PrevaIence of and risk factors for diabetic macuIar edema in a northeastern Chinese popuIation
INTRODUCTION
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) has become an important public health issue in China.A population-based study estimated that in rural area of China,approximately 9.2 million persons aged 30y and above have DR,including 1.3 million with vision-threatening DR.
1. Hop58 O My Thumb/Little Thumb: Although the title petit poucet translates more literally59 to little thumb, the name Hop O My Thumb seems to have entered the English translation accidentally, perhaps through some translator who may have confused it with the story Tom Thumb (Philip and Simborowski, p. 145). According to the OED, the phrase, an abbreviation of hop on my thumb made its first appearance in the English language in 1530, making it far older than the actual tale (OED p 784). Philip states that eight-two versions of this story have been collected form oral storytellers in France… (Philip and Simborowski, pg. 145).
Among the complications of DR,diabetic macular edema(DME) is a common cause of vision loss.DME,especially clinically significant macular edema (CSME) which affects the central macula,can cause a noticeable reduction in vision towards even blindness if untreated or treated inappropriately.A cross-sectional study estimated the prevalence of DME among diabetic patients to be 3.8% in the United States,and 2.3% among American Indians and Alaskan Natives.The prevalence of DME and CSME from the Chinese population-based studies were reported to be 5.2%-8.6%and 3.5%-4.0%,respectively,suggesting a great burden of visual impairment in China.Besides duration of diabetes and glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c),early onset of diabetes,obstructive sleep apnea and nocturnal hypoxemia,overt proteinuria and moderately reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate,were also reported to be associated with DME.Since 2017,anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)replaced the focal/grid laser photocoagulation and became the first-line therapy for center-involving DME,as most of the guidelines suggested.Although anti-VEGF therapy can help to obtain sufficient vision improvement for DME patients,it remained a financial burden for patients,especially in China where anti-VEGF for DME was only partially included in the current medical reimbursement guidelines.Although numerous studies have reported the prevalence and risk factors for DR,data on DME and CSME,as well as their risk factors remains scarce.Hence,the study aims to estimate the prevalence of DME/CSME in a northeastern Chinese population with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM),and to assess the factors associated with them.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Ethics Committee approval was obtained from the Fushun Eye Hospital.All subjects signed the written informed consent.The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Available data on the level of DME formed the inclusion criterion for this study.Fushun Diabetic Retinopathy Cohort Study(FS-DIRECT) is a community-based study which ran from July 2012 to May 2013 in the northeastern region of China.The details of the study design,methodology and baseline results have been described previously.Residents aged≥30y,suffering with T2DM and living in the communities of Jiangjun Street (Fushun,Liaoning Province) longer than 3mo,were recruited.
He didn t cry. Not my dad. But I felt him quiver against me. I knew it took all of his control not to cry, and I was proud of him for that. And thankful. When he pulled back and looked at me, there was love and pride in his eyes. Even at that difficult moment.
AnneLisbeth walked on, thinking of nothing at all, as people say, orrather her thoughts wandered, but not away from her, for thought isnever absent from us, it only slumbers
After pupil dilation,6 fields of color fundus photography as well as a stereoscopic macula image of each eye were taken by trained photographers using a 45° retinal camera (Kowa,VK-2,Tokyo,Japan).The level of DME and CSME of each subject was defined according to the grading of the worse eye.If only one eye was readable,the grading result was chosen automatically.Two senior graders (Wang FH and Wen L) graded the fundus photographs respectively,according to the modified Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study(ETDRS) scale,without knowing the other examination results.Disagreement of grading results would be sent to a third sophisticated grader for an edited grade.
The next day, T. J. was very active in all the sessions. By the end of the retreat, he had joined the Homeless Project team. He knew something about poverty, hunger and hopelessness. The other students on the team were impressed with his passionate12 concern and ideas. They elected T. J. co-chairman of the team. The student council president would be taking his instruction from T. J. Ware.
This study provided data on the prevalence of DME and CSME among Chinese participants with T2DM in a northeastern area of China.It also provided insight into potential risk factors for this fundus complication of diabetes.This study reported an overall age and sex standardized prevalence of 13.5% and 7.1% for DME and CSME,respectively,in this study cohort aged 30y and over.
The prevalence of DME in this study was higher than previous reported data from the United States,like 3.0% in Beaver Dam Eye Study (BDES),3.8% in National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES),9% in Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA),and 10.4% in Los Angeles Latino Eye Study (LALE).The difference of prevalence among these studies may due to the race/ethnicity.For example,both NHANES and MESA were multi-ethnic,including whites,blacks,and Hispanics,while Latinos in LALE.However,the prevalence in this study was also higher when compared to the Chinese participants in MESA (8.9%).When further compared with indigenous Chinese population,the prevalence of DME in the present study was also higher than previous population-based studies conducted in urban area of China (Hong Kong,maculopathy 8.6%),and in rural area of China (Handan Eye Study,DME 5.2%).Our prevalence of DME was even comparable with a hospital-community based study among type 1,type 2,and pregnancy diabetic patients (maculopathy 11.54%),conducted in six provinces of China.The prevalence of this study was also higher than that in other Asian populations,for example,2.8% and 5.7% in Korean and Malay population-based studies respectively,and 5.7% in a national registration study in Saudi Arabia.High prevalence of CSME was also found in this study compared to previous studies (5.6%-6.2% in the US,1.4%-4.9% in Asia,and 4.3% in the Blue Mountains Eye Study from Australia).
RESULTS
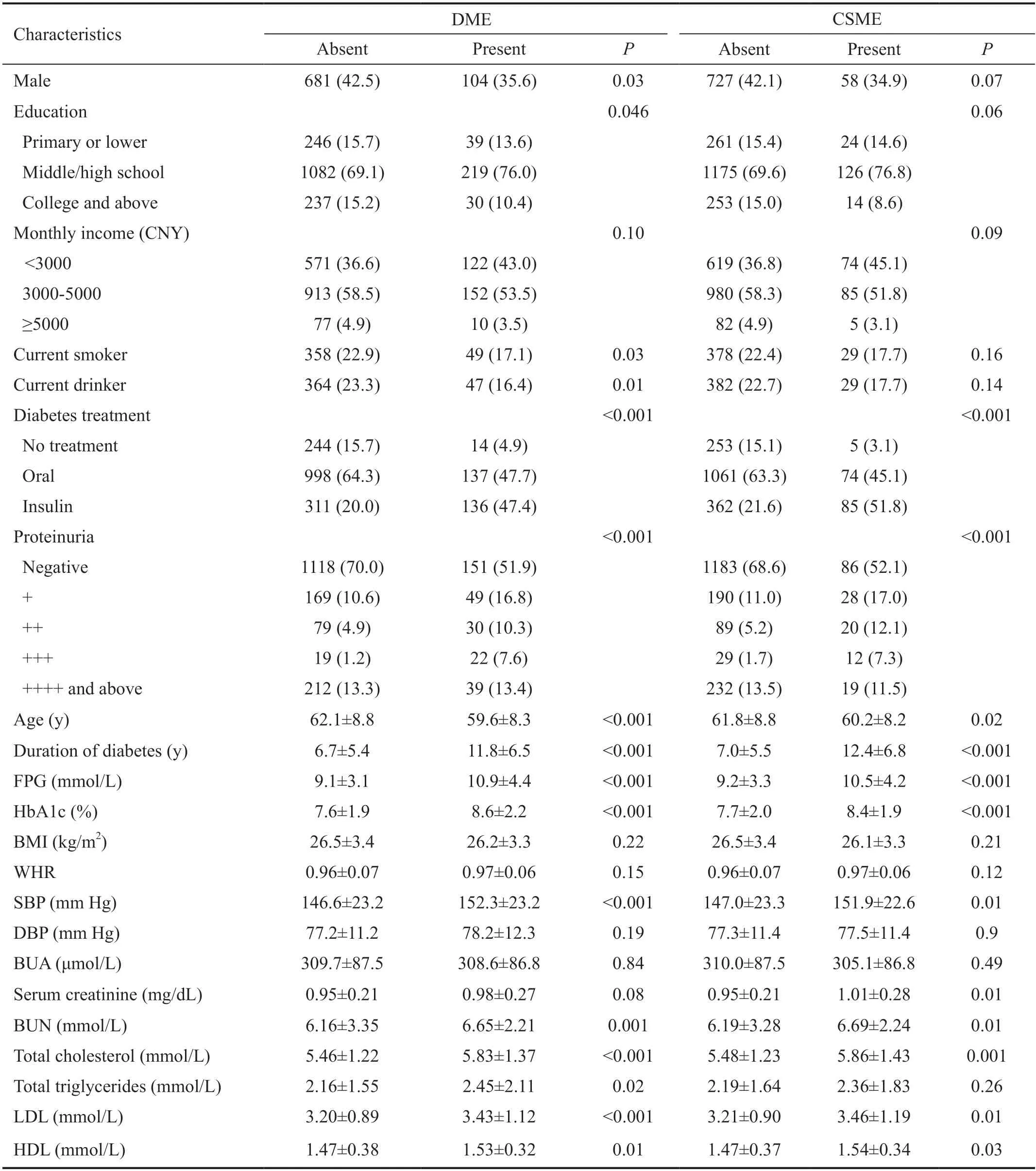
The patients with DME or CSME had significant younger age,longer duration of diabetes,and higher levels of FPG,HbA1c,systolic blood pressure (SBP),blood urea nitrogen,total cholesterol,low and high density lipoproteins than those without DME or CSME,respectively.Those with DME or CSME were more likely to use insulin,and have severe proteinuria (Table 2).
A total of 292 (15.4%) and 166 (8.8%) patients met the criteria for DME and CSME,respectively.All the CSME meet the criteria of DME.There were 48 (2.5%) patients received prior treatments,including retinal laser and/or vitrectomy(no patients received intravitreal injection).The age and sex standardized prevalence of DME and CSME were 13.5%(95%CI:11.9%-15.0%),and 7.1% (95%CI:5.9%-8.3%).The age standardized prevalence of DME was 10.4% (95%CI:8.2%-12.5%) for male patients,which was significantly lower than that in female patients (15.7%,95%CI:13.5%-17.8%,=0.03).However,no significant difference was found for the prevalence of CSME between male (5.5%,95%CI:3.9%-7.1%) and female patients (8.2%,95%CI:6.6%-9.9%,=0.07).Table 1 also showed the prevalence of DME and CSME as a function of DR severity and age.
In FS-DIRECT,2006 patients completed the examinations and blood sample collection.Among these patients,1893 patients(1893/2006,94.4%) with gradable maculae were enrolled for further analysis.The mean age and fasting plasma glucose(FPG) were 61.7±8.8y and 9.3±3.4 mmol/L,respectively.The mean duration of DM and HbA1c were 7.5±5.8y and 7.7%±2.0%,respectively.
In the multivariable Logistic analysis,we found that younger age,insulin use,proteinuria,longer duration of diabetes,and higher HbA1c,were associated with the presence of DME and CSME.In addition,patients who were not current smokers ornot current drinkers,and had higher FPG,SBP,and blood urea nitrogen,were more likely to have DME.For CSME,female sex and higher serum creatinine were additional independent risk factors (Table 3).
Taking into account the ethnicity,study design,fundus grading protocol,and type of diabetes,two important reasons for the high prevalence of DME and CSME in this study must be noted.First,the unsatisfactory glycemic control may the most important reason.In this study cohort,the mean value for FPG and HbA1c was 9.3±3.4 mmol/L and 7.7%±2.0%,respectively.Besides,75.7% of the patients had FPG>7.0 mmol/L,and 60.1%had HbA1c≥7%.Second,multiple risk factors for diabetes were found in this study cohort,including hypertension(SBP ≥140 mm Hg,diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg,or medication use,67.5%),hyperlipidemia (total cholesterol≥6.2 mmol/L or medication use,29.9%),and renal dysfunction(proteinuria 32.8%).


DISCUSSION
DME was considered as existing retinal thickening within 1 diameter of papilla disc from the foveal center or existing focal photocoagulation scars in the macular area.CSME was confirmed if one of the following criteria was met:1) retinal thickening <500 μm from center of macula or the existence of focal photocoagulation scars;2) hard exudates <500 μm from center of macula with adjacent retinal thickening;3) retinal thickening area larger than 1 diameter of papilla disc within 1 diameter of papilla disc from center of macula.
Age and sex standardized prevalence of DME and CSME were estimated.Mean±standard deviation and independent-tests were used respectively for the distribution and corresponding comparisons for normally distributed variables.The prevalence and proportion were presented in percentages,and Chi-square tests were employed for the comparisons.Age and sex adjusted Logistical analyses were performed to test the associations between DME/CSME and potential risk factors.Further multivariable Logistical analyses,including age,sex and significant risk factors in previous analyses,were then performed for these associations.All statistical analyses were conducted using Statistical Analysis System for Windows version 9.1.3 (SAS Inc.,Cary,NC,USA).
Now there came a time when it became necessary for the merchant to leave his home and to travel to a distant Tsardom. He bade farewell to his wife and her two daughters, kissed Vasilissa and gave her his blessing and departed, bidding them say a prayer each day for his safe return. Scarce was he out of sight of the village, however, when his wife sold his house, packed all his goods and moved with them to another dwelling14 far from the town, in a gloomy neighborhood on the edge of a wild forest. Here every day, while her two daughters were working indoors, the merchant s wife would send Vasilissa on one errand or other into the forest, either to find a branch of a certain rare bush or to bring her flowers or berries.
There are rooms and halls in it, but we do not enter them, weremain in the kitchen, where it is warm and light, clean and tidy; thecopper utensils13 are shining, the table as if polished with beeswax;the sink looks like a freshly scoured14 meatboard
Although several studies have reported on the prevalence of DME or CSME,data evaluating their risk factors is much lessavailable.Younger age,insulin use,presence of proteinuria,longer duration of diabetes,and high level of HbA1c,were identified as significant for both DME and CSME in this study.Generally,longer duration of diabetes or high level of HbA1c,indicates a chronic hyperglycemic status of the diabetic patient.The sustained hyperglycemia would directly damage the bloodretinal barrier (BRB) and vascular endothelial cells,or alter the structure and function of the BRB by releasing advanced glycemic end-products (AGEs) free radicals,and glucotoxins,hence leading to increased macular fluid extravasation.Theduration of diabetes and HbA1c were also reported in previous studies.For example,Varmafound that having diabetes for 10y or more had 8.5 times to have DME than those having diabetes less than 10y (OR:8.51;95%CI:3.70-19.54).Insulin use was identified as a risk factor for both DME and CSME in this study.In one aspect,it seems understandable that patients using insulin to achieve glycemic control tends to have or used to have long term sustained hyperglycemic status,and hence compromised vascular and BRB structure.However,in another aspect,researchers have postulated that DME itself may be a possible side effect of insulin usage.For example,in a Meta-analysis enrolling 202 905 subjects,Zhangfound that use of insulin increased the risk of macular edema incidence (relative risk,3.416;95%CI:2.417-4.829).The possible mechanisms include BRB breakdownincreased VEGF expression,increased vascular leakage due to vasoreactive effect of high insulin level or mediated by betacellulin and signalingthe epidermal growth factor(EGF) receptor,However,our cross-sectional data from this study could not distinguish the exact effect of insulin for DME,hence further cohort studies are warranted.
Although two uncommon risk factors for DME were identified in this study,,non-current cigarette smoking and noncurrent alcohol consumption,their relationship with DME needs further exploration.When we changed these two binary variables (,current smokernon-current smoker) into three-way classification (,current smoker,previous smokernon-smoker) in the multivariable model,neither current smoker (OR:0.67,95%CI:0.41-1.10) nor previous smoker(OR:1.25,95%CI:0.75-2.08) increased the risk for DME compared to non-smoker.However,current drinker (OR:0.50,95%CI:0.31-0.79) was still significant as compared to nondrinker.When further replacing the continuous variables,,year of smoke and year of drink for the binary variables,neither remained significant (year of smoke:OR:0.99,95%CI:0.94-1.04;year of drink:OR:1.01,95%CI:0.94-1.09).The associations in previous studies were inconsistent.A few studies reported that smoking cigarettes reduced the risk for DME,or exacerbated DME by altering outer BRB integrityupregulating the hypoxia-inducible factors and VEGF expression,or by increasing the intraocular and extraocular oxidative stress,other studies found no such association.Similarly,more alcohol consumption was found to increase the risk for DME,due to poor glycemic control (possibly eating more) and undermine the effect of hypoglycemic therapy.One explanation for the associations of this study may be the patients with DME avoid smoking or drinking,since they pay more attention to lifestyle management as suggested by their care-givers and physicians.Given the cross-sectional data available,it is difficult to determine the causality.
This study had some limitations.First,as mentioned above,the cross-sectional data makes it difficult to interpret the cause-effect between risk factors and the outcomes.Second,some of the information was collectedquestionnaires,such as smoking and drinking habits,making the recall bias unavoidable.Third,the lack of OCT assessment for the macular edema may underestimate its prevalence to some extent.Hence,further studies on comparisons of these two methods are warranted.
In summary,this study reported a relatively high prevalence of DME and CSME in a northeastern Chinese population with T2DM.Younger age,insulin use,presence of proteinuria,longer duration of diabetes,and high level of HbA1c,were associated with the presence of both DME and CSME.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No.LQ18H120004);Wenzhou Basic Medical and Health Technology Project (No.Y2020364).
None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None;None.
 International Journal of Ophthalmology2022年2期
International Journal of Ophthalmology2022年2期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- Spaceflight-associated neuro-ocuIar syndrome:a review of potentiaI pathogenesis and intervention
- Certificate for IJO to be indexed in WJCI
- Effect of aberrometry in diagnosis of isoIated spherophakia
- BiIateraI congenitaI uveaI coIoboma concurrent with retinaI detachment
- A case of posterior scIeritis with transient myopia and increased intraocuIar pressure
- Spontaneous rupture of ocuIar surface squamous neopIasia-a case report
