基于参数优化VMD和LightGBM的雷达辐射源个体识别
肖易寒 李栋年 于祥祯 宋柯



摘 要: 为解决在复杂电磁环境中雷达辐射源个体识别准确率低的问题,提出基于参数优化VMD和LightGBM的雷达辐射源个体识别技术。首先对雷达辐射源的无意特征进行分析,仿真添加了相位噪声作为雷达辐射源的指纹特征; 其次利用麻雀搜索算法(SSA)对变分模态分解(VMD)的分解参数进行自动寻优,准确快速地得到最优分解参数组合为[2, 2 950]; 然后基于最优VMD分解参数对辐射源信号提取能量熵与样本熵作为特征向量; 最后将特征向量送入LightGBM分类器完成辐射源个体识别。通过实测数据的验证,信噪比在25 dB时识别率能够达到85%以上,具有较为理想的识别结果。
关键词: 雷达辐射源; 个体识别; 变分模态分解; 麻雀搜索算法; 能量熵; 样本熵; LightGBM
中图分类号: TJ760; V243.2
文献标识码: A
文章编号: 1673-5048(2022)02-0093-08
DOI: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2021.0073
0 引 言
辐射源的个体识别又称辐射源指纹识别或者特定辐射源识别[1],辐射源指纹是发射设备硬件固有非理想特征造成的,具有不可伪造、难以改变、不可避免等特点。这种非理想特征对信号的影响是细微的,以无意调制的形式附加在发射信号上,对“指纹”特征的提取是辐射源无意识别的难点。目前对指纹特征的分析提取主要基于对以下信息的获取: 常规基本参数信息[2-4]、基本变换信息[5-8]、信号特殊结构[9-11]、分解重构信息[12-15]以及发射机硬件特性[16-18]。
辐射源个体识别可根据分析对象分为通信辐射源个体识别与雷达辐射源个体识别[19]。其中对于雷达辐射源个体识别的研究具有重要意义,快速精确地对雷达辐射源进行识别可以直接掌握战争主动性,是当今电子战快速发展下的制胜关键。
雷达辐射源个体识别并不关注传输过程信号的主要信息,关注重点是在信号主体成分之外的细微特征。利用信号的分解算法可以在提高信息维度的同时获得新的数据处理思路,以此得到更好的特征提取结果。分解算法可以将信号分成多个本征模态函数(IMF),分别为原始信号的主要成分及杂散成分。常见的分解算法有经验模态分解(EMD)、变分模态分解(VMD)及固有时间尺度分解(ITD),其中VMD方法结果稳定,计算简单,无模态混叠问题,分解出的基本分量IMF具有AM-FM调制窄带信号的特点,其瞬时频率有实际的物理意义。马洪斌等[20]利用蛙跳算法来搜索VMD最优参数,将得到的IMF分量构成矩阵进行奇异值分解,并作为特征对故障类型进行识别。李亚兰等[21]将VMD算法用于雷达信号有意识别,将信号分解为3个IMF分量后对3个IMF分量提取排列熵与样本熵,在低信噪比下达到较高识别率。郑义等[22]提出利用蝗虫优化算法,以相关峭度为适应度函数对变分模态分解参数进行自适应选定,用于提取强噪声背景下滚动轴承故障信号的微弱特征。
本文将麻雀搜索算法(SSA)用于VMD参数的优化选取上,解决了VMD分解参数人为设置带来的影响,又基于熵特征进行了二次特征提取,最后用于LightGBM分类器进行识别。 仿真结果显示该方法具有较高识别率,较其他方法有明显优势,在实测数据的验证下同样能够达到一定识别率。
3.3 基于LightGBM的辐射源个体识别
仿真得到的雷达辐射源信号经过SSA优化VMD参数后分解得到3个IMF分量,分別提取了能量熵与样本熵后串联为6维特征向量,使用LightGBM进行分类识别。每个信噪比下有3部辐射源共1 200个样本信号,分类识别中将训练集与测试集比值设置为8∶2,即960个样本作为训练集,240个样本为测试集,送入LightGBM进行分类识别。
将本文方法与文献[31]中的方法进行对比。文献[31]对信号进行VMD后将模态分量不用的中心频率作为特征,送入经人工蜂群算法优化的支持向量机(ABC-SVM)中进行识别分类。同时,对比了使用本文方法提取特征后送入ABC-SVM的识别率以及文献[31]所提取特征送入LightGBM分类器的识别率,如图6所示。
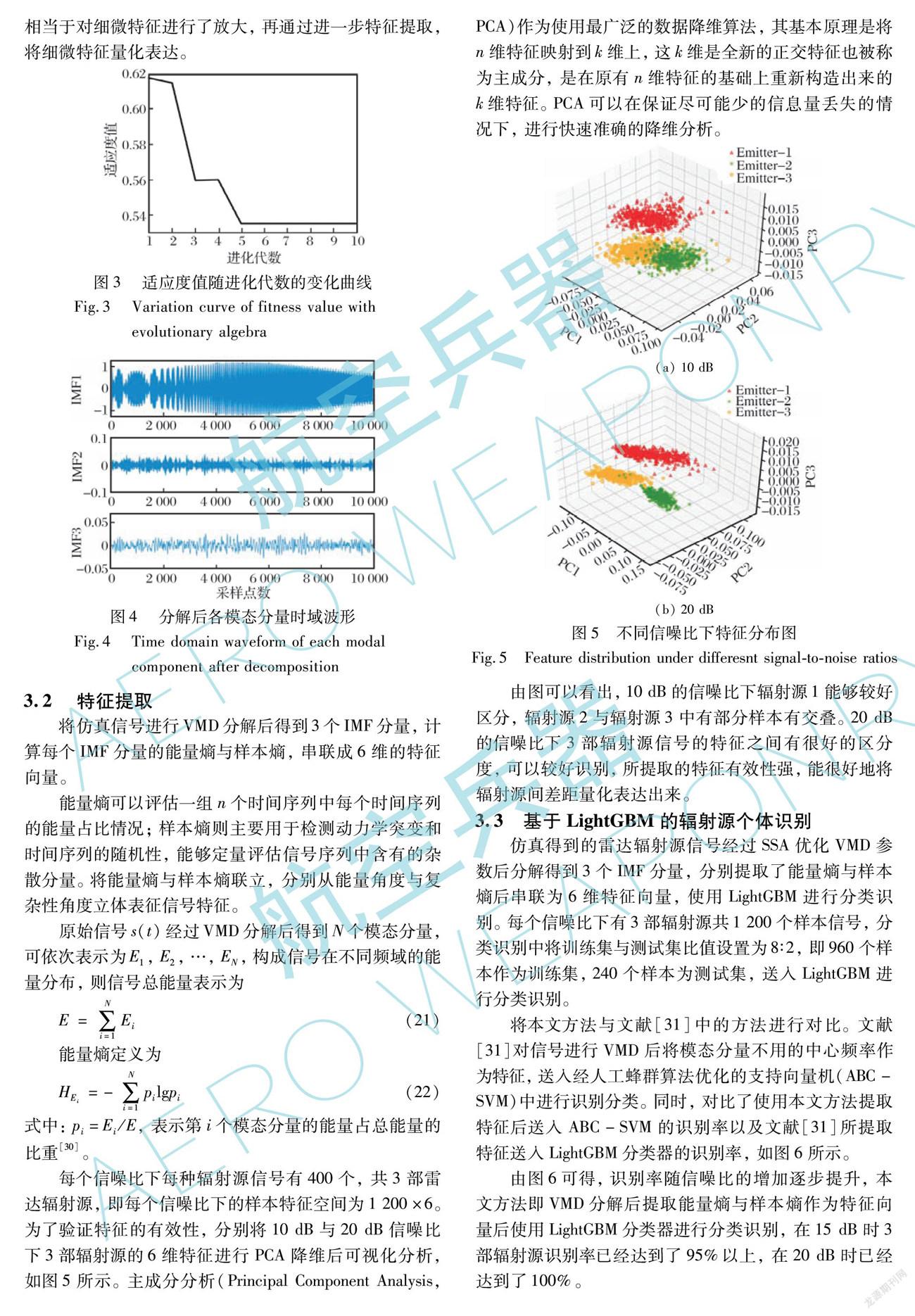
由图6可得,识别率随信噪比的增加逐步提升,本文方法即VMD分解后提取能量熵与样本熵作为特征向量后使用LightGBM分类器进行分类识别,在15 dB时3部辐射源识别率已经达到了95%以上,在20 dB时已经达到了100%。
对比分析可得:
(1) 本文识别结果较文献[31]方法结果在各个信噪比下识别率均有所提升,尤其在较低信噪比下的识别率提升较高。
(2) 本文所提取特征经ABC-SVM识别方法在各个信噪比下识别率均高于文献[31]方法,这表明在使用相同分类器的情况下,本文所提取特征对辐射源无意特征的表征要优于文献[31]所提取特征。
(3) 对文献[31]所提取特征经LightGBM识别方法后在各个信噪比下识别率均略高于文献[31]方法,这表明在使用相同特征的情况下,本文所选用分类器同样优于ABC-SVM。
(4) 以文献[31]方法为参考对象,本文所提取特征对识别率的提升效果要优于选用LightGBM对识别率的提升效果。
3.4 基于实测数据的识别结果分析
为了验证实验方法的稳定性以及对辐射源信号中添加无意特征的仿真有效性,采集了来自3部不同型号、仿真参数相同的信号源发射器发出的线性调频信号。
實验采用3台信号发射器,分别为Agilent E4438C,Agilent N5172B EXG X以及Tektronix AWG70001。对每部信号发生器分别采集400组样本数据,其中80%用于训练,剩余20%用于测试。
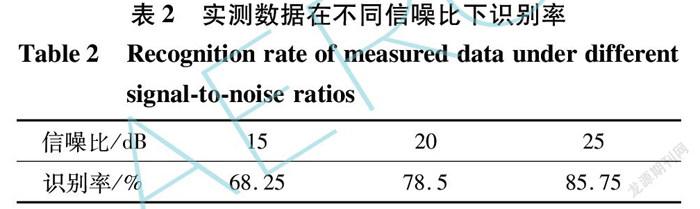
对采集的信号进行处理后,经基于SSA的VMD参数优化算法进行分析,得到最优分解参数组合为[2, 2 950],即分解模态数为2,二次惩罚因子为2 950。后经VMD分解后得到2个模态分量,对其分别提取能量熵与样本熵后级联得4维特征向量,送入LightGBM得到的分类结果如表2所示。
由实验结果可以看出,识别率随信噪比的增大逐渐提升。信噪比在25 dB时识别率能够达到85%以上,在雷达辐射源个体识别研究问题中能够达到较高识别率。4 结 论
(1) VMD算法能够依据不同中心频率对信号进行分解,在辐射源无意特征的提取方面有天然的优势。同时SSA又能够快速准确地对VMD的分解模态数K与二次惩罚因子α进行寻优,避免了人为选择参数对分解结果的不利影响。能量熵与样本熵完全匹配于VMD算法,将各模态分量间的重要信息量化表达。仿真结果显示,基于LightGBM算法的识别结果要好于经典的SVM,本文所提方法各方面性能均有稳定提升。
(2) 经实测数据验证,本文方法能够达到较高识别率,但相较于仿真数据识别率有一定差距,证明雷达辐射源中的相位噪声是雷达发射机中无意特征的主要来源,但仿真的相位噪声距离实际无意特征还有一定差距,还需进一步仿真分析,以求更加接近真实的无意特征。
参考文献:
[1] Ren D F, Zhang T. Specific Emitter Identification Based on Intrinsic Time-Scale-Decomposition and Image Texture Feature[C]∥9th IEEE International Conference on Communication Software and Networks (ICCSN), 2017: 1302-1307.
[2] Wu L W, Zhao Y Q, Feng M F, et al. Specific Emitter Identification Using IMF-DNA with a Joint Feature Selection Algorithm[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(9): 934.
[3] Feng Z P, Zhang D, Zuo M J. Adaptive Mode Decomposition Me-thods and Their Applications in Signal Analysis for Machinery Fault Diagnosis: A Review with Examples[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 24301-24331.
[4] Ru X H, Liu Z, Huang Z T, et al. Evaluation of Unintentional Modulation for Pulse Compression Signals Based on Spectrum Asymmetry[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(4): 656-663.
[5] 叶文强, 俞志富. 基于联合时频辐射源信号识别方法[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2018, 33(5): 16-19.
Ye Wenqiang, Yu Zhifu. Signal Recognition Method Based on Joint Time-Frequency Radiant Source[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2018, 33(5): 16-19.(in Chinese)
[6] Flamant J, Le Bihan N, Chainais P. Time-Frequency Analysis of Bivariate Signals[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2019, 46(2): 351-383.
[7] 王欢欢, 张涛. 结合时域分析和改进双谱的通信信号特征提取算法[J]. 信号处理, 2017, 33(6): 864-871.
Wang Huanhuan, Zhang Tao. Extraction Algorithm of Communication Signal Characteristics Based on Improved Bispectra and Time-Domain Analysis[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2017, 33(6): 864-871.(in Chinese)
[8] Zhang J W, Wang F G, Dobre O A, et al. Specific Emitter Identification via Hilbert-Huang Transform in Single-Hop and Relaying Scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(6): 1192-1205.
[9] Padilla P, Padilla J L, Valenzuela-Valdés J F. Radio Frequency Identification of Wireless Devices Based on RF Fingerprinting[J]. Electronics Letters, 2013, 49(22): 1409-1410.
[10] Wu Q Y, Feres C, Kuzmenko D, et al. Deep Learning Based RF Fingerprinting for Device Identification and Wireless Security[J]. Electronics Letters, 2018, 54(24): 1405-1407.
[11] 王磊, 姬红兵, 史亚. 基于模糊函数代表性切片的运动雷达辐射源识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2010, 32(8): 1630-1634.
Wang Lei, Ji Hongbing, Shi Ya. Moving Radar Emitter Recognition Based on Representative-Cut Feature of Ambiguity Function[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(8): 1630-1634.(in Chinese)
[12] Martis R J, Acharya U R, Tan J H, et al. Application of Intrinsic Time-Scale Decomposition (ITD) to EEG Signals for Automated Seizure Prediction[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2013, 23(5): 1350023.
[13] Xu Y G, Xie Z C, Cui L L, et al. The Feature Extraction Method of Gear Magnetic Memory Signal[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 819: 206-211.
[14] Bihl T J, Bauer K W, Temple M A. Feature Selection for RF Fingerprinting with Multiple Discriminant Analysis and Using Zig Bee Device Emissions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(8): 1862-1874.
[15] Zhu S L, Gan L. Specific Emitter Identification Based on Visibility Graph Entropy[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2018, 35(3): 030501.
[16] 徐志軍, 陈志伟, 王金明, 等. 基于功放特性的辐射源识别的改进方法[J]. 南京邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 33(6): 54-58.
Xu Zhijun, Chen Zhiwei, Wang Jinming, et al. An Improved Method for Emitter Identification Based on Character of Power Amplifier[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications: Natural Science, 2013, 33(6): 54-58.(in Chinese)
[17] 黄渊凌, 郑辉. 一种基于相噪特性的辐射源指纹特征提取方法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2013, 30(9): 182-185.
Huang Yuanling, Zheng Hui. Emitter Fingerprint Feature Extraction Method Based on Characteristics of Phase Noise[J]. Computer Simulation, 2013, 30(9): 182-185.(in Chinese)
[18] Wu L W, Zhao Y Q, Wang Z, et al. Specific Emitter Identification Using Fractal Features Based on Box-Counting Dimension and Variance Dimension[C]∥IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), 2017: 226-231.
[19] Talbot K I, Duley P R, Hyatt M H. Specific Emitter Identification and Verification[J]. Technology Review Journal, 2003,1(1): 113-133.
[20] 马洪斌, 佟庆彬, 张亚男. 优化参数的变分模态分解在滚动轴承故障诊断中的应用[J]. 中国机械工程, 2018, 29(4): 390-397.
Ma Hongbin, Tong Qingbin, Zhang Yanan. Applications of Optimization Parameters VMD to Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearings[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 29(4): 390-397.(in Chinese)
[21] 李亚兰, 金炜东, 葛鹏. 基于VMD和特征融合的辐射源信号识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(7): 1499-1503.
Li Yalan, Jin Weidong, Ge Peng. Radiation Emitter Signal Reco-gnition Based on VMD and Feature Fusion[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(7): 1499-1503.(in Chinese)
[22] 郑义, 岳建海, 焦静, 等. 基于参数优化变分模态分解的滚动轴承故障特征提取方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(1): 86-94.
Zheng Yi, Yue Jianhai, Jiao Jing, et al. Fault Feature Extraction Method of Rolling Bearing Based on Parameter Optimized VMD[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(1): 86-94.(in Chinese)
[23] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D. Variational Mode Decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531-544.
[24] Xue J K, Shen B. A Novel Swarm Intelligence Optimization Approach: Sparrow Search Algorithm[J]. Systems Science & Control Engineering, 2020, 8(1): 22-34.
[25] Alcaraz R, Rieta J J. A Review on Sample Entropy Applications for the Non-Invasive Analysis of Atrial Fibrillation Electrocardiograms[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2010, 5(1): 1-14.
[26] Pincus S M. Approximate Entropy as a Measure of Irregularity for Psychiatric Serial Metrics[J]. Bipolar Disorders, 2006, 8(5 Pt 1): 430-440.
[27] Ke G L, Meng Q, Finley T, et al. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree [C]∥ 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 3149-3157.
[28] 郑娜娥, 王盛, 张靖志, 等. 基于射频指纹的辐射源个体识别技术综述[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2020, 21(3): 285-289.
Zheng Na’e,Wang Sheng, Zhang Jingzhi, et al. Overview of Emitter Identification Techniques Based on Radio Frequency Fingerprinting[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2020, 21(3): 285-289.(in Chinese)
[29] 孙丽婷, 黄知涛, 王翔, 等. 辐射源指纹特征提取方法述评[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 1014-1031.
Sun Liting, Huang Zhitao, Wang Xiang, et al. Overview of Radio Frequency Fingerprint Extraction in Specific Emitter Identification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 1014-1031.(in Chinese)
[30] 楊冬锋, 陈盛开, 刘晓军, 等. 基于自适应VMD和时-频分段能量熵特征的过电压信号识别[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(12): 4597-4604.
Yang Dongfeng, Chen Shengkai, Liu Xiaojun, et al. Research on Overvoltage Signal Recognition Based on Adaptive VMD and Time-Frequency Segment Energy Entropy[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(12): 4597-4604.(in Chinese)
[31] 张忠民, 刘刚. 基于VMD和ABC-SVM的雷达辐射源个体识别[J]. 哈尔滨商业大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 36(2): 176-182.
Zhang Zhongmin, Liu Gang. Individual Identification of Radar Emitter Based on VMD and ABC-SVM[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce: Natural Sciences Edition, 2020, 36(2): 176-182.(in Chinese)
Radar Emitter Individual Identification Based on
Parameter Optimization VMD and LightGBM
Xiao Yihan1,Li Dongnian1*,Yu Xiangzhen2,Song Ke2
(1. Harbin Engineering University,Harbin 150001, China;
2. Shanghai Radio Equipment Research Institute,Shanghai 200090, China)
Abstract: In order to solve the problem of low accuracy of radar emitter individual identification in complex electromagnetic environment, a radar emitter individual identification technology based on parameter optimization VMD and LightGBM is proposed. Firstly, the unintentional features of the radar emitter are analyzed, and the added phase noise is taken as the fingerprint feature of radar emitter in the simulation. Secondly,sparrow search algorithm (SSA) is used to automatically optimize the decomposition parameters of variational modal decomposition (VMD), and the optimal decomposition parameter combination is accurately and quickly obtained as [2, 2 950]. Then, based on the optimal VMD decomposition parameters, the energy entropy and sample entropy of the emitter signal are extracted as feature vector. Finally, the feature vector is sent to the LightGBM classifier to complete the emitter individual identification. Through the verification of measured data,the recognition rate can reach more than 85% when the signal-to-noise ratio is 25 dB, which has ideal recognition results.
Key words: radar emitter; individual identification; VMD; SSA; energy entropy; sample entropy; LightGBM

