Hemizygous deletion in the OTC gene results in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency:A case report
INTRODUCTION
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD,OMIM:311250),also known as hyperammonemia type II,is an X-linked genetic disorder of the ornithine cycle (urea cycle)[1].The incidence of OTCD is approximately 1/80000–1/56500.OTCD is the most common type of ornithine circulation disorder and accounts for 50%-66% of total ornithine circulation disorders.Both neonates and adults can be affected by complex clinical symptoms of this disorder,with varying degrees of severity.Due to this lack of specificity,OTCD is often misdiagnosed[1-3].OTCD has a high mortality rate in neonates,and survivors often have varying degrees of neurological sequelae.Early diagnosis,individualized diet,medication,and liver transplantation are the main strategies for reducing the mortality and disability rates of patients with OTCD.
No one thought of finding any faults, till at length an old woman, who had been walking through the rooms with a crowd of people, suddenly exclaimed, Yes, it is a splendid palace, but there is still something it needs! And what may that be? A church
Thegene (OMIM:300461) is located on chromosome Xp11.4,contains 10 exons and 9 introns,and encodes a 354 amino acid protein.Thegene is highly expressed in the liver[4].Pathogenic variants in thegene lead to a reduction or absence ofenzyme activity and the shutdown of citrulline synthesis and the ornithine cycle,resulting in an ammonia metabolism disorder and an increase in levels of ammonia in the blood[5].Excessive accumulation of ammonia is highly toxic to the central nervous system,interferes with the energy metabolism of brain cells,and causes cytotoxic cerebral edema and acute or chronic traumatic encephalopathy as well as neuropsychiatric damage[5].
Based on the time of onset,patients with OTCD are divided into neonatal onset and late onset (age of onset>28 d) groups[6].Enzyme activity between the two groups is notably different.In the neonatal onset group,enzyme activity is completely reduced,and in the late onset group,enzyme activity is partially reduced.Most patients with neonatal-onset OTCD are males with hemizygous variants[7].They demonstrate no symptoms at birth but gradually refuse to feed and begin to exhibit symptoms of vomiting,irritability,hyperventilation,and lethargy within a few hours to days after birth.Onset is sudden with rapid and complex clinical features,such as convulsions,coma,hypothermia,and respiratory failure[8].Due to the lack of specificity in clinical features,patients are often misdiagnosed with neonatal sepsis,neonatal hypoxicischemic encephalopathy,birth injury,food poisoning,acute gastroenteritis,encephalitis,epilepsy,encephalopathy combined with visceral steatosis (Wright's syndrome),neurodegenerative disease,or schizophrenia.Elevated ammonia in the blood is a main abnormal indicator in patients with OTCD,andgene variants are another crucial factor in the diagnosis of OTCD[9].To date,over 530 variants in thegene have been reported,but no hotspot mutations have been found.Therefore,the collection of as many pathogenic variants as possible is important for clinical diagnosis and screening.
But no sooner had they done this than the young man called out, Oh, wretched people! what have you done? and before they had time to look round he had changed himself into a dove, and dashing against the window he broke a pane22 of glass, and flew away from their sight
A five-day-old boy who did not feed and showed no movement or responsiveness was referred to our department for further treatment.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
This study involved a male neonate with a pathogenic variant in.We comprehensively investigated the clinical features and enzymatic activity through genetic testing.
History of present illness
The proband was deliveredcesarean section due to "fetal distress" at 40 wk.There was no meconium-stained amniotic fluid,no abnormalities in the umbilical cord,and no premature rupture of membranes.His birth weight was 2350 g,and his Apgar score was normal.He was diagnosed as a "low birth weight infant with gastrointestinal bleeding” and showed improvement after unknown treatment.The amount of ordinary formula milk fed was increased gradually until he consumed 30 mL of milk at each feeding.Five days later,he stopped feeding,showed no movement,and exhibited poor responsiveness,which was accompanied by an abnormal increase in muscle tone,shortness of breath,moaning,foaming at the mouth,screaming,pumping,vomiting,abdominal distention,and blood in the stool.
Physical examination
Physical examination revealed a low body temperature (35 °C),low blood pressure (35/15 mmHg),bradycardia (97/min),and lack of spontaneous breathing.
Meantime the Fairy had prepared a chariot, to which she harnessed two powerful eagles; then placing the cage, with the parrot in it, she charged the bird to conduct it to the window of the Princess s dressing-room
Laboratory examinations
The patient remained in a coma since admission with weak heart sounds.After active rescue and treatment,the patient’s condition remained critical,with no remission or spontaneous breathing.His blood pressure,oxygen saturation,and heart rate were unstable;there was no response to stimulation.The patient was still in a coma when discharged and died soon after.
The tears flowed freely when I entered the dining room. The clock stood forlornly quiet. As quiet as the funeral parlor6 had been. Hushed. The clock even seemed smaller. Not quite as magnificent without my grandfather s special touch. I couldn t bear to look at it.
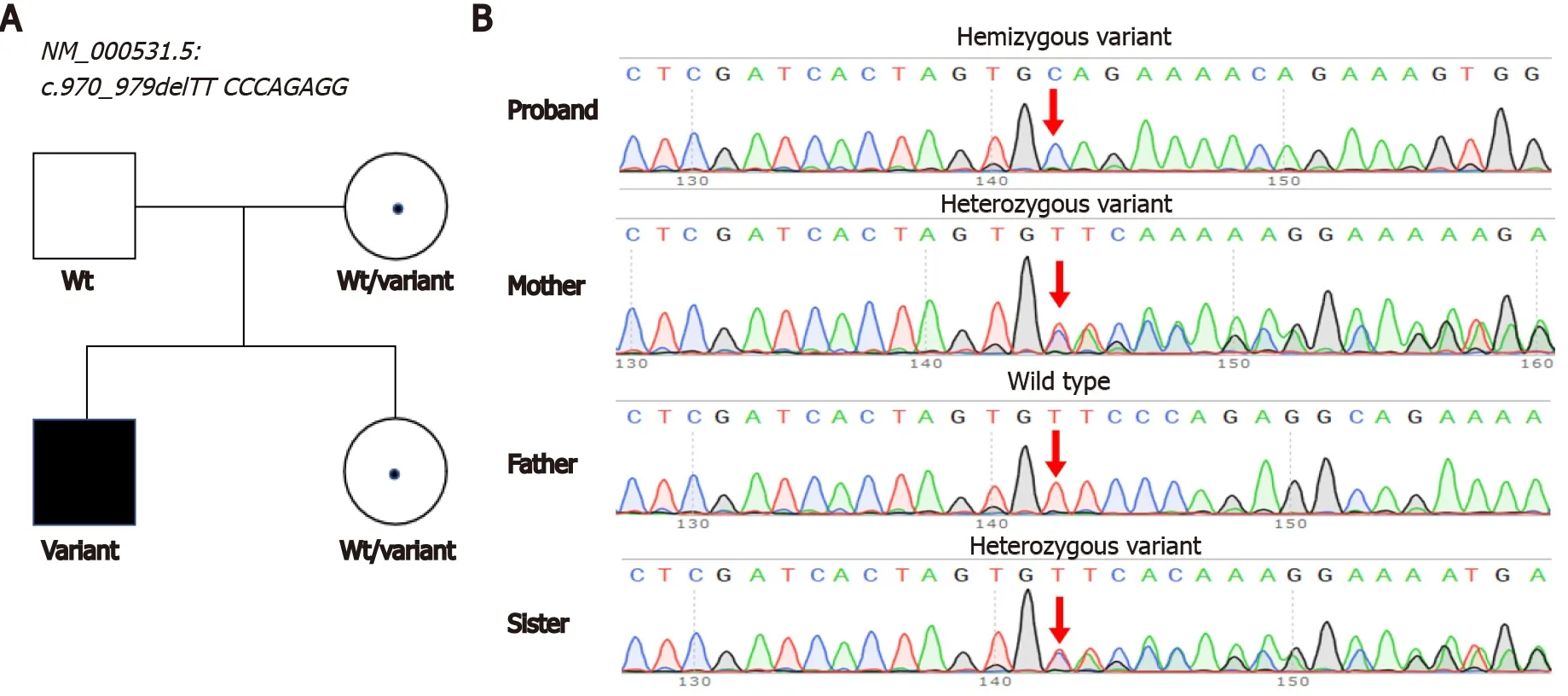
A hemizygous variant in the[NM_000531.5,c.970_979delTTCCCAGAGG,p.Phe324GlnfsTer16] gene was identified by exome sequencing.The variant caused a 10-bp deletion and early translation termination in thegene.Sanger sequencing confirmed that this variant was inherited from his mother (Figure 1).The variant was absent in public databases (gnomAD,Exome Aggregation Consortium,or 1000 Genomes).The variant was classified as likely pathogenic according to the ACMG guidelines (Table 2).Pathogenic variants in other genes associated with hyperammonemia have not yet been identified.We reported this variant in the ClinVar database (accession number:VCV001256051).


FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The clinical symptoms and related examinations of OTCD patients lack specificity and should be differentiated from those of hyperammonemia caused by other factors,including different ornithine circulatory disorders;miscellaneous genetic metabolic diseases,including organic acid hematic disease,fatty acid oxidation disorder,beta oxygen defects,high insulin,and hepatic encephalopathy;severe liver damage;exogenous toxicity (,carbamidine);and drugs (,valproic acid).All these factors can elevate blood ammonia levels and should be identified according to the patient’s medical history and clinical symptoms[9].Genetic testing of thegene is another crucial factor in the diagnosis of this disease.
TREATMENT
OTCD diagnosis is mainly based on clinical symptoms,blood ammonia levels,and other general biochemical tests,such as blood amino acids,urine organic acids,and genetic tests.For suspected cases,such as those in which patients present intermittent or progressive encephalopathy and high blood ammonia levels with unknown causes,blood amino acid analysis and urine organic acid analysis should be performed as early as possible.If blood citrate is reduced or normal and urine whey acid or uracil is increased[9],OTCD diagnosis can be confirmed by combining these results with genetic testing.For neonates whose blood amino acid screening by tandem mass spectrometry indicates reduced citrulline levels,dynamic observation should be carried out,and urine organic acid and genetic tests should be performed.
“I have long been wishing for a dear little maiden8 like you,” said the old woman, “and now you must stay with me, and see how happily we shall live together
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
The final blood glucose level of the patient was 2.6 mmol/L.He had high blood ammonia [461.0 μmol/L (ref:18–72)],high lactic acid [10.80 mmo1/L (ref:1.06–2.09)],and high homocysteine [29.21 μmol/L (ref:<15)] levels (Table 1).
DISCUSSION
After admission,we ensured that the patient's airway was unblocked,warmed the body,monitored vital signs,assisted breathing with the use of a ventilator,and corrected the blood pH with the administration of sodium bicarbonate.Meropenem and penicillin were utilized to combat infection,phenobarbital for spasms,dopamine for circulation,and 10% glucose to maintain the stability of the internal environment.
Arginine was used to reduce blood ammonia,and levocarnitine was used to promote metabolism.Lidocaine was used for nonparoxysmal ventricular arrhythmia,which was indicated by an electrocardiogram.
The male infant patient was diagnosed with OTCD caused by anmutation.
Liver transplantation is regarded as an effective treatment for OTCD.For patients with neonatal onset,liver transplantation should be performed at the earliest identification of disease.Surgery is recommended between three months (and/or body weight>5 kg) and one year[9].Once OTCD is suspected,clinical examinations for blood ammonia,blood amino acids,and urine organic acids should be performed rapidly in a specialized metabolic laboratory.Our case shows high blood ammonia [461.0 μmol/L (ref:18-72)],high lactic acid [10.80 mmo1/L (ref:1.06-2.09)],and high homocysteine [29.21 μmol/L (ref:<15)] levels.After interpreting the sequencing results,we confirmed the diagnosis of OTCD in this patient.
Genetic testing is a crucial method for the diagnosis of OTCD.As a routine practice of next-generation sequencing (NGS),high-throughput sequencing will rapidly uncover many pathogenic variants in neonates who are suspected to have OTCD with abnormal hyperammonemia.Array CGH or multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification fails to detectgene deficiency in SNVs or microinsertions and deletions in patients[10,11],whereas NGS has the advantage of detecting these variations.Our study uncovered an unreported variant in thegene [NM_ 000531.5,c.970_979delTTCCCAGAGG,p.Phe324GlnfsTer16],which caused the early termination of OTC.Our results provide a reference for the accurate diagnosis of patients with the same variant.A previous study reported that approximately 15% of female carriers become symptomatic[12].Our findings also suggest heterozygote detection of at-risk female relatives as a promising direction for further investigation.
Right about the time Bill took his “seat,” a deacon began slowly making his way down the aisle from the back of the sanctuary11. The deacon was in his eighties, had silver gray hair, a three-piece suit and a pocket watch. He was a godly man -- very elegant, dignified12 and courtly. He walked with a cane13 and, as he neared the boy, church members thought, “You can’t blame him for what he’s going to do. How can you expect a man of his age and background to understand some college kid on the floor?”
CONCLUSION
In our case study of one individual,a rare variant in thegene was identified and confirmed by Sanger sequencing.This finding broadens thevariant spectrum and provides evidence for further OTCD screening and clinical consultation.
We thank the patient's family members for their participation in this study.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年4期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年4期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Surgical treatment of acute cholecystitis in patients with confirmed COVID-19:Ten case reports and review of literature
- Rituximab as a treatment for human immunodeficiency virusassociated nemaline myopathy:What does the literature have to tell us?
- Eustachian tube involvement in a patient with relapsing polychondritis detected by magnetic resonance imaging:A case report
- Endoscopic clipping for the secondary prophylaxis of bleeding gastric varices in a patient with cirrhosis:A case report
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor after breast prosthesis:A case report and literature review
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting as an isolated brain tumour:A case report
