Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy of Liqi Huoxue drop pill in the treatment of angina pectoris in coronary artery disease
HAN Yi, HAN Yu-bo, ZOU Guo-liang, SUI Yan-bo, DONG Xin-yu, LIU Li✉
1. Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, China
2. The First Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
Coronary artery disease is short for coronary heart disease, also known as ischemic heart disease, and is clinically divided into five types, namely asymptomatic, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction,ischemic cardiomyopathy and sudden death, among which the coronary angina pectoris type is more common. The pathological mechanism of coronary angina is atherosclerosis or the formation of plaque in the inner wall of blood vessels, which leads to luminal narrowing or blood rheology changes, resulting in impaired coronary circulation, which in turn affects the blood supply to cardiomyocytes. The main clinical symptoms of coronary angina are chest discomfort or posterior sternal paroxysmal pressure during episodes that affect patients' quality of life, and in severe cases,myocardial infarction or even life-threatening [1]. Coronary angina has been one of the major causes of death in China. The index of suffering from coronary angina in China has increased significantly compared to previous years, mainly due to the dramatic deterioration of the prevalence of coronary angina-causing risk factors such as hypertensive disease, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes[2]. At present, the clinic mainly adopts a comprehensive program of anticoagulation,cardiac strengthening, vasodilatation, and lipid regulation[3], and conventional Western medicine treatment can be effective, but also has certain toxic side effects, while Chinese medicine has little side effects and significant therapeutic effects, which provides a new treatment idea for the clinic.
Chinese medicine is often used as a supplement and alternative to Western medicine in the treatment of coronary angina, and the combination of Chinese and Western medicine can improve the efficacy of coronary angina treatment, reduce the incidence of coronary angina, and avoid the adverse reactions and side effects of Western medicine treatment. It is a new Chinese medicine developed by China for the treatment of angina pectoris in coronary heart disease, and it is a proprietary Chinese medicine preparation based on Chinese medicine theory and modern preparation technology. It consists of four Chinese herbal medicines, namely, Daguomujiangzi,Bingqi (natural ice chips), Chuanxiong and Allium, which have the effects of broadening the chest and dispersing knots, regulating Qi and activating blood flow [4]. There have been a certain number of RCT trials on the combination of Li qi huo xue dropping pills with western medicine on angina pectoris in coronary heart disease, but evidence from evidence-based medicine is still lacking. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of combining Li qi huo xue dropping pills with western drugs in the treatment of angina pectoris in coronary heart disease, with the aim of providing evidencebased medical evidence for the clinical application of Li qi huo xue dropping pills in the treatment of angina pectoris in coronary heart disease. Because there are few clinical randomized controlled trials on the combination of Li qi huo xue dropping pills with Western medicine for the treatment of angina pectoris in coronary heart disease, a more convincing subgroup analysis of outcome indicators could not be performed, so only Meta-analysis of relevant indicators was performed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Literature search strategy
Search by computer in Chinese databases (CNKI, VIP, WanFang Data and CBM) with"理气活血滴丸","心绞痛","冠心病","冠心病心绞痛","胸痹", etc.In English databases (PubMed,Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library) with "Lifting qi and activating blood drop pills", "Li qi huo xue dropping pills", and "Coronary heart disease", "CHD", "angina pectoris", "random control trial", etc.The search was conducted using a combination of subject terms and free words. For PubMed, for example, see Box 1 for the specific search strategy.Box 1 PubMed search strategy
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.2.1 Study type
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) of Li qi huo xue drop pill for the treatment of angina pectoris in coronary artery disease, with no restrictions on the publisher's rank or region and restrictions on language to Chinese or English only.
2.2.2 Research subjectsThe subjects included in the study must be patients diagnosed with coronary angina, and the diagnostic criteria were referred to the relevant diagnostic criteria for coronary angina in Nomenclature and diagnostic criteria of ischemic heart disease [5].
2.2.3 Interventions
Control group: conventional Western medical treatment with unlimited types, doses and courses of Western medicine.
Intervention group: Combined with the Li qi huo xue drop pill on the basis of the control group.
2.2.4 Ending indicators
① clinical efficacy, ②efficacy of angina symptoms, ③number of angina attacks, ④serum inflammatory index interleukin-6 (IL-6),⑤serum interleukin-18 (IL-18), ⑥high-sensitivity C-reactive protein(hs-CRP), ⑦endothelial function index nitric oxide (NO)
2.2.5 Exclusion criteria
①literature in which the type of study was animal experiments or pharmacological studies;②literature in which severe cardiac, hepatic,or renal insufficiency and drug allergy were combined;③literature in which the control and treatment groups included acupuncture,surgery, or other treatment modalities;④literature with obvious data errors;⑤literature with missing data;⑥literature in languages other than Chinese or English;⑦iterature with duplicate publications;⑧literature that has not been published.
2.3 Risk of bias evaluation of included studies
The included clinical randomized controlled studies were assessed for "risk of bias" using the "risk of bias assessment" tool recommended in the Cochrane 5.1.0 manual. The assessment was based on random sequence generation, allocation concealment,blinding of patients and participants, blinding of outcome assessors,completeness of outcome data, selective reporting, and other biases.Two investigators gave low risk, unclear, or high risk assessments for the included as-randomized controlled trials, and the two cross-checked their respective results after completion. If the two investigators disagreed with the results, they were referred to a third person for risk of bias assessment.
2.4 Statistical treatment
Meta-analysis of the included literature data was performed using RevMan 5.4 software provided by the Cochrane Collaboration Network. Measured variables (continuous variables) Weighted mean difference (WMD) was used as a statistic when the same intervention was measured by the same method or unit, otherwise, standard mean difference (SMD) was used as a statistic. The relative riskiness (RR)of the count variable was used as an effect size analysis statistic.Heterogeneity in the included studies was determined using the χ2test (detectionlevela= 0.1). When P≥0.1 and I2≤50%, the heterogeneity of the study data was low and a fixed-effects model should be used; when P < 0.1 and I2> 50%, it indicated that there was significant heterogeneity in the study data and a heterogeneous random-effects model should be used and the source of heterogeneity should be further analyzed. If significant clinical heterogeneity was present, subgroup analysis was performed. If clinical heterogeneity was evident but subgroup analysis could not be performed, Metaanalysis could not be performed and only descriptive analysis could be used. When the number of primary data indicators in the included studies was greater than 10, funnel plots should be used to assess publication bias.
3. Results
3.1 Literature screening process and results
Based on the above search criteria, a total of 87 relevant papers were obtained. The full text was carefully read and screened according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and only 9 papers met the inclusion criteria [6-14]. The observation group was treated with the combination of Western medicine using the Li qi huo xue drop pill and included 491 patients. The control group was treated with conventional Western medicine only and included a total of 491 patients. The literature screening process is shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Quality evaluation results of the included studies
Regarding the method of random assignment, one study was high risk [8]and randomized by time of visit, hospitalization number,and clinical treatment intention method. seven studies mentioned randomization only and did not specify the random assignment scheme [6,9-14]. one study was low risk [7] and reported specific random grouping methods, including random number table methodassignment. The random assignment scheme was concealed, and aspects of blinding and other sources of bias were unclear, resulting in low risk for both data completeness and selective reporting. The results of the risk of bias assessment for the included studies are shown in Figure 2.

Tab1 Basic information of literature included

Fig1 Flowchart of literature screening

Fig2 Risk of bias of literature included
3.3 Meta-analysis results
3.3.1 Clinical efficacyFive clinical randomized controlled trials reporting clinical efficacy were included [6-10], as shown. Each study was homogeneous(P=0.90; I2=0%). Statistical analyses were performed using homogeneity fixed-effects models. The RR and 95% CI for clinical efficacy were RR = 1.20 and 95% CI = [(1.12, 1.29) P<0.000 01];the results showed that the intervention group had better clinical efficacy than the control group, and the difference was statistically significant. (Figure 3)

Fig3 Forest plot of clinical efficacy of angina in coronary heart disease between intervention and control group
3.3.2 Efficacy of angina pectoris symptomsThree clinical randomized controlled trials reporting the efficacy of angina symptoms were included [11-13], as shown. Each study was homogeneous (P=0.85; I2=0%). Statistical analyses were performed using a homogeneous fixed effects model. The RR and 95% CI for angina symptom efficacy were RR = 1.17 and 95% CI = [(1.07, 1.29)P = 0.001]; the results showed that the intervention group had better angina symptom efficacy than the control group, and the difference was statistically significant. (Figure 4)
3.3.3 Number of angina attacks
The number of angina episodes reported by the 3 clinical randomized controlled trials [8,13,14] was included, as shown. Each study was heterogeneous (P<0.000 01; I2=97%). Statistical analysis was performed using a heterogeneous random-effects model. for the number of angina attacks [SMD= -2.26, 95% CI (-4.10,-0.42),P=0.002]; the results showed that the number of angina attacks was lower in the intervention group than in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant. (Figure 5)
3.3.4 Serum inflammatory indicator interleukin-6 ( IL-6)
Four clinical randomized controlled trials reporting interleukin-6 were included [6,9,11], as shown. Each study was heterogeneous(P=0.11; I2=55%). Statistical analysis was performed using a heterogeneous random effects model. The [MD= -4.65, 95% CI(-6.91,-2.39), P<0.000 1] for interleukin-6; the results showed that interleukin-6 was lower in the intervention group than in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant. (Figure 6)
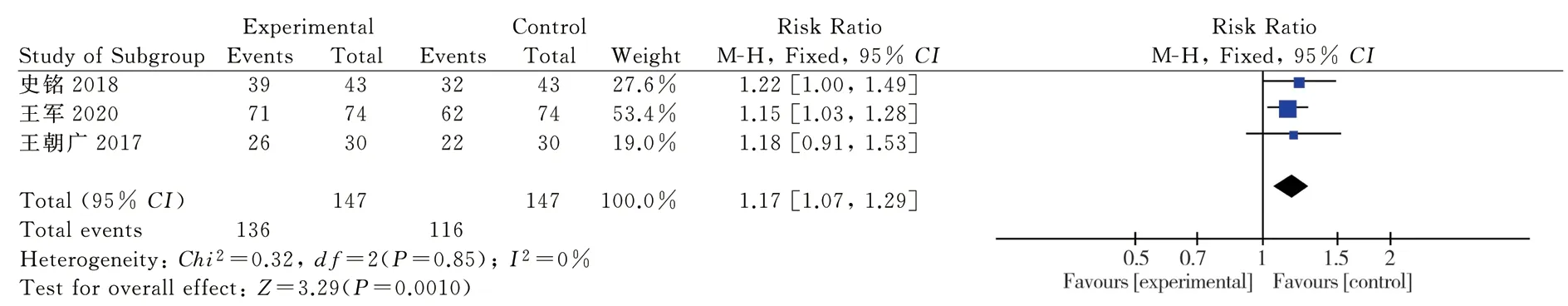
Fig4 Forest plot of clinical efficacy of angina in coronary heart disease between intervention and control group
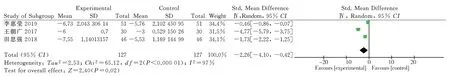
Fig5 Forest plot of angina attacks in coroary heart disease of both groups

Fig6 Forest plot of IL-6 comparison of angina in coronary heart disease of both groups
3.3.5 Serum inflammatory indicator interleukin-18 ( IL-18)
Interleukin-18 reported in 3 clinical randomized controlled trials were included [9,10,12], as shown. Each study was homogeneous(P=0.23; I2=32%). Statistical analysis was performed using a homogeneity fixed-effects model. Interleukin-18 of [MD=-2.53, 95%CI (-2.84,-2.22), P<0.000 01]; the results showed that interleukin-18 was lower in the intervention group than in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant. (Figure 7)

Fig7 Forest plot of IL-8 comparison of angina in coronary heart disease of both groups
3.3.6 High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (HS-CRP)
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein reported in four clinical randomized controlled trials [6,9,11,14] was included, as shown. Each study was heterogeneous (P=0.31; I2=55%). Statistical analysis was performed using a heterogeneous random effects model. The[MD=-0.08, 95% CI (1.81,-0.75), P<0.000 01] for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; the results showed that the intervention group had lower high-sensitivity C-reactive protein than the control group, and the difference was statistically significant. (Figure 8)
3.3.7 Endothelial function indicator nitric oxide (NO)
Three clinical randomized controlled trials reporting on endothelial function indicators of nitric oxide were included[8,11,14], as shown.Each study was heterogeneous (P<0.000 01; I2=96%). Statistical analysis was performed using a heterogeneous random effects model. for the endothelial function index nitric oxide [MD= 8.03,95% CI (0.93,15.14), P=0.03]; the results showed that the endothelial function index nitric oxide was higher in the intervention group than in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant.(Figure 9)

Fig8 Forest plot of Hs-CRP comparison of angina in coronary heart disease of both groups
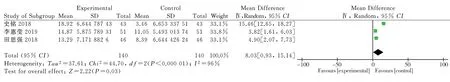
Fig9 Forest plot of NO comparison of angina in coronary heart disease of both groups
3.3.8 Adverse drug reactionsIn one study, there was one case of headache and dizziness, three cases of gastrointestinal discomfort, and one case of rash in the control group; in the intervention group, there were two cases of headache and dizziness and five cases of gastrointestinal discomfort;in one study, there were two cases of vomiting, three cases of abdominal pain, and two cases of rash in the control group; and in the intervention group, there were two cases of epigastric discomfort and one case of rash. (Table 2)

Tab2 Adverse reaction events of the drug used
3.3.9 Sensitivity analysis
All the outcome indicators included in the study were ranked one by one to find the source of heterogeneity. When sensitivity analysis was performed on the indicator IL-6, it was found that excluding the study of Shi Ming et al [11], heterogeneity was reduced (P<0.000 01, I²=0%), and the results showed that IL-6 was significantly lower in the intervention group than in the control group [MD= -5.82,95% CI (-6.92,-4.71), P<0.000 01]. When sensitivity analysis was performed on the index IL-18, a reduced heterogeneity (P<0.000 01,I²=0%) was found excluding the study of Weng Jiao et al [9], which showed that IL-18 was lower in the intervention group than in the control group [MD= -2.66, 95% CI (-3.01,-2.31), P<0.000 01]. When sensitivity analysis was performed on the index HS-CRP, a reduction in heterogeneity (P<0.000 01, I²=0%) was found excluding the study of Li Yan et al [6], which showed that HS-CRP in the intervention group was lower than in the control group [MD=-1.53, 95% CI(-1.93,-1.14) , P<0.000 01]. When sensitivity analysis was performed on this indicator of NO, it was found that excluding the study of Shi Ming et al [11], heterogeneity was reduced (P<0.000 01, I²= 0%),and the results showed that NO was higher in the intervention group than in the control group [MD=4.23, 95% CI (2.49,5.97), P<0.000 01]. The final results were not significantly different from those before the exclusion of heterogeneous sources. When analyzing the heterogeneity of other indicators, the heterogeneity did not vary significantly and is not listed. The results of the heterogeneity analysis indicate that the results of this study are relatively stable and have reference value.
3.3.9 Publication bias
Because of the small number of studies included for individual outcome indicators, this study was not tested for publication bias.
4. Discussion
In recent years, the incidence of coronary angina has increased significantly in China. The symptoms of clinical patients during attacks are no longer limited to pain in the anterior region of the heart, but have even seriously affected their psychological status and quality of life. At present, the drugs commonly used clinically for the treatment of coronary angina are mainly western drugs such as nitroglycerin, beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers. However,the long-term use of these western drugs may cause side effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding, slow heart rate or low blood pressure,and the long-term efficacy is not satisfactory. Therefore, there is a great need to find a treatment option for angina pectoris with few side effects and significant efficacy.
Angina pectoris in coronary artery disease belongs to the category of "chest paralysis" in Chinese medicine. According to Chinese medicine, "chest paralysis" is mainly due to deficiency of qi and blood and blood stasis blocking the heart arteries. The pathogenesis of pain in the anterior region of the heart is due to deficiency of qi,blood, yin and yang in the body, and phlegm, cold, qi stagnation and blood stasis blocking the heart arteries and channels, resulting in"pain when it does not pass". The effect of Li qi huo xue dropping pill is to benefit Qi, warm Yang, activate blood circulation and remove blood stasis, which can effectively reduce the clinical symptoms of patients. The main ingredient of Li qi huo xue dropping pills is Dagongmujiangzi, which was found to have a protective effect on myocardial injury in a rat model of atrial fibrillation and acute myocardial ischemia[15,16]. Ice chips have the effect of opening the body and waking the mind, clearing heat and relieving pain, and based on modern network pharmacological investigation, it was found that there are three targets in ice chips that have important efficacy in the treatment of coronary heart disease, effectively targeting the symptoms and eliminating the disease[17]. Allium sativum has the ability to move qi and channel stagnation, pass yang and disperse nodules, which can eliminate blood stasis and ensure smooth blood circulation. The other main ingredient, Chuanxiong,has the function of activating blood circulation, dispelling wind and relieving pain. Modern research has proved that Chuanxiong has the function of promoting blood circulation, anti-inflammatory, anticoagulation and vasodilation, it can significantly reduce the viscosity of whole blood and plasma, inhibit platelet aggregation, increase coronary blood flow, improve cardiac microcirculation, and reduce plaque formation [18], and Chuanxiong has a protective effect on cardiovascular endothelial cells, which is the one of the best drugs to choose in the treatment of chest paralysis[19]. Combined together,the four drugs promote qi-blood circulation, harmonize qi and blood,and exorcise stasis, ventilate qi, and relieve pain.
In this paper, through Meta-analysis of nine included studies,the results showed that the intervention group was significantly better than the control group in improving clinical efficacy and the efficacy of angina pectoris symptoms, indicating that Li qi huo xue dropping pill can effectively improve the clinical symptoms of patients with coronary angina pectoris. The increase of highsensitivity C-reactive protein indicates the high level of vascular inflammation, which leads to the instability of arterial plaque,and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein is an effective independent predictor of cardiovascular disease [20]. The changes in endothelial function and coronary angina are closely related to each other [21],and damage to endothelial structure and function is an important cause of atherosclerotic plaque formation and the earliest sign of vascular lesions[22],and have a predictive value for long-term cardiovascular events, which were lower in the intervention group than in the control group, indicating that Li qi huo xue dropping pill can effectively inhibit the inflammatory response of the body to have a protective effect on the myocardium; the results of this study showed that Li qi huo xue dropping pill can improve the clinical efficacy of angina pectoris in coronary heart disease to some extent,and can reduce IL-6, IL-18.The results of the present study showed that Li qi huo xue dropping pills could improve the clinical efficacy of angina pectoris in coronary heart disease to a certain extent, and could reduce IL-6, IL-18, HS-CRP levels and the number of angina attacks, and improve NO levels and the efficacy of angina symptoms,indicating that Li qi huo xue dropping pills has a better therapeutic effect on angina pectoris in coronary heart disease, and can also improve patients' quality of life and delay disease progression. In terms of safety, two studies reported adverse reactions. 8 cases of gastrointestinal discomfort, 1 case of dizziness and 3 cases of skin rash were observed in the control group. In the intervention group,there were 8 cases of gastrointestinal discomfort, 2 cases of dizziness and headache, 7 cases of gastrointestinal discomfort, and 1 case of rash. There were no serious adverse reactions in the intervention group, and the incidence of adverse reactions in the intervention group was lower than that in the control group, suggesting the relatively high safety of the treatment with Li qi huo xue dropping pills.
In conclusion, the combination of Li qi huo xue dropping pill with conventional western medicine treatment for patients with coronary angina can effectively improve the clinical outcome, the efficacy of angina symptoms, the number of angina attacks, the NO index of endothelial function, and reduce serum inflammatory indexes IL-6,IL-18, and HS-CRP.
However, the consistency among studies was not high due to the low quality of the literature of the original studies included and the limited number of samples included, the different control measures, and the large variety of drugs included in the conventional treatment in Western medicine. This meta-analysis also has some limitations:①None of the nine studies included in this paper mentioned blinding and allocation concealment, one study used the randomized numerical table method, and the rest did not describe the randomization method, which made the quality of the studies poor;all studies did not describe patient loss or withdrawal, which did not correspond to the clinical reality and the data may be untrue; different drug doses, length of intervention The differences in drug doses,duration of intervention, and measurement of indicators may lead to increased heterogeneity of the studies. Therefore, more multicenter,large sample, double-blind and other high-quality randomized controlled clinical trials are needed for further confirmation to better guide clinical drug use.②The number of studies included in this study was small, and the included studies were published in China,and the populations were all Chinese populations or even small parts of China, and it is unclear whether the findings of this study are also applicable to other regions or other ethnic groups.③Also, due to language ability limitations, our search was limited to Chinese and English literature, and we may have overlooked studies or reports in other languages. Therefore the above study findings still need to be supported by more high-quality clinical randomized controlled trials and high-quality literature to provide a more reliable therapeutic basis for modern clinical practice.
Author Contribution Description
(First author)Han Yi:research design, implementation of the study,data collection and statistical analysis, and article writing.
(Second author)Han Yubo:work supervision, article content review.
(Third author) Zou Guoliang:work supervision, technical support,etc.
(Fourth author) Sui Yanbo:work supervision, technical support, etc.
(Fifth author) Dong Xinyu:collection and statistical data, etc.
(Corresponding author) Liu Li:research design, work direction,article review, etc.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the content and opinions expressed in the paper are neutral and objective, and that there is no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年21期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年21期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on depression models of different strains of rats and mice
- Study on TCM intervention of NF-κB signal pathway in the treatment of bronchial asthma
- Systematic review and meta-analysis on efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of inflammatory factors in patients with poststroke depression
- Mechanism of Gan Dou Ling in improving liver fibrosis in Wilson disease based on network pharmacology and experimental verification
- Screening and comprehensive analysis of key genes in liver hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatics
- Design and characterization of a bi-functional bybrid antibacterial peptide LLM against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
