Imaging presentation of biliary adenofibroma:A case report
INTRODUCTION
In 1993,Tsui[1] were the first to describe biliary adenofibroma (BF),which is a benign,complex,tubulocystic liver tumor with a bland spindle-cell stromal component.BF is a rare disease that is usually misdiagnosed due to its nonspecific clinical symptoms and laboratory examination findings.Imaging [including ultrasound,computed tomography (CT),and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)] usually reveal a multicystic tumor or complex mass with both solid and cystic components;these findings are very similar to cystadenoma or cystadenocarcinoma[2],intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[3],liver metastasis[4],and other lesions.However,the MRI findings have certain characteristics.We herein describe a case in which we analyzed the contrast-enhanced ultrasound and MRI findings of a patient with BF who was misdiagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma by contrast-enhanced ultrasound and with hepatic cystadenoma by MRI before surgical resection of the lesion.We also summarize the imaging findings of BF in previous literature.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 68-year-old man reported abdominal discomfort without obvious inducement for 2 mo.
In front of the book, he discovered the previous owner s name, Miss Hollis Maynell. With time and effort he located her address. He wrote her a letter introducing himself and inviting3 her to correspond.
History of present illness
The patient had no other symptoms.
He spake to the King: Your loyalty46 shall be rewarded, and taking up the heads of the children, he placed them on their bodies, smeared the wounds with their blood, and in a minute they were all right again and jumping about as if nothing had happened
History of past illness
His past medical history indicated hypertension and mild cerebral infarction for more than ten years.After regular drug treatment,these conditions were well controlled.
Personal and family history
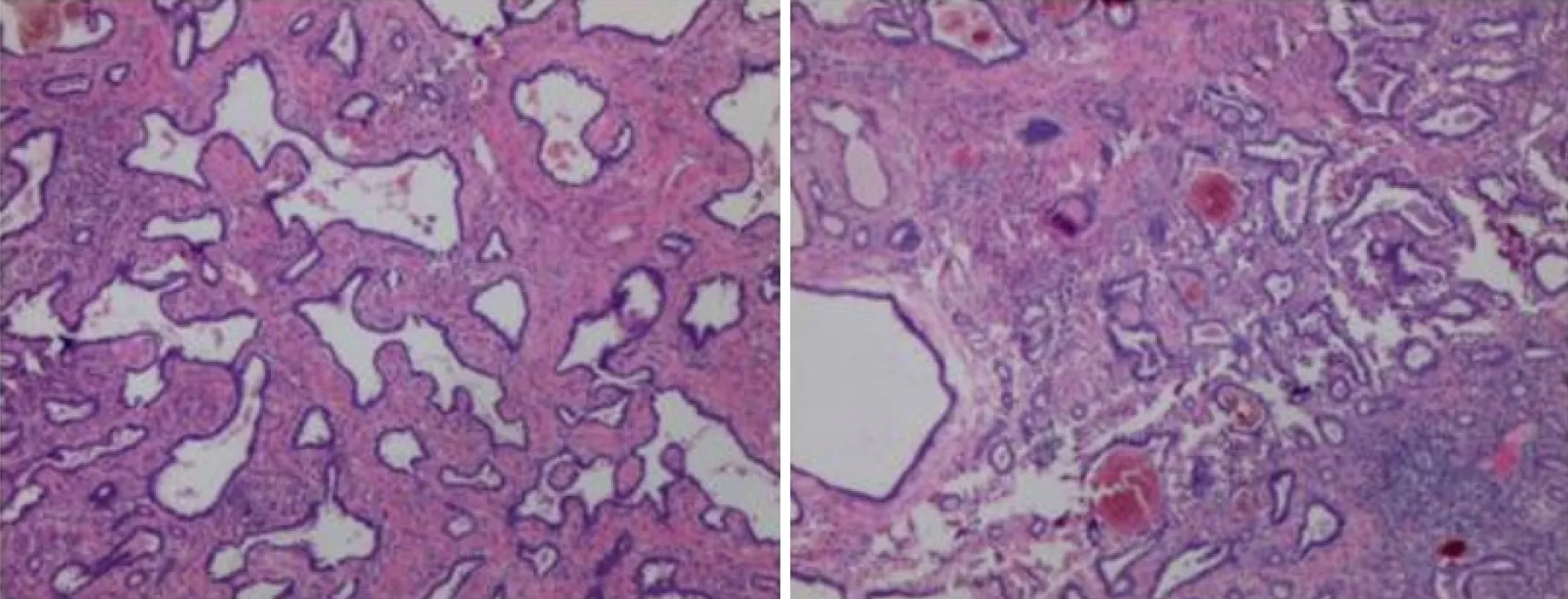
Pathology confirmed BF (a rare biliary epithelial tumor) in this patient (Figure 2).Microscopy showed irregular hyperplasia of the bile duct with varying amounts of intervening fibrous stroma and inflammatory cell infiltration.Some bile ducts were dilated and the wall thickened,cholestasis was seen in the bile duct.The cells showed no atypia,and some of them showed apocrine secretion.
Physical examination
No abnormal laboratory examinations were observed,including liver function,tumor markers,infection markers,coagulation tests and complete blood count.
Currently,although BFs are classified as benign bile duct tumors and precursors by the 2019 World Health Organization tumor classification system[5],some cases of BF are characterized by malignant transformation,invasion,and even distant metastasis (Tsui[1] first proposed in 1993,postoperative pathology showed malignant transformation in 3 cases[6-8],3 cases of biliary adenofibroma with invasive carcinoma[9-11],3 cases were complicated with liver tissue invasion[12-14],2 cases were complicated with lymph node metastasis[15],local recurrence occurred in 2 cases[16]).The clinical manifestations and imaging characteristics of BF are nonspecific.A definitive diagnosis is difficult to achieve by preoperative imaging.The diagnosis mainly depends on postoperative pathological examination.Pathologically,the lesions are gray or dark red irregular masses that can show cystic,honeycomb,or solid changes and have a relatively clear boundary and no capsule.
Laboratory examinations
On physical examination,there was no tenderness or rebound pain in the abdomen,and percussion pain in the liver area was negative.His blood pressure was 121/75 mmHg,pulse rate was 67 bpm and body temperature was 36.4 ℃.
Imaging examinations
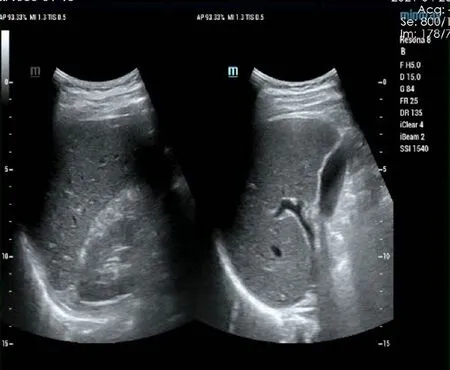
The patient had no signs of recurrence at the 1-mo postoperative re-examination (Figure 3).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
He had no personal or family history of other diseases.
TREATMENT
Including the present case,25 cases of BF have been reported to date (Tsui[1] in 1993,Parada[17] in 1997,Haberal[12] in 2001,Akin[18] and Garduño-Ló pez[19] in 2002,Gurrera[20] in 2010,Kai[6] and Nguyen[7] in 2012,Jacobs[13] in 2015,Godambe[9];Thai[10] and Thompson[15] in 2016,Kaminsky[8] and Arnason[16] in 2017,Esteban[11] in 2018,Sturm[14] in 2019),and no differences in sex or age at onset are evident.The mean age at onset is 57.2 ± 17.79 years.Of the 25 cases reported 12 were male and 13 were female.The mean diameter of the lesions was 8.22 ± 4.65 cm.Eight patients presented due to upper abdominal discomfort and pain,one patient had jaundice due to an intrahepatic bile duct lesion,and the remaining 16 patients had no reported abdominal pain and were diagnosed by related examinations.The results of laboratory tests were generally nonspecific.One patient had an elevated carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) concentration[19],and all of the remaining patients had normal concentrations of tumor markers including alpha fetoprotein,carcinoembryonic antigen,CA19-9,and CA125.Liver function indices were within normal limits.One patient had a history of hepatitis B[21],but the hepatitis status was not mentioned in the remaining patients.The location of the lesion was the left lobe in 11 patients and the right lobe in 13 patients (the specific location of the liver lesion was not mentioned in the remaining patient).One patient had three lesions[16],and the remaining patients had single lesions.We carefully reviewed the previous literature (including the imaging findings and intraoperative descriptions of the lesion locations) and found that the most common location of BF was under the liver capsule,as was true in the present case.Thus,the lesion location has a certain particularity.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
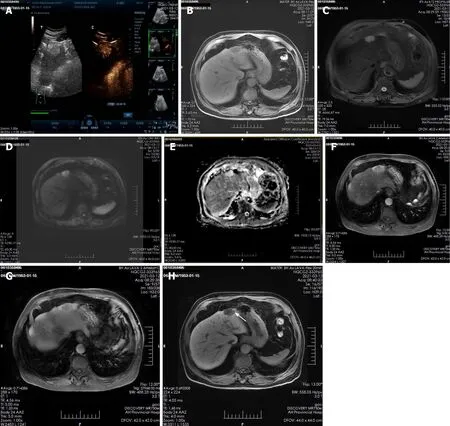
A plain CT scan at a local hospital showed a space occupying lesion in the left lobe of the liver and the patient was admitted to our hospital for further treatment.Ultrasonography showed hyperechoic nodules in the left lobe of the liver.Following injection of contrast agent,early and obvious enhancement was observed (Figure 1A).Plain MRI showed hypointensity on T1-weighted imaging (T1WI) and hyperintensity on T2-weighted imaging (T2WI).In this case,iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least square estimation-iron quantification (IDEAL-IQ) and intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI) sequences were performed.The water phase of the IDEAL-IQ sequence showed that the signal of the lesion was higher than that of the liver.DWI showed moderate hyperintensity and isointensity according to the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC).The ADC and pure diffusion coefficient (D) values were 2.78 and 2.12 × 10mm/s,respectively,which indicated that there was no obvious limitation in the diffusion of the lesion.There was no significant change in the signal of the lesion in the in-phase and out-phase sequence.The early and late arterial phases showed obvious enhancement of solid components and separation of lesions.The degree of lesion enhancement decreased in the portal phase and delayed scan.In the hepatobiliary phase,enhancement of the bile duct structure was found in the lesion (Figure 1B-H).
DISCUSSION
So there was no one left belonging to the house but the landlord s daughter, who was a good, well-meaning girl, and had taken no part in all the evil doings
The lesion was removed by laparoscopic surgery under general anesthesia.
Then the young man gave her his promise to make her his wife, and the girl fulfilled her part of the bargain, and food was plentiful23 on the island all through the long winter months, though he never knew how it got there
On plain CT and MRI scans,BF is mainly a cystic lesion containing septal and varied solid components.Only three lesions were described as solid tumors.In the present case,the lesion was small and mainly composed of solid components,and ultrasound showed that it was slightly hyperechoic.Plain MRI showed hypointensity on T1WI and hyperintensity on T2WI.In this case,IDEAL-IQ and IVIM-DWI sequences were performed.The water phase of the IDEAL-IQ sequence showed that the signal of the lesion was higher than that of the liver.DWI showed moderate hyperintensity and isointensity according to the ADC.The ADC and D values were 2.78 and 2.12 × 10mm/s,respectively,which indicated that it was more likely a benign lesion (there was no obvious limitation in the diffusion of the lesion).There was no significant change in the signal of the lesion in the in-phase and out-phase sequence.In previous cases,the bile duct epithelial components of the lesions had no secretory function,but some lesions showed a tendency to enlarge and develop cystic components during the follow-up period[21].The diameter of the solid lesions in three cases[8,10,20] and the solid lesions in the present case were smaller (4.08 ± 1.16 cm) than the mean diameter of the cystic and solid lesions (7.00 ± 3.03 cm).Therefore,whether the bile duct epithelial components in BF have a secretory function requires further study.The intrahepatic bile duct was dilated in only one case (the lesion was located within the bile duct).Enhanced CT and MRI scans showed enhancement of the solid components and septa of the lesions;one report described a wash-in and washout enhancement pattern in the literature[8].Gd-EOB-DTPA (Primovist,Bayer Schering,Pharma AG,Berlin),a hepatocyte-specific contrast agent,was used in this case.The early and late arterial phases showed obvious enhancement of solid components and separation of lesions.Areas of abnormal perfusion could be seen around the lesion.The degree of lesion enhancement decreased in the portal phase and delayed scan,and the areas of abnormal perfusion disappeared.A similar enhancement pattern was seen on contrast-enhanced ultrasound.In one case,the lesion displaced the hepatic vein[14],and in another case,the lesion was accompanied by adjacent hepatic tissue invasion[12],indicating malignancy.In two cases,enlarged lymph nodes were found in the hepatic hilum,and postoperative pathological examination showed metastasis[15].The remaining reports did not mention imaging signs of a malignant tumor,although pathological examination after surgical resection of the lesions showed that the lesions were combined with cytological atypia or invasive cancer and even exhibited distant metastasis.
Pathological examination revealed that the fibrous tissue matrix of the tumor showed the histological pattern of a partially cystic bile duct.The bile pigment component in the tumor duct indicated direct continuity between the lesion and the biliary system,although postoperative pathology showed that the lesion was not clearly connected with the bile duct[6,21].Primovist is a hepatobiliary-specific contrast agent that can show the biliary system in the hepatobiliary phase.In this case,enhancement of the bile duct structure was found in the lesion in the hepatobiliary phase,suggesting that the lesion was closely related to the intrahepatic bile duct system;postoperative pathology also showed a bile duct structure and intrabiliary cholestasis.In a previous report,MRI failed to show a relationship between biliary duct adenofibroma and the intrahepatic bile duct.The author speculated that because most of the lesions were located under the liver capsule and the terminal bile duct was slender,it was difficult to show the relationship between the lesion and the bile duct by conventional MRI scanning sequences.Primovist-enhanced MRI,especially hepatobiliary phase images,was a good supplement.
Thirsty as he was, he did not wait to drink, but he told his mother that he smelt the blood of a Christian man, and that she had better bring him out at once and make him ready to be eaten
CONCLUSION
BF is a rare biliary tumor that exhibits malignant transformation and usually occurs under the liver capsule.The lesions are mostly cystic and solid.On enhanced scans,the solid part can show a wash-in and wash-out enhancement pattern,and enhancement can be seen in the separation of lesions.The hepatobiliary phase of Primovistenhanced MRI can better show the lesions and intrahepatic bile duct structure,providing more clues and value for the diagnosis.BF can be treated by surgical resection,but regular postoperative review is needed to identify recurrence or distant metastasis,such as that to the lung.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年4期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年4期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Surgical treatment of acute cholecystitis in patients with confirmed COVID-19:Ten case reports and review of literature
- Rituximab as a treatment for human immunodeficiency virusassociated nemaline myopathy:What does the literature have to tell us?
- Eustachian tube involvement in a patient with relapsing polychondritis detected by magnetic resonance imaging:A case report
- Endoscopic clipping for the secondary prophylaxis of bleeding gastric varices in a patient with cirrhosis:A case report
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor after breast prosthesis:A case report and literature review
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting as an isolated brain tumour:A case report
