The value of preoperative PLR and NLR in the prognostic evaluation of lung cancer
Zi-Yan Shangguan, Qi Chen, Min Jiang, Kai-Wen Hu
1. Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2. Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China
Keywords:Lung neoplasms PLR NLR Prognosis Overall survival
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the relationship between platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and prognosis of lung cancer patients before cold ablation. Methods: Retrospectively analyze the case data of primary lung cancer patients who underwent cryoablation of lung argon helium knife in our hospital from January 2012 to March 2018. PLR and NLR were calculated based on the blood routine data of the patients within 1 week before the operation. value. The patients were followed up. The deadline for follow-up was June 2021. The survival curve (ROC curve) was drawn according to the patient's survival prognosis, and the Youden index was calculated to determine the optimal cutoff value of PLR and NLR, and grouped based on this analysis. The correlation between pre-PLR level and NLR level with clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic survival time of patients with primary lung cancer. Results: The best cut-off point was calculated according to the ROC curve and divided into high PLR group (PLR≥155.72, n=127) and low PLR group (<155.72,n=87); high NLR group (≥2.91, n=120) and Low NLR group (<2.91, n=94); preoperative high PLR, high NLR group pT, pN, pM and TNM staging compared with low value group,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); Cox multivariate Analysis shows that high PLR, high NLR, high pT staging, high pM staging, and high TNM staging are independent risk factors affecting postoperative survival; the postoperative survival rate of the high-level PLRNLR group was significantly lower than that of the other groups, and the difference was statistically significant. significance. Conclusion: The significant increase of NLR and PLT before operation in patients with primary lung cancer is associated with poor prognosis; the combination of the two has potential clinical application value in assessing the survival of patients after surgery.
1. Introduction
Malignant tumors are one of the important diseases that endanger human health. According to the latest statistical report of the World Health Organization [1], there will be 19.3 million new cancer patients worldwide in 2020, and lung cancer is still the leading cause of cancer deaths. The data also showed that the incidence and death of lung cancer patients in China accounted for 37.0% and 39.8% of the global total respectively [2]. Therefore, lung cancer will be an important issue facing my country's public health field for a long time to come.Due to the lack of effective early diagnosis methods, only 20%-30% of lung cancer patients can be diagnosed early and treated with conventional radical surgical treatment. Most lung cancer patients are in the middle and advanced stages at the time of diagnosis and have lost the opportunity for surgery or due to underlying diseases.Surgical treatment is not suitable for many reasons, such as poor cardiopulmonary function. At this time, palliative radiotherapy and chemotherapy, biological targeted therapy, and various minimally invasive treatment techniques provide more choices for such patients. Cold ablation therapy is currently the main technology for minimally invasive treatment of tumors. Ultra-low temperature cold ablation represented by the argon-helium knife is currently the main clinically used tumor cold ablation technique in my country. It can be used for the radical treatment of early lung cancer and the palliative treatment of advanced lung cancer. Sexual treatment [3]. However,due to the large individual differences of patients, the postoperative curative effects are also completely different for patients who also undergo cold ablation with argon-helium knife. Therefore, early prediction and evaluation of the impact of cold ablation on the prognosis is crucial for the choice of patient treatment. Modern studies have shown that the platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and neutrophil/lymphocyte (NLR) can reflect the immune status of the body, and are closely related to the prognosis of gastrointestinal tumors, liver cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and cervical cancer[4-8],it may become a sensitive and effective prognostic evaluation index.Therefore, this study observes the relationship between preoperative PLR and NLR on the survival of patients with lung cancer cold ablation, and provides an objective basis for clinical prediction of patient prognosis.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Research object
The case data of primary lung cancer patients who underwent cryoablation of lung argon helium knife in our hospital from January 2012 to March 2018 were selected. A total of 214 patients were enrolled in this study, including 152 males and 62 females, ranging in age from 39.2 to 84.8 years, with a median age of 66.5 years.According to histopathological classification, there were 106 cases of adenocarcinoma; 62 cases of squamous cell carcinoma, 3 cases of large cell carcinoma, 7 cases of adenosquamous carcinoma, 10 cases of sarcomatoid carcinoma, 1 case of mucinous adenocarcinoma,and 25 cases of small cell lung cancer; according to TNM staging ,The number of people in Phase I, Phase II, Phase III and Phase IV were 7, 30, 60, and 117, respectively. Inclusion criteria: (1) Patients who were diagnosed with primary lung cancer and underwent cryoablation of lung cancer with argon helium knife in our hospital;(2) Patients with complete clinical case data; Exclusion criteria:(1) Patients with other malignant tumor diseases in the past ( 2)Patients with blood system disease or immune deficiency, immune system disease (2) Patients receiving radiotherapy or chemotherapy or targeted therapy 1 month before surgery; (3) Patients receiving immunotherapy 1 month before surgery; (4) Patients Patients with severe infection; (5) Patients with other diseases that seriously affect the prognosis, such as heart failure and renal failure.
2.2 Operation specifications
Combining the patient’s medical history, clinical symptoms, signs and examination results, according to the "Experts Consensus on Imaging Guided Lung Cancer Cryoablation Treatment 2018 Edition"[9] on the requirements for surgical indications and contraindications and the professional judgment of the chief physician to determine that the patient is suitable for cold treatment.Surgical method: The patient takes a supine position, establishes venous access, and gives ECG monitoring. Combined with the preoperative imaging results, a local CT scan of the lung was performed to locate the tumor before surgery. Avoid large blood vessels and choose the best needle insertion point and direction.Routine body surface disinfection drapes, 1% lidocaine and 1%ropivacaine 10ml local anesthesia, a scalpel blade makes a 0.5cm incision at the needle entry point of the argon-helium knife, the puncture needle is guided by CT to penetrate the puncture needle into the predetermined After confirming the correct position by CT scan, turn on the argon-helium knife freezing system to reduce the temperature of the knife tip to -140℃~-160℃ within 1 min. After entering the predetermined position and freezing for 5 minutes,the formation of ice balls will be seen, and the operation will be interrupted. The freezing range was monitored. After about 25 minutes, an ice ball was seen covering the target lesion. After the freezing was completed, helium gas was used to draw the knife.During the operation, the ECG monitoring was continuously recorded. After the postoperative scan, there was no compression bandaging of the pneumothorax.
2.3 Data collection
By querying the Haitai medical record system, a database of research subjects was established, including gender, age, smoking and drinking history, lung history, tumor staging, postoperative survival, surgical methods, pathological types, and routine peripheral blood cell counts. Calculate the PLR and NLR values according to the blood routine results of the patient within one week before the operation, draw the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC)according to the patient’s survival status at the end of the follow-up,and calculate the Youden index to determine the maximum value of PLR and NLR. The patients were divided into high PLR group, low PLR group, high NLR group, and low NLR group. The correlation between preoperative PLR level and NLR level, clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic survival time of the two groups was analyzed.
2.4 Statistical analysis
SPSS 22.0 software was used for data analysis. The measurement data conforming to the normal distribution are expressed as ±s,and the comparison between groups is by t test; the non-normal distribution is expressed as the median, and the non-parametric test is used to compare the differences between groups. The enumeration data was expressed as an example, the comparison between groups was performed by the chi-square test; the Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analysis; the analysis of factors affecting the prognosis was performed by the Cox proportional hazard regression model.
3. Results
3.1 The best cut-off value of PLR and NLR before surgery
After screening, a total of 214 patients were included in the study,and the ROC curve was drawn. The best cut-off point for calculating the preoperative PLR is 155.72. At this time, the area under the ROC curve is 0.766, the sensitivity is 0.875, and the specificity is 0.653.This study defines the low PLR group PLR <155.72, 87 cases in total, defined high PLR group as PLR ≥155.72, 127 cases in total; the optimal cut-off point of NLR before surgery was 2.91, at this time the area under the ROC curve was 0.732, the sensitivity was 0.654,and the specificity This study defines low NLR as NLR<2.91, a total of 94 cases, and high NLR group as NLR≥2.91, a total of 120 cases,as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
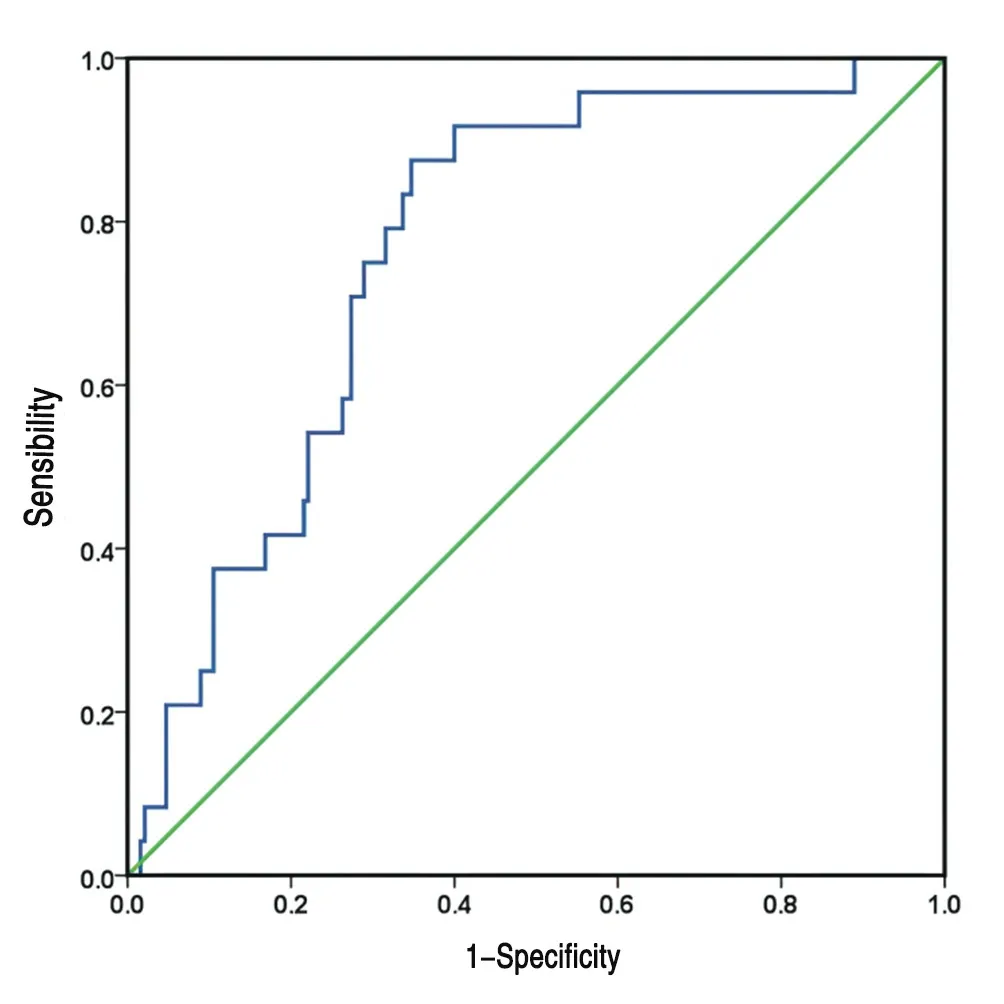
Figure 1 ROC curve of survival status after preoperative PLR diagnosis of lung cancer
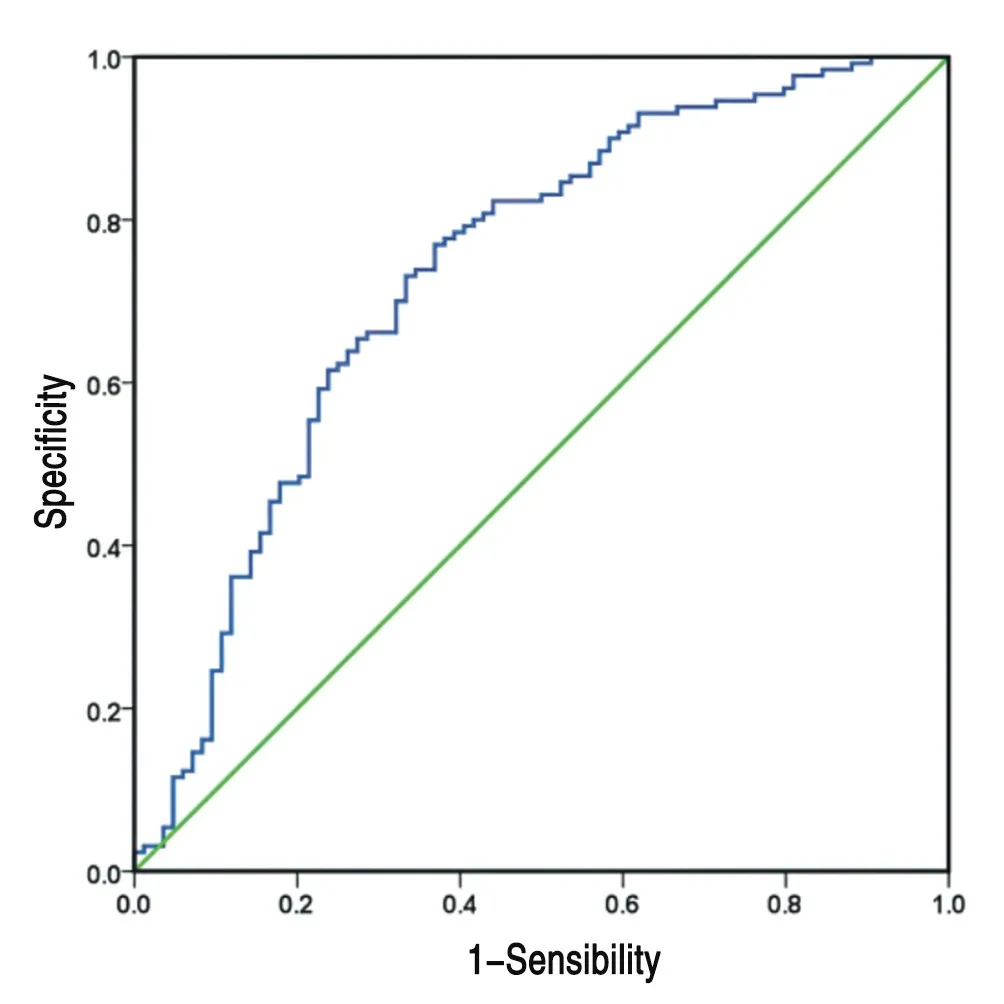
Figure 2 ROC curve of preoperative NLR diagnosis of lung cancer survival status after surgery
3.2 The correlation between NLR and PLR and preoperative clinical features of patients with primary lung cancer
The clinical characteristics of patients with primary lung cancer such as age, gender, pulmonary sarcoidosis, history of hypertension,history of dust exposure, and family history of tumors have nothing to do with the level of PLR and NLR, while the pT staging of primary lung cancer patients in the high PLR group , PN staging,TNM clinical staging compared with low PLR group, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Similarly, comparing the clinical characteristics of patients with high NLR and low NLR group, the same results were obtained (P<0.05). See Table 1.
3.3 Analysis of risk factors affecting the prognosis of patients
Univariate analysis showed that high PLR (P<0.001), high NLR(P<0.001), high pT stage (P<0.001), high pN stage (P<0.001), high pM stage (P=0.006), TNM Staging (P=0.004) is a risk factor that affects the survival of patients with primary lung cancer after argonhelium knife surgery. Gender, age, history of pulmonary sarcoidosis,history of hypertension, history of dust exposure, family history of tumors, and pathological types The patient's postoperative survival was irrelevant (P>0.05); variables related to postoperative survival were included in the cox multivariate analysis by univariate analysis,and the results showed that preoperative high PLR (P=0.036, HR:1.467, 95%CI: 1.025-2.099), high NLR (P=0.001, HR: 1.768,95%CI: 1.244-2.513), pT staging (P=0.027, HR: 1.441, 95%CI:1.043-1.991), pM staging (P= 0.032, HR: 1.392, 95%CI: 1.029-1.882), TNM staging (P=0.037, HR: 1.598, 95%CI: 1.045-1.812) are independent influencing factors of postoperative survival decline, see Table 2.
3.4 Correlation between PLR, NLR and TNM staging of lung cancer
Pearson correlation analysis shows that PLR, NLR and TNM staging are all positively correlated (r is 0.178, 0.181, P<0.01), see Table 3.
3.5 Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis of PLR combined with NLR
According to statistics, the median survival time of 214 patients was 5.5 months. Since PLR and NLR are independent factors influencing the survival time of patients after surgery, the patients were divided into groups according to the best cut-off values of PLR=155.72 and NLR=2.91. , Carrying out Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis, the results showed that the postoperative median survival time of the high NLR group and the low NLR group were 5.3 months and 11.9 months, respectively, and the 1-year survival rate of the two groups was 21%. And 47.9%, the difference was statistically significant; the postoperative median survival time of the high PLR group and the low PLR group were 5.63 months and 11.87 months, respectively,and the 1-year survival rates of the two groups were 23% and 47.1%,respectively, The difference is statistically significant; see Figure 3 and Figure 4.Since both PLR and NLR are independent influencing factors of patient prognosis, we combined NLR and PLR to divide patients into four groups. The one-year survival rate of patients with high NLR and high PLR group was 19%, and the median survival time was 4.83 Months; the one-year survival rate of patients in the high NLR and low PLR group was 27%, and the median survival time was 8.17 months; the one-year survival rate of patients in the low NLR and high PLR group was 37%, and the median survival time was 10.7 months; The one-year survival rate of the low NLR and low PLR group was 52%, and the median survival time was 12.17 months; the difference was statistically significant, as shown in Figure 5.f

Figure 3 Comparison of Survival Curves of Patients with Lung Cancer in Different PLR Levels

Table 2 Analysis of Risk Factors Affecting the Prognosis of Patients

Figure 4 Comparison of survival curves of lung cancer patients with different NLR levels

Table 3 Pearson correlation analysis of preoperative PLR, NLR and TNM staging of lung cancer

Figure 5 Comparison of survival curves of lung cancer patients with different PLR combined with NLR levels
4. Discussion
The treatment of patients with advanced lung cancer is an important part of the lung cancer system. According to research investigations[10], about 57% of lung cancer patients have already developed distant metastasis at the time of discovery. The expert consensus proposed [11] that patients with advanced lung cancer should take Comprehensive, systemic, and individualized treatment, with the goal of maximizing the survival time of patients, controlling tumor progression, and improving the quality of life. Argon-helium cryoablation is currently a more mature cryoablation treatment technology [12], which refers to the use of helium and argon as the heat and refrigerant to perform rapid heating and ultra-low temperature freezing of local tumor tissues to achieve the effect of destruction. The concept of cryoablation combined with "green treatment"[13] directly eliminates tumors with minimal adverse reactions, and can effectively reduce the adverse reactions of modern medical treatment, thereby achieving the dual effects of improving the quality of life and prolonging the survival period. However,because patients have different postoperative reactions, there is an urgent need for effective prognostic indicators to better choose individualized treatment strategies.
In this study, with PLR=255.72 and NLR=2.91 as the critical value,the postoperative survival rate and median survival time of lung cancer patients in the low-value group were significantly higher than those in the high-value group. For patients in the low-PLR and NLR group, In other words, it often indicates a longer survival time and a higher survival rate; and multivariate cox regression analysis shows that high PLR, high NLR, and TNM staging are independent risk factors for the prognosis and survival of lung cancer patients.
Pearson correlation analysis shows that PLR, NLR and TNM staging are all positively correlated, and the three have the same influence on survival after cryoablation of lung cancer. Therefore, observing the results of preoperative whole blood cell analysis can effectively predict the survival of patients after surgery.
The ten major characteristics of tumors include the promotion of tumor inflammation and continuous angiogenesis [14], solid tumors are infiltrated with neutrophils and other immune cells,and this process is often accompanied by inflammation [15]. More and more evidences show that platelets, neutrophils, lymphocytes and tumor cells interact [16, 17] and participate in tumor growth and invasion, abnormal angiogenesis, and inflammatory processes.First, the number of platelets It will increase in the blood of cancer patients, and it is obviously related to the degree and progression of malignancy [18]; neutrophils are important immune defense cells of the human body [19], which can pass NETs (neutrophil extraneous trapping nets). ) Activate the activity of tumor cells, promote the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells [20,21]. At the same time, systemic inflammation of tumor cells is conducive to the growth of neutrophils, which makes them highly expressed in a variety of tumors and promotes each other. Tumor progression;In addition, lymphocytes include T lymphocytes, B cells and NK cells, which have immune monitoring and defense functions. Their density is related to the increase in patient survival [22], but they are secreted by tumor cells (vascular endothelial growth factor) (VEGF)is inhibited, and as the tumor progresses, VEGF secretion continues to increase, resulting in a lack of immune cells and creating a microenvironment that is beneficial to tumor growth [23]. PLR and NLR reflect the dynamic balance between the three [24, 25], and the results are more stable, reflecting the body's inflammatory response and immune response, and are superior to platelets, lymphocytes or neutrophils in the dynamic assessment of tumor development A single indicator of counting, so PLR and NLR become valuable prognostic assessment methods.In conclusion, this study shows that preoperative PLR and NLR are related to the survival of patients after surgery, and are simple and effective predictors. PLR and NLR are calculated based on blood routine results. The method is simple, low-cost, and reproducible. It is useful for predicting prognosis. Optimizing clinical diagnosis and treatment plan has certain significance. As a retrospective study, this study may be biased, and it still needs further verification by a multicenter and large-sample prospective study.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年3期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年3期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress of TCM characteristic treatment and research on diabetic foot
- Preventive and therapeutic effect of long snake moxibustion on psoriasis with yang deficiency and external cold syndrome based on the theory of"treatment of winter disease in summer"
- Research on law of acupoints selection for acupuncture treatment of postpartum depression based on data mining method
- Determination of the microstructure and chemical composition of tophi
- Epidemiological characteristics of 369 tuberculosis patients with multidrug resistance inHainan Island: A cross-sectional study
- Research progress on detection methods of the asymptomatic COVID-19 infected persons
