基于指令滤波和期望补偿的液压位置跟踪系统控制研究






摘 要:针对液压控制系统中存在的强非线性、参数不确定性和高频干扰等问题,提出一种基于指令滤波和期望补偿的鲁棒控制算法。该控制算法结合扩展状态观测器(ESO),实现了对速度及外干扰的估计;所设计的自适应控制算法可以在线估计系统的不确定参数;利用期望补偿方法,将实际速度信号替换为相应的期望值,以减少对控制效果的影响。此外,利用指令滤波技术避免了反步控制法里的微分膨胀问题,基于Lyapunov函数证明了所设计控制器的稳定性,且所有信号均有界。仿真结果表明,系统期望跟踪指令幅值为40 mm时,在1 Hz和0.5 Hz工况下,平均跟踪误差分别约为0.088 mm和0.0481 mm,可见跟踪误差收敛到了极小值,系统跟踪精度得到了提高。
关键词:液压控制系统;指令滤波;期望补偿;扩展状态观测器;位置跟踪控制
中图分类号:TP273 文献标识码:A
Research on Control of Hydraulic Position Tracking System based on Command Filtering and Expectation Compensation
YUAN Xiaokang
(School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China)
Abstract: Aiming at the problems of strong nonlinearity, parameter uncertainty and high-frequency interference in hydraulic control systems, this paper proposes a robust control algorithm based on command filtering and expectation compensation. The control algorithm combines Extended State Observer (ESO) to realize the estimation of speed and external disturbance. The designed adaptive control algorithm can estimate the uncertain parameters of the system online. With the expectation compensation method, the actual speed signal is replaced by the corresponding expected value to reduce the impact on the control effect. In addition, command filtering technique is used to avoid the differential expansion problem in the backstepping control method. The stability of the designed controller is proved based on Lyapunov function and all signals are bounded. The simulation results show that when the expected tracking command amplitude of the system is
40 mm, the average tracking error is about 0.088 mm and 0.0481 mm under the conditions of 1 Hz and 0.5 Hz, respectively. It can be seen that the tracking error has converged to a minimum value, and the system tracking accuracy has been improved.
Keywords: hydraulic control system; command filtering; expectation compensation; extended state observer; position
tracking control
1 引言(Introduction)
液壓控制系统具有功率密度大、动态响应快和控制精度高等优点,在工业自动化领域具有广泛的应用[1-5]。然而,液压伺服系统本身具有强非线性、外干扰及无法建模的动态误差等缺点,极大地增加了控制器的设计难度。
近年来,为了提高非线性系统的控制效果,国内外学者将一些先进的控制算法运用到非线性系统中。文献[6]提出了一种自适应反步算法,有效地减小了伺服阀盲区的影响,提高了跟踪性能。文献[7]利用扩展状态观测器对速度信号和不匹配扰动进行观测,实现了优异的跟踪性能。文献[8]将干扰观测器和滑模面相结合,有效地降低了噪音对跟踪性能的影响。YUCELEN等提出了一种基于低频学习算法的控制策略,可以过滤掉控制响应中的高频振荡,保持系统动态误差的渐近稳定性[9-10]。而实际应用中,由于液压伺服系统安装速度传感器难度较大,而通过全状态观测器得到的信号也难免受到噪音等外部干扰的影响,这也增加了提高控制精度的难度。
基于以上分析,本文提出了一种基于指令滤波和期望补偿的自适应鲁棒控制策略,通过在传统反步法基础上加入指令滤波器来避免微分爆炸的情况。在液压系统模型上设计扩展状态观测器对速度及外干扰进行估计,同时将速度信号用其期望值来代替以减小外部干扰的影响,并使用自适应算法对液压系统不确定参数进行估计。最后通过MATLAB/Simulink搭建数学模型,仿真对比结果证明了所设计控制器的有效性。
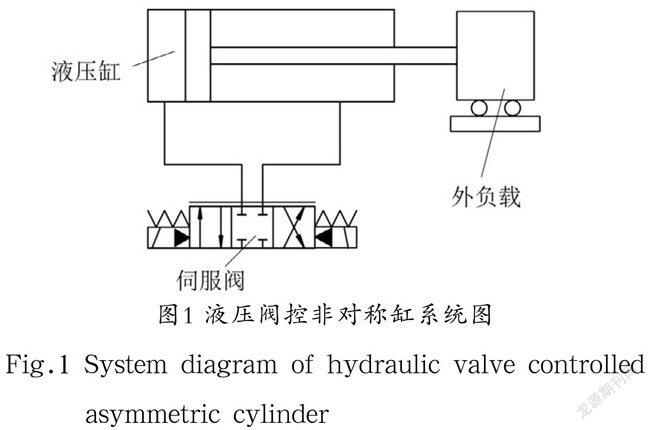
2 液压阀控非对称缸模型(Hydraulic valve controlled asymmetric cylinder model)
本文所研究的液压控制系统的工作原理如图1所示。
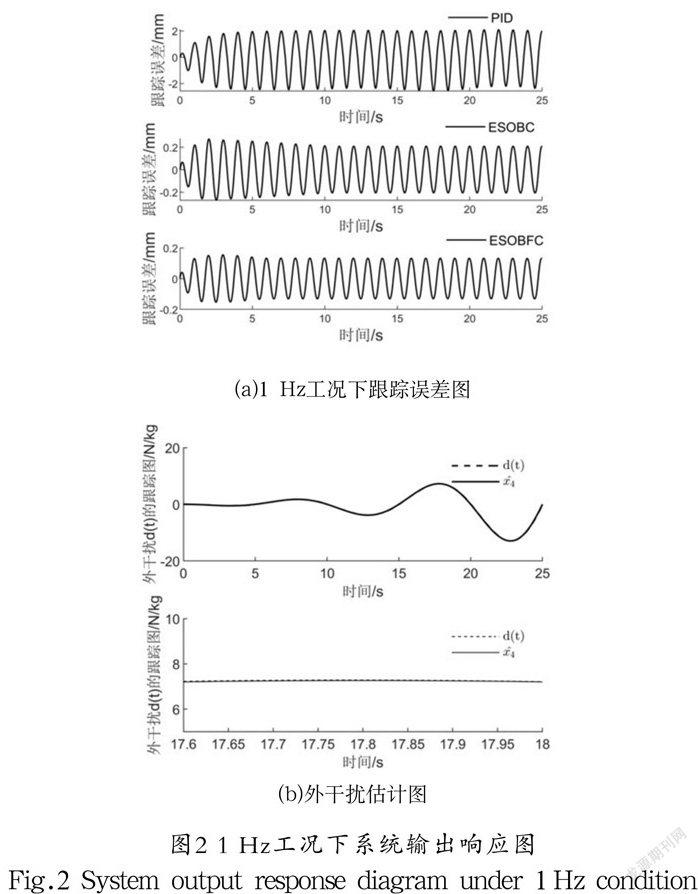
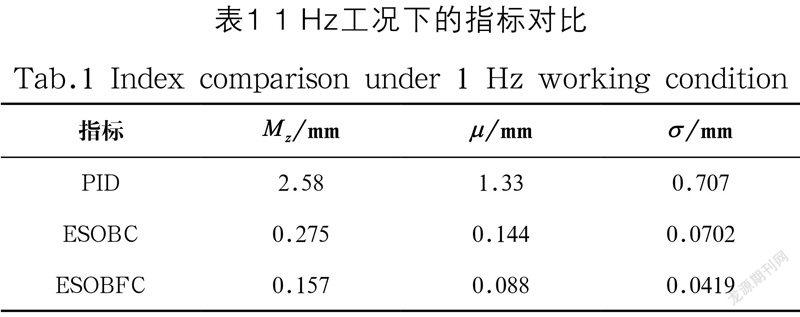
如图2(a)所示为在1 Hz对应的工况下,ESOBFC控制算法对应的跟踪误差,可以看出基于指令滤波算法的跟踪误差相比其他两种误差明显更小,这表明了本文算法优异的跟踪性能。如图2(b)所示,状态观测器完成了对外干扰的估计。
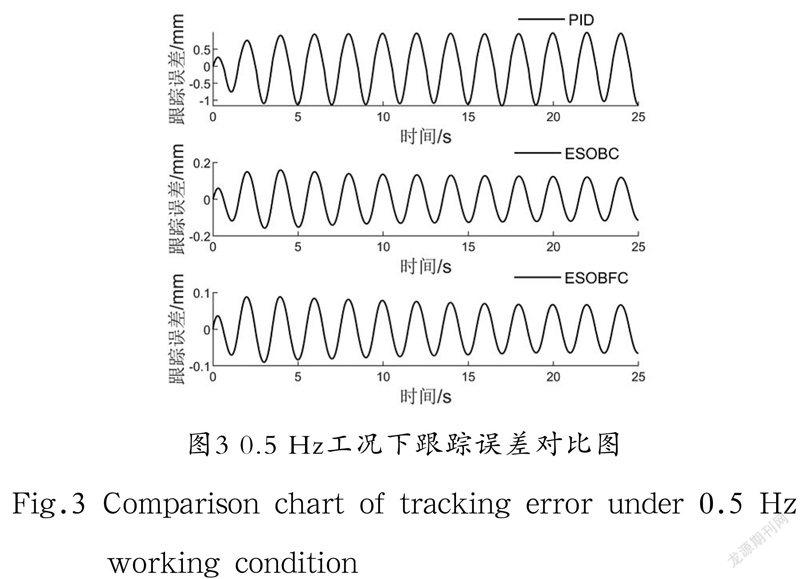
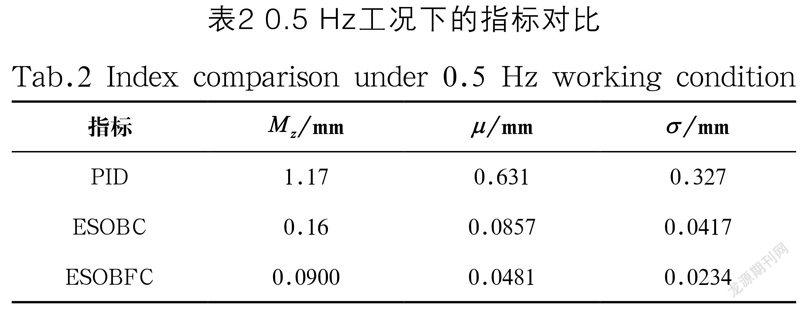
为了进一步验证所提出控制策略的控制性能,第二种工况选择一个稍低频率的轨迹,即x1d=40(1-e-u)sin(πt)mm。实验结果如图3所示,性能指标如表2所示。在此工况下,相比于其他两种算法,本文算法的跟踪误差依旧最优。
6 结论(Conclusion)
本文研究了一类具有参数不确定性和强非线性特点的液压控制系统的位置控制问题。针对无速度测量的液压伺服系统,基于模型设计了扩展状态观测器,可以同时观测速度及不确定性外部干扰,结合基于实际位置的期望补偿的自适应算法,实现了对不确定性参数的自适应和补偿。基于Lyapunov理论证明了所提出控制策略在保持系统稳定性的同时,具有渐近跟踪性能。通过仿真分析,验证了与传统的PID控制策略及一般的自适应反步控制策略相比,本文提出的ESOBFC控制算法具有更好的位置跟踪控制效果。
参考文献(References)
[1] LU L, YAO B. Energy-saving adaptive robust control of a hydraulic manipulator using five cartridge valves with an accumulator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(12):7046-7054.
[2] SUN W, GAO H, KAYNAK O. Vibration isolation for active suspensions with performance constraints and actuator saturation[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2014, 20(2):675-683.
[3] LI Y, HE L. Counterbalancing speed control for hydrostatic drive heavy vehicle under long down-slope[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2015, 20(4):1533-1542.
[4] PARK J, CHO D, KIM S, et al. Utilizing online learning based on echo-state networks for the control of a hydraulic excavator[J]. Mechatronics, 2014, 24(8):986-1000.
[5] SERON J, MARTINEZ J L, MANDOW A, et al. Automation of the arm-aided climbing maneuver for tracked mobile manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2013, 61(7):3638-3647.
[6] DENG W, YAO J, MA D. Robust adaptive precision motion control of hydraulic actuators with valve dead-zone compensation[J]. ISA Transactions, 2017(70):269-278.
[7] DENG W, YAO J. Extended-state-observer-based adaptive control of electrohydraulic servomechanisms without velocity measurement[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, 25(3):1151-1161.
[8] 劉龙,姚建勇,胡健,等.基于干扰观测器的电液位置伺服系统跟踪控制[J].兵工学报,2015,36(11):2053-2061.
[9] YUCELEN T, CALISE A J. Kalman filter modification in adaptive control[J]. Journal of Guidance Control and Dynamics, 2012, 33(2):426-439.
[10] YUCELEN T, HADDAD W M. Low-frequency learning and fast adaptation in model reference adaptive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 58(4):1080-1085.
[11] SHEN W, LIU X, SU X. High-precision position tracking control of electro-hydraulic servo systems based on an improved structure and desired compensation[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems,2021, 19(11):3622-3630.
作者简介:
袁小康(1996-),男,硕士生.研究领域:电液伺服控制.

