Theoretical predict structure and property of the novel CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal by systematic search approach
Ho-jie Li ,Jin-cho Liu ,Li Yng ,* ,Zhen-zhn Yn ,Yue-wen Lu ,Ji-min Hn ,Xio-ting Ren ,Wei Li
a State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology,Beijing Institute of Technology,Beijing,100081,China
b Science and Technology on Aerospace Chemical Power Laboratory,Hubei Institute of Aerospace Chemotechnology,Xiangyang,441003,Hubei,China
Keywords:CL-20 2,4-DNI Cocrystal Intermolecular interaction Systematic search
ABSTRACT Cocrystallization integrates the merits of high energy and insensitivity between energetic molecules to obtain energetics with satisfying performance.However,how to obtain supramolecular synthons accurately and rapidly for predicting the structure and property of cocrystal remains a challenging problem.In this research,an efficient systematic search approach to predict CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal has been proposed that 2,4-DNI revolves around CL-20 with a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1 in accordance with the specified rules (hydrogen bond length:2.2-3.0 Å;search radius:6.5 Å;the number of hydrogen bond:1-3).Eight possible supramolecular synthons were obtained by combining quantum chemistry with molecular mechanics.Crystal structure prediction indicated that there are four structures in cocrystal,namely P21/c,P212121,Pbca and Pna21,and CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal is likely to be P21/c and the corresponding cell parameters are Z=4,a=8.28 Å,b=12.17 Å,c=20.42 Å,α=90°,β=96.94°,γ=90°,and ρ=1.9353 g/cm3.To further study the intermolecular interaction of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal,a series of theoretical analyses were employed including intermolecular interaction energy,electrostatic potential (ESP),Density of State (DOS),Hirshfeld surface analysis.The C-H…O hydrogen bonds are demonstrated as the predominant driving forces in the cocrystal formation.The mechanical properties and detonation properties of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal implies that the cocrystal shows better ductility and excellent detonation performances (9257 m/s,39.27 GPa) and can serve as a promising energetic material.Cocrystal structure predicted was compared with the experimental one to verify the accuracy of systematic search approach.There is a less than 8.8% error between experiment and predict results,indicating the systematic search approach has extremely high reliability and accuracy.The systematic search approach can be a new strategy to search supramolecular synthons and identify structures effectively and does have the potential to promote the development of energetic cocrystal by theoretical design.
1.Introduction
Faced with the development of modern weapon technology and the increasingly harsh environment of war,"efficient damage"and"high safety"have become two major goals urgently pursued in the development of modern weapon equipments [1-6].Energetic materials are the core of weapon equipments to achieve long-range delivery,precision strikes,and efficient damage,as well as a key factor in determining their safety during use.Therefore,the two seemingly contradictory characteristics of high energy and low sensitivity in the field of energetic materials have become the highest pursuit of researchers [7-9].In decades,the development of insensitive high energy materials (IHEM) has two main directions:one is to design and synthesize new single energy materials,such as Bis(4-nitraminofurazanyl-3-azoxy)azofurazan and 5,5-dinitramino-3,3-azo-1,2,4-oxadiazole,whose safety issues are still far away from industrial standard of IHEM[10,11].The other is to modify existing single energetic materials,there are three main methods:one is making the size of particles change into nano level[12-14];the second is coating,compounding high energy explosives by adding insensitive agent [15,16];the third is mixing different explosive molecules to form cocrystal from the molecular level.Compared with the previous two modification methods,cocrystal is more significant and has great development potential[17-22].Supramolecular chemistry and crystal engineering define that the cocrystal is a periodic system formed by hydrogen bond and electrostatic interaction between different kinds of molecules[23,24].The first application of cocrystal technology in the field of energetic materials provides a new strategy for constructing novel energetic materials at the molecular scale and regulating the contradiction between energy and safety of explosives[25].
However,current insensitive high-energy-density cocrystal materials were obtained by accidental and random,and the lack of a set of theoretical design methods for accurately and rapidly predicting the structure of cocrystal cannot provide theoretical guidance for the experimental preparation,which greatly restricts the development of CL-20-based cocrystal energetic materials.Ruijun Gou et al.[26] made a detailed summary for the packaging structures of 27 CL-20-based cocrystal,and found that hydrogen bonds nearly existed in all cocrystal and played a dominant role in weak intermolecular interactions.Hongzhen Li[27]suggested that the most negative ESP sites(~31 kcal/mol)on the coformer interact with CL-20 more strongly through hydrogen bonds and other intermolecular interactions,it is beneficial to form CL-20-based cocrystals.Pang [28] utilized pyrazine derivatives with the most negative ESP(-40 kcal/mol~-30 kcal/mol)to verify whether they have ability to form cocrystals with CL-20 again,and concluded that five,six-membered symmetrical N-heterocyclic compounds with electron-donating groups become the possible choice to cocrystallize with CL-20.Desiraju [29,30] applied supramolecular synthons to the design of cocrystal materials.Supramolecular synthons,as the smallest repeated structural units,are further formed into specific structures with one-dimensional chains,twodimensional layers or three-dimensional dimensions through intermolecular hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interaction.Gavezzotti et al.[31]used the PIXEL method to systematically evaluate the cohesive energies and thermal stability of supramolecular synthons,and judged the stability by binding energies and stretching vibrational amplitudes.The absolute and relative strength data of the supramolecular synthons provides guidance for the application of supramolecular synthons in crystal engineering.However,the difficult point is how to quickly and accurately determine the structure of supramolecular synthons formed.
Herein,we proposed a systematic search approach to search for possible supramolecular synthons rapidly and comprehensively.Based on these synthons obtained from systematic search,the Monte Carlo (MC) algorithm was used to predict the crystal structure.In 2001,Price and Day et al.[32,33]used the MOLPAK program to generate hypothetical crystal structures and combined kinetic as well as thermodynamic factors to screen the crystal structures with the global minmum in lattice energy.In 2009,Price et al.[34] reported a multistage lattice energy minimization methodology to predict crystal structure,which has high search efficiency.Day et al.[35] used GLEE program to carry out research on the crystal structure prediction of organic semiconductor materials.This program can uniformly sample the lattice energy surface to obtain a crystal structure with minimal lattice energy in 2018.In 2021,Day et al.[36] used a combination basin hopping (BH) with quasirandom (QR) sampling to locate low energy structures and obtained crystal structures.Compared with various global optimization methods,MC algorithm [37] can truly simulate the actual physical process,and the final result is very consistent with the reality.The accuracy of this approach was verified by comparing the experiment and prediction date (see the Supporting Information,section SI 2).Guest molecule revolves around the host molecule with a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1 according to the certain rules,as shown in Fig.1,and then the initial configurations that can produce hydrogen bonds are optimized by employing molecular mechanics and quantum chemistry to obtain the lower energy configuration.We choose respectively CL-20,2,4-DNI(Scheme 1)as host and guest molecules with a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1 to form the new insensitive high-energy-density cocrystal materials and predict the crystal structures of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal.CL-20 is availably the most powerful explosive [38],as the cocrystal component,it guarantees the energy level of the energetic materials.However,its wide application is limited due to its high sensitivity.The rotation of nitro group on the CL-20 cage has high freedom[39],resulting in formatting cocrystal with other molecules easily.Conversely,2,4-DNI is the excellent insensitive single explosives applied to propellant [40].The calculated detonation properties indicate that its performance is about 30% better than TATB [41].Results from impact sensitivity,friction sensitivity,explosion temperature and vacuum stability tests indicate that 2,4-DNI is less sensitive than both RDX and HMX [41].The stoichiometric ratio of host-guest molecules in the cocrystal material determines whether it can form a stable cocrystal structure.Job’s method [42] reveals the reason why cocrystal materials are most easily formed when the host-guest stoichiometric ratio is 1:1.Different host-guest stoichiometric ratios in the obtained supramolecular synthons have a good match with the absorbance curve,which basically conforms to the rule that the closer the host-guest stoichiometric ratio is,the easier it is to form a stable supramolecular structure.The cocrystallization of CL-20 and 2,4-DNI with a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1 is expected to attract the advantage of high energy and low sensitivity.Crystal structures,mechanical and detonation properties,and intermolecular interactions of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal were investigated.Systematic search approach with high accuracy is significant,and provides an insight into cocrystal structure predict theoretically.
2.Computational section
2.1.Search conditions of supramolecular synthons
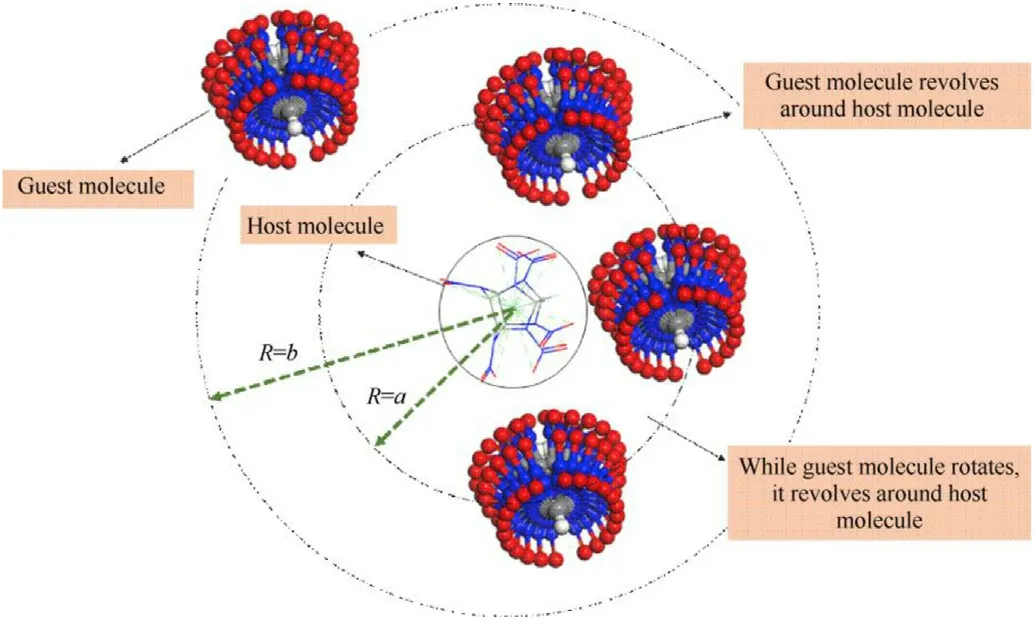
Fig.1.The search process of the supramolecular synthons.
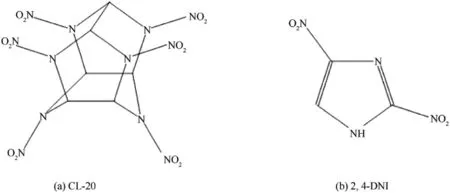
Scheme.1.Chemical structures of CL-20 and 2,4-DNI.
In order to improve the search efficiency of supramolecular synthons,reduce the impossible initial structures and obtain supramolecular structures closer to the experimental results,systematic search conditions were set in detail,such as search area,search radius,bonding types,hydrogen bond length,the number of hydrogen bond and so on.Eight CL-20-based cocrystals (see the Supporting Information,Fig.S1) that have been obtained from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC) [27,43-47] were analyzed to screen search conditions.The structures of the eight cocrystals were optimized employing the B3LYP functional [48]with the 6-311G (d,p) basis set to obtain the bonding types,bond length and the number of hydrogen bonds between CL-20 and coformers.Hydrogen bond becomes the main driving forces in cocrystal forming,and most of cocrystals have two hydrogen bonds with 2.286-2.895 Å (see the Supporting Information,Fig.S2).The intermolecular centroid distance is between 5.338 and 7.616 Å,6.5 Å as the search radius,these conditions provide great convenience for screening supramolecular structures rapidly.
The key to improve the search efficiency is to determine the search area and greatly reduce the initial structures.Electrostatic potential (ESP) of CL-20 molecule was calculated by using B3LYP functional with 6-311G(d,p)basis set to get surface extremums and extreme distribution of ESP.We found the maximum and minimum are mainly distributed near C-H bond,NObond,respectively(Fig.2(a)).The positive ESP has an area of 50.41%(Fig.2(b)),and the value lager than 17.37 kcal/mol is 27.26%.However,there is no ESP lower than-17.37 kcal/mol in the whole surface.CL-20 molecule shows strong attraction to the electron-rich groups and tends to be a hydrogen bond donor.
By studying the ESP of the CL-20 molecule,it is inferred that the probability of forming supramolecular synthon is high near the C-H bond through intermolecular hydrogen bond,however,it is lower relatively near the NO,as shown in Fig.3.
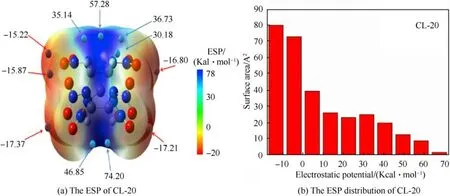
Fig.2.The ESP and ESP distribution of CL-20 molecule.

Fig.3.The search area of CL-20 supramolecular synthons。.
2.2.Systematic search approach
By analyzing the hydrogen bond characteristics formed between CL-20 and 2,4-DNI molecules,we can significantly reduce the search range of the system.The differential search is performed on the regions with different formation probability of supramolecular synthons,which greatly reduces the initial configuration and improves the search efficiency.The strategy for establishing the initial configuration of supramolecular synthons is as follows:Combined with the self-written Perl code and Matlab operable interface,2,4-DNI molecule rotates around CL-20 molecule according to the hydrogen bond length(2.2-3.0 Å),the number of hydrogen bonds(1-3),the scanning radius (6.5 Å) and search area.In areas where the probability of supramolecular synthons is high,2,4-DNI revolves around the CL-20 every 30,and spins every 30at the position of each revolution;Similarly,2,4-DNI revolves around CL-20 every 60and then rotates in the low formation region,as shown in Fig.4.The structures that may form intermolecular hydrogen bonds are used as the initial structures,utilizing molecular mechanics to optimize synthon structures and finally outputting the optimized structures with lower energy in Dmolmodule.
2.3.Computational methods
Interaction energy was calculated employing M062X functional,6-311++G (d,p) basis set with BSSE correction.ESP and ESP exterme of coformers and cocrystals were studied by Gaussian16 W and Multiwfn 3.7 [49] The crystal structure is predicted by Monte Carlo (MC) algorithm in MS-8.0 Polymorph module with Compass field.Density of State (DOS) calculation was performed using CASTEP module based on the density functional theory.The exchange related energy of electrons was described utilizing PBE(Perdew-Burke-Enzerhof) functional of generalized gradient approximation (GGA) by plane wave ultrasoft pseudoppotentials,and the dispersion force was corrected by Grimme.The cutoff energy of the plane wave was 380 eV,and k-points of the first Brillouin zone were both γ point.BFGS algorithm was used to optimize geometric structure with the total energy change of 0.01 eV/Å,the force of 0.1 GPa.Hirshfeld surfaces and associated 2D fingerprint plots were generated by the CrystalExplorer17 program [50].The mechanical properties were studied using MD simulations with the Compass force field by Forcite module.Detonation properties were calculated via the empirical nitrogen equivalent equations [51].
3.Computational results and analysis
3.1.Structural analysis
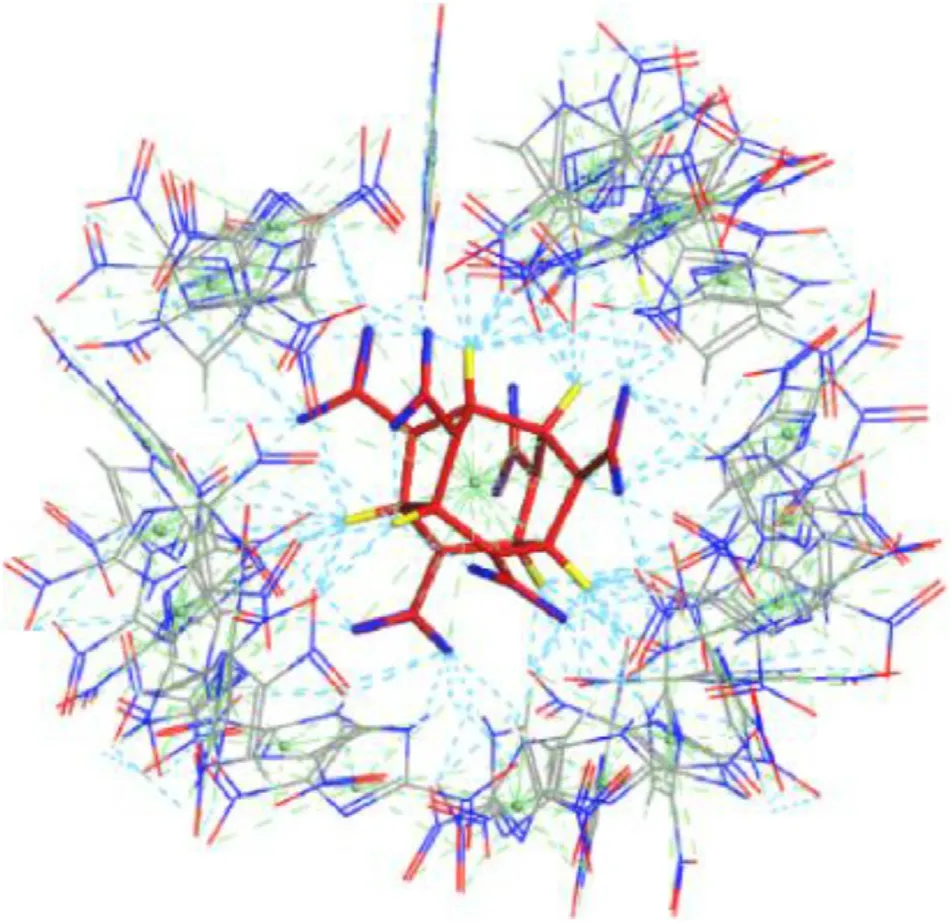
Fig.4.The search process of CL-20/2,4-DNI supramolecular structures.
The whole systematic search process obtained eight possible supramolecular synthons,as shown in Fig.5.Hydrogen bonds are the main driving force in the CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal forming.Most of hydrogen bonds are formed between C-H donor in CL-20 and NOacceptor in 2,4-DNI,which is consistent with above design rules.To study the strength of intermolecular interaction,interaction energy of cocrystal was calculated at 25.42-32.65 kJ/mol,as shown in Table 1,which is a weak interaction.Configuration 6 shows the largest intermolecular interaction energy with 32.65 kJ/mol,indicating there are stronger interaction between CL-20 and 2,4-DNI,consistent with hydrogen bond analysis.
3.2.Surface electrostatic potential
ESP is one of the most important physicochemical properties of compounds,because it provides information about the surface charge density distribution and molecular reactivity[40],which is attributed to analyze the electronic properties and further understand intermolecular interactions.Politzer et al.[52-55] have proposed that the impact sensitivity of explosives is related to the electrostatic potential maxima,namely,the impact sensitivity increases as the electrostatic potential maxima increases.Explosives with high sensitivity show strong positivity in the covalent bond region,whereas the insensitive explosives do not exhibit this feature.As can be seen from Table 2,the global Vof 1(73.32 kcal/mol),2 (72.84 kcal/mol) is between CL-20 (74.20 kcal/mol) and 2,4-DNI (71.71 kcal/mol),indicating that the impact sensitivity of 1,2 is significantly lower than that of CL-20,but higher than that of 2,4-DNI.As illustraed in Fig.6 (a),the positive and negative electrostatic potentials are combined between CL-20 and 2,4-DNI molecules in cocrystal 1 and 2,and the junction of ESP tends to be neutral,indicating that there is positive and negative electrostatic interaction between molecules,which reduces the ESP maxima.The positive and negative ESP obviously penetrate each other in the area of O atom on the nitro group and the C-H or N-H(Fig.6(b)),reflecting the complementary characteristics of electrostatic potential and the nature of electrostatic attraction interaction.The depth of penetration accounts for the strength of the interactions between the molecules,cocrystal 1,2 are obvious deeper than others,indicating the interactions are stronger consistent with hydrogen bond length and interaction energy analysis.Considering the molecular van der wals surface penetration pattern of each configuration,the mutual penetration of positive and negative ESP leads to the decrease of the positive ESP area in the framework of CL-20,we conclude that the impact sensitivity of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystals are lower than that of CL-20.
3.3.Crystal structure predict
We employed systematic search approach to obtain eight lowenergy supramolecular synthons by combining quantum chemistry and molecular mechanics.We know that supramolecular synthons,as a basic structure unit,are connected together by noncovalent bonds,such as intermolecular hydrogen bonds,and penetrate the entire crystal interior to form a cocrystal.Based on the above 8 reasonable structure units,the crystal structure was predicted by Monte Carlo (MC) algorithm.The Belsky theory [56]believes that 88.6% of the organic molecular crystals belong to the following nine point groups,namely,P21/c,P212121,Pbca,Pna21,P-1,P2c,C2/c,Pbcn,Pnma.We studied space group of 32 CL-20-based cocrystals obtained by experiment,including 8 space groups,namely,Pbca,P-1,C2/c,P21/c,P212121,P21,Pna21,P2c.Among them,Pbca,P212121,Pna21,and Pbcn are orthorhombic crystal systems.Therefore,In the polymorph module,we set the following 10 space groups to screen possible crystal structures,which are P21/c,P212121,Pbca,Pna21,P-1,P2c,C2/c,Pbcn,Pnma,P21,including 5 kind of orthorhombic crystal system,P212121,Pbca,Pna21,Pbcn,Pnma.We select the COMPASS force field and the charge is Forcefield assigned.The Quality is fine,the upper limit of the number of steps is 10,000 steps,the heating index is 0.025,the cutoff radius is 7.0 ± 0.11 Å,and the cooling factor is 0.0005.The lower the lattice energy,the more stable the crystal structure.Finally,four crystal structures (Fig.7) were screened based on the lattice energy,P21/c,P212121,Pbca,Pna21,respectively,and found that the four space group structures are based on supramolecular synthons 1,2,1,and 1,respectively.As shown in Table 3,cocrystal is most likely to crystallize in P21/c,the corresponding cell parameters are Z=4,a=8.28 Å,b=12.17 Å,c=20.42 Å,α=90,β=96.94,γ=90,and ρ=1.9353 g/cm.

Fig.5.The possible supramolecular structures of eight CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystals.
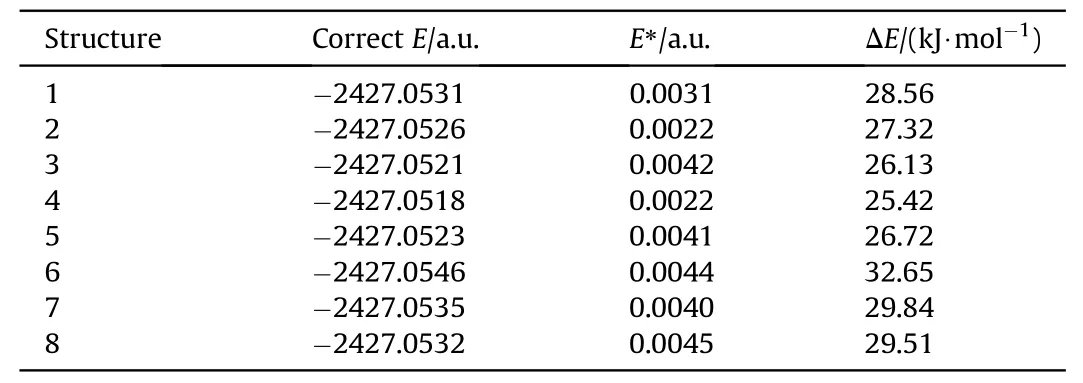
Table 1 The interaction energy of eight CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystals.
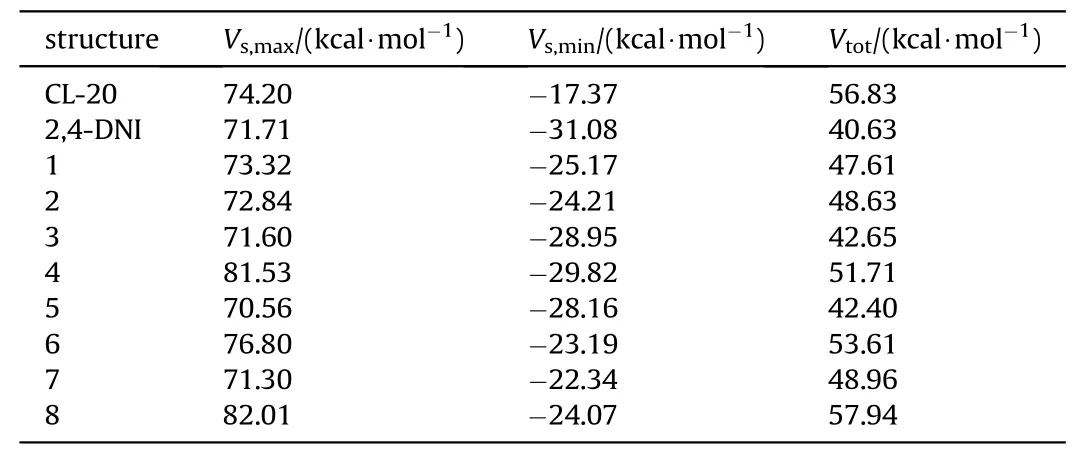
Table 2 The ESP extreme of CL-20,2,4-DNI and cocrystals.
3.4.Density of states
The density of states(DOS)and energy gap are closely related to the safety in the field of energetic materials.In the compounds with similar structure,homologues or isomers,the narrower energy gap,the lower the safety,and the rule is widely used to evaluate the stability and sensitivity of energetic materials [57,58].In order to make a better comparative analysis,firstly,DOS and partial density of states (PDOS) of CL-20,2,4-DNI was studied,as presented in Fig.8.CL-20 and 2,4-DNI exhibit an energy gap of 3.522,1.266 eV,respectively.CL-20 is dominated by N-p,O-p contributions and less C-sp,H-s contributions near the Fermi energy level.The electron states at the top of valence band indicate that active group is mainly concentrated in the N-NOand C-H bond.C-p,N-p and O-p contributions is most significant near the Fermi energy level for 2,4-DNI,corresponding to the active N-O and C-N bond.
The DOS and PDOS of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal with different space group are further analyzed and showed consistent similarity,as shown in Fig.9.This is due to the fact there are similar molecular structure in cocrystal except for the difference of contacts between CL-20 and 2,4-DNI molecules.The energy gaps of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal with Pbca,P222,Pna2,P2/c cell were 1.871 eV,1.848 eV,1.827 eV,1.797 eV,respectively,all of which are smaller than that of CL-20.P2/c cell structure shows the lowest energy gap,indicating high activity and worse stability.Compared with CL-20 and 2,4-DNI single component,the formation of cocrystal did not result in the significant change of DOS near the Fermi energy level.The DOS of the valence band top is dominated by C-p,N-p and O-p electron contributions from the two components,corresponding C-N,N-O,N-NObond,which become the trigger bonds for breaking easily in the thermal decomposition.The number and strength of the electron peaks in cocrystal are both reduced relative to that of the single component,and the dispersion attraction between the two components in cocrystal is weakened.After the cocrystal is formed,the stability of the molecules in cocrystal is reduced relative to the original molecules,which means that the two pure substances are conducive to the formation of a cocrystal rather than simple physical mixing.We found the orbital hybridization of bonding electrons H-s,O-sp in the C-H and N-O bonds,indicating the existence of hydrogen bond interaction between molecules.The hydrogen bond interactions are obvious especially in the Pbca cell structure,and the corresponding energy gap increases,resulting in higher stability.The analyzing of DOS indicates that the stability of cocrystal structure depends on the equilibrium of the mutual attraction of C-H…O-N and the mutual repulsion of N-O…O-N between two molecules,and the attraction interactions determine the stability and chemistry activity of cocrystals.

Fig.6.ESP of cocrystal mapped onto the molecular surfaces of ρ=0.001 au and van der Waals surface penetrability.
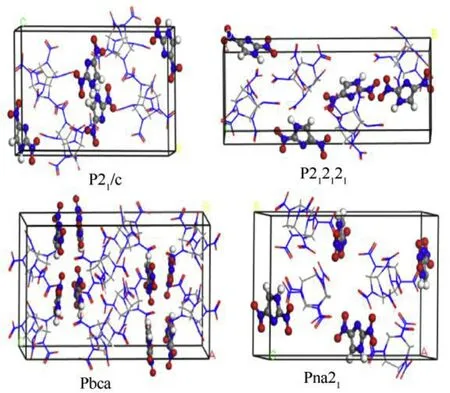
Fig.7.Four structures of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal.
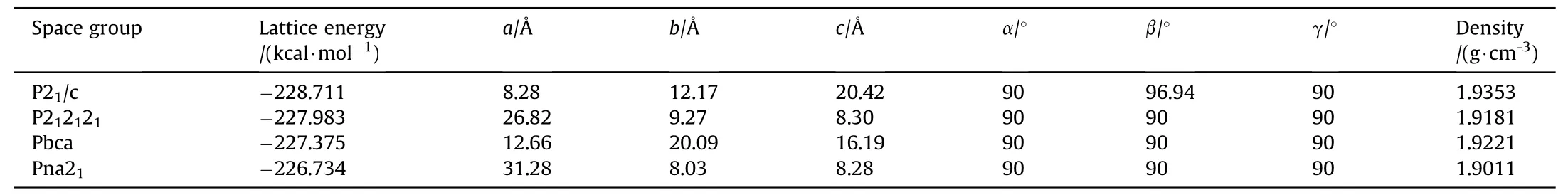
Table 3 The cell structure parameters of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal.
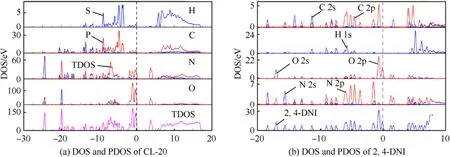
Fig.8.DOS and PDOS of CL-20,2,4-DNI.
3.5.Hirshefeld surface
Hirshefeld surface is an effective tool to analyze and visualize the types and regions of intermolecular interactions in the crystal packing [59,60].Hirshfeld surface and two-dimensional (2D)fingerprint plots of CL-20 molecule in CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal are presented in Fig.10,the color suggests the strength of interaction.The red and blue on the surface represent the high and low intensities of close contacts,respectively.We find that there are relatively strong interaction in all hirshfeld surface.Combined with 2D fingerprint,it concluded that the main contribution arises from the O…H,O…N,O…O contacts.The larger population of the O…H contacts plays a dominant role,with approximately 35.0% of the total weak interactions(Fig.11),suggesting that hydrogen-bonding interactions are the major driving forces in the formation of cocrystals [61].In contrast,O…O contacts also have a higher population,which can be assigned to the van der Waals interactions between the NOgroups in CL-20 and 2,4-DNI.The van der Waals interactions can not be neglected,and the coordination of hydrogen bonds and the van der Waals interactions improves the stability of cocrystals.O…H interactions have the largest population of 36.2%in CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal with Pbca space group,corresponding to the high stability of cocrystal,which is in good agreement with DOS analysis.
3.6.Mechanical properties
The mechanical properties of energetic materials are an important characteristic indicator in practical application.The quality of elastic mechanical properties will directly affect the production,storage and safety of energetic materials,based on the above close contact between safety and mechanical properties of energetic materials,the mechanical properties (tensile modulus E,bulk modulus K,shear modulus G,Cauchy pressure C12-C44,Poisson’s ratio γ and the ratio of bulk modulus to shear modulus K/G) of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal were simulated by molecular dynamics.E,K and G are usually taken to evaluate the stiffness of the materials [62] and show certain positive correlation.K also can be employed to indicate the fracture strength of materials.The larger the value of K,the higher the energy of materials,and namely the greater the breaking strength.γ represents the plasticity of materials,and materials can show certain plasticity within 0.2-0.4.K/G is used to measure the toughness of the material,and the higher the K/G value,the better the toughness [63].C12-C44 shows the ductility of materials.When C12-C44 is positive,the materials have ductility,and the greater the positive value,the higher the ductility.When C12-C44 is negative,the materials show brittleness [64].
As can be seen from Table 4,compared with the (E,G,K)modulus of the pure CL-20,the modulus of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystals decrease dramatically,which means that the stiffness decreases while the elasticity of the cocrystals increase.γ has a significant increasing for CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal,which shows strong plasticity.We can see that K/G and C12-C44 of the CL-20/2,4-DNI co-crystal are larger than that of pure CL-20,indicating the toughness and ductility of the cocrystals are better than that of CL-20.As a result,fewer faults and voids are formed inside the column in the process of pressing and loading.According to the hotspot theory,the probability of forming a hot spot is less,so that CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal is more insensitive than CL-20 and the safety is better.
3.7.Detonation velocity and pressure
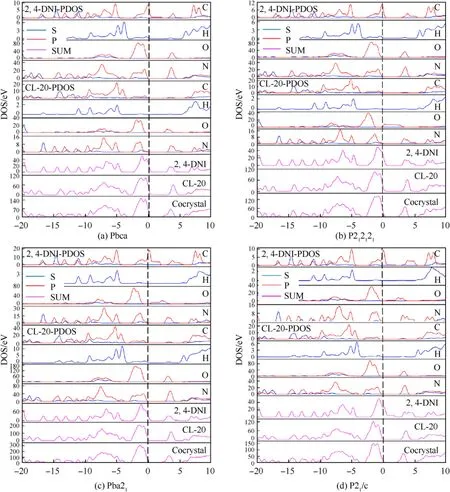
Fig.9.DOS and PDOS of CL-20,2,4-DNI.
Detonation velocity and pressure,two important parameters for HEDMs,were predicted by the empirical nitrogen equivalent equations (see the Supporting Information,section SI 3) [65].The detonation velocity and detenation pressure of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal are 9257 m/s and 39.27 GPa (Fig.12),respectively,which are lower than those of CL-20 (9792 m/s,45.07 GPa) [46].This is attributed to the decrease of the density and more negative oxygen balance.The traditional nitroaromatic cocrystals can be used as references,and CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal exhibits excellent detonation performances compared with CL-20/TNT (8558 m/s,32.69 GPa) and CL-20/1,4-DNI (9242 m/s,39.01 GPa) [46].CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal is expected to become a promising high explosive candidate.
4.Conclusions

Fig.10.Hirshfeld surface and two-dimensional (2D) fingerprint plots of CL-20.
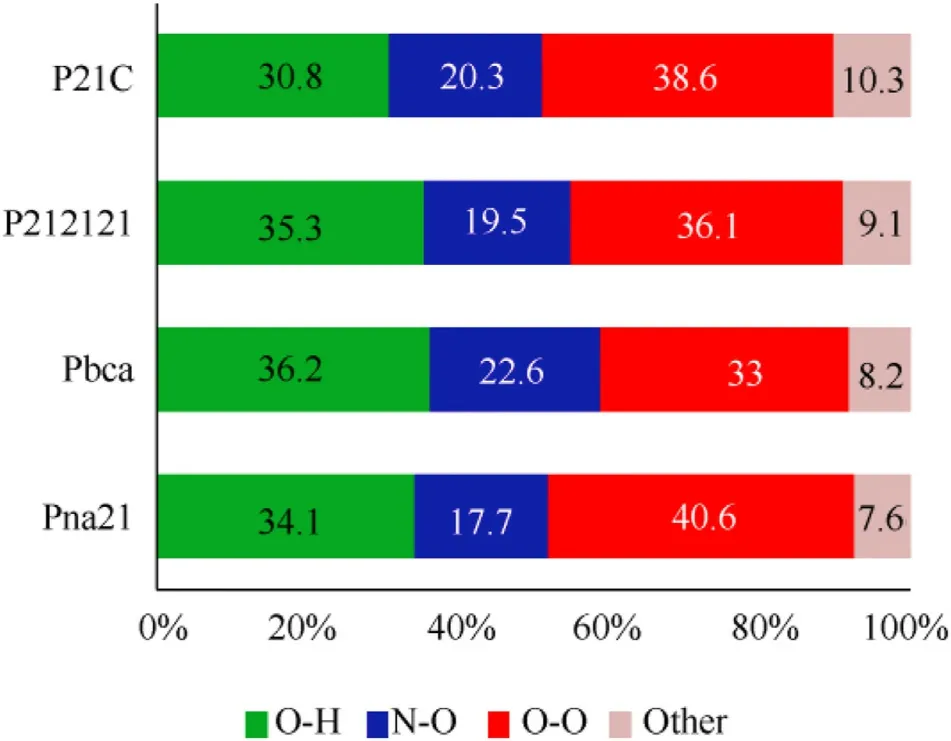
Fig.11.Distribution of intermolecular interaction types in CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal.
In summary,we propose a systematic search approach to determine whether cocrystal is formed and predict its performances rapidly and accurately.The high accuracy of the systematic search approach was verified with an error of less than 8.8%.CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal with a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1 is most likely to crystallize in P2/c,the corresponding cell parameters are Z=4,a=8.28 Å,b=12.17 Å,c=20.42 Å,α=90,β=96.94,γ=90,and ρ=1.9353 g/cm.The intermolecular interactions,sensitivity,mechanical properties and detonation properties were investigated.The formation of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal depends primarily on C-H…O hydrogen bonds between the hydrogen atoms in CL-20 and the oxygen atoms in the NOgroups of 2,4-DNI.By the analysis of ESP,the sensitivity of CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal decreased obviously,showing certain insensitivity compared to CL-20.The mechanical properties perdicted implied favorable ductility of cocrystal,indicated that the probability of forming a hot spot is less and have better safety.More importantly,CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal exhibited excellent detonation performances (9257 m/s and 39.27 GPa).Thus,these advantages of high energy and low sensitivity make it as a promising energetic materials.There is nodenying that the systematic search approach provides a new strategy for cocrystal predict and has great potential be a practical tool to search cocrystals with high energy and low sensitivity.
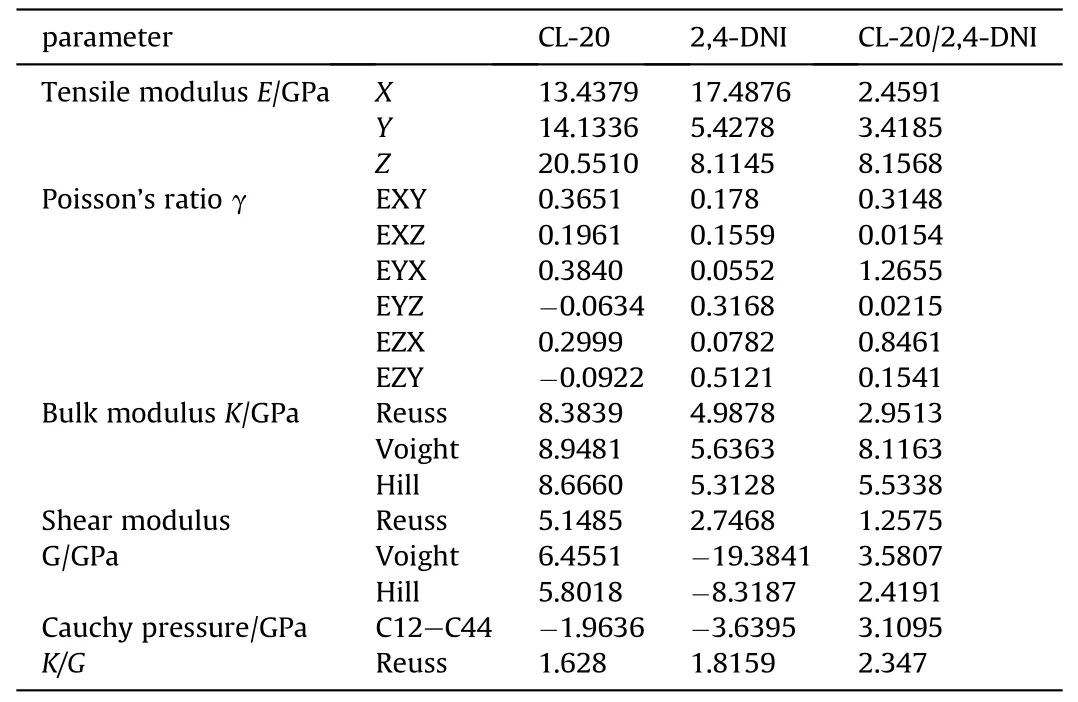
Table 4 Mechanical property parameter of CL-20,2,4-DNI and CL-20/2,4-DNI cocrystal.
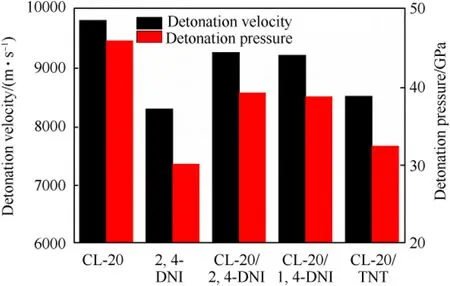
Fig.12.The detonation performances of cocrystals and coformers.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
We gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.22005090),Beijing Institute of Technology Research Fund Program for Young Scholars,the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.11672040 and No.21801016),Open Research Fund Program of Science and Technology on Aerospace Chemical Power Laboratory(STACPL120201B02)and the State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology(No.YB2016-17).
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2021.03.027.
- Defence Technology的其它文章
- Ultra-lightweight CNN design based on neural architecture search and knowledge distillation:A novel method to build the automatic recognition model of space target ISAR images
- Dense copper azide synthesized by in-situ reaction of assembled nanoporous copper microspheres and its initiation performance
- Ballistic impact response of resistance-spot-welded (RSW) doublelayered plates for Q&P980 steel
- Calculating detonation performance of explosives by VLWR thermodynamics code introduced with universal VINET equation of state
- Design and motion analysis of reconfigurable wheel-legged mobile robot
- A Multi-UCAV cooperative occupation method based on weapon engagement zones for beyond-visual-range air combat

