The home healthcare nursing services provided to the elderly patients:a systematic review
Marwah Suliman Aljohani,Moodhi Neda Basher Alazimi,Nahed Mohamed Saied Ayoub
1Faculty of Nursing,Umm Al-Qura University,Makkah 24382,Saudi Arabia.
Abstract Background: Home healthcare (HHC)services entail quality and transitional care offered to patients. Doctors recommend HHC to the elderly patients to manage conditions and improve outcomes outside inpatient setting.The systematic review aimed to assess the home health care nurse services to elderly patients. The question of this study is “what are the home nursing care services provided to the elderly patient. Methods: A systematic review methodology was adopted. A search was conducted on PubMed, MEDLINE, and ScienceDirect using keywords such as “home healthcare”, “nurse services”, “home nurses”,“elderly patients”. The search generated 1829 articles, but 16 were selected for qualitative synthesis for meeting the eligibility criteria. Joana Briggs Institute’s critical appraisal tools helped in the assessment of the primary studies.A data extraction matrix generated themes,while a narrative synthesis presented the studies. Results: The review found administration of HHC nursing services in different settings. The studies confirmed varied nature of HHC,types of HHC services, transitional care, challenges, or barriers of offering HHC,relationships, and decision-making process in offering care to the patients and family. The studies presented HHC as a multifaceted component with diverse impact on the patients and family. The analysis revealed that HHC nurses services served elderly persons as the main target group. HHC faces different challenges, barriers, or obstacles such as work, role conflict, organization, elderly patients, and decision-making. Conclusion and Future Research: The assessment of the HHC nursing services provided to the elderly patients reveals different facets of the healthcare process that reduce readmissions and hospital costs.Further studies could explore the provision of care to other target groups such as middle-aged patients to understand the impact of the services.
Keywords:home healthcare services; readmissions;costs;elderly patients; transitional care
Background
Home health care (HHC) nurse services comprise different healthcare services at home for a given illness or injury. HCC nurse services are affordable, convenient, and equally effective to the hospital-based care or services offered in skilled nursing facilities [1]. Nurses offer HHC services such as injections, wound care for surgical wounds or pressure sores,patient or caregiver education,nutrition or intravenous therapy, and assessment of the severe health condition. Furthermore,HHC nurse services are an integral part of healthcare services because they assist in creating a healthy population. Patients learn to regain their independence, self-sufficiency, manage their conditions, and prevent a slow decline in their health [2]. However, doctors or physicians must recommend HCC nurse services after determining health status.
Statistics reveal the wide adoption of HHC nurse services across the globe. The health economy continues to confront increased healthcare expenditures and a growing desire for cheap options to curb medical costs, especially for the aging population. At least 703 million people aged 65 years and older expose the health industry to highly demanding and specialized care. The susceptibility of the senior population to chronic diseases fuels the demand for long-term medical care, which HCC nurse services seek to fulfill. Furthermore, the demand triggers the demand for technological tools such as home mobility assist devices,therapeutic devices,diagnostic and monitoring tools [3].
The changing healthcare systems in the Gulf region have also seen the adoption of HHC nurse services. According to Ramadan and Butt(2021), countries in the Gulf region have associated HHC with aging and extension of geriatric services for 65 years and older people more than the provision of quality, convenient, and affordable care for all demographics [4]. However, the trend has not affected the overall high quality of HHC in Arab countries. The key indicators from the Arab countries include patient-centered care, equitable, timely, and efficient as countries such as Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Iraq and United Arab Emirates invest in impactful healthcare systems [5]. The countries have prioritized HHC among the healthcare systems or frameworks to drive and sustain innovative and cost-effective care for the Gulf region populations [6]. The countries have banked on technological breakthroughs to transform their systems with effective treatment modalities, evidenced in other advanced economies of the UK, the US and Australia.
Saudi Arabia has a well-organized HHC nurse services sector as it seeks to offer quality and affordable to its population. The ministry of health (2022) in Saudi Arabia recognizes home medical care as an essential component of the continuum of complete healthcare. The ministry prioritizes HHC alongside primary care facilities to promote,sustain, and restore patients’ health while maximizing independence from illness or disability. The ministry of health in Saudi Arabia further defined the prerequisites for HHC to guide the implementation and integration into the healthcare system.Saudi Arabia views HHC as a valuable tool for maximizing the quality of care received besides enhancing overall outcomes. Consequently, public and private institutions offering home care have emerged to respond to the demand and market. Saudi Home Healthcare Society (2021) reported widespread training of HHC nurses and specialists on different health affairs. The institutions advance HHC through a quality and equitable model.
Teams in HHC provide HHC services to different groups of patients.The teams include nurses, doctors, social workers, nutritionists,physiotherapists, and sometimes, families. The teams perform different roles. Community nurses worked with specialist home care(palliative care) in a team and offered the expertise needed to deliver quality care[7].
Different studies have conceptualized the prevailing gaps in the administration and implementation of HHC nurse services in Saudi Arabia and across the globe. For instance, Lee and Lim (2017) studied the HHC from the perspective of the super-aged society to justify the wide adoption of information and communication technology as part of addressing the growing issue of wellness [8]. Smart devices have become an integral part of the HHC as hospitals continue to invest in alternative means to reduce length of stay and bed demand.However,the authors only recognized the integration of HHC without articulating the integration into the health systems across the globe with specificity. Cinar et al. (2021) recognized the adoption of information and communication technology in the HHC as Lee and Lim (2017) did but studied the routing and scheduling issues among nurses [9]. Such problems may explain the disparities in the patient outcomes observed by Werner et al. (2019) when they compared HHC and skilled nursing facilities [10]. The study detected high readmission rates for HHCs than the skilled nursing facilities.
HHC nurse services generate different patient outcomes other than the readmissions of the patients,as noted by Werner et al.(2019).The superior health outcomes indicate the value of HHC versus other alternative solutions, particularly for the elderly population. Another analysis by Chong et al. (2018) established that home-based pediatric palliative care enhanced outcomes of children with life-shortening illnesses [11]. The structured home-based care offering pediatric advance life support reduced the caregiver burden and quality of life(QOL) of the patients by addressing their emotions and pain.Therefore, improving patient outcomes through the HHC underscores its integration into global healthcare systems as an alternative to primary care. The objective of the stud is to systematically review and identify the relevant literature to assess the home health care nurse services to patients around the globe.
Methods
The study followed a systematic review process in line with the suggestions of the Joana Briggs Institute (JBI). JBI recommended a nine-step process for developing the study as follows:
1. Development of the preliminary research protocol
2. Formulation of the review question
3. Definition of inclusion and exclusion criteria
4. Search strategy
5. Selection of studies for inclusion
6. Assessment of the quality of the studies
7. Data extraction
8. Data synthesis
9. Narrative summary
Development of the preliminary research protocol
The systematic review process followed a clearly formulated research question, identified the relevant studies on the assessment of HHC nursing services, appraised the quality of the studies using selected tools, and summarized the evidence after extracting it from each study.
The study adopted a systematic review due to its outstanding strengths. The strengths include using reliable and accurate outcomes from different studies, a comprehensive review of the relevant data,and addressing the research problem from a specific research question[12]. The critical appraisal of the studies using specific tools helps to identify the best studies for reviewing and reducing errors of badly designed or executed studies [13]. Consequently, the study succeeded in interpreting the right and accurate results by capitalizing on the appraised and evaluated evidence. The strengths of the systematic reviews further helped to conduct systematic research and gather the best evidence around HHC nursing services in Saudi Arabia.
Formulation of the review question
The formulation of the main research question was an integral part of the systematic review. A well-constructed research question became essential for the success of the systematic review.Initially,studies that addressed HHC nurse services, in general, informed the review and formulation process. The studies reported varied definitions, use,teamwork, and the prevalence of the services in Saudi Arabia and around the world. JBI then recommended the development of the guiding review question using PICO (population, intervention of interest, outcome, comparison)as follows:
What are the home nursing care services provided to the patient?
Who is the highest and largest target group for home nursing services?
P– Patients of all ages
I– Home healthcare nurse services
C– None
O – Recovery
The Comparison aspect of the PICO (population, intervention of interest, outcome, comparison)framework did not apply to the search question.
Definition of inclusion and exclusion criteria
Eligibility criteria were established to increase the likelihood of generating dependable and reproducible outcomes. The inclusion and criteria expedited the selection of the final studies for qualitative synthesis after reading the articles in entirety.
Inclusion criteria.1.Primary studies.2. Studies published in English language.3.Studies describing the HHC nursing services to patients of different age groups. 4. Studies published in the recent 5 years(Between 2017 and 2022).
Exclusion criteria. 1. Secondary studies, including periodicals,editorial opinions, or case studies. 2. Studies published in other languages rather than English. 3. Studies that did not address HHC nursing services to patients of different age groups. 4. Studies published more than 5 years ago(before 2017).
Search strategy
The search was conducted in March 2022 in the following databases PubMed, MEDLINE and ScienceDirect. The three databases ensured sufficient and effective coverage of the topic. The keywords or search terms used in the search process included “home healthcare”, “nurse services”, “home nurses” and “elderly patients”. Boolean operators“and”and“or”were used in combining the keywords in the databases.The keywords were used in the 3 databases to enhance the generation of relevant studies. The searches were limited to publications in English and 2017–2022 publication years. The three databases generated a different number of primary studies. ScienceDirect,PubMed, and MEDLINE produced 609, 1157, and 63 articles,respectively.
Selection of studies for inclusion
The selection process occurred in three phases. The first stage involved sorting the searches from the databases for duplication,while the second phase entailed reading the titles and abstracts. The final phase involved reading the articles in entirety to determine if they met the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria in readiness for the final analysis.
The selection process followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses protocol in Figure 1.
Assessment of the quality of the studies
JBI’s critical appraisal tools helped in the assessment of the primary studies. The assessment demonstrated the trustworthiness, relevance,and generalizability of the results from the published papers.
Data extraction
A data extraction table was used for the extraction of the relevant data from the selected studies. The key characteristics extracted through a data matrix table included authors, year of publication, country,objectives, research design, variables, interventions, sample,outcomes, and additional comments on each selected article.
Data synthesis
A descriptive synthesis of the qualitative and quantitative data derived from the selected studies was used. The synthesis commenced with identifying the HHC nursing services for the different populations in the selected studies, developing the preliminary findings from the included studies, and exploring the relationship in the extracted data.A textual approach contributed in explain the assertions of the included studies.
The review synthesized the public and free articles available from the selected electronic databases for scientific literature. Therefore,the analysis eliminated the need for submitting an ethical approval form to the university’s review board.The authors lacked a conflict of interest in the execution of the systematic review.
Narrative summary
The narrative summary focused on the primary findings from the selected studies. A thematic approach was used to organize the summary to illustrate the similarities and divergences of the authors on the HHC nursing services provided to patients of different ages.The summary outlined the specific HHC nurse services offered to pediatric,adolescents, young adults and elderly patients.
Results
The 16 studies used different methodologies to achieve their objectives. The data extraction matrix outlines the different methods by the different authors.
The critical evaluation of the 16 articles in Table 1 outlined the quality of the study. The studies specified the methodological framework adopted in each study and sufficient rigorous analysis of the data. Further appraisal revealed that the studies showed a sufficient link between their objectives and the research design. The clear relationship then enabled a proper description of the findings to contribute to further understanding of the study’s objectives.Moreover, the critical evaluation of the study involved separation according to the type of research. The critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) checklists for appraisal were used for specific quantitative and qualitative analysis [14, 15].
Table 1 outlines the appraisal for the qualitative studies [16–20].All the studies met the criteria outlined in the 10 screening questions.
Table 2 highlights the critical appraisal for the RCT, whose CASP checklist is different from the checklists for non-randomized studies[21]. 11 questions helped to make sense of the systematic procedure used to complete the randomize control trial(RCT).

Figure 1 PRISMA flow diagram.PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.

Table 1 Critical appraisal of qualitative studies with critical appraisal skills programme qualitative studies checklist

Table 2 Critical appraisal of RCT using CASP randomized controlled trial checklist

Table 3 Critical appraisal of Cohort study using critical appraisal skills programme checklist
A different CASP checklist was used for the critical appraisal of the non-randomized quantitative studies[22–31].The CASP Cohort Study Checklist was used for the appraisal of the 10 studies that did not use randomization as outlined in Table 3.groups of HHC and the specific services offered by the nursing staff.Transitional care for elderly patients is vital for reducing readmissions. The nursing staff struggled with communication,decision-making challenges, and vague roles or responsibilities while offering care.The quality of the services offered to the patients shaped their experience with nurses and fostered their recovery. In general,qualitative studies confirmed the primary services of HHC nurses as transitional care and home care amidst different challenges in the process of offering care. The qualitative studies further clarified that elderly persons were the primary target groups for the HHC nurse services.
Synthesis of the results of RCT
One RCT was found from the 16 studies searched and selected from the search process. Fernández-Barrés et al. (2017) conducted a multicenter RCT of 6 months and made a follow-up of 12 months[21].The RCT further pursued an achievable objective that then helped to generate key topics for the review. The authors purposed to assess the effect of nutrition education programs for caregivers to curb malnutrition of dependent patients. The relevant topics from the analysis included the intervention of nutrition education and prevention of malnutrition provided by the HHC nursing staff.Additionally, it was evident that elderly persons aged 65 years or older were the target group for the intervention aimed to reduce susceptibility to malnutrition.
The chart further outlines a unique RCT that implemented the procedure well. The recruitment, randomization, blinding, and assignment to intervention and control were evident. The process met all the required parameters of an effective and replicable RCT. The nursing staff was the primary caregiver required to implement the home care program for preventing the risk of malnutrition among elderly persons aged 65 years or older. On the other hand, the follow-up period was important for defining the impact of the intervention in the long term while ascertaining the safety profile or hazards for outlining different interventions for elderly persons in home care settings.
The findings supported the objectives and questions developed for the review. The authors presented the nursing staff as primary providers of the HHC nursing services to elderly persons. The elderly persons were the target group for the HHC intervention comprising adaptation to solving the common cooking problem. The 6-months educational interventions ascertained the value of offering convenient and quality care to patients outside the primary care centers.
Synthesis of results of quantitative studies
The non-randomized quantitative studies relied on different methods and engaged participants with different sociodemographic data as outlined in the data extraction matrix. The studieswere published between 2017 and 2020 [22–31].
HHC nurse services were the highlight of the 10 studies despite varying in the data collection and analysis. The investigations found HHC nurses who undertook infection control and practices within the home environment for elderly patients. The service provision faced different enablers and barriers, such as organizational issues, home environment, relationships, and personal issues of the HHC nurses who participated in the survey.The services further included attention
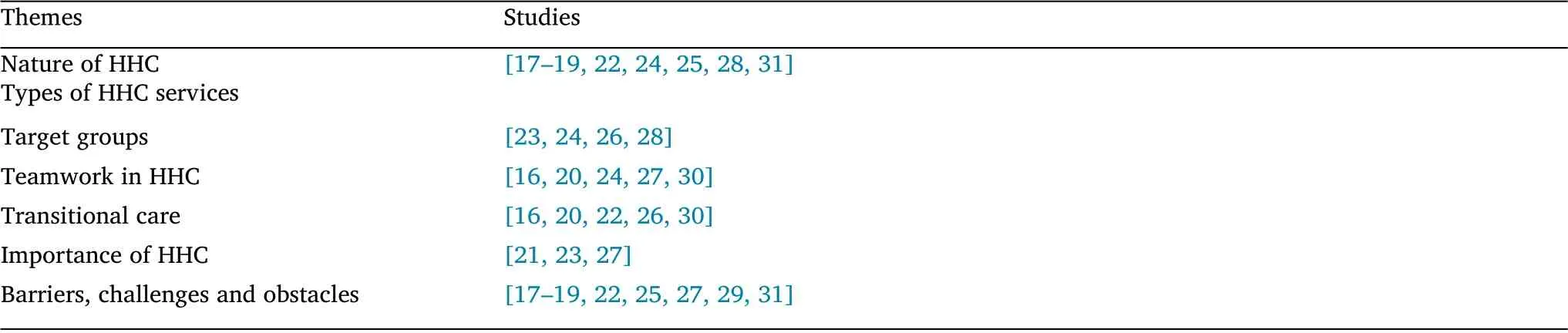
Table 4 Themes and respective studies
The non-randomized quantitative studies fulfilled the expectations of the CASP cohort study checklist further by providing clear and comprehensive results to answer their respective research questions.The high precision of the results of each study helped to answer the research questions and fulfill the objectives of the study.
Table 4 outlines the primary themes discussed by different authors after extracting data from the data extraction matrix.
Synthesis of the results of qualitative studies
The qualitative studies used different designs and were published between 2017 and 2020. The studies contained the most recent ideas and findings about HHC. The emerging themes from the qualitative studies were nature of HHC, types of HHC services, transitional care,challenges or barriers of offering HHC, relationships, and decision-making process in offering care to the patients and family. As outlined in Table 3, the nature of HHC discussed in the qualitative studies captured aspects such as relational care practices and invisible care services offered to different actors such as patients, family, and social-care workers. The actors delivered team-based care at home with elderly patients.
The studies further covered transitional care, where the primary actors were healthcare and social-care workers who shared a common understanding through team-based conversations.The clinical nursing staff worked with general physicians to offer uninterrupted chains of healthcare transfer and meet patients’ needs; it emerged that transitional care from hospital to home for elderly persons could reduce readmissions. The challenges or barriers of offering HHC to elderly patients were evident in the qualitative studies. The barriers included communication, trial and error work, uncertainty, trust,complex decision-making processes on care, and strained social relationships. The HHC nurses faced working relationship difficulties,information sharing, and vague definitions of their roles.Collaboration challenges between HHC nurses and other healthcare workers were reported.
The studies further pursued different objectives. One of the studies aimed to enhance knowledge and understanding of the nature of HHC practice, while another explored the varied perspectives of nurses on transitional care between hospital and home. Another study conducted among HHC nursing staff purposed to find the difficulties faced by HHC nurses during the interprofessional collaboration for delivering seamless patient care. The final study pursued the objective of finding the challenges of HHC and solutions for each challenge.
The authors in the qualitative studies outlined different results as outlined in the matrix. The results of qualitative studies considered HHC nursing staff as primary actors in the provision of invisible care practices. It was evident that nurses and physicians delivered transitional care between hospital and home while seeking commitment to patients’ needs or removing ambiguities and support.Issues arose in the provision of HHC,including collaboration,creating working relationships, and outlining specific responsibilities. The results further entailed strained relations, intricate decision-making,neglecting care, and communication barriers with family. It was evident from this systematic review that the nursing staff prioritized the needs of the elderly patients as they collaborated and made decisions in line with predefined standards.
The qualitative studies offer satisfactory outcomes on the target to the emotional needs of the patients in the home care settings assigned to registered nurses and their assistants.On the other hand,a Japanese context of HHC nurse services comprised community involvement activities and the response to the preferences of elderly patients needing end-of-life care. Another group of nurses dedicated their practice to the medication management process as part of the offering specialized HHC while maximizing the autonomy, integrity,and active participation of the patients. The studies agreed that home care nurses faced facilitators and barriers as they used symptom practice guides to manage the symptoms of cancer patients. The sub-themes demonstrated the effort by the HHC nurses to offer services that reduced the morbidity and mortality of the patients.
The sub-themes further entailed the nursing care needs for home-dwelling elderly persons. The nurses also used their skill set for skin and wound care, administering drugs, and solving eating difficulties. The nurses faced barriers and common facilitators such as system changes and guides for the nurses handling different symptom management guides. The provision of nursing services further meant using clinical practice guidelines to oversee the implementation of quality care. On the other hand, the nurses delivered their home care services through self-directed teams, which demonstrated their autonomy in the delivery of quality patient care to elderly persons.The role of the healthcare nurses administering care was to fulfill the needs of the patients with epilepsy despite the varied attitudes,practices, and knowledge. It was evident that HHC nurse services occurred within the home setting for the elderly persons living within the community.
The nature of the results varied due to the different forms of analysis undertaken by the authors. The analysis generated satisfactory outcomes on the various nursing services offered in the context of HHC to the various groups of elderly patients. The dominant form of analyses were descriptive statistics, hypothesis, and regression setting.The studies further relied on representative samples that enhanced the representativeness of the outcomes and the subsequent transferability to the various patients receiving care in home care settings. On the other hand, the analysis found a link between skilled nurses offering HHC and the recovery of elderly patients.The services reduced the cost of care and the readmissions in primary care settings. The ten non-randomized quantitative studies affirmed the demand for HHC for elderly persons in developing and developed healthcare systems.
Discussion
The analysis assisted in generating the HHC nursing services offered to different patients of different ages. The studies presented HHC as a multifaceted component with diverse impacts on patients and families. The analysis of the RCT revealed that HHC nurses’ services served elderly persons as the main target group. The qualitative, RCT and non-randomized quantitative studies highlighted the reality of HHC nurse services provided by nurses to different target groups.The nature of HHC nurse services entails relational care practices and invisible care services to the patients,families,and social workers.The actors adopt a team-based approach at home to deliver collaborative care to elderly patients. The city’s HHC services capitalized on the government’s incentive scheme and the wide demand for the utilization of home-based services by skilled nurses. The elderly Chinese adults received services on medical examinations and overall fitness. The outcomes further concur with the assertions of Persson et al. (2019) after analyzing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients requiring HHC [32]. Although the patient utilized the hospital-based HHC, they prevented the exacerbations and the complications leading to deaths for the elderly patients studied in the period.The findings reflect the overall value of the quality transitional care offered by the HHC nurses to the patients seeking urgent and sensitive care to their chronic emergency conditions as opposed to relying on hospital-based care exclusively.
The concept of transitional care was a prominent theme in the studies where the nurses, social care workers, and related healthcare practitioners deliver team-based care. Transitional care for elderly persons seeks to reduce readmissions and align with patient or family needs. The value of the transitional care model in HHC nursing services aligned with the findings of Rezapour-Nasrabad (2018) when they observed the definitive benefits of the framework executed by nurses or healthcare teams for elderly patients [33]. The review of studies found that transitional care delivered screening, overcome staffing gaps,built relations,and expedited the assessment of risks and symptoms. The transitional care nurses provide in HHC is an opportunity for education, continuity of care, and coordination of ideas to optimize patient experience, outcomes, and satisfaction. The concept of transitional care in HHC designates the effective role of nurses and other clinical practitioners hoping to deliver the best possible care to the patients at home as opposed to the hospital.
The scope of the HHC services further included medication management process for elderly patients. the non-randomized quantitative studies were effective in revealing how the medication process optimized patient outcomes. However, Dowding et al. (2020)do not consider medication management as the exclusive service offered to the patients by the HHC nurses[34].The services are a facet of identifying risks facing the patients, including infections, and the ultimate risk mitigation in home-based care settings. The present study and previous study concur on the infection prevention behaviors and subsequent adjustment of plan of care for the patients to accommodate pharmacological management. Consequently, Elliott et al. (2017) found the beneficial impact of nurses in home health settings presiding over the pharmacogenetic profiling of patients[35].The 50 or older adults rely on the best medication management to reduce hospitalizations and emergency department visits between the visits by the assigned physicians. However, the practice must align with the preferences of elderly patients seeking quality outcomes in home health settings.
The provision of HHC nurse services further encompasses symptom management issues. The services outside the hospital setting enable the HHC nurses to assist patients with terminal illnesses such as cancer to manage the complications. HHC nurses’ services seek to reduce morbidity and mortalities associated with chronic conditions,particularly for senior patients. The findings reflected the results of Murtaugh et al. (2016) when they noted that reporting symptoms for heart failure patients under HHC was important for curbing readmissions [36]. The symptoms management defines close coordination of the HHC with medical providers and the frequency of doctor visits.Comparatively,Werner et al.(2019)found from a cohort of 17 million hospitalizations that improper symptom identification reduced the patient’s chances at the nursing facilities[10].The nurses are part of the HHC team charged with coordinating effective and timely care to the patients discharged for HHC by their hospitals or physicians.
The nature of the services further entailed the provision of infection control practices within the preferred home environment. The infection and risk controls are an imperative part of the actions by the HHC was the focus of another analysis by Dowding et al. (2020) [34].The qualitative interviews of 50 HHC nurses revealed risk prediction was important for informing the nurses’ clinical judgment and modifying the care plan interventions for their patients. The risk control process in the home care setting helped in operationalizing response and informing the care in between the physician visits.However, risk prediction necessitates the identification of the patients and subsequent management of the risks, as it became evident in another analysis by Dowding et al. (2020). The qualitative interview of 50 nurses with varied experiences in the HHC nursing services revealed that infection control was imperative for the implementation and success of the care plan in mitigating risks of different patient groups.
The HHC nurse services execute different programs guided by the patient’s condition. It emerged from the RCT that the provision of nutrition education curbed malnutrition for dependent patients.According to Fernández-Barrés et al. (2017), nutrition education intervention was effective in preventing malnutrition.The nurses were skilled in overseeing proper protein intake and vitamins during the study period [21]. While the arguments emerged from a systematic review rather than primary studies, it emphasized the role of HHC nurses in using their experience to coordinate nutritional awareness and transitions for adults receiving HHC services. Bernocchi et al.(2017) consider nutrition as part of home-based rehabilitation for assisting older patients discharged for HHC to deal with chronic conditions such as obstructive pulmonary diseases or heart failure[37]. Consequently, the nutritional education services in HHC builds QOL and curb morbidity and mortalities.
Self-directed teams are essential for the success of HHC nursing services.The 16 studies analyzed in the review emphasize the value of teamwork in delivering care with ease, participative decision-making,and an autonomous approach to elderly patients. Current studies validate the findings from the review on self-directed teams dominating the execution of HHC nursing services for elderly patients.Sommerfeldt et al. (2022) established that interprofessional teams offering timely and quality services to older patients discharged for home care developed performative understandings [38]. The interpretation of findings from six individuals and 24 participants in two focus groups in senior homecare settings revealed the value of using interdisciplinary consultation and self-direction to harness the power,control,and minimize threats.The nurses and other healthcare practitioners managed the care process and provided the ultimate emotional and social support to the family members.Therefore, teams focus on navigating the complexities of HHC through professional diversity and management of care and emotions after the death of the patients.
The actors adopt a team-based approach at home to deliver collaborative care to elderly patients. The team approach described in the 16 studies aligned with the outcomes of Danielsen et al. (2018)when they conducted a qualitative analysis of home care nurses and general practitioners offering home-based palliative care[39]. The 19 Norwegian participants considered their teamwork as the tool for passing the batons to the families and coordinating the multifaceted care to the healthcare teams. The families needed the input of different professionals to handle and understand care for patients. On the other hand, the home care nurses and their collaboration with the general practitioners avoided new hospitalizations of patients with chronic conditions. The nurses provided the much-needed assessment and monitoring while the scheduled visits by specialists or physicians served the interests of the patients while minimizing conflicts in the execution of care.
The ultimate impact of the HHC nursing services was reducing the cost of care and readmissions to the primary care settings. The involvement of self-directed and autonomous teams with skilled nurses enhanced the recovery of elderly patients. Therefore, the success of the HHC in preventing costs and readmission rates in hospitals mitigates the high-risk patterns. The nurses’ and physicians’collaboration and self-direction minimize failures and gaps in the HHC nursing services.
The quality and safety of transitional care were evident in the studies. The qualitative analysis emphasized the need for delivering continuous healthcare services to elderly patients through HHC nurse services to reduce reliance on in-patient settings for intervention.Previous studies confirm the link between the quality and safety of transitional care offered by HHC nurses and related teams.Gonzalez-Jaramillo et al. (2020) established from another systematic review that using home-based care was effective in reducing costs and increasing hospital use in emergency cases [40]. The patients treated at home consumed lesser in-patient resources than the patients spending more time in the hospital. The transitional care provided to the discharged patients entails follow-up and consistent assessment of patients’ conditions by individual nurses or specialists in between the scheduled visits.
Contribution to the nursing practice
The review generated important findings that could change the nursing practice. The outcomes inform the nature of the transition from the hospital to the designated home care for elderly patients.Nurses should provide different nursing services to optimize the outcomes of the elderly patients recommended for home care by physicians. The services should comprise teamwork of relatives or family, social workers, and physicians for the scheduled visits. On the other hand, working in teams to provide transitional care in HHC context should be a priority for the nurses and managers. The effort should enable the nurses or teams to navigate the different complexities of HHC nursing services. Teamwork and constant collaboration among the nurses and other healthcare providers should prioritize issues of infections, organizational challenges, home environment,and communication challenges. Additionally, the nurses should work with other providers, including trial and error work,collaboration issues, information-sharing roles, and the vague nature of the roles during the scheduled visits by the doctors or physicians.Consequently, nurses will enhance the quality and performance of HHC nurses in enhancing the health and QOL of elderly patients.
Study limitations
The review shows limited studies on the topic of HHC nurse services for elderly patients.Authors have not exhausted the multifaceted topic of HHC to help in understanding its perspective well. The synthesis found 16 studies only after a comprehensive and focused search. The insufficient studies limit the volume of knowledge and awareness needed around HHC despite its importance.
The review requires more methodological rigor rather than relying on 16 publications to inform the assessment of home health care nurse services. The systematic review lacked the theoretical framework,reference, and analysis that could have given the qualitative synthesis a robust conceptual foundation. The gaps in the methodological rigor affected the quality of the research and findings reported on the services provided by the HHC.
The review presents a degree of reporting bias for relying on the expertise of one reviewer. One independent review undertook the complex process of searching, reviewing, screening, and selecting articles to inform the qualitative synthesis. Another review would have expedited faster organization and analysis of the information retrieved for the 16 articles to increase the overall accuracy of the systematic review. One review limited the methodological expertise and the evaluation of studies and methods for data extraction,synthesis, and reporting.
Using different study designs rather than relying on studies with one research design exposed the review to systematic and random errors.Proper review should consider all the potential sources of errors, such as selection bias, inadequate blinding in RCTs, and inconsistencies in clinical or statistical reporting.Consequently, the review relied on the qualitative synthesis of the review rather than considering the statistical significance of the results. The limitation affects the overall transferability of the outcomes to other HHCs in other locations or healthcare systems.
Recommendations
Nursing practice should maintain teamwork when providing HHC.The nurses should work with physicians, doctors, physiotherapists,counselors, families, nutritionists and social workers. The team delivers quality care and timely interventions. Multidisciplinary care should reduce readmissions and ultimate healthcare costs.
The national government should focus on expanding HHC services at the local level. The review demonstrates the value of the HHC in reducing the costs of hospital readmissions. The HHC should dedicate services to elderly patients. The implementation should eliminate the burden of care for the elderly population at the national level.
Academicians and scholars should study HHC more than they have done. The effort will popularize the practice to interested audiences,including governments seeking affordable and quality care. The studies could cover teamwork effects and value for other demographics other than elderly adults. The studies can clarify gaps found in the review further and contribute to the discourse on HHC comprehensively.
Conclusion
The assessment of the HHC nursing services provided to elderly patients reveals different facets of the healthcare process. The nurses work in teams with other healthcare professionals to deliver quality and effective care to elderly patients. Elderly patients are the primary target groups for HHC nursing services.The care reduces readmissions and cost of care. However, further studies could explore the provision of care to other target groups, such as middle-aged patients to understand the impact of the services.
The review further indicates the importance of teams in providing HHC nursing services. The qualitative synthesis reveals the value of using teamwork to expedite participative decision-making while maintaining the autonomy of the nurses in caring for home care patients. The team delivers timely and quality services by incorporating the different views on handling the care demands of the patients. Moreover, the studies agree on the maintenance of self-directed teams with the hope of exploiting different knowledge levels, attitudes, and different practices to enhance the satisfaction and experience of the HHC patients.Therefore,a team-based approach delivers quality and prompt care to the patients while preventing extreme complications of signs or symptoms before the scheduled visits by the specialists or physicians. Nurses work within healthcare teams to minimize conflicts about care.
The systematic review further illustrates the importance of HHC.The synthesis considers transitional care for elderly patients as the ultimate source of care for their different conditions.The care process by experienced nurses eliminates the burden for the family members while reducing the physical and emotional burden of dealing with complications. Additionally, the HHC nursing services reduce the cost of care and readmissions to the hospital, where the patients cannot receive as much as dedicated care they can get in HHC settings. The HHC nursing services prevent the readmission of elderly patients so that hospitals deal with other complex cases. Overall, the timely,quality, and safe care provided through the HHC nurses optimizes the outcomes of the patients, including their health and overall QOL after discharge.
The qualitative synthesis outlines the elderly patient as the primary target group for HHC care. While one of the studies mentioned cases of middle-aged persons, elderly adults featured prominently in the studies. Physicians recommend that elderly patients for the discharge in the hope of receiving care from nurses and dedicated teams of specialists. Elderly patients receive quality and timely services from the HHC teams of nurses,social workers,and physicians as they target recovery or effective management of a chronic condition. The effort reduces the chances of readmitting elderly adults and overcoming the high cost of care during hospitalizations. Elderly patients require the involvement of family members, besides nurses working with other practitioners to oversee infection control, symptom, and medication management.
The studies further reveal the challenges or obstacles of implementing HHC nurse services to elderly patients. The containment of the challenges is imperative for the nurses hoping to enhance experience and achieve a high satisfaction level of the patients. The key challenges include organizational conflicts,involvement of family members, working within culturally sensitive communities, and communication issues between the patients and the team. Issues of the complex decision-making process on care, strained social relationships, and working relationships may emerge to the extent of disrupting the provision of quality and safe care to elderly patients with sensitive healthcare conditions between the scheduled visits.
 Nursing Communications2022年13期
Nursing Communications2022年13期
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Delphi and Analytic hierarchy process for the construction of a risk assessment index system for post-stroke shoulder-hand syndrome
- A review of obstacles and facilitating factors of implementing Clinical Ladder Programs in nursing
- Spiritual health, empathy ability and their relationships with spiritual care perceptions among nursing students in China:A cross-sectional correlational study
- Qualitative study on influencing factors of refusal of gastric tube placement in stroke patients with dysphagia
- The influence of professional identity and ageism on turnover intention in nursing homes: a cross-sectional study from suzhou, China
- The relationship of family separation and nutrition status among under-five children: a cross-sectional study in Panti Public Health Center, Jember Regency of East Java, Indonesia
