Bibliometrics analysis of clinical decision support systems research in nursing
Lan-Fang Qin,Yi Zhu,Rui Wang,Xi-Ren Gao,Ping-Ping Chen,Chong-Bin Liu*
1School of Nursing, Huzhou University, Huzhou 313000, China. 2Department of Life Sciences and Health, School of Science and Engineering, Huzhou College,Huzhou 313000,China. 3Department of Nephrology,Huzhou First People's Hospital,Huzhou 313000,China.
Abstract Objective: Artificial intelligence (AI) has a big impact on healthcare now and in the future.Nurses play an important role in the medical field and will benefit greatly from this technology. AI‐Enabled Clinical Decision Support Systems have received a great deal of attention recently. Bibliometric analysis can offer an objective, systematic, and comprehensive analysis of a specific field with a vast background.However,no bibliometric analysis has investigated AI‐enabled clinical decision support systems research in nursing.The purpose of research to determine the characteristics of articles about the global performance and development of AI‐enabled clinical decision support systems research in nursing. Methods: In this study, the bibliometric approach was used to estimate the searched data on clinical decision support systems research in nursing from 2009 to 2022,and we also utilized CiteSpace and VOSviewer software to build visualizing maps to assess the contribution of different journals,authors,et al.,as well as to identify research hot spots and promising future trends in this research field. Result: From 2009 to 2022, a total of 2,159 publications were retrieved. The number of publications and citations on AI‐enabled clinical decision support systems research in nursing has increased obviously in recent years.However, they are understudied in the field of nursing and there is a compelling need to develop more high‐quality research. Conclusion: AI‐Enabled Nursing Decision Support System use in clinical practice is still in its early stages. These analyses and results hope to provide useful information and references for future research directions for researchers and nursing practitioners who use AI‐enabled clinical decision support systems.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; clinical decision support systems; nursing; bibliometric analysis
Background
The world has consistently undergone social, economic, political, and technical development, and artificial intelligence (AI) is one of them that is expected to alter society fundamentally. Since its birth in the 1950s, AI has been used to solve medical problems in the fields of medical management, clinical decision support, patient monitoring,and health intervention [1].
AI‐Enabled Clinical Decision Support Systems(CDSSs)are computer programs that make use of large amounts of data, expert knowledge,and analysis engines to produce patient‐specific evaluations and recommendations for healthcare providers as well as to support clinical decision‐making through human‐computer interaction. The application of CDSSs promises examples in many areas and has been widely discussed following the increased computer technology available [2–8].
Nursing is a profession that consists of five interconnected processes: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation [9]. The nursing process is a problem‐solving process in nursing practice that helps determine the needs of patients.At each of those steps, nurses are required to use critical thinking and clinical judgment to make complex decisions about patient care. In addition,the nursing process is a dynamic process and often requires multiple iterations as the patient’s condition changes. The use of the nursing process for continuous care designing implies that nurses are perpetually making choices. For every decision made, they are going through the four distinct stages of human information processing:information acquisition, information analysis, decision choice, and action implementation [9]. For example, to prevent falls, nurses should formulate care by collecting data about the patient’s history,physical and psychological state, and current practical status. Using this information, the nurse analyzes the patient’s risk for falls and chooses the foremost appropriate actions to ensure the best patient outcomes. CDSSs play a critical role in facilitating the nursing process by executing information acquisition, analysis, decision and action choice, and action implementation on behalf of nurses.
By providing individualized information support, nursing practitioners’ and managers’ work has become very simple and fairly accurate. Recently, many scientific articles have been published in the field of CDSSs in nursing, for example, pain management, fall prevention, pressure ulcer management, etc. [10–13]. It can help nurses improve the quality of care by providing individualized information,including medication safety,diagnostic test ordering,and reducing care costs. The use of information technology advances in nursing holds great promise for the profession. Therefore, these AI applications represented by CDSSs have unprecedented potential to manipulate virtually every aspect of nursing care, and we will soon see even more applications.
Bibliometric analysis has become a central component of research assessment,which can provide a general, quantitative,and qualitative overview of a specific topic with a vast background [14, 15]. Nursing researchers have been paying close attention to this strategy in recent years. It can help scholars understand the development trend of specific research fields and assess the contributions of journals,institutions, and countries in specific research fields. In particular, for the medical field,it can provide a basis for the development of clinical guidelines [16–18].
To the best of our knowledge, there is no bibliometric study and visualization map on the use of clinical decision support systems in nursing. To address this gap, the present study is the first comprehensive systematic study, attempting to determine the characteristics of articles about the worldwide performance and development of nursing clinical decision support system research,summarize the current achievements in this field, grasp its research directions and hot spots, and provide certain references for future research directions by utilizing a visualization tool. These analyses and results will assist researchers in having an in‐depth understanding of the research status and frontier trends in clinical decision support systems utilization in nursing, hoping to provide useful information and references for future publication interest and further investigation on this topic.
Materials and methods
Design
The bibliometric study aimed to map and investigate the scientific production of CDSSs utilization in nursing fields/professionals.
Data collection and search strategy
Data from the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI‐Expanded,1998–present) of the Web of Science Core Collection database(WoSCC) were accessed via Huzhou University Library. To have relevant research articles in the WoSCC database, the selection of publications was prudently made and executed on a single day, 10 April 2022, to dodge biases established by routine database updating.We employed an advanced search strategy of topic search, and the query was (topic: “clinical decision support system” or “decision support system” and “nursing” (MeSH terms) or “nurse*” (MeSH terms) and language (English) and document types (articles and reviews). A total of 2,159 records from 2009 to 2022 were identified from WoSCC, and those of the following types were excluded:“editorial material”, “meeting abstract”, “correction”, and “letter”.Two authors separately searched the WoSCC database for relevant literature and downloaded the relevant information (title, keyword,author information, abstract, publishing journal, reference, etc.) in TXT format. Any divergences were resolved by consultation or by seeking external experts to reach a consensus. A total of 2,130 different articles were eventually incorporated and imported into bibliometrics and transferred to CiteSpace and VOSviewer software for bibliometric analysis. The retrieval strategy and flow used in this survey are shown in Figure 1.
Analysis tool
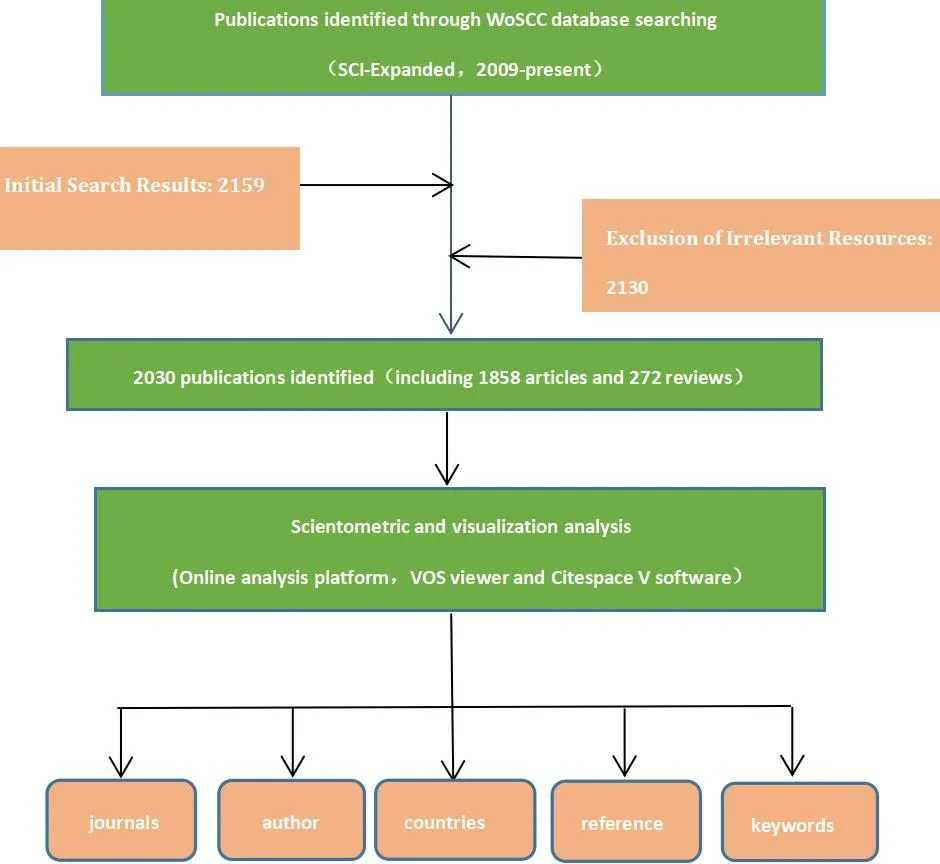
Figure 1 Flow chart of studies used in the analysis selection of articles and research design description
The exported data was imported into CiteSpace 5.8.R3, 64‐bit(Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, United States) and VOSviewer 1.6.16(Leiden University, Leiden, Netherlands) [19, 20, 21]. The bibliometric online analysis platform (http://bibliometric.com/) was used to identify co‐cited articles, journals, countries, and network characteristics of keywords Bursts and visually present the results.Before performing the co‐word analysis and document co‐citation analysis, we utilized CiteSpace’s “eliminating duplicates function”. As a result,the finished dataset had two duplicates.Using Microsoft Excel(version 16.46),a simple descriptive analysis was carried out (such as the number of publications per year, publications with the most citations, etc.). To calculate the distribution of academic journals and co‐cited academic journals, countries/regions, authors, keyword bursts and their trends, and co‐cited references were used by CiteSpace or VOSviewer. In this survey, we still used VOSviewer to produce density maps and visually investigate the co‐occurrence of terms. Keywords could be grouped into distinct clusters using co‐occurrence analysis in VOSviewer, where different colors designated the different clusters. A keyword co‐occurrence network can be used to display and discover development trends using cluster analysis of research hotspots.Results
Results
Analysis of publication characteristics and citation trends
Generally speaking, the number of publications and citations in a research field is a vital bellwether to assess the development trend,current situation, and prospects in related fields. In this study, Figure 2A shows an upward trend, and the related literature on CDSSs research in nursing can be roughly divided into three stages. The period 2009–2013 was the initial phase of the study. In the five years from 2014 to 2019 represented the second developmental stage; the yearly number of articles in this field increased steadily and was comparatively minor with the maximum being 209, which implies that the development of this field was relatively slow and had a lack of productive breakthroughs in this stage. However, from 2019 to 2021,publications on CDSSs research in nursing entered the third stage of development. The total number of publications was 840, and the average was roughly 261.6 per year. In addition, the most significant increase in output occurred between 2020 and 2021. Model fitting conducted a significant correlation between the publications per year and year (R2= 0.959); the number of publications will continue to rise in the following years (Figure 2B). The total number of citations also showed a modest upward trend (R2= 0.991) (Figure 2C).
Analysis of journals
Statistical analysis of journal distribution is helpful for scholars to quickly choose the best‐fit journals for publication of their research finding. All publications in this study came from 129 different journals. Table 1 shows the top ten most productive journals. They could be the foundational journals that scientific scholars in this field have eagerly awaited. The journal ofJournal of Medical Internet Research(n = 36, IF 2021 = 5.428) had the highest impact factor among the top 10 journals,with more than 35 articles,followed by theJournal of the American Medical Informatics Association(n = 51, IF 2021 = 4.497).Plos onewas the most productive journal (98 publications), followed by the journal ofInternational Journal ofMedical Informatics(68 publications) andCIN Computers Informatics Nursing(58 publications) (Figure 3A). The citation network map showed that 20 publications had more than 155 citations (Figure 3B).
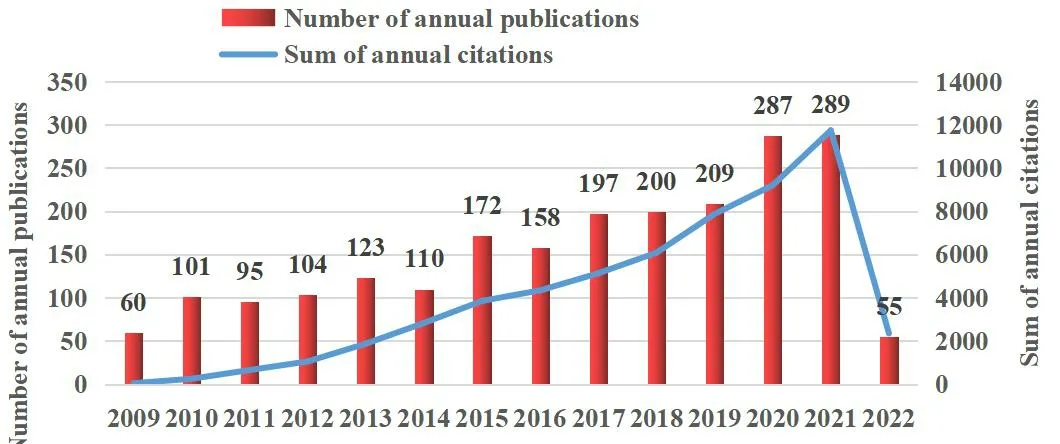
Figure 2A Distribution of publications from 2009 to 2022

Figure 2B Publications trend prediction

Figure 2C Publication citations trend prediction
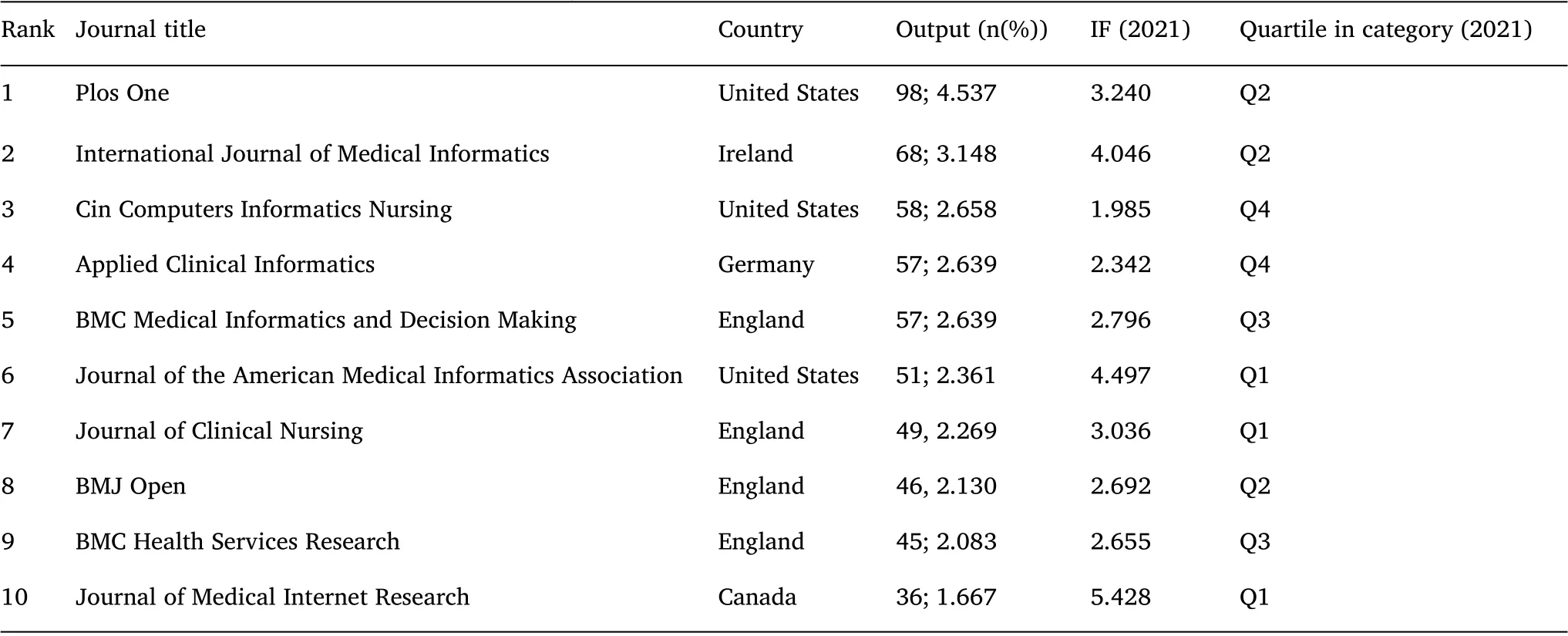
Table1 Top 10 journals in terms of publications from 2009 to 2022
Analysis of authors
The number of publications appraised the impactful authors.A total of 339 authors contributed to the study.The twenty most prolific authors in this field are listed in Figure 4A. The most productive authors were David W, Gagnon, and Legare, France. They each contributed 17 papers, followed by Carron,Pascale (13 articles), and Cho, insook (13 articles). In this study, VOSviewer was used to visualize authors who had at least five publications,as shown in Figure 4B.Each node on the graph represented a different author. The size of the circle reflected the number of articles produced by the researcher. The lines linking the circles showed the collaboration of the authors; the thicker the line, the tighter the cooperation of the authors. Visualization analysis results showed that there was little collaboration among these authors(Figure 4B).
Analysis of countries
Generally speaking, data analysis of countries/regions can identify which countries and locations have more influence and the best research foundation in this area. The publications on CDSSs nursing research came from 55 different countries. Figure 5A depicts the top ten countries that have significantly contributed to the field’s progress.The United States was placed first out of 2,130 articles, with 1,140 articles contributing 53.52 percent of the total. With 292 papers,Canada ranked second, accounting for 13.7 percent of all research on the topic. With 270 articles, England ranked third (12.67 percent).Australia was fourth with 12.62 percent. The rest of the contributions are depicted in Figure 5A. We also constructed the country’s collaboration network map involved in this research (Figure 5B). The network map also reflected the state of research activities and communication between different countries/regions.The visualization map showed the partnership between countries. The USA was the most collaborative country with the highest link to South Korea. It could also be reasoned that USA researchers produced most of the documents (as per color code), and their cooperation network spread widely at the international level.

Figure 3A The top 10 journal analysis related to CDSSs research in nursing.CDSSs, clinical decision support systems.

Figure3BJournalscitationanalysiswasperformedwithVOSviewer

Figure 4A The top 20 authors analyses related to CDSS research in nursing.CDSS, clinical decision support system.

Figure 4B Authors analysis was performed with VOSviewer

Figure 5A The top 10 countries analysis related to CDSSs research in nursing.CDSSs, clinical decision support systems.

Figure 5B Countries analysis was performed with VOSviewer
Analysis of references
The co‐citation reference indicates the authority of the field and the writer’s significant contributions. This survey used CiteSpace to build the network of co‐cited references, resulting in a broad perspective on CDSSs research in nursing. Figure 6A displays the visual network of the citation analysis of publications on CDSSs research in nursing. A cited article was represented by each node. The links between the nodes represented the number of times the same article was cited.These references, which were shown in the network map, were cited more than 9 times, with the top two receiving more than 20 citations each. For readability purposes, the information in Figure 6A was illustrated in Table 2 below, and the top 10 citation analysis of publications on CDSSs research in nursing were displayed. The top 10 most cited original articles related to CDSSs research in nursing are given in Table 2.
An approach to data viewing that combines time slicing and clustering algorithms is called timeline view. This study aimed to assess the structure and development path of research subjects in this discipline. CiteSpace was used to produce a co‐word timeline view.Notably,as illustrated in Figure 6B,each cluster consisted of papers on similar topics. Cluster #0 computerized and #7 nutritional support,and #12 smartphone were mainly included in the early time, and cluster #3 machine learning, #4 nursing information, #11 alert fatigue, and #14 Palliative care appeared in recent times. These data displayed the research hot spots and trends in recent years.
Analysis of keywords
The keywords with the highest co‐occurrence frequency and strongest citation bursts may represent hot topics within the research field. The top 25 keywords with the strongest citation bursts were captured in this survey using CiteSpace and shown in Figure 7A. A blue line displayed the time interval, whereas the burst period was illustrated by a red reflective line, which also showed the beginning and ending years as well as the burst period. To concentrate on terms that indicated the trends of CDSSs research in nursing,keywords with little to no research significance were removed. As shown in Figure 7A, in the beginning, studies in this domain focused on “clinical decision support”, “performance”, “medical errors” and “adverse drug events”.From 2014 to 2018, the research focus shifted to “elderly patients”,“alerts”, “shared decision‐making”, “electronic health records” and“physical activity”. Following 2018, the following keywords had strong bursts: “delivery” (2018–2019) and “epidemiology”(2019–2020). After 2020, the keywords were “strategy”, “challenge”and“burden”.In this case,219 keywords were identified as appearing more than 15 times, and the whole counting method was used to generate the network visualization map (Figure 7B) and overlay(Figure 7C). During the period 2004–2022, “care” had the highest burststrength,followedby“management”,“impact”,“implementation” and “quality”, indicating that the study focus had shifted to finding solutions to these perplexing issues. Furthermore,VOSviewer could calculate the density of the keywords based on their frequency, which could be exhibited as a graph (Figure 7D). The warmer the color (toward yellow), the higher the density. Research hot spots in this field tended to be found in regions with larger grayscale levels.

Figure 6A CiteSpace visualization map shows the co-occurrence network of co-cited references

Figure 6B References Timeline view was performed with citespace

Table 2 The top 10 references analysis related to CDSSs research in nursing.CDSSs, clinical decision support systems.

Figure 7A The top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts from 2009 to 2022
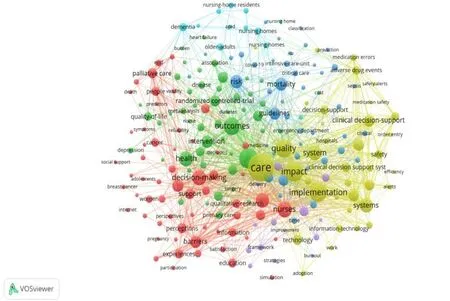
Figure 7B The network visualization map of the keywords by using VOSviewer software

Figure 7C The overlay visualization map of the keywords by using VOSviewer software

Figure 7D A density visualization map was performed with VOSviewer
Discussion
Innovation and science of research methods
This paper is, to our knowledge, the first attempt to reveal the knowledge maps of global scientific publications related to CDSSs research in nursing from 2009 to 2022 by employing a scientometric analysis. We provided details for the research output by year, country of output, country and author‐wise international collaboration patterns, essential keywords, and a frequency visualization of those keywords.This methodological approach also provides information on the degree of maturity or saturation of the subject matter under study,where research is heading, and whose areas have not yet been addressed.
Journals analysis of CDSSs research in nursing Number of publications distributed.
In the 1970s, clinical nursing practice started to be incorporated in this system. Articles on the subject were published in 2009. Based on the data coming from the annual number frequency of publications and citations (Figure 2A–Figure 2C), this article reports that the number of CDSSs research in nursing has increased yearly. In the initial stage, from 2003 to 2010, most studies focused on chronic disease management [22–24]. Research finds that CDSSs can benefit nurses and allied health professionals in terms of performance and patient outcomes. However, The quality of this study phase was poor and lacked the necessary implementation details. In the second stage,from 2011 onwards in this field, the annual number of publications increased steadily and reached 172 papers for the first time in 2015.In the third stage, from 2016 to 2022, particular interest in the latter period has been researched on the impact of focusing on barriers during implementation [25, 26]. Research shows a shift from exploratory research to specific clinical practice, The possible problems involved in the introduction and construction use are discussed [25, 27, 28]. At the same time, the analysis shows they are understudied in the nursing field, and there is a compelling need to develop more high‐quality research.
characteristics of publications
So far, Clarivate has published the latest impact factors for a total of 182 journals(SCIE edition)in the nursing field.In our study,a total of 129 journals published research on CDSSs in nursing. Journals with a high frequency of publication of related literature provide researchers with publication guidelines for documents. In this study, as journal network map (Figure 3B ) and Table 1 show thatPlos one(United States) ranks first in terms of total publications, followed byInternational Journal of Medical Informatics(Ireland)andCIN Computers Informatics Nursing(United States), indicating that these journals are particularly interested in articles regarding CDSSs research in nursing.These data will help future scientists in select journals when submitting CDSSs‐related manuscripts. However, journals with various categories also rank higher in this study,such asThe Journal of Clinical Nursing,BMJ open,andBMC Health Services Research. This finding explains that CDSSs research in nursing is not restricted to one specific academic field and that journals with wider and various readerships can also publish research on CDSSs research in nursing.
Authors’analysis of CDSSs research in nursing
The number of publications appraised the impactful authors.Based on the data coming from individual publications David W,Legare,France and Gagnon have the highest number of individual publications, and all make significant contributions to the progression of CDSSs research in nursing. In addition, studies by Legare, France, Stacey, and dawn have the highest average number of citations, indicating that these authors publish high‐quality research in this field. Moreover, the developed country has an overwhelming impact in this field since most authors are from the USA, Australia, and Canada. However, we found that the network structure was looser, and there were fewer relationships among authors who belonged to different countries.Collaboration between researchers from different institutions and countries should be encouraged to promote the coordinated development of international scientific research in this field.
Countries analysis of CDSSs research in nursing
Regarding the country distribution (Figure 5A, Figure 5B), among the top 10 countries, we found that the USA and Canada are the major players in this field of study. The USA has contributed the most in publications, indicating that the USA is particularly influential in this field of CDSSs research in nursing. Developed countries with a higher GDP and abundant research institutions compared to other countries enable them to create high‐caliber articles. In terms of the international cooperation network, China, Rwanda, and Pakistan are found to collaborate with other nations to a lesser level. This may account for their low ranking in terms of the number of citations.China, Rwanda, and Pakistan should increase their international cooperation in order to spread publications of a higher caliber.However, the accuracy of the analysis about various countries is somewhat impacted by the fact that this research is mostly focused on the English publications of WoSCC.
Key themes evolution analysis of CDSSs research in nursing
In this study, the idea behind the reference co‐citation analysis can provide us with a wealth of helpful information,allowing us to gain a better understanding of the evolution of the knowledge structure relating to CDSSs research in nursing. As Figure 6A, Figure 6B and Table 2 show that most of the top 10 citation references are focused on the exploration from theory to clinical practice of CDSSs and the impact of CDSSs on the quality and costs of medical care. The co‐cited references represent the frequency of two publications being cited together by other publications. The more often a piece of literature is cited, the more significant it is perceived in a certain field. As shown in Table 2,the co‐cited references are mainly from top‐ranked journals and are mostly composed of reviews on the effect of CDSSs in clinical practice. That is to say, although Many studies have shown benefits,the effect remains controversial, and more high‐quality studies are needed to provide evidence [29, 30]. What aspects of CDSSs can be used to bring greater benefits to patients is the direction of future research.
Research hot spots analysis of CDSSs research in nursing
Keyword co‐occurrence analysis provides insight into the distribution and evolution of various research hot spots and future frontiers within a certain field. As for the analysis of the evolution of the subject matter,a set of topics that have been researched in a related way over time and that form part of the main driving theme of each period analyzed is evident. These form the main core of the research on CDSSs in the field of nursing and revolve around “care”,“management”, “impact”, “implementation”, “outcomes” and“quality”. The analysis of the literature that has investigated CDSSs in the nursing field, the results unequivocally suggests that the most prolific and centralized line of research over time has been that which has analyzed CDSSs clinical utilization research. These have focused mainly on aspects related to wound management, predicting risk of infection, blood glucose control, blood coagulation management,obesity screening,fall and pressure ulcer prevention and management,Intelligent Reminding and alerting in the latter period has been researching on the impact of focusing on barriers/challenges during implementation [25, 26, 29, 31–38]. Research suggests a shift from clinical research to exploratory practice. The possible problems involved in the introduction and use of practice are discussed [25,27,28]. The analysis shows that the challenge and burdens encountered by CDSSs in clinical practice and the strategies to cope with them are current research hotspots.
Future prospects and challenges for CDSSs in nursing
Throughout the past several decades, CDSSs have been beneficial to many sectors of the healthcare industry [39–43]. Nursing informatics is a new interdisciplinary subject. With the advent of the big data age,information technology may offer benefits in nursing areas. The savings from using big data in health care are estimated to be in the billions per year in the United States due to waste reduction and improved outcomes [44]. In this context, CDSSs are a useful tool for providing good clinical care. Studies have shown that using CDSSs in clinical settings can enhance the quality of care and provide solid evidence to support evidence‐based practice [39, 42, 45, 46]. We will see more and more applications in the near future.
Research shows that the first challenge that must be addressed is the availability of high‐quality data that can be readily captured and accessible and can be integrated into the clinical process.The complex nature of medical data makes data quality problems more evident because missing, incorrect, or vague information may lead to useless or even harmful results [26, 47]. Before CDSSs are considered for implementation, a deep understanding of the clinical workflow and care delivery process is the key to these systems for clinical practice.
We find the second challenge about implementing CDSSs in our study. The legal and regulatory challenges are facing AI‐based decision support tools. Legal problems have plagued decision support systems for many years, and the lack of case law involving medical AI makes the navigation of medical liability complex. Moreover, many medical workers are concerned about the level of patient safety and their legal responsibility for diagnostic errors made by AI [48]. As a result, ambiguous malpractice liability policies may remain a significant barrier to adopting AI into routine practice.
Thirdly, we recommend training and educating the current and future nurse workforce and leadership to become proficient adopters of AI‐based CDSSs and to stimulate and expand. AI tools will potentially transform our practice by leveraging massive amounts of data to personalize care to the right patient, in the right amount, at the right time.
Conclusions
Based on the bibliometric analysis, this study provides an objective,systematic, and comprehensive analysis of the global status and research frontiers of studies investigating CDSSs research in nursing.The results of this research have highlighted the lack of studies. The research focuses on developed countries in Europe and America and relatively few other countries. However, we found that the network structure was looser, and there were fewer relationships among authors who belonged to different countries. Collaboration between researchers from different institutions and countries should be encouraged to promote the coordinated development of international scientific research in this field. What aspects of CDSSs can be used to bring greater benefits to patients is the direction of future research.The challenges encountered by clinical decision support systems in clinical practice and strategies to address them are current research hotspots, which provide some guidance and reference for researchers and clinicians engaged in CDSSs research in nursing.
Limitation of this study
There are some limits to this study.First,the literature included in our study may not be exhaustive. The analysis of this study is only based on publications in the WoSCC (SCIE) database. Although this collection includes most of the research publications in this field,other databases, such as PubMed, Embase, and Scopus, may provide broader coverage. Besides, variation in the continuously updated database may lead to discrepancies between the search results and the actual number of included publications.What is more,the omission of books/chapters/letters and the consideration of articles published in English only may lead to some bias in the analysis.
 Nursing Communications2022年13期
Nursing Communications2022年13期
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Nurses’ knowledge and skills concerning cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a descriptive study
- Surgical operation of a massive retroperitoneal tumor
- Progress in the application of Meleis transition theory in the nursing field
- Importance of teamwork communication in nursing practice
- From the perspective of traditional Chinese medicine nursing in the context of COVID-19
- Surgical first aid and nursing care of a parturient with massive hemorrhage in natural delivery
