Diaphragm Rupture 膈肌破裂
医学词汇注释与简要讲解
Key facts
Synonym:diaphragm tear,traumatic herniation of the stomach.Definition:traumatic laceration or tear of the diaphragm usually associated with herniation of abdominal viscera into the chest.
Classic imaging appearance:abdominal viscera located above the diaphragm.Other key facts:(1)caused by penetrating or blunt traumas;(2)left-sided injuries more common;(3)diagnosis of herniated abdominal viscera may be immediate or delayed months to years after the injury.
laceration 裂伤
viscera 内脏、脏器
Imaging findings
Best imaging clue:visualization of abdominal viscera above the diaphragm.
Chest film findings:(1)majority of patients have an abnormal chest film;(2)hemothorax;(3)pneumothorax;(4)loss of visualization of the diaphragm;(5)basel pulmonary opacity;(6)apparent elevation of the diaphragm;(7)upward extension of the nasogastric tube above the diaphragm;(8)stomach or bowel above the diaphragm;(9)shift of the mediastinum to the opposite side;(10)bowel contrast examination (upper GI series or barium enema) may show stomach or bowel above the diaphragm.
CT findings:(1)Collar sign of herniated stomach,bowel or liver extending above the diaphragm.(2)Collar sign refers to a waist-like constriction of herniated viscera at the site of herniation.(3)Stomach,loops of bowel or mesentery above the diaphragm.(4)Coronal and sagittal reformations can show discontinuity the diaphragm and herniated abdominal viscera.
MR findings:(1)Focal discontinuities of the diaphragm well shown on coronal and sagittal MR images.(2)On T1WI the hyperintense abdominal and mediastinal fat permit optimal visualization of the hypointense diaphragm.
Imaging recommendations:(1)Chest-abdomen CT scans with oral and IV contrast materials and with coronal and sagittal CT reformations.(2)Coronal and sagittal T1WI MR scans.
【prefix】hemo-血的
hemoglobin 血红蛋白
hemothorax 血胸
【prefix】pneumo-肺的、气的
pneumonia 肺炎
pneumothorax 气胸
nasogastric tube 鼻胃管
Differential diagnosis
Loss of visualization of the diaphragm due to hemothorax,or to atelectasis or air-space disease at the lung base.
atelectasis 肺不张
Pathology
General path comments:reported increase frequency of left side rupture although right side injuries often remain under diagnosed.With right side injury the liver may protect against significant organ herniation into the right thorax.Most ruptures involve the posteriorlateral portion of diaphragm near the junction of the central tendon and posterior leaves.
Visceral herniation occurs in 95%of left sided injuries but may be delayed and not recognized until later.The stomach is the most frequent organ to herniate.
Etiology-pathogenesis:Penetrating trauma is the most common cause of diaphragmatic injury.Rupture with blunt trauma is caused by a sudden increase in intrathoracic or intra-abdominal pressure against a fixed diaphragm.Injuries from blunt trauma are more often associated with large ruptures and herniated viscera.Injuries from penetrating trauma are usually small.
penetrating trauma 穿通伤
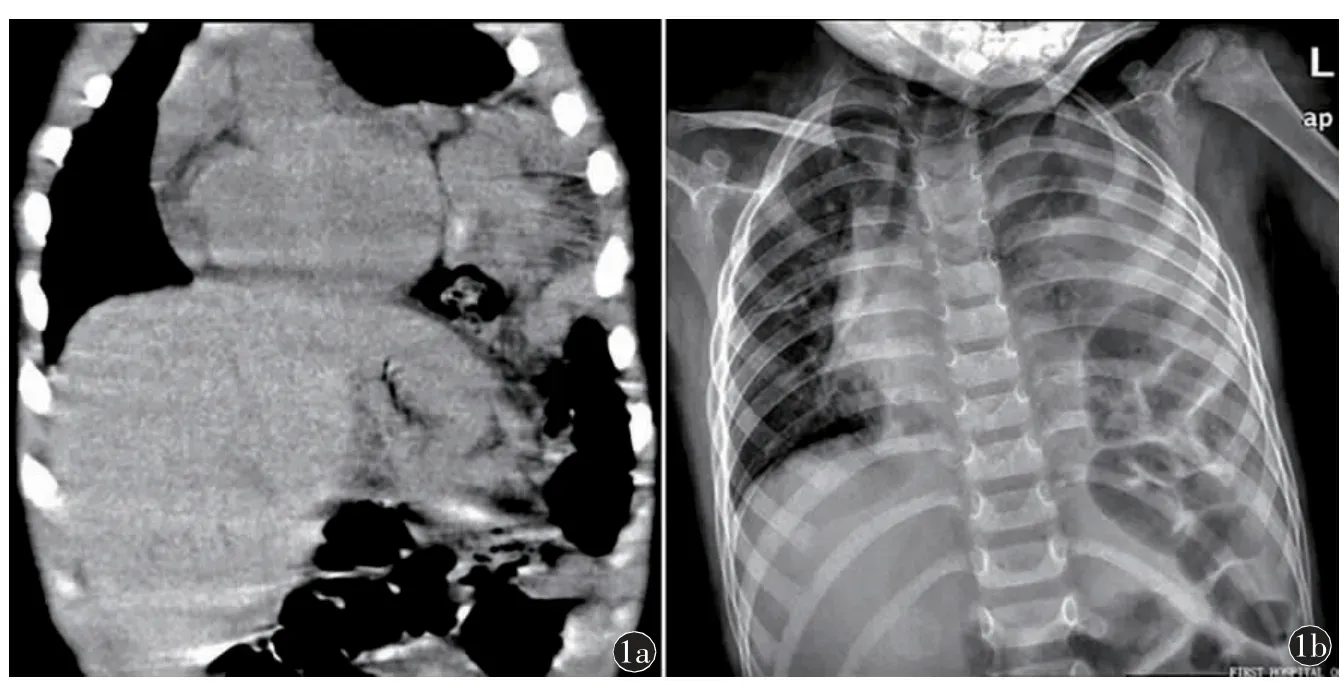
Fig.1 Left diaphragm rupture.a)Coronal CT scan showing herniation of the bowel into the chest.b)Chest X-ray film shows lack of visualization of the left diaphragm and the bowel is above the diaphragm with shift of mediastinum to the right side and increased opacity of left lung.
Epidemiology:diaphragmatic injuries seen in about 5% of patients undergoing laparotomy or thoracotomy for trauma.
Clinical issues
Presentation
Chest pain;decreased ventilation;bowel sounds in the chest;mediastinal shift.
Natural history
If not diagnosed and treated the patient may remain asymptomatic or may
later develop incarceration of herniated abdominal viscera.
主要表现包括:胸痛、通气减弱、胸腔内肠袢影、纵隔移位
incarceration 嵌顿
Treatment:(1)Laparotomy with reduction of herniated structures and transabdominal diaphragm repair.(2)Right thoracotomy may be required to facilitate repair of a right side rupture.
Prognosis
Patients undergoing early diagnosis and repair do very well.If the diagnosis is initially overlooked,patient may later experience incarceration of herniated viscera.

