川西坳陷中段须四段储层综合评价
陈贤良 纪友亮 杨克明

摘要:川西坳陷須家河组是典型的致密砂岩储层,勘探的首要目标是在致密背景下寻找相对高渗区,成岩相是现今储层面貌及品质的直接反映。针对川西坳陷中段须四段砂岩储层,利用岩石薄片、铸体薄片、阴极发光、扫描电镜等分析测试方法,开展定量成岩相储层综合评价。结果表明:须四段储层岩石类型以中粒岩屑砂岩和岩屑质石英砂岩为主,孔隙类型以粒内溶孔和粒间溶孔为主,孔隙结构为微-细孔、微-细喉型,孔隙度、渗透率低,属致密储层;基于压实、胶结、溶蚀等3种主要成岩作用强度计算结果和分级标准,须四段储层以中强-强压实、强胶结、弱溶蚀为主要特征,发育6种主要成岩相类型且下亚段压实与胶结强度高于上亚段、溶蚀强度弱于上亚段。结合沉积相、储集空间类型及储层物性特征等将须四段储层划分为4类,其中Ⅱ类储层为有利储层,分布在中江-洛带地区和新场构造带。研究成果可为进一步研究致密气提供地质依据。
关键词:川西坳陷中段;须四段;定量成岩相;储层评价;有利储层
中图分类号:P 624文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-9315(2022)04-0760-08
DOI:10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2022.0416
Comprehensive evaluation of reservoir in the forth Member of Xujiahe
Formation in the Middle Area of Western Sichuan DepressionCHEN Xianliang JI Youliang YANG Keming
(1.College of Geology and Environment,Xian University of Science and Technology,Xian 710054,China;
2.State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources and Prospecting,China University of Petroleum,Beijing 102249,China;
3.Research Institute of Exploration and Development,Southwest Oil & Gas Company,SINOPEC,Chengdu 610016,China)Abstract:The Xujiahe Formation is a typical tight sandstone reservoir in the Western Sichuan Depression.The primary goal of further exploration is to find relatively high-permeability areas under tight conditions.Diagenetic facies might well reflect the present reservoir appearance and quality.Therefore,aiming at the sandstone reservoir of the fourth member of the Xujiahe formation in the middle area of the western Sichuan Depression,a comprehensive reservoir evaluation was carried out based on quantitative diagenetic facies research by using petrographic thin sections,casting thin sections,cathodoluminescence,scanning electron microscopy and other analytical methods.The results show that reservoir rock types of the forth member of Xujiahe formation are mainly medium-grained lithic sandstone and lithic quartz sandstone.The pore types are mainly intragranular dissolved pores and intergranular dissolved pores and the pore structure is micro-fine pores and micro-fine throat type,and their porosity and permeability are low,belonging to tight reservoir.Based on the calculation results and three classification standards of compaction,cementation and dissolution,the reservoir of the fourth member of the Xujiahe formation are characterized by strong compaction,strong cementation and weak dissolution.Furthermore, six major diagenetic facies types were classified,and the compaction and cementation degree of the lower sub-member is higher than that of the upper sub-member,and the degree of dissolution is weaker than that of the upper sub-member.Based on quantitative diagenetic facies,with sedimentary facies in view,reservoir space type and reservoir physical properties,the reservoir was divided into four types,and Type II is a favorable reservoir in the study area,which mainly distributed in the Xinchang tectonic belt and Zhongjiang-Luodai area.The research results can provide geological basis for further exploration and development of tight gas in the study area.
Key words:the Middle Area of Western Sichuan Depression;the forth member of Xujiahe formation;quantitative diagenetic facics;reservoir evaluation;favorable reservoir
0引言
致密砂岩储层经历了复杂的成岩演化,造就了现今低孔低渗的储层面貌,成岩相则是现今储层品质的直接反映[1-5]。基于成岩相研究成果开展储层综合评价,更准确地指导有利储层预测,为制定合理的开发方案提供地质依据。
须四段为川西坳陷中段深层天然气产出的重要层位之一,现今埋深大于3 500 m,处于中成岩B期-晚成岩阶段,储层孔隙度平均4.88%,渗透率小于1×10-3μm2,为致密储层。ZHONG、吕正祥、张鼐等研究储层成岩作用、成岩演化及优质储层形成机制[6-8],WANG等分析储层微观孔隙结构及其成岩控制[9],李嵘等开展致密化机理研究[10],林小兵等针硅质碎屑颗粒溶蚀现象分析了溶蚀机理[11],王亚男等研究了自生高岭石的发育特征、形成机理及其对储层物性的影响[12]。研究成果主要涉及成岩作用、孔隙演化、致密化机理等方面,较少涉及定量成岩相研究[13-16],且多以须家河组为单元。利用岩石薄片、铸体薄片、阴极发光、扫描电镜等分析测试方法,结合定量成岩相研究成果,开展川西坳陷中段须四段储层综合评价,为进一步研究致密砂岩气奠定基础。
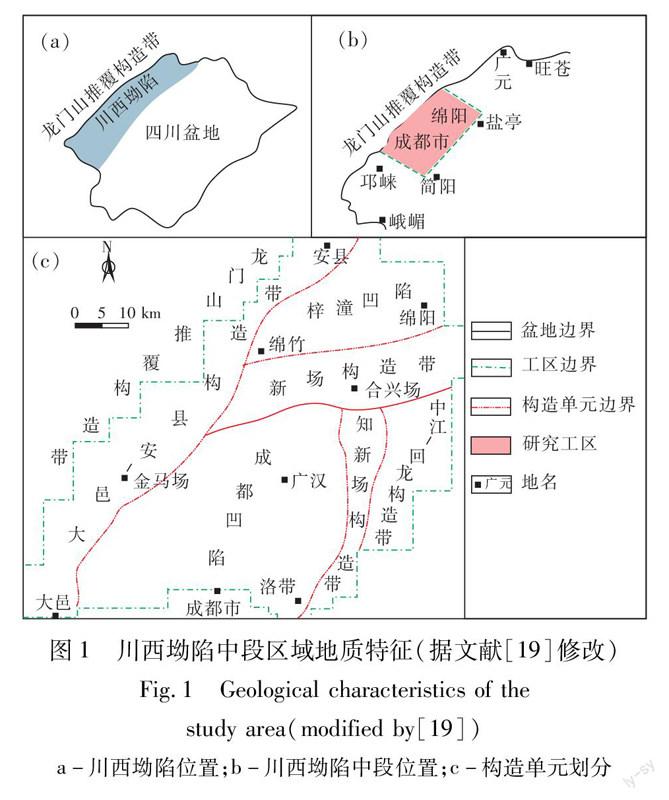
1区域地质概况
川西坳陷又称川西前陆盆地,位于四川盆地西部,西以龙门山逆冲带为界,东以龙泉山前陆隆起带为界,呈北东—南西向展布,其中安县—绵阳以南、大邑—成都以北地区为川西坳陷中段,内部可划分出6个构造单元(图1),面积约10 570 km2。须四段为晚三叠世周缘前陆盆地强烈活动阶段沉积充填,发育冲积扇-河流-三角洲-湖泊相沉积[17-18],岩性由细、中砂岩与页岩、煤层的不等厚互层组成。依据岩性特征可分为上、中、下3个亚段,其中上、下亚段岩性以砂岩为主,砂岩储层发育。
2储层特征
2.1储层岩石学特征
须四段储层岩石类型以岩屑砂岩和岩屑质石英砂岩为主,碎屑成分以低长石、高岩屑为特征(图2,表1);碎屑颗粒以中粒结构为主,分选好,磨圆较差,以次棱角状为主(图3(a)、(b)、(c));填隙物主要包括碳酸盐胶结物、硅质胶结物、黏土矿物和杂基(图3(d));颗粒间以线-凹凸接触为主,以颗粒支撑为特征,胶结类型以孔隙式胶结为主。须四段储层碎屑成分和结构成熟度均较低。
2.2物性特征
须四段储层孔隙度大小变化较大,其中下亚段储层孔隙度分布在2%~8%之间,平均5.2%,上亚段储层孔隙度分布在4%~10%之间,平均5.5%,渗透率小于1×10-3 μm2,为致密储层,局部发育低渗、特低渗储层(图4)。
2.3储集空间类型
通过铸体薄片鉴定分析,结合扫描电镜和阴极发光观察,须四段储层储集空间发育较差,原生孔隙基本消失殆尽,次生孔隙发育,以粒内溶孔和粒间溶孔为主(图5(a)~(c)),裂缝较发育;孔隙结构为微-细孔、微-细喉型,平均孔隙直径小于10 μm,最大进汞饱和度为2.9%~51.6%,分选系数为1.09~12.02,最大连通孔喉半径处于0.03~3 μm。整体上,上亚段储层较下亚段储层溶蚀孔更发育。
2.4储层成岩特征
须四段储层经历了多种成岩变化,形成了现今的储层面貌,其中压实、胶结和溶蚀成岩作用对储层质量起着绝对的控制作用。
2.4.1压实作用
须四段储层压实作用强,颗粒之间以线-凹凸接触为主,出现压实定向排列现象,可见长条状的云母等塑性岩屑等被压弯甚至折断(图5(d)、(e));压溶作用分布不均匀,仅在局部石英含量高的储层中发育。
2.4.2胶结作用
须四段储层主要胶结作用包括碳酸盐、硅质和黏土矿物胶结。其中碳酸盐胶结物是最常见的胶结物类型,主要包括方解石、铁方解石以及少量白云石、菱铁矿等,以方解石含量最高,主要以斑状、连晶状2种形式产出于孔隙间(图5(f)~(h)),早期以方解石胶结为主,晚期以含铁碳酸盐胶结为主;硅质胶结物含量一般较低,主要以次生加大边的形式产出于石英颗粒的边缘,主要为II~III级次生加大(图5(i)、(j));黏土矿物主要包括伊利石、绿泥石和少量高岭石,含量低,主要以孔隙衬边和充填孔隙为主(图5(k)、(l))。
2.4.3溶蚀作用
溶蚀作用是须四段砂岩储层中非常普遍的一种成岩作用类型。在酸性地层水作用下长石、沉积岩岩屑、岩浆岩岩屑及碳酸盐胶结物等发生部分、甚至全部的溶解,形成次生孔隙(图5(a)~(c)、(m)~(o))。长石、岩屑常被溶蚀形成粒内溶孔、粒间溶孔,甚至形成铸模孔等,常见长石沿解理缝溶解呈蜂窝状、条带状,胶结物的溶解作用相对比较微弱。
3定量成岩相
为定量表征3种主控成岩作用的成岩强度,采用视压实率、视胶结率、视溶蚀率进行定量表征[5,20-23],建立须四段储层成岩强度划分标准(表2)。
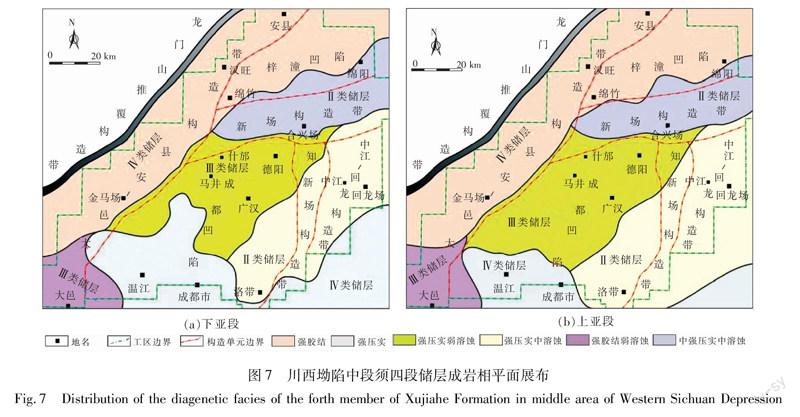
依据成岩强度计算结果和分级标准可知,整体以中强-强压实、强胶结、弱溶蚀为主(图6),下亚段压实与胶结强度高于上亚段、溶蚀强度弱于上亚段。建立测井响应并优选响应特征明显的声波、电阻率和密度辅助成岩相判别(表3),开展全井段成岩相分析,完成平面成岩相划分[24-28]。
上、下亚段储层成岩相展布特征相似,龙门山前地区主要发育强胶结成岩相,新场构造带以中强压实中溶蚀成岩相为主,中江-回龙至洛带地区以强压实中溶蚀成岩相为主,大邑地區以强胶结弱溶蚀成岩相为主,什邡、马井及广汉地区以强压实弱溶蚀成岩相为主,温江、成都地区以强压实成岩相为主(图7)。中溶蚀成岩相主要发育在三角洲前缘水下分流河道主体、砂体厚度大于10 m、长石等溶蚀组分含量较高的地区,且上亚段储层溶蚀程度大于下亚段。
4储层综合评价
须四段储层整体岩屑含量高,埋藏深、压实作用强,储集空间发育较差。Ⅰ类储层物性最好,但仅在局部深度范围内发育,以发育Ⅱ、Ⅲ类储层为主,其中Ⅱ类储层溶蚀作用较强,物性较好,为有利储层(表4)。
须四段下亚段Ⅱ类储层主要发育在新场构造带和中江-洛带地区(图7),属中压实中溶蚀和中强压实中溶蚀成岩相。须四段上亚段Ⅱ类储层展布特征与下亚段相似,仅中江-洛带地区有利储层分布面积有所增大。由于上亚段储层埋藏浅且砂体发育程度高,溶蚀强度大于下亚段、物性好于下亚段储层。
5结论
1)须四段储层主要由中粒岩屑砂岩和岩屑質石英砂岩组成,孔隙类型以粒内和粒间溶孔为主,孔隙结构为微-细孔、微-细喉型,孔隙度、渗透率低,属致密储层。
2)依据压实、胶结、溶蚀3种主要成岩强度计算结果和分级标准,须四段储层以中强-强压实、强胶结、弱溶蚀为主要特征,发育强压实、强压实弱溶蚀、强压实中溶蚀、中强压实中溶蚀、强胶结、强胶结弱溶蚀6种主要成岩相类型。
3)纵向上,下亚段压实与胶结强度高于上亚段、溶蚀程度弱于上亚段;平面上,上、下亚段储层成岩相展布特征相似。
4)须四段储层分为4类,其中II类储层物性较好,为有利储层,分布在新场构造带和中江-洛带地区,且上亚段储层物性好于下亚段储层。
参考文献(References):
[1]HEIDSIEK M,BUTSCHER C,BLUM P,et al.Small-scale diagenetic facies heterogeneity controls porosity and permeability pattern in reservoir sandstones[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2020,79(18):1083-1091.
[2]ZHOU X Q,ZHANG C,ZHANG Z S,et al.A saturation evaluation method in tight gas sandstones based on diagenetic facies[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,107:310-325.
[3]张彬,屈红军,李敏,等.鄂尔多斯盆地罗庞塬地区长8储层成岩相及其对物性的控制作用[J].西安科技大学学报,2013,33(2):156-160,189.ZHANG Bin,QU Hongjun,LI Min,et al.Diagenetic facies and its control over physical property of Chang 8 reservoir in Luopangyuan area of Ordos Basin[J].Journal of Xian University of Science and Technology,2013,33(2):156-160,189.
[4]邹才能,陶士振,周慧,等.成岩相的形成、分类与定量评价方法[J].石油勘探与开发,2008,35(5):526-540.ZOU Caineng,TAO Shizhen,ZHOU Hui,et al.Genesis,classification and evaluation method of diagenetic facies[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2008,35(5):526-540.
[5]陈贤良,纪友亮,杨克明.川西中段上沙溪庙组层序格架下成岩相及储层评价[J].断块油气田,2019,26(5):550-554.CHEN Xianliang,JI Youliang,YANG Keming.Diagenetic facies and reservoir evaluation in sequence framework of Upper Shaximiao Formation in middle area of Western Sichuan Depression[J].Fault-block Oil & Gas Field,2019,26(5):550-554.
[6]ZHONG Y J,HUANG K K,YE L M,et al.Diagenesis of tight sandstone reservoirs of Xujiahe Formation(Upper Triassic),the Xinchang Gas Field,Western Sichuan Basin,China[J].Geological Journal,2020,55(6):4604-4624.
[7]吕正祥,刘四兵.川西须家河组超致密砂岩成岩作用与相对优质储层形成机制[J].岩石学报,2009,25(10):2373-2383.LYU Zhengxiang,LIU Sibing.Ultra-tight sandstone diagenesis and mechanism for the formation of relatively high-quality reservoir of Xujiahe Group in Western Sichuan[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2009,25(10):2373-2383.
[8]张鼐,田作基,吴胜华,等.川西须家河组储层成岩演化[J].岩石学报,2008,24(9):2179-2184.ZHANG Nai,TIAN ZuoJi,WU Shenghua,et al.Study Xujiahe reservoir diagenetic process,Sichuan Basin[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2008,24(9):2179-2184.
[9]WANG Q C,CHEN D X,GAO X Z,et al.Microscopic pore structures of tight sandstone reservoirs and their diagenetic controls:A case study of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation of the Western Sichuan Depression,China[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology,2020,113:104119.
[10]李嵘,张娣,朱麗霞.四川盆地川西坳陷须家河组砂岩致密化研究[J].石油实验地质,2011,33(3):274-281.LI Rong,ZHANG Di,ZHU Lixia.Densification of Upper Triassic Xujiahe tight sandstones,Western Sichuan,China[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment,2011,33(3):274-281.
[11]林小兵,田景春,刘莉萍,等.四川盆地川西坳陷须家河组硅质碎屑颗粒溶蚀作用及机理[J].石油实验地质,2019,41(3):404-410,419.LIN Xiaobing,TIAN Jingchun,LIU Liping,et al.Dissolution mechanism of siliciclastic particles in Xujiahe Formation,West Sichuan Depression,Sichuan Basin[J].Petroleum Geology and Experiment,2019,41(3):404-410,419.
[12]王亚男,林良彪,余瑜,等.川西拗陷须家河组第四段致密砂岩高岭石及其对储层物性的影响[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,46(3):354-362.WANG Yanan,LIN Liangbiao,YU Yu,,et al.Characteristics of kaolinite in tight sand reservoirs of Member 4 of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in West Sichuan Depression and its influence on physical properties of reservoirs[J].Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition),2019,46(3):354-362.
[13]戴朝成,郑荣才,朱如凯,等.四川前陆盆地中西部须家河组成岩作用与成岩相[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2011,38(2):211-219.DAI Chaocheng,ZHENG Rongcai,ZHU Rukai,et al.Diagenesis and diagenetic facies of Xujiahe Formation in the central west of Sichuan Foreland Basin[J].Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition),2011,38(2):211-219.
[14]杜业波,季汉成,朱筱敏.川西前陆盆地上三叠统须家河组成岩相研究[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2006,36(3):358-364.DU Yebo,JI Hancheng,ZHU Xiaomin.Research on the diagenetic facies of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Western Sichuan Foreland Basin[J].Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2006,36(3):358-364.
[15]徐晨,陈洪德,刘佳庚,等.川西坳陷须四段上亚段致密砂岩岩石物理相划分[J].油气地质与采收率,2019,26(3):70-77.XU Chen,CHEN Hongde,LIU Jiageng,et al.Petrophysical facies division of tight sandstone in Upper 4th Member of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Depression[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2019,26(3):70-77.
[16]徐樟有,吴胜和,张小青,等.川西坳陷新场气田上三叠统须家河组须四段和须二段储集层成岩-储集相及其成岩演化序列[J].古地理学报,2008,10(5):447-458.XU Zhangyou,WU Shenghe,ZHANG Xiaoqing,et al.Diagenetic reservoir facies and their evolutionary sequences of the Members 4 and 2 of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang Gasfied,Western Sichuan Depression[J].Journal of Palaeogeography,2008,10(5):447-458.
[17]葉黎明,陈洪德,胡晓强,等.川西前陆盆地须家河期高分辨率层序格架与古地理演化[J].地层学杂志,2006,30(1):87-94.YE Liming,CHEN Hongde,HE Xiaoqiang,et al.The framework of the high-resolution sequence and the paleogeographic evolution of the Xujiahe Formation in the West Sichuan Foreland Basin[J].Journal of Stratigraphy,2006,30(1):87-94.
[18]叶泰然,李书兵,吕正祥,等.四川盆地须家河组层序地层格架及沉积体系分布规律探讨[J].天然气工业,2011,31(9):51-57.YE Tairan,LI Shubin,Lü Zhengxiang,et al.Sequence stratigraphic framework and sedimentary system distribution of the Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Industry,2011,31(9):51-57.
[19]沈忠民,刘四兵,吕正祥,等.川西坳陷中段陆相地层水纵向变化特征及水-岩相互作用初探[J].沉积学报,2011,29(3):495-502.SHEN Zhongmin,LIU Sibing,LYU Zhengxiang,et al.Vertical geochemical characteristics of continental formation water and its water-rock interaction in the middle area of Western Sichuan Depression[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2011,29(3):495-502.
[20]楚美娟,郭正权,齐亚林,等.鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长8储层定量化成岩作用及成岩相分析[J].天然气地球科学,2013,24(3):477-484.CHU Meijuan,GUO Zhengquan,QI Yalin,et al.Quantitative diagenesis and diagenetic facies analysis on Chang 8 reservoir of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2013,24(3):477-484.
[21]蒋裕强,王猛,刁昱翔,等.川中低孔渗砂岩成岩相定量评价与快速预测——以遂宁-蓬溪须二段为例[J].中国地质,2014,41(2):437-449.JIANG Yuqiang,WANG Meng,DIAO Yuxiang,et al.Quantitative evaluation and prediction of diagenesis facies with low porosity and permeability sandstone in central Sichuan:A case study of 2nd member of Xujiahe Formation in Suining-Pengxi area[J].Geology in China,2014,41(2):437-449.
[22]马瑶,李文厚,王若谷,等.鄂尔多斯盆地子洲气田北部山32段储层成岩作用及成岩相定量化分析[J].天然气地球科学,2015,26(11):2039-2052.MA Yao,LI Wenhou,WAND Ruogu,et al.Quantitative analysis of diagenesis and diagenetic facies of reservoir of Shan32Member in the North of Zizhou Gasfield,Ordos Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2015,26(11):2039-2052.
[23]张琴,朱筱敏,陈祥,等.南华北盆地谭庄凹陷下白垩统成岩相分布及优质储层预测[J].石油与天然气地质,2010,31(4):472-480.ZHANG Qin,ZHU Xiaomin,CHEN Xiang,et al.Distribution of diagenetic facies and prediction of high-quality reservoirs in the Lower Cretaceous of the Tanzhuang Sag,the Southern North China Basin[J].Oil & Gas Geology,2010,31(4):472-480.
[24]LAI J,FAN X C,PANG X J,et al.Correlating diagenetic facies with well logs(conventional and image)in sandstones:The Eocene Suweiyi Formation in Dina 2 Gasfield,Kuqa depression of China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2018,174:617-636.
[25]WU D,LIU S B,CHEN H D,et al.Investigation and prediction of diagenetic facies using well logs in tight gas reservoirs:Evidences from the Xu-2 member in the Xinchang structural belt of the Western Sichuan Basin,western China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2020,192.
[26]牟煒卫,王琪,田兵,等.珠江口盆地白云凹陷北坡中深部储层成岩相测井响应特征[J].天然气地球科学,2017,28(10):1601-1612.MOU Weiwei,WANG Qi,TIAN Bing,et al.The diagenetic facies logging response characteristics of medium-deep reservoirs in the north slope of Baiyun Sag,Pearl River Mouth Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2017,28(10):1601-1612.
[27]韩进,孙卫,杨波,等.低渗透储层不同成岩相微观孔隙结构特征及其测井识别差异性分析:以姬塬油田王盘山长61储层为例[J].现代地质,2018,32(6):1182-1193.HAN Jin,SUN Wei,YANG Bo,et al.Characteristics of micro-pore structure and differential analysis of logging identification for different diagenetic facies in low permeability reservoir:a case study on Chang 61 reservoir in Wangpanshan Area of Jiyuan Oilfield[J].Geoscience,2018,32(6):1182-1193.
[28]白烨,薛林福,石玉江,等.测井成岩相自动识别及其在鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格地区的应用[J].中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2013,37(1):35-41.BAI Ye,XUE Linfu,SHI Yujiang,et al.An automatic identification method of log diagenetic facies and its application in Sulige area,Ordos Basin[J].Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Sciences),2013,37(1):35-41.

