Femoroacetabular offset restoration in total hip arthroplasty;Digital templating a short stem vs a conventional stem
lNTRODUCTlON
In recent years,failure of anatomical restoration has gained more attention as a reason for persistent complaints after total hip arthroplasty(THA).Despite considerable improvement,up to 22% of the patients experience functional limitations in daily life[].Since there has been an increase of young and active patients receiving THA,who have higher expectations of their functional outcome[4,5],excellent results are needed.Nowadays,there is more focus on anatomical restoration as related to clinical outcome[6].An important part of accurate anatomical reconstruction is a restored femoroacetabular offset(FAO).A loss of ≥ 5 mm between the preoperative offset and postoperative offset is associated with altered gait and decreased functional outcome[7,8].Restoration of offset improves hip stability,range-of-motion,abductor function and reduced wear[9-13].
Conventional stems are the most common choice for elective THA,due to the amount of experience in placement of these stems and good long-term results.However,individual anatomy can hinder proper femoral offset restoration as the diaphyseal anchorage of this type of stem limits placement options.Short hip stems were designed for preservation of proximal bone stock,but it seems that anatomical restoration is also achievable with short stems.As there are many different designs,short stems can be classified based on osteotomy or anchoring principle.Metadiaphyseal anchoring short stems allow for excellent restoration of individual anatomy[6,14,15],as the placement of these curved short stems can be angled in the desired position to follow the natural curvature of the medial calcar.Due to this feature,it mimics the physiological load transfer on the proximal femur[16,17].
For correct placement of the hip stem,digital 2d-templating is common clinical practice and is a reliable method to estimate the correct size of hip stems prior to surgery[18-21].It provides information on the level of osteotomy,insight on the probable size of components,and whether anatomical restoration can be achieved.
The primary aim of this study was therefore to see if the FAO could be restored by use of preoperative digital 2d-templating with a short metadiaphyseal anchoring stem and a conventional stem,within a wide range of anatomical hip variations.The secondary aim was to examine the association of secondary measurements required for digital templating,such as the caput-colllumdiaphyseal angle(CCD-angle)and preoperative offset,with offset restoration.Additionally,the intraand inter-observer reliability of the measurements by use of digital 2d-templating was investigated,as there is limited data on this particular subject and its reliability[21,22].
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Patients
One hundred standardized preoperative hip measurement radiographs of patients were included,with primary or secondary osteoarthritis as indication for THA.The radiographs were randomly chosen from two ongoing cohorts,the Optimys trial(Mathys Ltd,Bettlach,Switzerland)and the CBH trial(Mathys Ltd,Bettlach,Switzerland).Fifty radiographs were randomly selected from either cohort,creating a variability in coxa norma,vara and valga.If preoperative measurement radiographs were missing,containing a magnification marker for determination of the amount of magnification used,these radiographs were excluded.Approval for inclusion has been attained from the medical ethics review committee,under registry numbers NL47055.048.13 and NL48211.048.14.
Radiological evaluation
Standardised preoperative hip radiographs with magnification marker were used for 2D-digital templating.An internal rotation angle of 20° was used to produce the full profile of the femoral neck on anteroposterior radiography[23,24].Computer-assisted measurements and 2d-templating were performed by use of Orthoview(Materialise NV,Leuven,Belgium)[25,26].
Not long after, the king of the country suffered from thedeepest melancholy17. He was diligent18 and industrious19, but employmentdid him no good. They read deep and learned books to him, and then the lightest and most trifling20 that could be found, but all to no purpose.
Pre-templating FAO was measured by first determining the femoral offset,defined as the distance of the longitudinal axis of the femur to the center of rotation.The longitudinal axis was determined from a 4-point box in the intramedullary cavity of the femur.The acetabular offset was determined next,defined as the distance from the center of rotation to the lateral edge of the pelvic teardrop[6,23,24,27-29].The CCD-angle was used to identify the difference in hip-anatomy,,to identify if patients had a coxa vara(< 120°),coxa norma(120°-135°)or coxa valga(> 135°).
Digital templating of the short and conventional stem was then performed,with the cup as fixed factor in both images.The variables were measured again after templating,with femoral offset now being defined as the distance from the longitudinal axis of the femur to the center of rotation of the prosthetic head.The post-templating acetabular offset was defined as the distance from the center of rotation of the cup to the lateral edge of the pelvic teardrop(Figure 1).
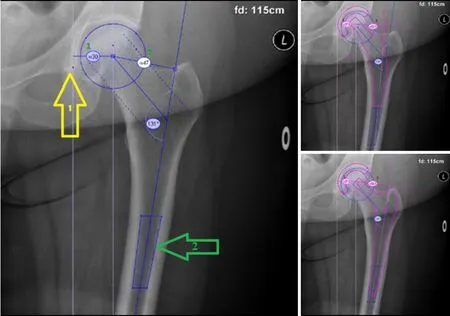
Radiological measurements and templating were performed independently by three observers.To assess intra-and inter-observer reliability,the measurements were performed twice by a medical student(Verboom T)and by a resident in orthopaedic surgery(de Waard S),and once by an experienced orthopaedic hip surgeon(Haverkamp D).
Be quiet, and do not weep, answered the frog, I can help thee, but what wilt4 thou give me if I bring thy plaything up again? Whatever thou wilt have, dear frog, said she -- My clothes, my pearls and jewels, and even the golden crown which I am wearing. 6
Implants
Implants used for templating in this study were the CBH as the conventional stem and the Optimys as the short stem.In both cases the RM Pressfit Vitamys(Mathys Ltd,Bettlach,Switzerland)cup was used.The CBH is a widely used conventional press fit hip stem with a diaphyseal anchorage.Since the CBH hip stem follows the longitudinal femoral axis,femoral offset can only be increased(after determining the correct stem size)by choosing a larger head size and/or a lateral neck.
The Optimys is a short press fit hip stem,which anchors in the metadiaphyse.The shape of the Optimys follows the curvature of the medial calcar and can be placed into varus or valgus position,allowing to increase or decrease the femoral offset as needed.Also,extra femoral offset can be given with head size and a lateral neck.
Statistical analysis
Patient characteristics and outcome variables are described as means with ranges or frequencies with accompanying percentages.Restoration of FAO was dichotomized into “restored” when < 5 mm from baseline or “not restored” when ≥ 5 mm from baseline[7,30].Differences between the short stem and the conventional stem concerning the proportions of correct restoration of the offset were analyzed by use of McNemar tests.To assess the association between absolute offset restoration and both CCD-angle and preoperative offset,multi-level analyses were performed by use of linear mixed model to account for paired measurements for both hip stems.In case of effect modification of stem type,linear regression analyses were performed for each stem separately.Avalue < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
It was a woman; the sailors said that she was quite dead, but the women thought they saw signs of life in her, so the stranger was carried across the sand-hills to the fisherman s cottage
The high level of inter-and intra-observer reliability is indicative of high accuracy and reproducibility of the measurements.This reliability has also been shown in other templating studies[21,29,34,35],along with a high predictive value for prosthesis placement[6,21].The found cutoff point may,after further clinical research,be a reason to introduce digital 2d-templating as a tool for stem type selection in combination with clinical considerations.Also,this study shows that preoperative templating can be performed reliably by medical students and orthopedic residents,after a learning curve.
For the determinants that were significantly associated with offset restoration(CCD-angle or preoperative offset),an operating curve(ROC)-analysis was performed to determine the optimal cutoff point of this independent variable for restoration within the limits of 5 mm.To provide a 95 %confidence interval(CI),bootstrapping procedure was performed.By using a 1000 bootstrap samples and calculating their respective cut-off values,the Standard Error was obtained to acquire the 95 %CI of the optimal cut-off point.Accompanying area under the curve(AUC)was calculated as measure of accuracy.
Additionally,to assess inter-observer and intra-observer reliability,intra-class correlation coefficients(ICC)were calculated.Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics,version 24.0(Armonk,NY:IBM Corp.).
She asked if he had gone out of his mind, but he answered crossly, What is that to you? Do as you are bid, and to-morrow I will bring you some treasures
Sample size
A pilot study was performed where 20 radiographs were randomly chosen and evaluated,in which 30%of conventional stems had more than 5 mm loss in FAO.Based on a 10% difference with the short stem being clinically relevant,a sample of 89 radiographs was required to identify superiority of the short stem in FAO restoration when compared to the conventional stem,with an a = 0.05 and a power of 90%.A total of 100 radiographs were included in this study.
Then the girl went down the steps where none could watch her and cracked her walnut, and out came the most splendid court dress that any dressmaker had ever invented; and, carrying it carefully in her arms, she knocked at the door, and asked if the princess wished to buy a court dress
RESULTS
Patient characteristics
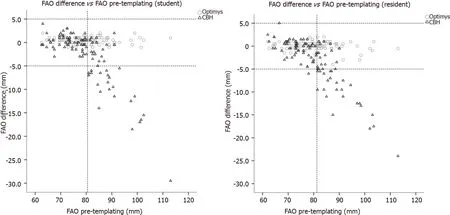
An FAO of more than 81.25 mm showed a failure in 79% of the templated conventional stems with the resident,compared to the student with a failure rate of 76% above 80.5 mm.A negative trend-line in FAO restoration is seen as the pre-templating FAO increases by both student and resident(Figure 3).For a correct cut-off point for failure in the conventional stem,bootstrapping was performed for a ROCanalysis for the pre-templating FAO with a restoration within 5 mm.The CCD-angle was not used for bootstrapping,as the AUC was smaller than 0.5.After bootstrapping the measurements of the resident,the optimal threshold of the pre-templating FAO was 81.25 mm(95%CI:80.75-84.75),above which the conventional stem could not restore the FAO(Figure 1),with a sensitivity of 0.96,specificity of 0.79,and an AUC of 0.94.
Restoring FAO
The short stem reached a post-templating difference of < 5 mm in FAO in all cases(100%)for both student and resident,whereas the conventional stem only achieved this in 76% and 72% of the radiographs for student and resident,respectively.The difference in FAO restoration was significant(< 0.001),in benefit of the short stem compared to the conventional stem.A varus hip showed a failure rate of 14.3%(= 4/24)of the non-restored hips,while a valgus hip showed no failure at all(Figure 2).
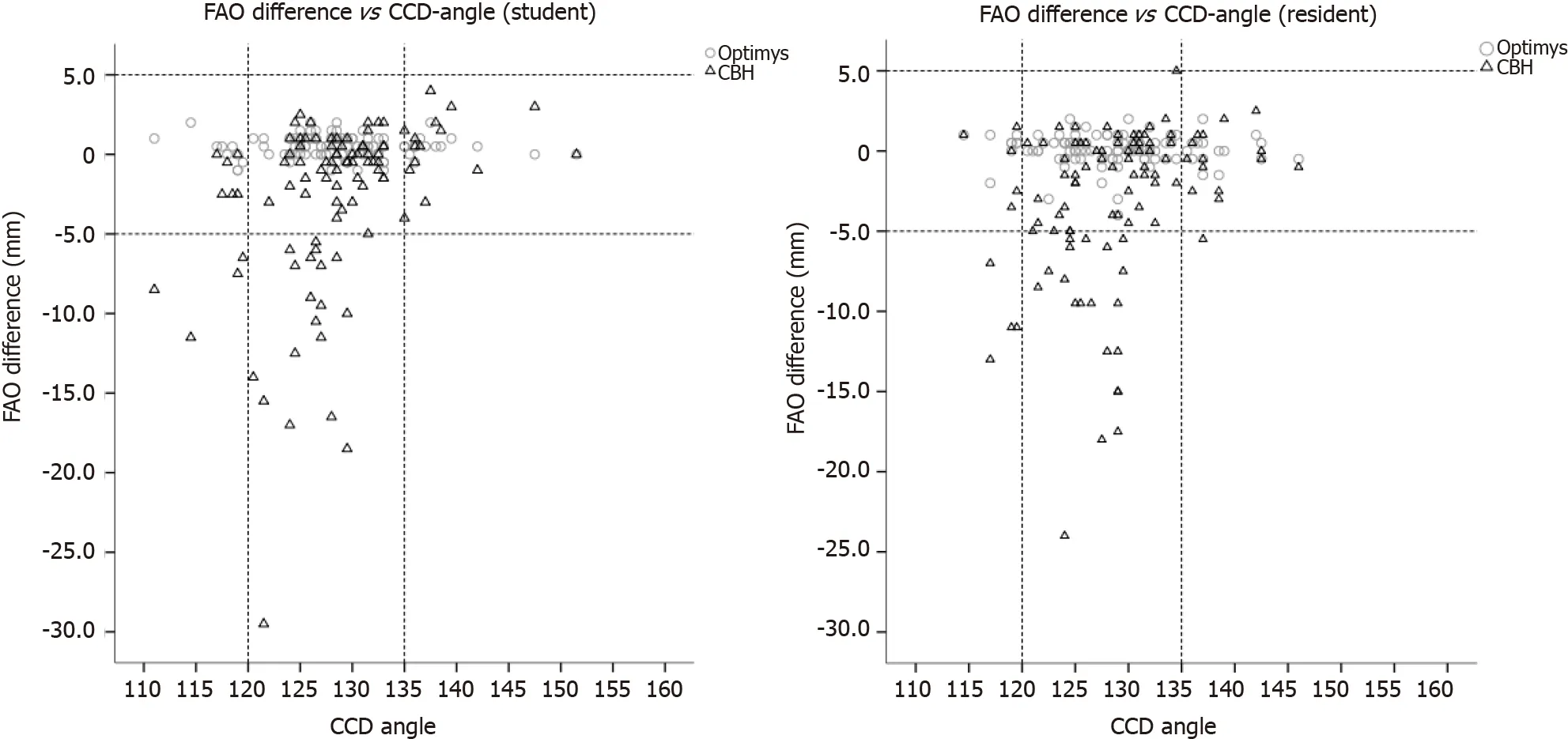
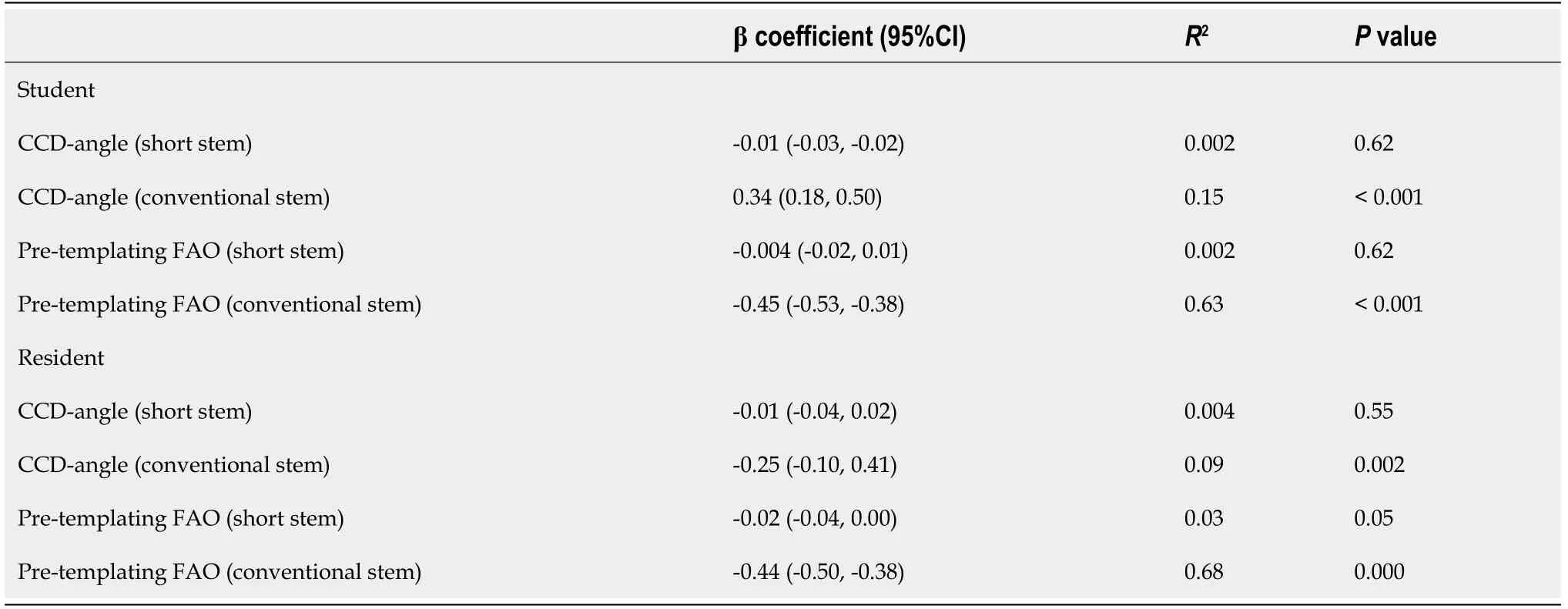
Significant interactions(< 0.001 for all analyses)were observed between the stems and the determinants(CCD-angle and preoperative FAO),therefore analyses of the stem types were performed separately.Significant association of the CCD-angle and pre-templating FAO with the FAO restorationwas only observed for the conventional stem,with the highest explained variance for the pre-templating FAO of 68%(Table 2).
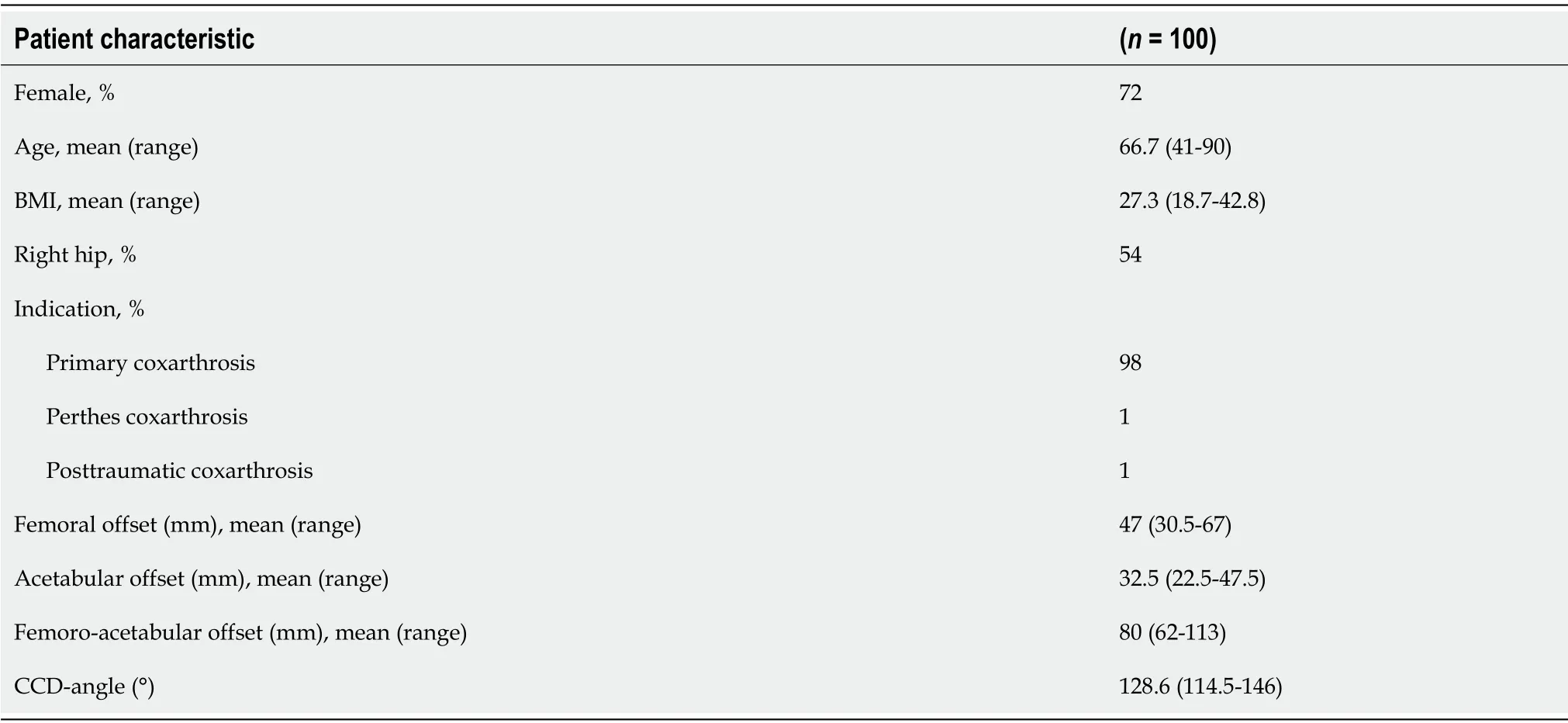
Radiographs in a total of 100 patients were included,72 were female.A mean age of 67 years was found,with a mean BMI of 27.Almost all patients were diagnosed with primary coxarthrosis.The mean preoperative FAO was 80mm,with a CCD-angle of 128.6°(Table 1).
Post-templating femoral and acetabular offset
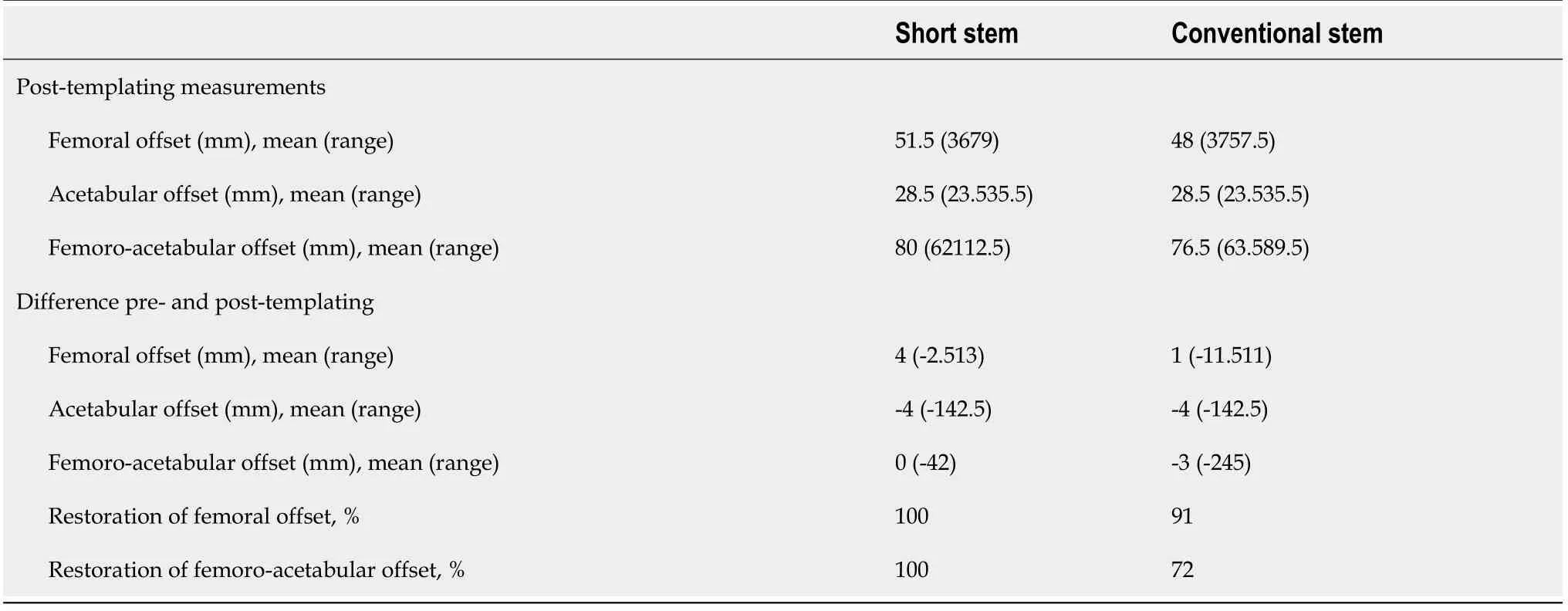
The results of the post-templating measurements are shown in Table 3.The short stem restored thefemoral offset in all cases,whereas the conventional stem restored the femoral offset in 91% of the cases.There was a mean decrease of acetabular offset of-4 mm.
Intra-observer reliability and inter-observer reliability
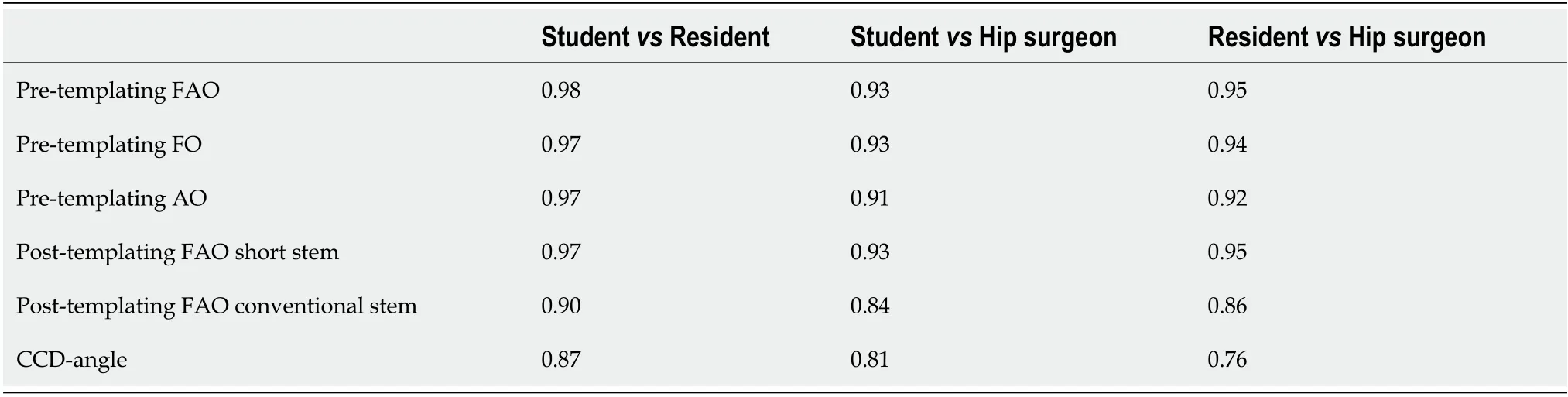
The intra-reliability of the student and the resident was both 0.99 for the pre-templating FAO.All other reliability scores were > 0.9 for both the student and the resident.Compared to the hip surgeon in pretemplating FAO,the inter-observer reliability was 0.93 and 0.95,between the studenthip surgeon and residenthip surgeon respectively(Tables 4 and 5).

DlSCUSSlON
The goal of this study was to determine whether a metadiaphyseal anchoring short stem potentially facilitated a better restoration of FAO in digital templating compared to a conventional hip stem.The FAO was taken as primary measurement and not the femoral offset,as the acetabular offset can decrease postoperative due to medial placement of the acetabular component[31].Therefore,thefemoral offset must increase additionally to compensate for the loss in acetabular offset or the cup must be placed more lateral.How the acetabular component is placed varies per orthopedic surgeon.However,the acetabular cup used in this study showed an average decrease of 3.7 mm in acetabular offset in literature[32,33].In this study there was a decrease in acetabular offset of 4 mm,which is comparable to the other studies.The FAO restoration rate within 5 mm limits for the short stem was achieved in all cases,whereas the conventional stem achieved a restoration rate of 72%(resident)and 76%(student)during digital templating.The pre-templating FAO was associated with failure in FAO restoration when using the conventional stem,as pre-templating FAO values > 81 mm had a nonrestoration rate of 60% in this group.The cutoff value was determined to use for a future reference standard,as it could provide a cutoff point if clinical relevance is shown.The cutoff point of 80 mm for pre-templating FAO was chosen conservatively,at the found cutoff value(81.25 mm),because of the rapid decrease in restoration rate beyond these points,to account for variance in the general population.The CCD-angle was not clinically relevant for FAO restoration,nor was the pre-templating FAO clinically relevant for the short stem.While it was expected that varus hips would comprise the majority of hips where a conventional stem would prove insufficient in FAO restoration,this was only observed
in 14%(= 4/24)of the cases.While it stands to reason that a varus angle would increase femoral offset,a varus hip is not the primary reason for failure of FAO restoration.There was no difference in FAO restoration between both stems in valgus hips.Since there is no prior data on this specific subject,these results cannot be compared to other studies.
It is also important to note that since their earthly father has abandoned them, the Grimms have the children turn to God the Father to save them (Zipes 1997). Return to place in story.
Conventional hip stems are anchored in the diaphysis,where placement variability is limited and increasing femoral offset is only facilitated by using a larger head size or a lateral neck.Due to this rigidity in placement options,the results of this study can be interpreted for all conventional hip stems.Conventional stems can be placed into a varus position using smaller stem size,resulting in an increased femoral offset.However,long term survival could be compromised due to increased stress on the tip of the prosthesis.Therefore,this manner of placement is not recommended.In the results between the experienced hip surgeon and resident and medical student,the ICC values were lower for the conventional stem than expected.However,the hip surgeon was inclined to sooner place the conventional stem into a varus position,restoring the FAO better than the resident and medical student.
Jewelry10 would be nice, but what can I afford that would not soon tarnish11 or grow quickly out of style? You deserve the gems12 of royalty13 for your perseverance14 and creativity, your devotion and talent.
There were some limitations to this study.Firstly,2d-templating was used to measure 3-dimensional distances,which may cause underestimation of femoral offset and modification of CCD-angles[28,34].However,radiographic 2d-templating is the method of choice for the majority of hip surgeons due to cost,radiation load,availability and has been shown to be similar in reliability and accuracy to 3dtemplating with use of computed tomography[36].The CCD-angle modification from 2d-templating may have been disadvantageous to the assessment of the CCD-angle as a predicting factor for FAO restoration.Secondly,other characteristics of the femoral canal were not examined in this study.The Dorr classification could help decide on type of femoral stem chosen for the surgery[37].A Dorr type A with a large offset would be very difficult for a conventional stem to restore the offset,whereas a Dorr type C could lead to inadequate fixation of a short stem.
Another limitation is the fact that no postoperative measurements were done,which means that the results cannot be directly translated to clinical practice.However,the short stem was able to restore the FAO postoperative in the study of Kutzner[6]and recent studies showed that preoperative digital 2d-templating assured a satisfying restoration of the individual anatomy in short stems[22,26,38].
An advantage in usage of conventional stems over short stems is that there are many available studies with long-term outcomes,while these are only limited for short stems.It may also be preferable to use conventional stems in patients with suboptimal bone quality,as there is a lower load per hip stem surface unit due to the larger diaphyseal anchoring area.Theoretically,short stems could lose initial press-fit in softer bone with a higher chance on subsidence,increasing the risk of implant instability or periprosthetic fractures.Especially in older patients,the advantage of short stems,,preservation of proximal bone stock,is less important and not worth the risk for potentially increasing the risk of complications.Another topic is the costs of hip stems.Conventional stems are less expensive than short stems,which is also relevant once all clinical factors have been properly considered.
The short stem used in this study is a metadiaphyseal anchoring stem,with a curved design.It is to be expected that other similar designs are capable to restore the FAO in the same manner,which has previously been shown with the Nanos stem(Smith and Nephew,Marl,Germany)[15].During surgery,the resection of the femoral neck determines for a large part the placement of the hip stem.In varus hips,a smaller part of the femoral neck will be resected for optimal placement as compared to valgus hips.Thus,a short stem thus can be neck preserving or trochanter sparing,depending on the anatomy of the patient.This is the main reason why the FAO can be restored within the 5 mm limit.Metaphyseal stems are not comparable to our outcomes,due to stem design differences.
If the native offset was > 80 mm,the short stem was better at restoring FAO than the conventional stem in digital templating.This could indicate that there is a specific patient population that could benefit if a short stem with a curve is chosen as femoral stem instead of the conventional stem.
CONCLUSlON
In preoperative planning of FAO restoration in THA,digital templating shows that short stems with a curve following the medial calcar are potentially better at restoring the FAO compared to conventional stems if the preoperative offset is ≥ 80.0 mm.
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research background
The following steps that are necessary to take are the postoperative measurements of the short stem to see if the offset can be restored.Also,a pilot study with gait measurements in a case-matched study of patients with either a short or conventional stem will help to define if there is a difference.
Research motivation
The advantage in FAO restoration in this study may contribute to the use of short stems in a broadened patient group with hips with a large offset.Clinical trials will have to show whether the improved restoration in FAO will grant the expected improved functional.Other reasons to choose conventional stems over short stems still may have priority over the advantage found in this study.
Research objectives
A FAO more than 80mm showed a large failure rate in restoration in the conventional stems,whereas the short stem could restore the offset in all cases.The reliability of all measurements were good between in both inter-as intra-reliability,with no difference in experience.
Research methods
Digital templating in a standardized X-ray of the hip were used from two ongoing cohorts,varying in hip anatomy.Orthoview was used as digital templating program.Pre-templating FAO was measured,as well as post-templating FAO measurements in the short and conventional stem.The results were divided into restored(< 5 mm difference in offset)or not-restored(> 5 mm difference in offset).
Absulum the Reindeer Elf,when he heard that happy noise,would wish he was a Workshop Elfmaking Christmas toys;but a Workshop Elf is wise and talland Absulum was notand that was why he was in that barn,well that is what he thought
Research results
Primary objective was the femoroacetabular offset restoration in all types of hip anatomy between a short and conventional hip stem,where the acetabular component is used as a fixed parameter.Second objectives were the reliability of the measurements.
Research conclusions
As digital templating is a reliable tool for measuring component sizes in total hip arthroplasty,this is used as measurement to see if there is a difference between a short and conventional hip stem in a wide range of hip anatomy.
Research perspectives
Short stems are gaining popularity,as one of the possible advantages is the restoration of offset.Offset restoration improves functional outcome.This could benefit the younger patient population,as they have higher expectations of their total hip arthroplasty in their more active lifestyle.
FOOTNOTES
de Waard S,Verboom T,Bech NH,Kerkhoffs GM,Haverkamp D drafted the manuscript;de Waard S and Haverkamp D did the measurements;Sierevelt I performed the statistical analysis,de Waard S assisted with data analysis;Sierevelt I,Haverkamp D participated in study design;Kerkhoffs GM and Haverkamp D participated in oversight of the study.
I kept cheering the runners. We had one in at home and three guys pouring it on from first to second, second to third, third to home. The second baseman yelled for the center fielder to get the ball to him. Excitedly, he obeyed, but the ball skipped across the grass and passed by the second baseman toward the right-field line. My job as coach was simple at this point. Run, guys, run, I yelled.
The cohort studies in which the X-rays were chosen from,were reviewed by and approved by the Medical Ethical review committee of the MC Slotervaart hospital in Amsterdam,under registry numbers NL47055.048.13 and NL48211.048.14.
All study participants provided informed written consent about personal and medical data collection prior to study enrolment.
The fishing boat was a scabby() old tub, but when you re only paying 15 dollars a person for three hours of fishing, you don t get the Queen Elizabeth II. There were several people on board, sitting on benches on each side of the deck. A few were in the cabin.
There are no conflict of interest from any of the authors regarding this paper.
No additional data are available.For information regarding the used data,contact the corresponding author at s.dewaard21@gmail.com.
The sea was quite black and thick, and it was breaking high on the beach; the foam18 was flying about, and the wind was blowing; everything looked bleak19
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial(CC BYNC 4.0)license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See:https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Netherlands
Sheryl de Waard 0000-0002-2271-806X;Tom Verboom 0000-0002-3196-8810;Niels Hendrik Bech 0000-0002-7772-2410;Inger N Sierevelt 0000-0003-0924-9358;Gino M Kerkhoffs 0000-0001-7910-7123;Daniël Haverkamp 0000-0001-7360-9763.
Liu M
A
Pride, said the dead woman; do you see him? The footman? asked the pastor. He is but a poor fool, and notdoomed to be tortured eternally by fire! Only a fool! It sounded through the whole house of pride: theywere all fools there.
Liu M
 World Journal of Orthopedics2022年2期
World Journal of Orthopedics2022年2期
- World Journal of Orthopedics的其它文章
- Developments in diagnosis and treatment of paediatric septic arthritis
- All-epiphyseal versus trans-epiphyseal screw fixation for tillaux fractures:Does it matter?
- Periprosthetic joint infections in femoral neck fracture patients treated with hemiarthroplasty-should we use antibiotic-loaded bone cement?
- Bone mineral density in fracture neck of femur patients:What's the significance?
- Liverpool carpal tunnel scoring system to predict nerve conduction study results:A prospective correlation study
- Clinical efficacy of the Ankle Spacer for the treatment of multiple secondary osteochondral lesions of the talus
