The relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being in Chinese college students:the mediating role of psychological resilience and the moderating role of peer influence
Lin Cai,Yu Yao,Deng-Hui Lu,Jia-Xin He,Yu-Ying Zeng,Bing-Yan Hu,Yao-Fang Lei*
1School of Marxism,Sichuan Institute of Industrial Technology,Sichuan,China.2Research Center of Psychology and Behavior,Key Research Base of Humanistic and Social Sciences of Deyang,Sichuan,China.3Physical Education College,Sichuan Institute of Industrial Technology,Sichuan,China.
Abstract
Objective:To explore the influence of physical exercise,psychological resilience,and peer influence on subjective well-being,and then build a model of moderated mediation.
Methods:Physical Activity Rating,Connor Davision Resilience Scale,Peer Influence Scale,and Index of Well-Being were used.This paper investigated 790 undergraduates.
Results:(1)Physical exercise has a significant positive predictive effect on subjective well-being(β=0.43,P< 0.001);(2)Psychological resilience plays a part in mediating the relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being.The mediating effect value is 0.18;(3)The relationship between physical exercise and psychological resilience moderated by the peer influence.Compared with the low peer influence(β simple=0.01,t=0.06,P > 0.05),physical exercise has a stronger positive predictive effect on psychological resilience in college students with high peer influence(β simple=0.87,t=2.07,P < 0.05).
Conclusion:Physical exercise affects college students'subjective well-being through psychological resilience,and peer influence moderates the mediating effect of psychological resilience.
Keywords:Physical exercise,subjective well-being,psychological resilience,peer influence
Background
The pursuit of pleasure and happiness has been the focus of human attention since ancient times.The ancient Greek philosopher Epicurus once said that "Happiness is the highest good that people are born with,and all trade-offs are made from happiness,and the ultimate goal is to be happy".In recent years,subjective well-being,as a positive subjective experience of individuals,has become a mainstream topic in the burgeoning field of positive psychology research[1].
Studies have pointed out that the higher the subjective well-being of college students,the better their mental health,as well as having better school adjustment and fewer behavioral problems[2].Thus,in order to deal with various adaptive behaviors and issues of college students,in addition to academic aspects and employment status,the subjective well-being of college students especially needs to be addressed and focused on.The activity theory of well-being emphasizes that individuals can develop their potential and satisfy their needs through interaction and feedback through activities such as work,leisure,and sports,which further generate pleasure and happiness[3].Later,researchers have argued that in addition to physical activity,there should be other variables that affect subjective well-being,including psychological resilience and peer influence on subjective well-being[4-5].What is the relationship between physical activity,psychological resilience,peer influence,and subjective well-being?It is necessary to conduct an in-depth study to provide a reference and theoretical basis for improving the subjective well-being of college students.
Subjective well-being refers to an individual's assessment of positive emotions,negative emotions,and life satisfaction,which is a subjective emotional and cognitive evaluation of one's overall life[6].It has been shown that physical activity has a significant positive correlation with subjective well-being[7],and that normal regular physical activity,in addition to promoting physical health,can reduce anxiety,lower stress[8],increase positive emotions,and change an individual's mood to make life more productive[9],and that the more frequent and more involved one is in exercise,the higher one's well-being and willingness to participate again[10].Hartman et al.[11]further found that the higher the level of involvement in physical activity among college students,the higher the subjective well-being of individuals.To this end,we propose Hypothesis 1:Physical activity among college students significantly and positively predicts subjective well-being.
Psychological resilience refers to a state of positive response of an individual in the face of challenges.Psychological resilience was first studied in health psychology,and later in sports psychology.It was found that the higher the psychological resilience of athletes,the better their athletic performance[12],and foreign scholars also found that psychological resilience is one of the important characteristics of good athletes and their teams in many sports[13].Wiley Shaw and Haviz[14]pointed out that individuals with different levels of athletic engagement can vary in the behavioral outcomes they extend,and usually the more engaged,the higher the level of commitment,the richer and more diverse the behavioral outcomes are.It has been shown that in marathon and billiard sports,sports commitment directly and positively influences the mental resilience of individuals,i.e.,the higher the sports commitment,the higher the mental toughness[15].
In the study of subjective well-being,optimistic people were found to have higher well-being[16],while psychological resilience had a significant positive and negative correlation with optimism and pessimism,respectively[17].In other words,optimistic people are more psychologically resilient,while pessimistic people are less psychologically resilient.If we speculate on the results of both studies,optimism may represent higher psychological resilience and higher well-being;pessimism may represent lower psychological resilience and lower well-being.In terms of empirical studies,Liu et al.[4]found that psychological resilience has an enhancing effect on subjective well-being when studying college students'psychological resilience and subjective well-being.The higher the psychological resilience,the higher the score of subjective well-being.In view of the relationship between physical exercise,psychological resilience,and subjective well-being.We propose Hypothesis2:Psychological resilience plays a mediating role between physical exercise and the well-being of college students.
Social factors are one of the main reasons affecting individuals'participation in physical activity,and especially significant others are the main factors affecting young students'participation in physical activity[18].Most of the previous studies have explored the influence of youth physical activity from the perspective of parents.Coaches or physical education teachers,and not many studies have explored it from the perspective of peer influence[19-20].As young students enter college,the interpersonal scope is expanding and the influence of peers on college students is becoming increasingly important,even replacing parents in some aspects[19-20].And,in some ways,even replacing parents[21].It has been found in the past that the biofeedback that adolescents receive from their experience during exercise influences their further engagement in the exercise scenario[22].In contrast,the higher the level of commitment to physical activity among college students,the higher the subjective well-being of the individual[11],and the higher the level of commitment to exercising among individuals,the higher their psychological resilience[15].Accordingly,we propose Hypothesis3:Peer influence significantly moderated the effect of physical exercise on subjective well-being,and Hypothesis 4:Peer influence significantly moderated the effect of physical exercise on psychological resilience.
Subjects and methods
Subjects
The sample size was determined,using the Raosoft sample size calculator(http://www.raosoft.com/samplesize.html),based on a margin of error of 5%,confifidence level of 95%,a population size of 36,000(total of registered physicians and dentists in Jordan)and a response distribution of 50%.The calculated sample size was 377.A stratified sampling method was used to randomly select 860 college students from four universities in Sichuan,Hubei,Hebei,and Shaanxi.A total of 860 college students were selected as subjects.A total of 790 valid questionnaires were collected with an effective rate of 91.86%.Among them,469 were male students(59.37%),and 321 female students(40.63%).There were 268 freshmen (33.92%),255 sophomores(32.28%),127Juniors(16.08%),and140seniors(17.72%).The mean age was 21.05 years(SD=1.63).The questionnaire was completed by the college students who meet all of the following inclusion criteria:
(1)The participants were fully informed of the relevant aspects of the survey,including its aim and methodology.
(2)The participant's age is greater than or equal to 18 years.
(3) All subjects participated in this study voluntarily,who had normal language organization and cognitive skills.
Institutional review board statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki,and approved by an independent Ethical Committee,the Ethics Committee of the Sichuan Institute of Industrial Technology(Ref.No.GYKJ2021/025).
Design of the questionnaire
Physical Activity Rating Scale.The Physical Activity Rating Scale-3(PARS-3),developed by Koyo Hashimoto,and revised by Liang[23],was used to measure physical activity,which consists of three items,including intensity of exercise,duration of exercise,and frequency of exercise.Each item is rated from 1 to 5,and the total physical activity score is computed by the following equation:intensity×(time-1)×frequency,with a range of 0 to 100.A total score that is equal to or less than 19 is defined as light,one that is 20 to 42 is defined as moderate,and one that is equal to or more than 43 is defined as vigorous physical activity.The internal consistency coefficient of the scale in this study is 0.73.
Connor Davision Resilience Scale.A simplified version of the psychological resilience scale(Connor Davision Resilience Scale,CD-RISC-10)was developed by Connor and Davidson,from which ten items were proposed by Campbell et al.and later Chineseized by Wang et al[24],was used to measure psychological resilience.The scale consists of 10 items divided into 3 dimensions.Resilience,Strength,and Optimism.The higher the score,the higher the psychological resilience of college students.The internal consistency coefficients of the total scale and its subscales in this study were 0.90,0.77,0.76,and 0.86.
Peer Influences Scale.The Peer Influence Scale(PIS),developed by Lau et al.,and modified by Xu and Chang[25]was used to measure peer influence on the movement.The scale consists of 6 items and is rated on a 5-point Likert scale,with higher scores indicating higher peer influence among college students.The internal consistency coefficient of the scale in this study is 0.84.Well-being Index Scale.The Index of Well-Being(IWB),developed by Campbell and Chineseized by Fan[26],was used to measure subjective well-being.This scale consists of two parts,one with eight categorical items to evaluate the overall emotional index,and the other with one categorical item to measure subjective well-being.Both items were rated on a 5-point Likert scale.The higher the score,the higher the subjective well-being of college students.The internal consistency coefficient of the scale in this study is 0.95.Statistical methods.SPSS statistics software 22.0 were used for result analysis.The deviations of common methods were tested by Harman single factor test.Descriptive analysis was carried out on the scores of each variable.Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient was used to study the relationship among physical exercise,subjective well-being,psychological resilience,and peer influence.The moderated-mediation model was analyzed by the Hayes PROCESS version 3.0 macro for SPSS.
Results
Common variance
This study was carried out utilizing a self-report.There will be the potential issue of common bias.Following the recommendations of Tehseen,Ramayah,and Sajilan[27],the experiments were done under control conditions.For example,the different sections were then run with backward entry.It was stressed that there were no right or wrong answers.We thus conducted Harman’s single factor test in order to rule out common method bias(Harman,1976).The Outcome revealed four eigenvalues greater than 1 explaining 64% of the variation,and the interpretation rate of the first factor was 25.60%,which was<40% of the reference value.
Descriptive statistics and correlation analysis
To examine the correlations among the four variables of physical activity,psychological resilience,peer influence,and subjective well-being among college students,descriptive statistics and Pearson correlation analysis were conducted for physical activity,psychological resilience,peer influence,and subjective well-being.The results showed psychological resilience was significantly correlated with peer influence(r=0.37,P<0.001)and subjective well-being(r=063,P<0.001);peer influence and were subjective well-being highly significantly correlated(r=0.47,P<0.001)(Table 1).
The relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being-a modified mediation effect model test.
The result showed that the moderating variable modulates the direct path and the first half path of the mediation effect:In equation 1,the effect of physical exercise on subjective well-being is significant,and the interaction between physical exercise and peer has a significant effect on subjective well-being(b)In equation 2,The process has then been standardized for all variables.We transformed the physical exercise and peer exercise influence to z-scores within each team,multiplied their score with the correlation coefficient,and summed the scores.And controlled for age,sex and.Little multicollinearity was observed for all independent variables,with the variance inflation factors being less than 2.27.VIF values of all independent variables in the model are below 5,which shows there are no multicollinearity problem symptoms.
The results of equation(1)show that physical exercise could significantly positively predict subjective well-being(β=0.43,P<0.001)(Table 2).The interaction effect of physical exercise and Peer influence on subjective well-being is not significantly different.(β=0.29,P>0.05)in Equation(2),the significant positive predictors of physical exercise were psychological resilience(β=0.58,P<0.001).The interaction effect of physical exercise and peer influence with a significant predictive effect is shown in psychological resilience(β=0.43,P<0.05).The result of Equation(3)showed that psychological resilience positively predicted subjective well-being(β=0.73,P<0.001)in Figure 1.
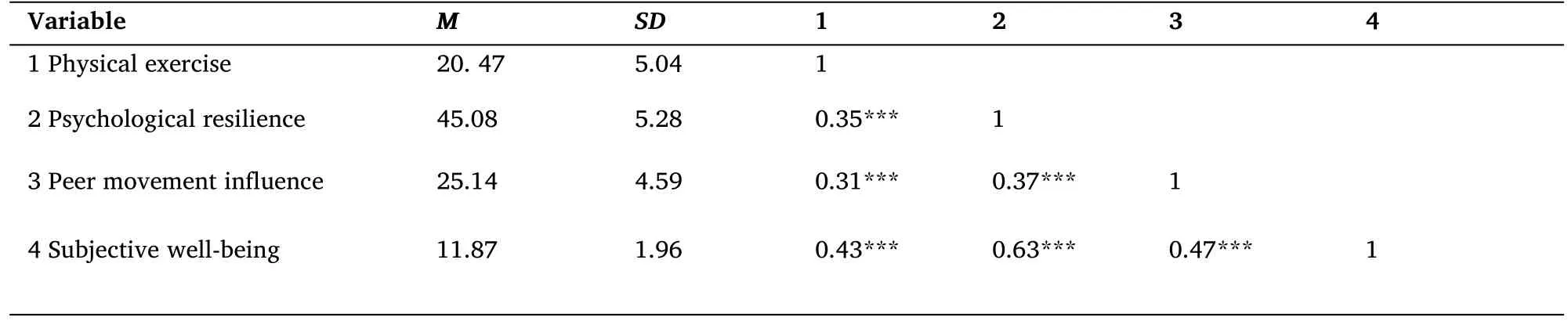
Table 1 Means,standard deviations and correlation matrix of each variable(n=790)
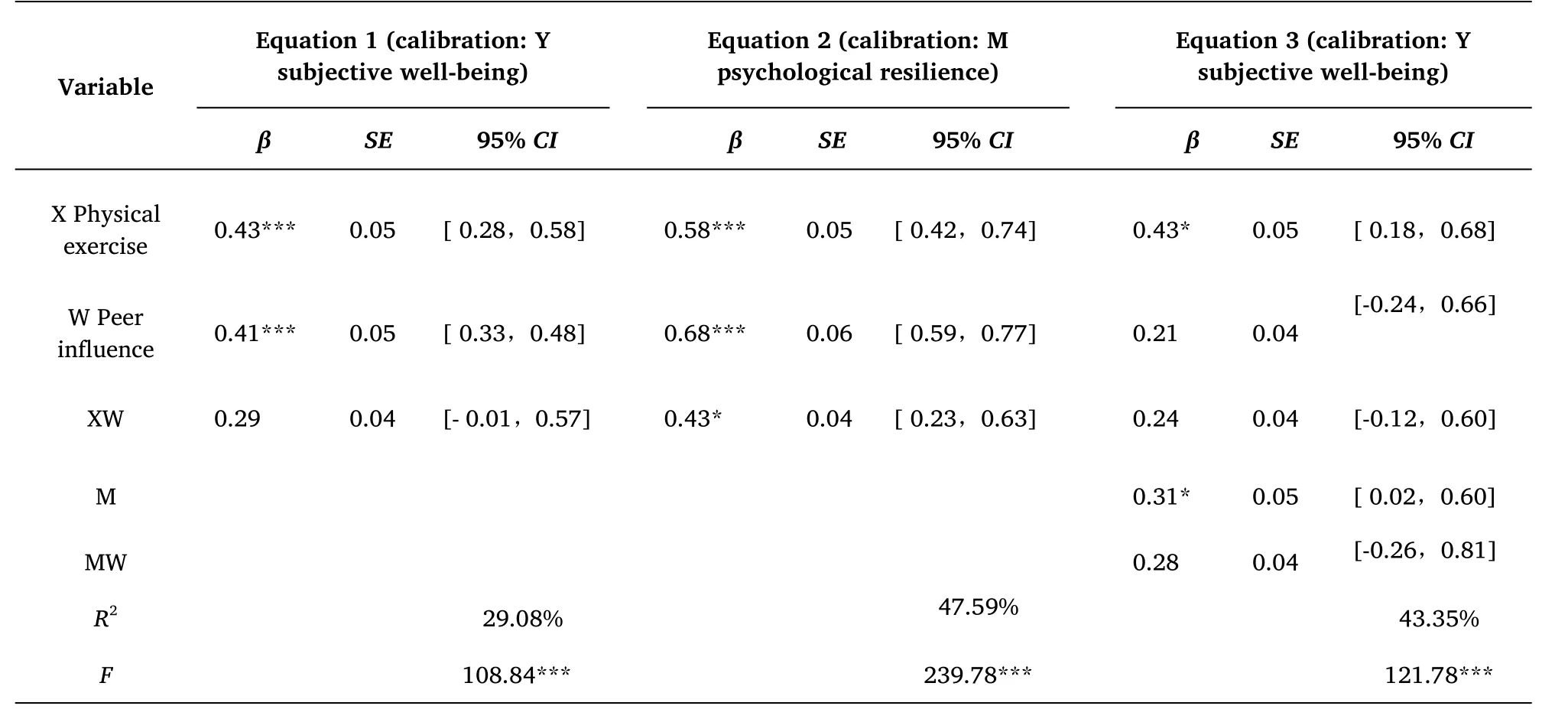
Table 2 The relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being:a modified mediation effect model test
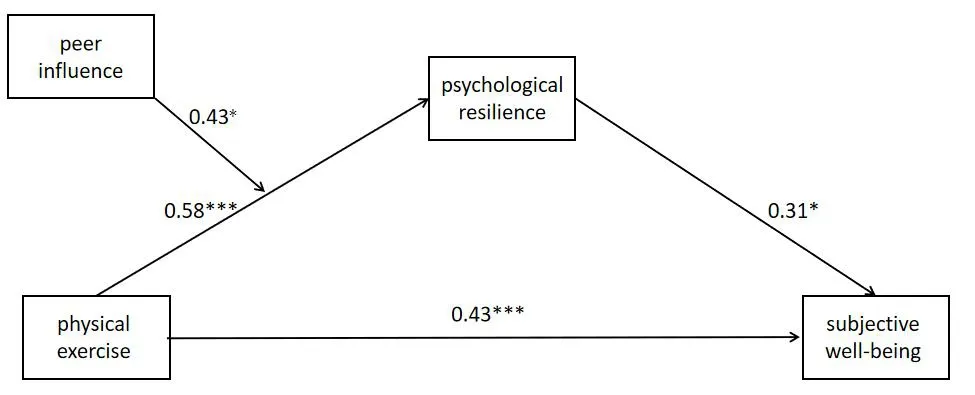
Figure 1 Diagrams of the moderated mediation model
To explore in more depth the moderating effects of the peer influence effect.The peer influence was categorized into high(Z≥+1 SD)and low(Z≤-1 SD)groups.Simple slopes were tested in the high and low groups,the role of peer influence effect in the relationship between physical exercise and psychological resilience was parsed by examining the main effect of both high and low peer influence separately.When the peer influence is high with larger physical exercise.Furthermore,the psychological resilience showed an obvious rising trend(β simple=0.87,t=2.07,P < 0.05).Effect of low intensity physical exercise,whereas physical exercise exerted no significant effect on psychological resilience(β simple=0.01,t=0.06,P>0.05)in Figure 2.
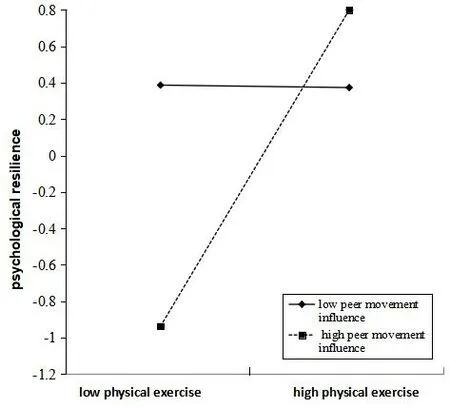
Figure 2 Plot of the moderating effect of peer influence on physical exercise and psychological resilience
Discussion
Relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being The results of this study showed that physical exercise had a significant positive predictive effect on subjective well-being among college students,andhypothesis1 was confirmed.This result further confirms that physical exercise has a positive effect on subjective well-being[11].From a physiological point of view,regular physical exercise can promote the physical and mental health of individuals,and when people exercise and exercise,it promotes the secretion of neurotransmitters such as endorphins and dopamine,which can easily lead to feelings of happiness and enhance the sense of well-being[29].From a sports psychology perspective,happiness comes from the fact that exercisers view physical exercise as a leisure activity and interest,that participation in physical exercise is doing what they like,and that they can obtain spiritual pleasure and satisfaction from physical exercise,so they can naturally feel joy and happiness[30].
The mediating role of psychological resilience
The results of the study showed that psychological resilience plays a mediating role in the relationship between physical activity and subjective well-being, and physical activity indirectly affects subjective well-being through psychological resilience,and hypothesis 2 was confirmed.According to the activity theory of well-being,individuals can develop their potential and satisfy their needs through interaction and situational feedback through activities such as work,leisure,and sports,which further generate pleasure and well-being[3].Situational feedback has an important impact on the psychological resilience of individuals,and if the feedback meets the individual's expectations,the level of psychological resilience will be enhanced[31].In turn,individuals with high psychological resilience possess characteristics such as the ability to effectively make realistic plans and execute necessary actions,possess a positive self-view and hold confidence in their abilities and strengths,demonstrate suitability for developing communication and problem-solving skills;and manage strong emotions and impulses in a healthy manner[32],which help individuals experience more positive emotions,be more easily satisfied,and feel confident in their development,thus enhancing the level of subjective well-being.Thus,physical activity can indirectly influence subjective well-being through psychological resilience.
Moderating effect of peer influence
The moderating effect of peer influence on the relationship between physical activity and psychological resilience is consistent with the hypothesis 4.Specifically,the positive predictive effect of physical activity on psychological resilience was significantly increased in the high peer sport influence condition,while the predictive effect of physical activity on psychological resilience was not significant in the low peer sport influence condition.This suggests that the relationship between physical activity and psychological resilience is constrained by the influence of peer.This is consistent with the facilitation hypothesis of the "protective factor-protective factor" model[33],which states that both physical activity and peer influence are enhanced,and the greater the peer influence,the greater the predictive effect of physical activity on psychological resilience,with peer influence acting as the "icing on the cake"[34].In addition,the moderating effect of peer influence in this study supports the view that social support from the school,parents,and peers is a moderating variable[35],which expands the study of peer influence in college students and once again verifies the applicability of social support theory in the field of college students'physical activity[36].
The positive predictive effect of physical exercise on psychological resilience was significantly enhanced in the high peer sport influence condition;the predictive effect of physical exercise on psychological resilience was not significant in the low peer sport influence condition.The possible reason for this is that students who received high peer influence received more support for physical activity and were willing to invest more time and experience in physical activity activities than students who received low peer influence[37].And physical activity itself can promote students'psychological resilience,so the positive predictive effect of physical activity on psychological resilience was significantly enhanced in the high peer sport influence condition.In contrast,the motivation of physical exercise may be somewhat affected by the lack of peer support among college students with low peer influence,thus reducing physical exercise behavior,and thus the predictive effect of physical exercise on psychological resilience is not significant.
This study also showed that peer influence did not moderate the relationship between physical activity and subjective well-being,which is inconsistent with research hypothesis 3.The possible reason for this is that peer influence,as an important coping resource,plays a stronger role for individuals in challenging situations and has a smaller effect on the relationship between physical activity and subjective well-being,focusing more on general rather than challenging individual variables or situations.
Empirical implications and limitations
This study found that psychological resilience plays a mediating role in the relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being of college students,which suggests that not only should we pay attention to the role of physical exercise in enhancing the subjective well-being of college students,but also should pay attention to the psychological resilience of college students,and continuously improving the psychological resilience of college students in physical exercise can also effectively promote the enhancement of their subjective well-being.In addition,peer influence plays a protective role in the relationship between physical exercise and psychological resilience,which suggests that the positive role of peer influence should be emphasized in physical exercise,and guiding students to strengthen the interaction with peers and enhance peer influence in physical exercise can effectively enhance college students'subjective well-being.
There are some limitations in this study:on the one hand,this study is a cross-sectional study,and it is not possible to know the change situation and development trend of subjective well-being in other movement development stages or to infer and verify the causal relationship between variables.Therefore,this study suggests that a follow-up study with a fixed sample could be conducted in the future,with multiple time points of sampling and design,to investigate the causal relationships between variables in more detail.On the other hand,this study only examined the moderating effect of exercise influence from peers,but the sources of exercise influence are parents and teachers in addition to peers,and whether support from these sources has a similar role in the relationship between physical activity and subjective well-being needs to be explored in depth.
Conclusion
(1)Physical exercise has a significant positive predictive effect on college students'subjective well-being;(2)Psychological resilience plays a partially mediating role in the relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being among college students;(3)The relationship between physical exercise and psychological resilience is moderated by peer exercise influence.Compared with low peer influence,physical activity had a stronger positive predictive effect on psychological resilience among college students with high peer influence.
 Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch2022年2期
Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch2022年2期
- Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch的其它文章
- Psychological Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease and Hemodialysis:Narrative Review
- Health behaviours and wellbeing of health workers amidst the COVID-19 pandemic
- Discussion on the mechanism of Xiaoyao Powder in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome based on network pharmacology
- Survey and analysis of the current situation of humanistic care ability of first-year nursing students after COVID-19
- Electronic Cigarette Use Scale:Development and evaluation of a measure among Chinese students
