter proteins that bind to DNA.p105 changes to p50,and p100 to p52 as a result of limited proteolysis or,perhaps in some cases,via arrested translation.NF-κB subfamily members are generally not transcription activators,but they become transcription activators once they form dimers with Rel subfamily members[6].A Rel homology domain is present in the N-terminus of both NF-κB proteins;in contrast,the C-termini of the Rel proteins contain a transactivation domain.The ubiquitin/proteasome pathway mediates the processing of p105 and p100 by selective degradation of the C-terminal region,which contains ankyrin repeats[7].
Interaction with inhibitory IκB proteins tightly regulates NF-κB activity.NF-κB is present in the cytoplasm of most cells in the form of a dormant and inactive IκB-bound complex.Activation of the IκB kinase(IKK)complex is required for NF-κB complex functioning.IKK comprises two catalytic units:IKKα and IKKβ,and a regulatory unit,IKKγ.IKK causes phosphorylation-induced degradation of the IκB inhibitor,which enables nuclear translocation of NF-κB,leading to target gene expression[8].
2.NF-κB transduction pathway
Two NF-κB signal transduction pathways operate in the cytoplasm:the classical or canonical NF-κB pathway,and the alternate or non-canonical NF-κB pathway.
In the classical NF-κB pathway,the NF-κB dimer p50/RelA is maintained in the cytoplasm by interacting with an independent molecule of IκB.In a number of cases,when a ligand binds to the receptors,such as tumor necrosis factor receptor(TNF-R)or tolllike receptor(TLR),at the cell surface,adaptors for the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor are recruited.These receptors then assemble an IKK complex and two NF-κB essential modulator(NEMO)molecules,which act as regulatory scaffolds,directly onto the cytoplasmic adaptors as a result of the k63-ubiquitin-binding activity of NEMOs.The IKK complex is activated by the clustering of molecules at the receptors.IκB phosphorylation by IKK occurs at two serine residues,and the proteasome causes K48 degradation and ubiquitination.Target genes are thus turned on by the entry of NF-κB into the nucleus.The capability of the canonical pathway to auto-regulate IκB α gene expression is activated by NF-κB,causing the newly synthesized IκB protein to re-sequester the complex in the cytoplasm.
The alternative NF-κB pathway activates the p100/RelB complex during the development of B-and T-cells.In contrast to the classical pathway,the alternative pathway is activated by very few receptor signals,such as lymphotoxinβ (LTβ),B-cell activating factor(BAFF),and cluster of differentiation 40(CD40).Another difference is that it moves through an IKK complex with two IKKα subunits and no NEMO.In the case of the alternate pathway,receptor binding activates the NF-κB-inducing kinase(NIK),resulting in IKKα complex phosphorylation and activation.Phosphorylation of the serine residues adjoining the ankyrin repeats in the C-terminal of the IκB domain causes the liberation of the p52/RelB complex via partial proteolysis[4,9].A stepwise diagrammatic representation of the classical and alternative pathways is outlined in Fig.1.
Other NF-κB pathways also exist.For example,in another pathway,the p50 or p52 homodimers enter the nucleus and interact with IκB,such as co-activator B-cell lymphoma 3(Bcl-3),and become transcriptional activators;however,this pathway requires further exploration[10].

Fig.1.The two NF-κB pathways:the classical and alternate pathways.
3.NF-κB in homeostasis
The NF-κB pathway is a central regulator of cellular responses that maintain physiological status and disease pathology due to its unique properties.In innate immunity,inflammation acts as a key defense mechanism against bacterial/viral infections to maintain tissue homeostasis and facilitate wound healing.A wide array of stress-inducing stimuli activate inflammation rapidly,providing the cell with a swift and sensitive detection system for protection against potential threats in its microenvironment.
Genetic mouse model studies have provided evidence that NF-κB signaling in keratinocytes in the epidermis is important for maintaining immune homeostasis in the skin.Epidermises deficient in RelA/c-Rel develop TNF-dependent skin inflammation and epidermal hyperplasia when grafted onto recombination activating gene 1(Rag-1)knock out animals.This suggests that RelA and c-Rel mediate the skin immune homeostasis maintenance function of NF-κB in keratinocytes[11].In another study,it was found that targeted deletion of IKKβ in dendritic cells inhibited non-lymphoid tissue dendritic cell accumulation in lymph nodes,as well as the regulatory conversion of T-cells in vivo.This causes autoimmune responses and impaired tolerance.NF-κB has been shown to play a role in immune homeostasis and tolerance,and is thus a possible factor affecting autoimmune diseases and immunity[12].Recent studies on NF-κB cell-specific function in intestinal epithelial cells(IECs)suggest that NF-κB activation plays an important role in the maintenance of immune homeostasis.Specific ablation of NEMO in mouse model IECs manifested in severe chronic colitis accompanied by intestinal bleeding,diarrhea,and weight loss[13].
Mice embryos deficient in RelA died in-utero due to fetal liver degeneration induced by tumor necrosis factor(TNF),providing key evidence for the necessity of NF-κB signaling for hepatocyte functioning.Normal homeostasis in the adult liver also becomes compromised in liver parenchymal cells(LPCs),and the hepatocytes become sensitized to acute injury caused by TNF[13].Mice exhibiting LPC-specific ablation of NEMO develop chronic hepatitis,characterized by inflammation of the liver,hepatocyte apoptosis and compensatory proliferation,steatosis,and liver progenitor activation[13].
A comparative study between cells with NF-κB-p65 overexpression and those containing the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2(Nrf-2)transcription factor,which is well known to be involved in antioxidant homeostasis,indicated similar increases in glutathione peroxidase activity and protein levels of glutamyl cysteine transferase and superoxide dismutase.In addition,a decrease in reactive oxygen species(ROS)levels was observed,suggesting that NF-κB signaling is directly involved in maintaining antioxidant homeostasis[14].
4.NF-κB in cancer
NF-κB plays a constitutive role in human cancer due to the inflammatory microenvironment of cancer cells.Chronic inflammation leads to oncogenic mutations that promote the initiation and development of tumors[15].Tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis suppression are promoted by NF-κB activity.NF-κB also induces angiogenesis and aids in distant metastasis.The pro-tumorigenic environment is directly perpetuated by the accumulation of proinflammatory cytokines at the tumor site.In patients with inflammatory bowel disease(IBD),pro-tumorigenic cytokines,such as TNF-α,interleukin-1(IL-1),and IL-7,are secreted by immune cellsthat enter the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract,causing elevated levels of NF-κB activity and increasing the risk of colon cancer[16].
A positive feedback loop is formed when the NF-κB pathway is activated by immune cells,resulting in enhanced NF-κB activity at the site of inflammation in various types of cells.NF-κB activation also leads to the expressions of activation-induced cytidine deaminase(AID),an enzyme that induces mutations in p53,Myc,and other cellular genes[17].
Genes that regulate apoptosis,such as cellular apoptosis inhibitor proteins1/2(c-IAP1/2 and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein(XIAP),FLICE-like inhibitory protein(FLIP),and members of the B-cell lymphoma 2(BCL-2)family,are stimulated by NF-κB.Mice embryos lacking RelA,IKK2,or NEMO perish between E12.5 and E15,primarily due to TNF-α-induced hepatocyte toxicity[18].This indicates that tumor cells probably also depend on the NF-κB pathway to avoid apoptosis.
Vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF)is among the most studied angiogenic factors,the expression of which is actively regulated by hypoxia inducing factor(HIF)-1α during hypoxic conditions,as well as by stimuli such as cytokines and oncogenes[19],which are also critical mediators of NF-κB activation.Additionally,it has been established that NF-κB inhibition leads to the cessation of VEGF production and angiogenesis.
Factors such as basic fibroblast growth factor(bFGF),IL-8,matrix metallopeptidase 9(MMP-9),and other NF-κB target genes are engaged in multiple steps of angiogenesis[20].
4.1.Growth signals
Cyclin D proteins are key regulators of the cell cycle,and NF-κB binds to the promoter of the three Cyclin D proteins:CyclinD1,D2,and D3,as well to several other essential transcription factors[21].Cell proliferation is thereby monitored by NF-κB activation,triggering genes for growth factors,such as hepatocyte growth factor(HGF)[22],granulocyte-colony stimulating factor(G-CSF)[23],and bone morphogenic protein(BMP)[24].
4.2.Anti-apoptosis
The classical NF-κB pathway turns on the transcription of antiapoptotic genes,such as c-FLIP,BCL-XL,A20,and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein(cIAP).Along with transcription,NF-κB inhibition initiates apoptosis and enhances c-Jun N-terminal kinase(JNK)activity[25].
4.3.Angiogenesis
Mitogens,such as IL-6,are produced via the activation of tumor cells by adjoining myeloid cells or Kupffer cells.NF-κB present in hematopoietic-derived Kupffer cells leads to the production of these mitogens,which results in the initiation of angiogenesis and tumors[26].As mentioned,HIF is a major regulator of VEGF,but NF-κB is also partially responsible for VEGF regulation.In addition to VEGF,numerous other angiogenic factors exist;chemokines such as IL-8,monocyte chemoattractant protein-1(MCP-1),and growth regulated oncogene(Gro-a)are representative examples.NF-κB primarily regulates these chemokines,and their secretion levels in cancer cells decrease when the activity of NF-κB is inhibited in colorectal cancer cells.
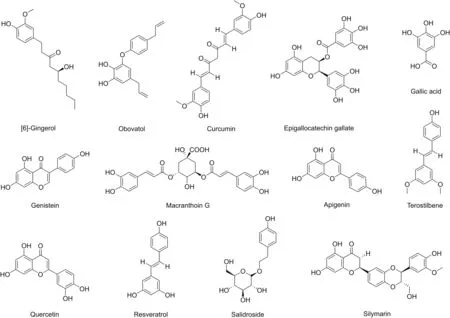
Fig.2.Chemical structures of Polyphenols targeting NF-κB.
4.4.Metastasis
Activation of NF-κB has been shown to enhance cancer cell metastasis in various tumors.Maintenance and accelerated induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition(EMT)occurs in cancer cells,and transforming growth factor- β (TGF-β)family members have been shown to promote EMT[16].Studies have shown that EMT also promotes NF-κB activation.NF-κB regulates Snail,a zinc finger transcription factor[27].E-cadherin is regulated by Snail,and intercellular cadherin-mediated adhesion is also promoted,causing EMT promotion[28].Studies have demonstrated that macrophages are activated by tumor cells through Tolllike receptors(TLRs),and these activated macrophages promote metastasis[29].NF-κB target genes that promote various phases of cancer development and progression are shown in Table 1.

Table 1Target genes of NF-κB that participate in various stages of cancer.
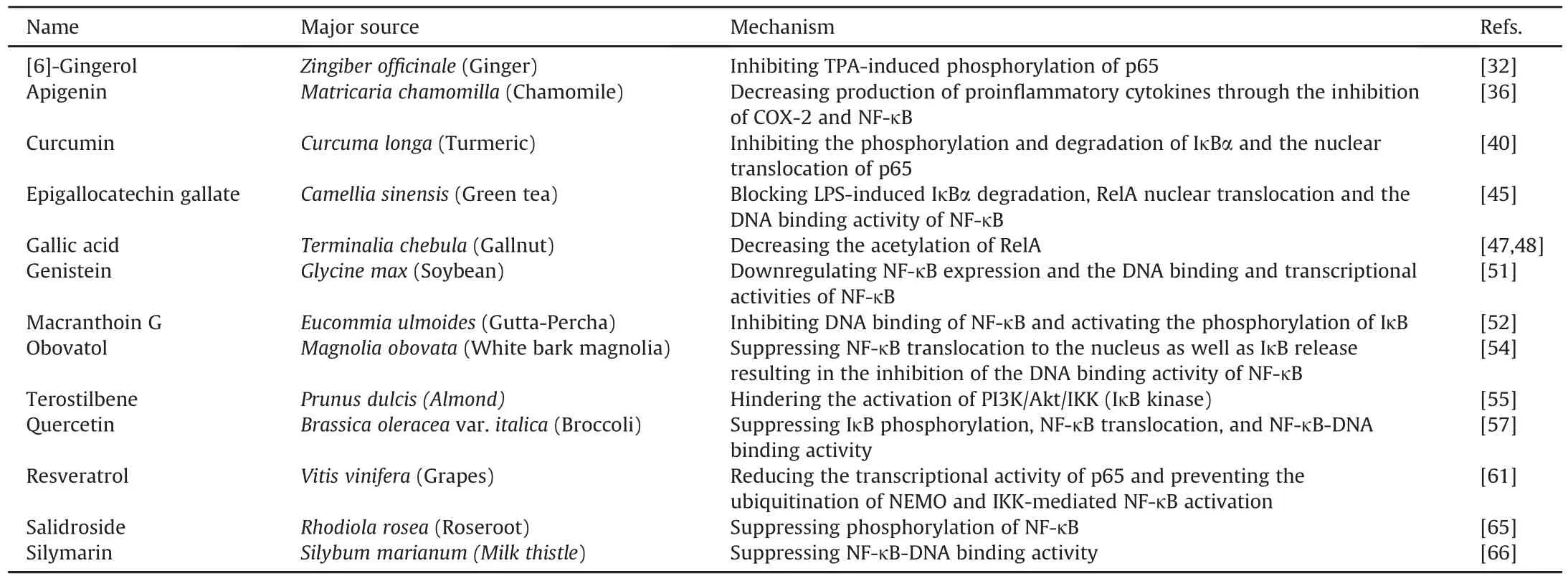
Table 2Polyphenols modulating NF-κB activity.
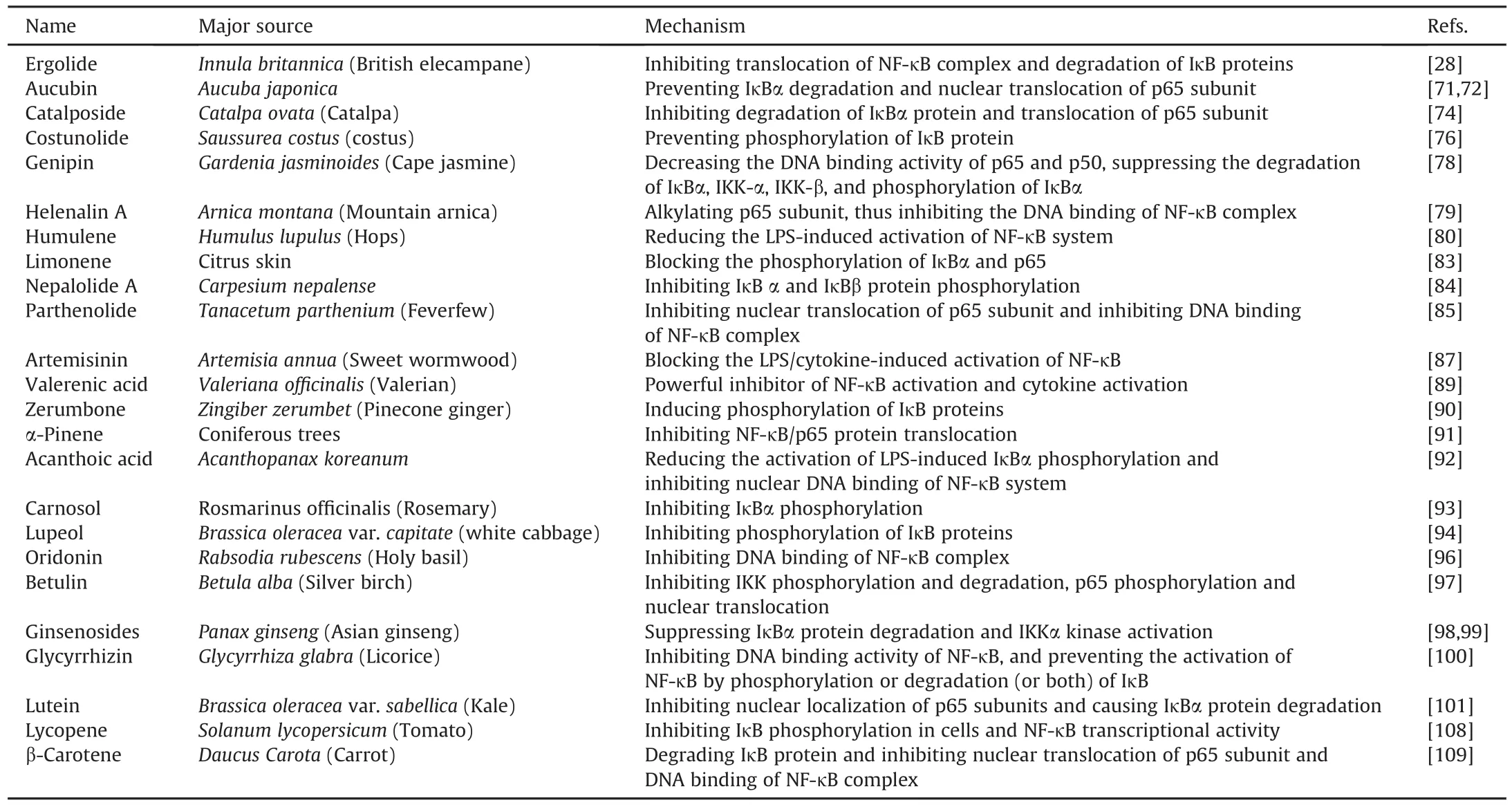
Table 3Terpenoids modulating NF-κB activity.
5.NF-κB-targeting phytochemicals
Phytochemicals are broadly defined as naturally occurring compounds produced by plants.Phytochemicals are bioactive compounds that possess the ability to interact with living tissue to elicit a wide range of effects[30].Based on their chemical structure and characteristics,phytochemicals are divided into six categories,namely,polyphenols,terpenoids,alkaloids,carbohydrates,lipids,and other nitrogen-containing compounds.
In the following section,we discuss the various phytochemicals that affect the expression of NF-κB.
5.1.Polyphenols
Polyphenol compounds contain hydroxyl functional groups and a minimum of one aromatic ring.Natural polyphenols vary from small molecules to extensively polymerized high-molecularweight derivatives.Many polyphenols exhibit pro-inflammatory gene expression.Numerous studies have documented the anticancer effects of natural polyphenols.Polyphenols that affect NF-κB activity are discussed below.
为避免高拱坝拱肩槽开挖开裂,在高拱坝拱肩槽开挖期间进行合理加固措施非常必要。因此,在高拱坝拱肩槽开挖工程实施过程中,可在高拱坝拱肩槽开挖前期,采取锚杆束预灌浆的方式,提高基层岩体稳定效力。
5.1.1.[6]-gingerol
The common ginger plant(Zingiber officinale)is a major source of[6]-gingerol.[6]-Gingerol imparts the characteristic pungent aroma to ginger.It inhibits the production of tissue-type plasminogen activator(TPA)induced TNF-α and ornithine decarboxylase activity and was found to arrest skin tumors in female mice in a study conducted at the Institute of Cancer Research(ICR)[31].[6]-Gingerol inactivates NF-κB by inhibiting p65 phosphorylation at Ser 536 induced by TPA,and via its interaction with the CREB binding protein(CBP)and its homologue p300 protein when it is applied topically[32].The NF-κB inhibitory activity of[6]-gingerol is also considered to be associated with the inhibition of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase(MAPK).[6]-gingerol inhibits ultraviolet B(UVB)-induced activation of COX-2 and NF-κB in the skin of hairless mice and in the immortalized human keratinocyte cell line[33].
5.1.2.Apigenin
Apigenin belongs to the flavone family and can be obtained from a vast variety of fruits,vegetables,and nuts,including onion,orange,and chamomile tea[34].Along with its anti-inflammatory and anti-tumorigenic properties,apigenin exhibits antioxidative and antiviral effects[35].Primary inhibition of COX-2 and NF-κB gene expression is thought to be one of the mechanisms by which apigenin exerts its anti-inflammatory effects[36].One study concluded that apigenin exhibits a protective effect by decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines via inhibition of COX-2 and NF-κB activation[36].
5.1.3.Curcumin
Curcuma longa or turmeric,a rich source of curcumin,is a staple spice used in Indian cuisine[37].Curcumin is a hydrophobic polyphenol and has been reported to exhibit anti-cancer activity[38].It displays various anti-inflammatory and cytokine inhibitory activities,and lysyl oxidase(LOX),inducible nitric oxide synthase(iNOS),and COX-2 gene expressions are downregulated by curcumin.It suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines,such as TNF-α,various interleukins,and neurotoxic factors in lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-stimulated monocytes and alveolar macrophages[39].NF-κB pathway inhibition is a well-studied anti-inflammatory mechanism of curcumin.It acts by inhibiting the phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα and translocation of p65 into the nucleus[40].
5.1.4.Epigallocatechin gallate(EGCG)
EGCG is a type of catechin found in high quantities in the dried leaves of green tea and white tea,as well as in smaller quantities in black tea[41].EGCG has been reported to inhibit the activation of NF-κB and activator protein-1(AP-1)in mouse skin in vivo and/or in the MCF10A cell line[42].EGCG also upregulates antioxidant enzymes via activation of the Nrf2-antioxidant response element(ARE)signaling pathway[43,44],which activates or represses NF-κB signaling in a circumstantial-dependent manner.EGCG also blocks LPS-induced IκBα degradation,translocation of RelA into the nucleus,and the DNA binding activity of NF-κB[45].
5.1.5.Gallic acid
Gallic acid is a polyphenol that occurs naturally in various plants,such as gallnuts and tea leaves[46].It curtails RelA acetylation through direct inhibition of histone acetyl transferase(HAT)and subsequent downregulation of numerous inflammatory signaling pathways[47].Consequently,beta-amyloid-activated NF-κB activity and the expression of cytokines in microglial cells are attenuated as a result of impaired RelA acetylation[48].
5.1.6.Genistein
Genistein is one of many active isoflavones found in soybean[49].It exhibits anti-estrogenic,antioxidant,and anti-inflammatory activities and has the capacity to alter signaling pathways[50].In BV-2 microglial cells,beta-amyloid-induced damage caused by cytotoxicity and inflammation is diminished by genistein.
It significantly reverses amyloid beta protein fragment 25-35(Aβ25-35)-induced upregulation of TLR4 and NF-κB expression and the DNA binding and transcriptional activities of NF-κB[51].
5.1.7.Macranthoin G
Macranthoin G is naturally derived from chlorogenic acid methyl ester and caffeic acid and is isolated from Eucommia ulmoides.Cell damage in PC12 cells is minimized in cells treated with macranthoin G,as it inhibits the NF-κB pathway and activates the phosphorylation of IκB,p38,and extra-cellular regulated kinase(ERK)[52].
5.1.8.Obovatol
The biphenolic compound obovatol is extracted from Magnolia obovata.It has neuroprotective properties against neuroinflammation.Obovatol inhibits the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB induced by LPS[53].It has been reported that obovatol suppresses translocation of p50 and p65 into the nucleus as well as IκB release,resulting in suppressed DNA binding activity of NF-κB in LPS-treated RAW264.7 cells[54].
5.1.9.Pterostilbene
Chemically related to resveratrol,pterostilbene is ubiquitous in grapes,blueberries,and almonds.Pterostilbene inhibits NF-κB by hindering the activation of phosphorinositide 3 kinase(PI3K)/Akt/IKK(IκB kinases)and MAPK,which consequently downregulates inflammatory iNOS and COX-2 gene expression in macrophages[55].
5.1.10.Quercetin
Quercetin,a common constituent of many fruits and vegetables,is a major bioflavonoid.It has numerous biological activities,such as anti-inflammatory,anti-tumor,and antioxidant ones,and is also reported to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases[56].Quercetin alters the NF-κB pathway via several different mechanisms;it restrains phosphorylation of IκB-p,inhibits NF-κB translocation into the nucleus,and blocks NF-κB-DNA binding and reporter gene transcription in RAW264.7 cells[57].
5.1.11.Resveratrol
Wine grapes are a major source of resveratrol,which has diverse beneficial biological activities.It is an antioxidant and exhibits antiinflammatory,anti-aging,and neuroprotective activities[58,59].In RAW264.7 and BV-2 cells,LPS-stimulated phosphorylation of IKK and IκB was impaired by resveratrol,and consequently,NF-κB activity was inhibited[60].Some reports suggest that resveratrol reduces the transcriptional activity of p65 and prevents the ubiquitination of NEMO and IKK-mediated NF-κB activation[61].
5.1.12.Salidroside
Rhodiola rosea L.is the major natural source of salidroside.Salidroside reportedly exhibits various pharmacological activities,including anti-aging,anti-fatigue,antioxidant,anti-cancer,and anti-inflammatory ones[62,63].In aD-galactose-induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease,salidroside regulated the expressions of NF-κB pathway proteins,such as NF-κB p65,IκBα,IKKα,and IKK[64,65].
5.1.13.Silymarin
Silymarin is a bioflavonoid obtained from Silybum marianum,or milk thistle,and has been reported to suppress NF-κB-DNA binding activity.Silymarin blocks NF-κB-DNA binding activity and its dependent gene expression induced by okadaic acid in the HepG2 cell line.It has also been reported that silymarin does not affect TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation[66].
5.1.14.Sulforaphane
Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate present in cruciferous vegetables,such as broccoli,and is considered as a “blocking”agent that modulates Nrf2-kelch like ECH associated protein1(Keap1)signaling and exhibits anti-inflammatory effects[67].In cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages,LPS-induced activation of NF-κB and COX-2 expression was prevented by sulforaphane[67].Inactivation of NF-κB by sulforaphane is not related to the degradation of IκB or suppression of nuclear translocation of NF-κB,but as a result of its direct binding to the thiol groups of p50.However,in human mammary epithelial cells,NF-κB activation was suppressed by the inhibition of TPA-induced COX-2 expression,and executed by blocking IKK activity and the subsequent phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα [68].
Polyphenols influencing NF-κB activity are listed in Table 2,along with their source and mode of action.The chemical structures of these polyphenols are provided in Fig.2.
5.2.Terpenoids
NF-κB is a key facilitator of inflammation-mediated cancer pathogenesis,and the involvement of various terpenoids in anticancer signaling and activation of apoptosis provides an insight into their role in NF-κB regulation.Naturally occurring terpenoids are known to possess NF-κB inhibitory properties.Terpenoids that exhibit NF-κB regulatory activity are discussed below.
5.2.1.Monoterpenoids
Monoterpenes comprise two isoprene units,with a general formula of C10H16.Monoterpenoids exist in three forms,namely,acyclic,monocyclic,and bicyclic.
They naturally occur as derivatives of terpene and can be generated via methylation and oxidation,as well as undergo glycosylation[69,70].The majority of monoterpenoids are volatile.NF-κB signaling is restricted by monoterpenoids through their inhibition of various mechanisms,such as IκB degradation,DNA binding,and p65 translocation[71,72].
Monoterpenoids that regulate NF-κB activity are discussed below and their structures are provided in Fig.3.
5.2.1.1.Aucubin.Aucubin is the most common iridoid glycoside and is obtained from Aucuba japonica(Cornaceae)[73].In stimulated mast cells,aucubin prevents IκBα degradation and nuclear translocation of p65.Due to its capacity to inhibit NF-κB activity,aucubin is potentially applicable for the prevention of cancer,hepatotoxicity,and inflammation[71,72].
5.2.1.2.Catalposide.Catalposide is an iridoid glycoside that is known to inhibit NF-κB signaling.It is a single compound isolated from the plant Catalpa ovata.Studies on HT29 cells have shown that NF-κB inhibition is subject to the capacity of catalposide to constrain IκBα degradation and p65 translocation into the nucleus[74].
5.2.1.3.Costunolide.Costunolide is predominantly isolated from the roots of Saussurea costus and Magnolia grandiflora[75].It prevents the phosphorylation of IκB proteins,consequently inhibiting NF-κB signaling.Costunolide also inhibits basic inflammatory signaling pathways induced by LPS,by terminating NF-κB activation and preventing downstream gene expression in RAW264.7 cells[76].
5.2.1.4.Genipin.Genipin,a metabolic product of giniposide,is found in the fruit of Gardenia jasminoides[77].Genipin inhibits NF-κB activation induced by LPS and is linked to a decline in the DNA binding capacity of p65 and p50 subunits in RAW264.7 cells.Genipin also suppresses the phosphorylative degradation of IκBα,IKKα,IKKβ,and IκBα [78].
5.2.1.5.Helenalin A.Helenalin A is a constituent of Arnica montana with NF-κB inhibitory properties.Helenalin inhibits the binding of the NF-κB complex with DNA and alkylates the p65 subunit in Jurkat T cells and 293 cells[79].
5.2.1.6.Humulene.Humulene is a monocyclic sesquiterpene sourced from Humulus lupulus.Humulene effectively reduces LPS-induced activation of the NF-κB complex and inflammation in rat paw edema[80].

Fig.3.Chemical structures of monoterpenoids targeting NF-κB.
5.2.1.7.Limonene.Limonenes are cyclic aromatic monoterpenes extracted largely from citrus rind in the form of oil.They possess chemo-preventive and antitumor properties[81].Menthol and perillyl alcohol,which are derivatives of limonene,can induce NF-κB-dependent apoptosis.In lymphoma cells,these compounds inhibit NF-κB signaling[82].Limonene blocks the phosphorylation of IκBα and NF-κB p65 to prevent LPS-induced inflammatory responses in acute lung injury[83].
5.2.1.8.Nepalolide A.Nepalolide A is found in the Carpesium nepalense plant,traditionally used in Chinese medicine.In C6 glioma cells,it suppresses LPS-induced NF-κB signaling and cytokines and inhibits IκBα and IκBβ protein phosphorylation[84].
5.2.1.9.Parthenolide.Parthenolide is a powerful NF-κB signaling inhibitor present in Tanacetum parthenium.Parthenolide exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting IκBα depletion,resulting in the suppression of excessive NF-κB activation[85].Parthenolide also inhibits the nuclear translocation of the p65 subunit and DNA binding of the NF-κB complex.
5.2.2.Sesquiterpene
Sesquiterpenes are C13 compounds formed from three isoprene units.They are biosynthesized from farnesyl pyrophosphate.Sesquiterpenoids occur widely in nature and are found in a multitude of fungi and plants.The carbon skeleton of sesquiterpenes exists in forms that differ significantly from the rest of the terpenes.Several sesquiterpene lactones exhibit antitumor properties that influence the NF-κB complex.Chemical structures of mentioned sesquiterpenes targeting NF-κB are provided in Fig.4.
5.2.2.1.Artemisinin.Artemisinin is a traditional Chinese medicine known as qinghaosu in the Chinese language.It can be acquired from the leaves of Artemisia annua.
Artemisinin inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB signaling[86].It also prevents LPS-induced degradation of the IκB protein,and consequently the activation and translocation of NF-κB[87].Artesunate,a synthetic derivative of artemisinin,inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines and activation of NF-κB signaling in TNF-αtreated human synoviocytes.Artemisinin has been reported to play a crucial role in the binding of NF-κB to DNA[88].
5.2.2.2.Ergolide.Ergolide is extracted from Innula britannica.It induces apoptosis against inflammatory and tumor stimuli.In RAW264.7 cells,the mechanism of action of ergolide involves the degradation of IκB proteins and inhibition of translocation of the NF-κB complex into the nucleus[28].

Fig.4.Chemical structures of sesquiterpenes targeting NF-κB.
5.2.2.3.Valerenic acid.Valerenic acid is a sesquiterpene that can be effectively used against inflammation and cancer.It is a component of Valeriana officinalis.Valerenic acid is a strong inhibitor of cytokine and NF-κB activation[89].
5.2.2.4.Zerumbone.Zerumbone is found in Zingiber zerumbet.It causes phosphorylation and degradation of IκB proteins,which blocks the functioning of the IKK complex.This leads to decreased translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus[90].
5.2.2.5.α-Pinene.Pinene,a bicyclic monoterpene,is found in coniferous trees.It inhibits p65 protein translocation in LPS-induced TPH-1 cells.Increased IκBα expression and inhibition of NF-κB signaling were observed in cells treated with α-pinene[91].
5.2.3.Diterpenoids
While monoterpenoids are derived from two isoprene units,diterpenoids comprise four isoprene units and are generally nonvolatile.Diterpenoids generally appear as monocyclic,bicyclic,or tetracyclic compounds.Some diterpenoids exhibit antitumor activity through direct or indirect inhibition of NF-κB signaling.Diterpenoids that affect NF-κB activity are listed below and Fig.5 depicts their chemical structures.
5.2.3.1.Acanthoic acid is a constituent of Acanthopanax koreanum root bark.Acanthoic acid and its analogues act by reducing IκBα phosphorylation induced by LPS and by inhibiting the NF-κB-DNA binding activity[92].
5.2.3.2.Carnosol.The diterpenoid cornosol is present in Rosmarinus officinalis.It inhibits the phosphorylation of IκBα and the production of iNOS and NO.Carnosol exhibits antioxidant activity,which contributes to the inhibition of NF-κB signaling[93].
5.2.3.3.Lupeol.Lupeol is a common component of numerous vegetables and fruits,such as strawberries,mangoes,olives,grapes,white cabbage,and green pepper.Lupeol is a pentacyclic diterpenoid.It inhibits the phosphorylation of IκB proteins and prevents NF-κB signaling activation[94].

Fig.5.Chemical structures of diterpenoids targeting NF-κB.
5.2.3.4.Oridonin.Isolated from Rabdosia rubescens,oridonin is a kaurane diterpenoid.Oridonin moderates the p50 or p65 forms of NF-κB and causes upstream regulation of IκB[95].While TNF-αinduced translocation of NF-κB and IκBα is suppressed by other members of the diterpenoid family,oridonin inhibits NF-κB signaling by restricting the DNA binding capacity of the NF-κB complex[96].
5.2.4.Triterpenoids
Triterpenoids comprise 30 carbon atoms arranged in six isoprene units and are structurally similar to steroidal compounds.Triterpenoids are classified as tetracyclic or pentacyclic.They exist either in a free state or as esters or glycosides.Triterpenoids that exhibit NF-κB-inhibiting properties are listed below.Chemical structures of the triterpenoids are provided in Fig.6.
5.2.4.1.Betulin.Betulin,extracted from the bark of Betula alba,is a pentacyclic triterpenoid.It inhibits phosphorylation and degradation of IKK,nuclear translocation,and phosphorylation of p65[97].Betulin derivatives display activity against inflammation and human immunodeficiency virus(HIV)by affecting IKKα-and NF-κB-dependent gene expression.
5.2.4.2.Ginsenosides.Ginsenosides are steroids present in the root of the perennial plant species Panax,such as ginseng.They have been established as anti-inflammatory agents.Ginsenosides inhibit NF-κB activity either by suppressing the degradation of the IκBα protein,or by inhibiting IKKα kinase activation.Studies have also recorded the inhibitory effect of ginsenosides on the DNA-binding capacity of the NF-κB complex[98,99].
5.2.4.3.Glycyrrhizin.Glycyrrhizin is widely used in Chinese and Egyptian medicine.Structurally,it is a triterpenoid saponin.Glycyrrhizin is present in the roots and stolons of Glycyrrhiza glabra.Glycyrrhizic acid,a component of glycyrrhizin,inhibits NF-κB-DNA binding.Glycyrrhizic acid prevents the activation of NF-κB either by phosphorylation or degradation(or both)of IκB[100].
5.2.5.Carotenoid tetraterpenoids
Carotenoid terpenoids comprise eight isoprene units and are pigmented tetraterpenoids.They are beneficial in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders and osteoporosis by virtue of their antioxidative properties,which are responsible for their therapeutic effects.Their ability to affect the NF-κB signaling pathway endows them with anticancer properties.
5.2.5.1.Lutein.Various fruits and leafy vegetables,such as peas,lettuce,kale,broccoli,and spinach,as well as egg yolk,contain the cyclic tetraterpenoid lutein.Lutein causes degradation of the IκBα protein and inhibits nuclear localization of p65 subunits.It is also responsible for the inhibition of NF-κB activation.Lutein pigment can protect against oxidative stress and cataracts[101].
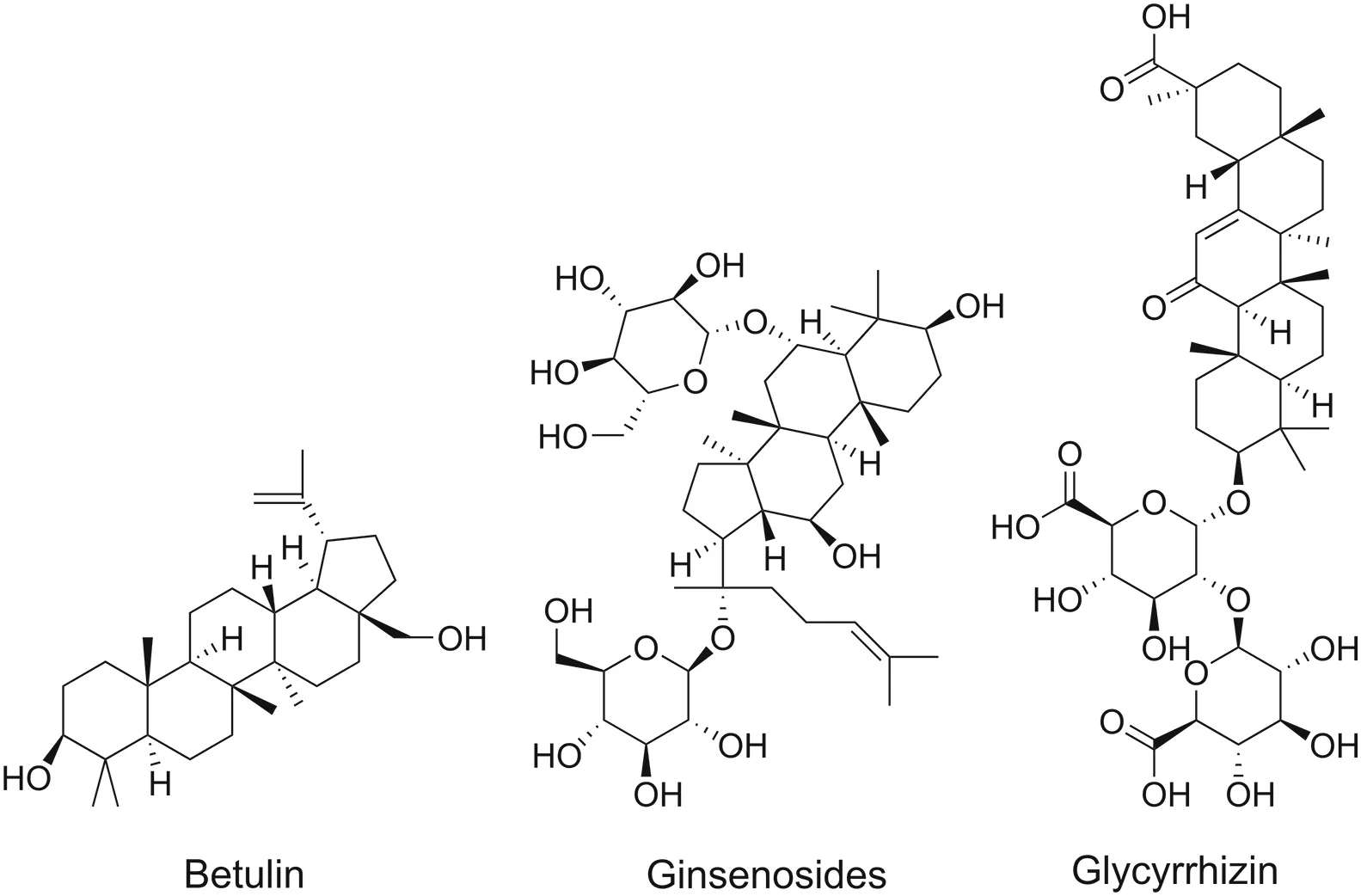
Fig.6.Chemical structures of triterpenoids targeting NF-κB.
5.2.5.2.Lycopene.Lycopene is an extremely potent antioxidant found in tomatoes[102].Lycopene exhibits potential neuroprotective[103],anti-proliferative and anti-cancer activities[104].It also causes a reduction in chemokines in macrophages and pro-inflammatory chemokines[105,106].It improves intracerebroventricular (ICV) beta amyloid1-42-activated spatial learning,and by inhibiting inflammatory cytokines and NF-κB signaling,it improves memory[107].Lycopene inhibits IκB phosphorylation in cells,NF-κB transcriptional activity and suppresses TNF-induced nuclear translocation of the p65 subunit in lycopenetreated MDA-MB-231 cells[108].
5.2.5.3.β-Carotene.This cyclic carotene accumulates in liver cells and is converted into vitamin A.NF-κB signaling induced by LPS is suppressed by β-carotene.It degrades the IκB protein and suppresses nuclear translocation of p65 and the DNA binding capacity of NF-κB. β-carotene inhibits cancer growth owing to its prooxidant characteristics[109].
Terpenoids modulating NF-κB activity are shown in Table 3.Chemical structures of carotenoid terpenoids targeting NF-κB are provided in Fig.7.

Table 4Alkaloids modulating the NF-κB activity.
Fig.7.Chemical structures of carotenoid terpenoids targeting NF-κB.
5.3.Alkaloids
Alkaloids are naturally occurring organic compounds that possess nitrogen atoms in a negative oxidation state.Alkaloids are among the most diverse therapeutic plant substances.Various alkaloids that modulate NF-κB activity are described below.
5.3.1.Anatabine
Anatabine is an alkaloid found in plants of the Solanaceae family,such as green tomatoes and tobacco.Anatabine curtails NF-κB activation by inhibiting beta-amyloid production in vitro[110].Anatabine suppresses p65 NF-κB phosphorylation induced by LPS or TNF-α[111].
5.3.2.Berberine
Berberine is isolated from Hydrastis canadensis.It is a potent anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of inflammation-related diseases.It diminishes the phosphorylation and expression of p65.Inhibition is also caused by berberine in the phosphorylation of IκBα in Aβ-activated microglial cells.It also suppresses Aβ-activated ERK,p38,and Akt signaling pathways[112].
5.3.3.Galantamine
Galantamine is found in Galanthus species and is used in the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease.The protective effect of galantamine is mediated through NF-κB activation via the induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene.Galantamine also restricts proteosomes from degrading IκB[113].
5.3.4.Tetrandrine,derived from Stephania tetrandra,tetrandrine is a bisbenzylisoquiniline alkaloid

Fig.8.Chemical structures of alkaloids targeting NF-κB.
Tetrandrine,derived from Stephania tetrandra,is a bisbenzylisoquiniline alkaloid.Tetrandrine can be used for the treatment of various diseases as it exhibits a range of biological activities,including anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor[114].It inhibits NF-κB and downregulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines.It decreases the degradation of IκB,which suppresses p65 translocation and inhibits NF-κB activation[115].
Alkaloids that modulate NF-κB activity are shown in Table 4 along with their source and mode of action.Chemical structures of alkaloids targeting NF-κB are provided in Fig.8.
6.Conclusion
NF-κB is an inducible transcription factor that mediates the expressions of a wide array of genes associated with various immune and inflammatory responses.Research has established the crucial role of dysregulated NF-κB activation in the pathogenesis of various inflammation-driven diseases,including cancer.The involvement of NF-κB in the induction and proliferation of cancer cells via metastasis,angiogenesis,regulation of growth signals,and inhibition of apoptosis makes it a suitable therapeutic target against cancer.While substantial efforts are being made to develop antineoplastic agents,they suffer limitations such as high cost and the occurrence of severe side effects.Therefore,considering the adverse effects of existing NF-κB inhibitors,exploring the available naturopathic formulations can provide an ideal platform for identifying new NF-κB inhibitors considering the multi-target effects of phytochemicals,specifically and non-specifically,on various components of the NF-κB transduction pathway.In this review,we highlighted phytochemicals that have been proven to regulate the expression of NF-κB and discussed their mechanism of inhibition,which can be further explored for potential future antineoplastic therapy.Many of the phytochemicals reported herein have not yet been tested in cancer models and/or human clinical trials for their biocompatibility,bioavailability,and anticancer effects.These phytochemicals are natural compounds that have an advantage over existing synthetic NF-κB inhibitors in terms of their safety and efficacy.The use of these phytochemicals as adjunctive chemotherapy along with conventional cancer treatment may constitute an improved therapeutic strategy.Nevertheless,structural modifications of these phytochemicals should be explored to possibly enhance the antineoplastic potential of the original compounds.
CRediT author statement
Akansha Chauhan:Writing-Original draft preparation,Resources,Data curation;Asim Ul Islam and Hridayesh Prakash:Writing-Reviewing and Editing;Sandhya Singh:Conceptualization,Formal analysis,Supervision.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The author is thankful to the lab mates Mr.Aniket Angira and Ms.Pooja Singh for their support in completion of this review article.
 Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis2022年3期
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis2022年3期
- Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis的其它文章
- Recent advances in quantum dots-based biosensors for antibiotics detection
- Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of Flos Puerariae by using chemical fingerprint in combination with chemometrics method
- Multiple rapid-responsive probes for hypochlorite detection based on dioxetane luminophore derivatives
- Nitrogen-doped carbon@TiO2double-shelled hollow spheres as an electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of dopamine and paracetamol in human serum and saliva
- Compatibility and stability studies involving polymers used in fused deposition modeling 3D printing of medicines
- A preparation strategy for protein-oriented immobilized silica magnetic beads with Spy chemistry for ligand fishing
