共轭梯度子空间基追踪算法及其相关结果
郝嘉骏, 张茜雯, 王金平
共轭梯度子空间基追踪算法及其相关结果
郝嘉骏, 张茜雯, 王金平*
(宁波大学 数学与统计学院, 浙江 宁波 315211)
压缩感知可以在低于Nyqiust采样率条件下实现稀疏信号的精确恢复. 重构算法是压缩感知的主要研究内容之一. 本文基于子空间基追踪算法的回溯思想与共轭梯度法, 提出了共轭梯度子空间基追踪算法. 通过仿真实验验证了算法的有效性, 并讨论了该算法利用几种常见测量矩阵对稀疏信号的重构效果. 结果显示, 当测量矩阵为部分Fourier矩阵时, 该算法具有最优的重构效果.
压缩感知; 测量矩阵; 共轭梯度; 迭代算法
压缩感知理论由Donoho和Candes等在2004年首次提出, 目前压缩感知理论的主要研究方向分为信号稀疏性、测量矩阵和恢复算法3种. 有别于传统的Nyqiust采样定理[1], 压缩感知理论指出, 若一个信号是稀疏信号或者可以在某个变换域上表现为稀疏信号, 那么可以通过一个与变换基不相关的矩阵将此信号投影到低维空间上, 且此投影过程不会损失原信号中的信息, 因此通过该投影可以精确地重构出原信号[2]. 压缩感知中的采样过程相对简单, 但恢复非常复杂, 所以对于恢复算法的研究是压缩感知中相当重要的一方面, 而对于测量矩阵的讨论不可避免地成为了重建算法的主要内容之一. 压缩感知的关键在于可以从线性测量中获取信息, 而无需从先前的测量中学习.
压缩感知理论经过十几年的快速发展, 已产生了许多具有不同复杂性和性能特征的有效算法, 其中贪婪算法因其结构简单、易于实现而得到广泛关注. 人们提出了很多改进算法, 例如正交匹配追踪(Orthogonal Matching Pursuit, OMP)算法[3]、原子正则化正交匹配追踪(Regularized OMP, ROMP)算法[4]、压缩采样匹配追踪(Compressive Sampling MP, CoSaMP)算法[5]、子空间基追踪(subspace pursuit, SP)算法[6]、分段正交匹配追踪(Stagewise OMP, StOMP)算法[7]、迭代硬阈值(Iterative Hard Thresholding, IHT)算法[8]以及硬阈值基追踪(Hard Thresholding Pursuit, HTP)算法[9]. 近几年来, 人们开始关注将共轭梯度法与贪婪算法结合. 2015年Blanchard等[10]提出了共轭梯度硬阈值(Conjugate Gradient Iterative Hard Thresholding, CGIHT)算法. 在此之后又相继出现了共轭硬阈值基追踪(Conjugate Gradient Hard Thresholding Pursuit, CGHTP)算法[11]与改进的共轭硬阈值基追踪(Modified Conjugate Gradient Hard Thresholding Pursuit, CCGHTP)算法[12]. 受此启发, 本文将共轭梯度法与SP算法相结合, 对SP算法加以改进得到相关结果.
1 预备知识
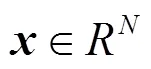
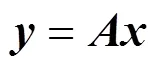
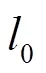
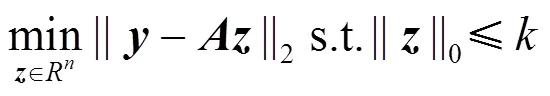
1.1 投影与残差
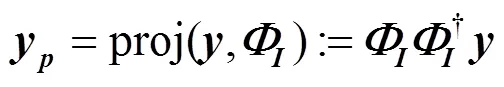
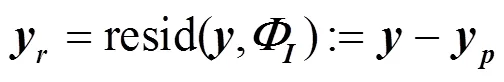
1.2 SP算法
初始化:
迭代: 在第次迭代中, 作
1.3 测量矩阵的限制等距性质
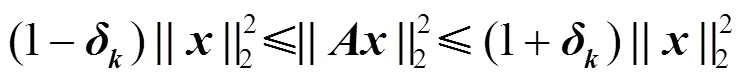
这等价于
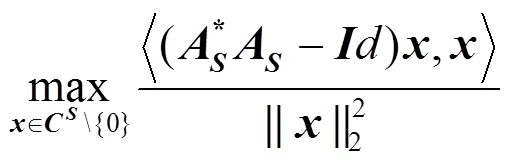
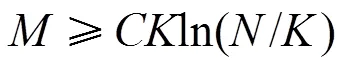
1.4 常见的测量矩阵
1.4.1 Gauss随机测量矩阵
1.4.2 Bernoulli随机测量矩阵
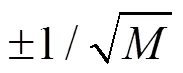
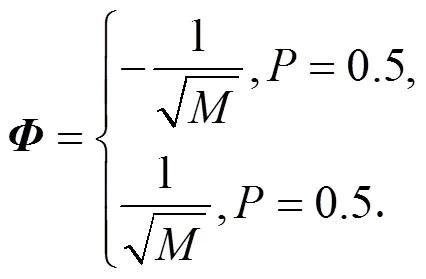
1.4.3部分Fourier矩阵
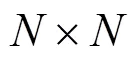
1.4.4部分Hadamard矩阵
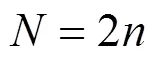
1.4.5稀疏随机测量矩阵
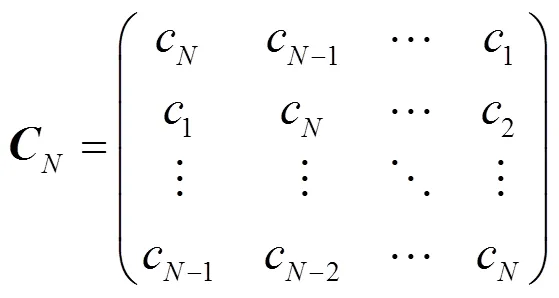
1.4.6 Toeplitz矩阵和循环矩阵
Toeplitz矩阵通过行向量循环位移生成. 因为矩阵容易实现, 所以应用前景较好. 一般形式为
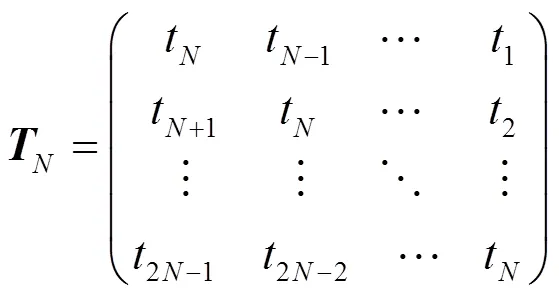
循环矩阵则是Toeplitz矩阵的一种特殊形式, 可表示为
2 共轭梯度子空间基追踪算法
共轭梯度法最早是由Hestenes和Stiefle提出来的, 在此基础上, Fletcher[18]首先提出了解非线性最优化问题的共轭梯度法. 共轭梯度法是介于最速下降法与牛顿法之间的一种方法, 它仅需要利用一阶导数信息, 既克服了最速下降法收敛慢的缺点, 又避免了牛顿法需要存储和计算Hesse矩阵并求逆的缺点. 共轭梯度法不仅是解决大型线性方程组最有用的方法之一, 也是解大型非线性最优化最有效的算法之一. 在各种优化算法中, 共轭梯度法是非常重要的一种, 其优点是所需存储量小、具有步收敛性、稳定性高, 而且不需要任何外来参数.
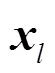
CGSP算法:
迭代: 若迭代次数小于等于2次,
(4)若支撑集未发生变化,
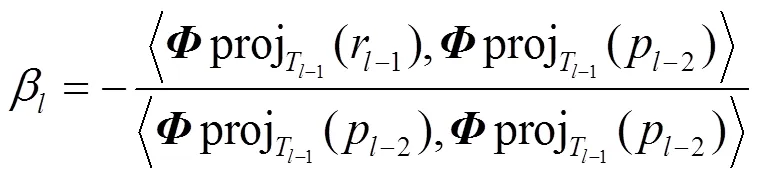
(6)给出最佳步长
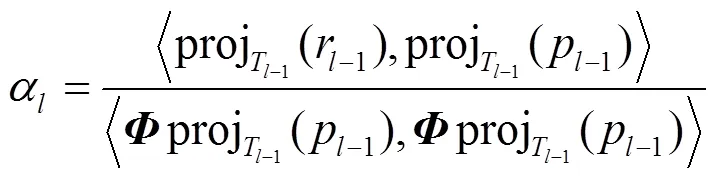
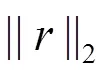
3 仿真实验
3.1 稀疏信号单次恢复实验
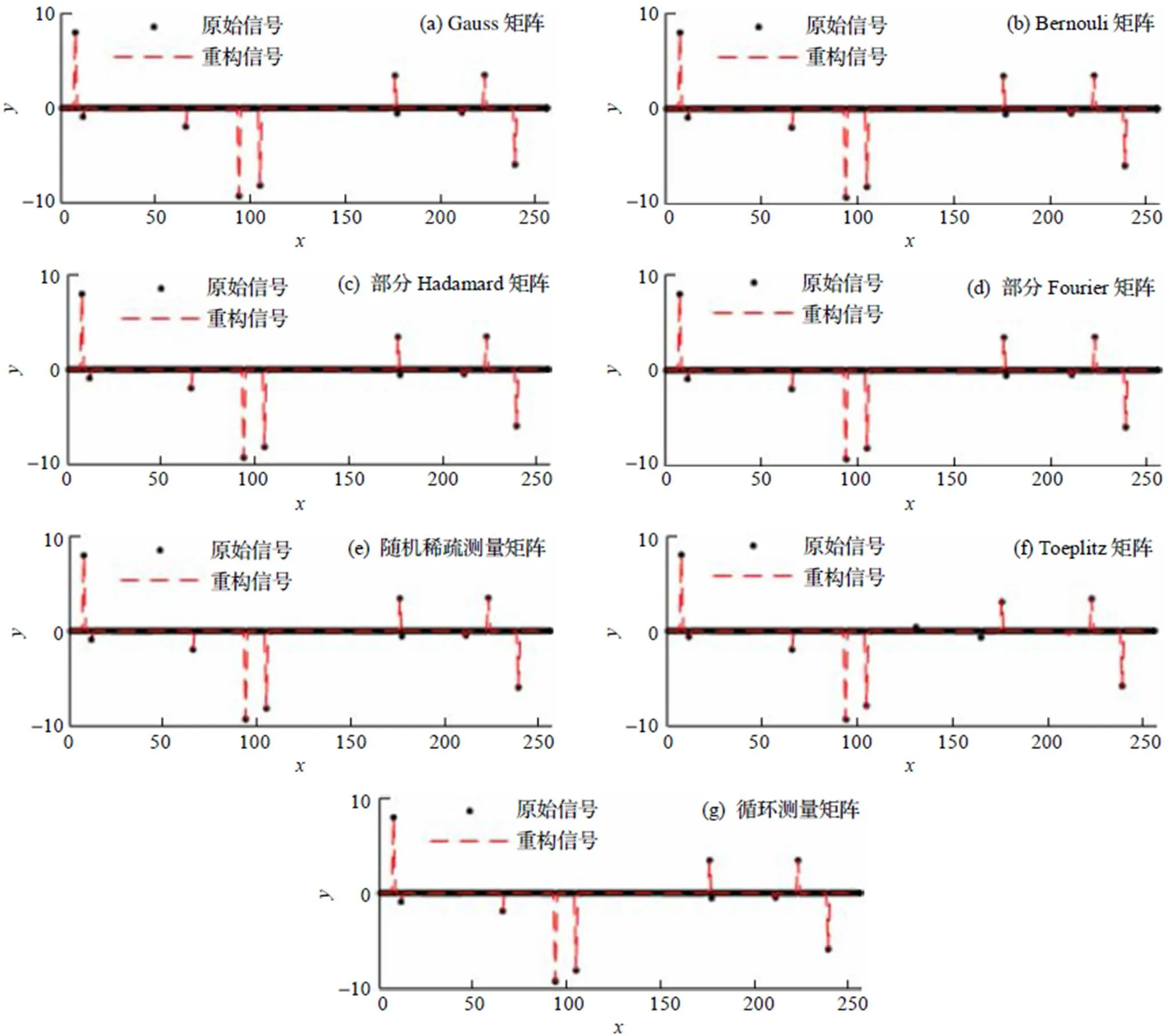
图1 不同测量矩阵单次恢复结果
通过不同测量矩阵恢复该稀疏信号时, 对应的误差值见表1.
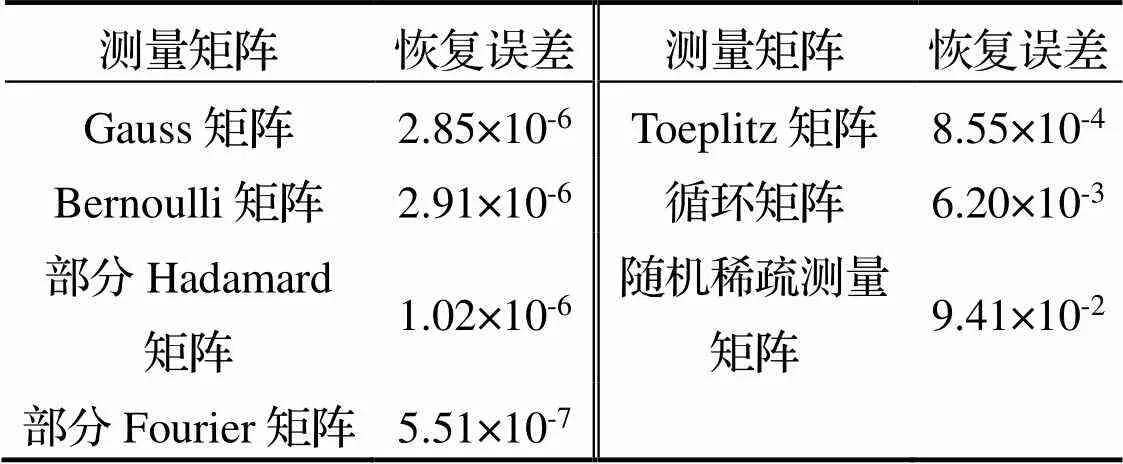
表1 不同测量矩阵恢复误差
由图1与表1可以看出, 在实验所设条件下, CGSP算法以7种常用矩阵为测量矩阵时均可以实现稀疏信号的精确恢复, 且测量矩阵为Fourier矩阵时重构误差最小, 测量矩阵为随机稀疏测量矩阵时误差最大. 实验初步证明本文所提算法可以对满足要求的稀疏信号进行精确恢复.
3.2 无噪声稀疏信号测量矩阵效果实验
本实验为特定情况下测试算法对稀疏信号的恢复效果, 共分为3部分.
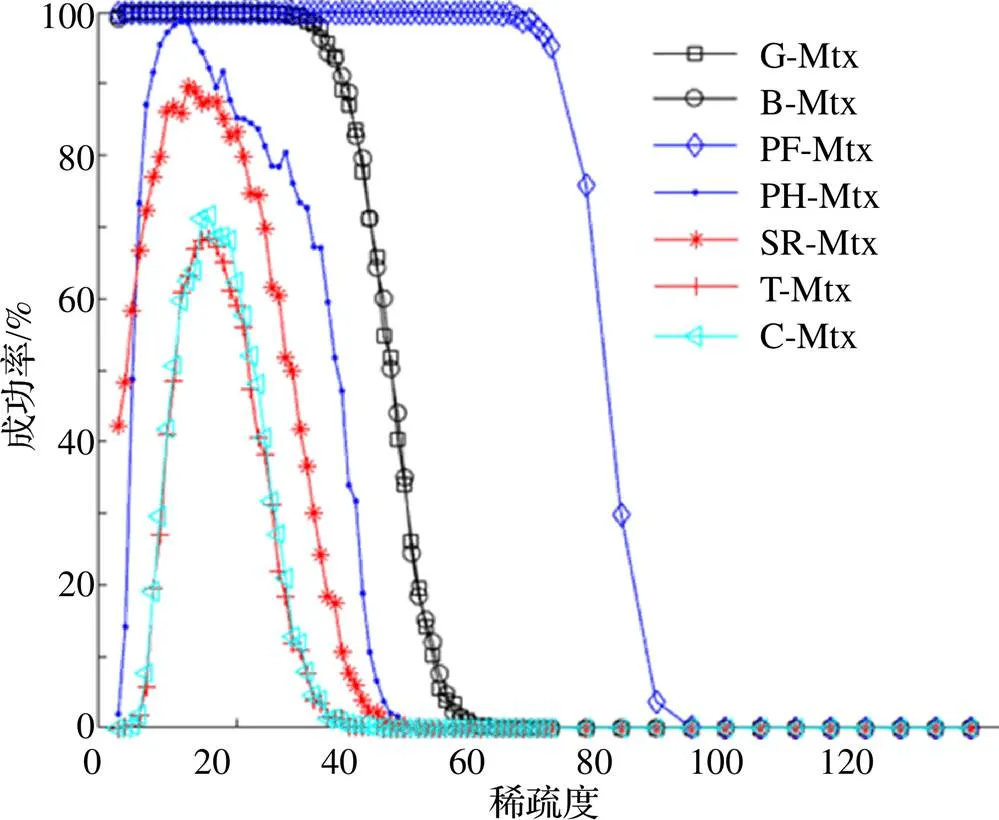
图2 不同稀疏度的恢复成功率

表2 4种测量矩阵实现稳定恢复的稀疏度区间
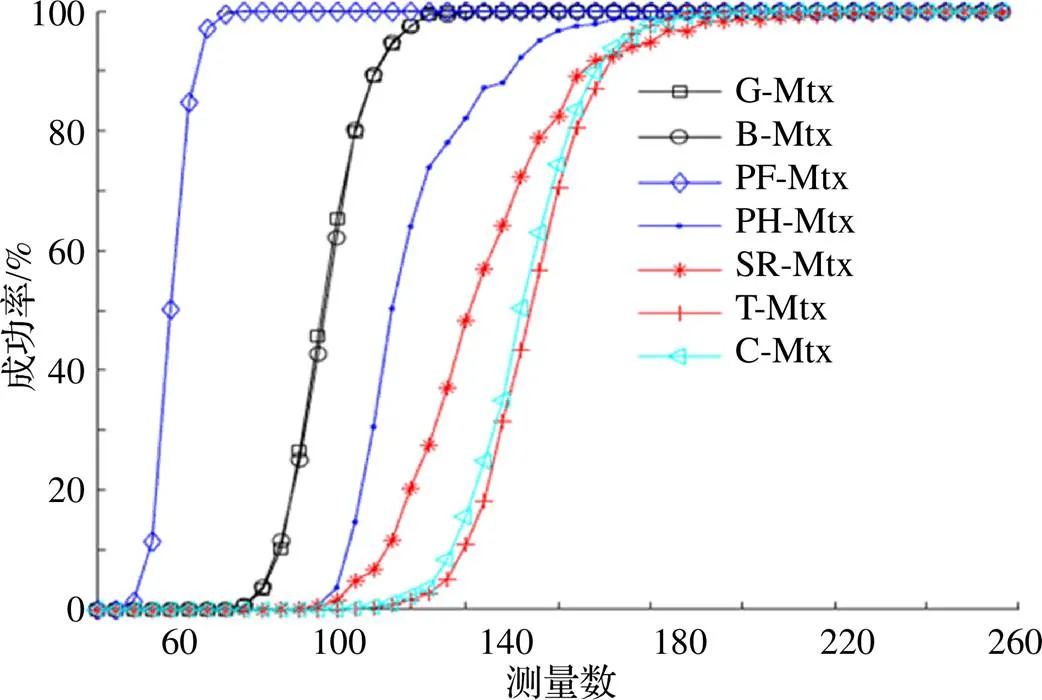
图3 不同测量数的恢复成功率

表3 4种测量矩阵稳定重构最小测量数
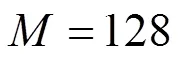
(b)稀疏度满足首项为1, 公差为5, 末项为矩阵行数的等差数列;
(c)在对应的稀疏度和测量矩阵行数对稀疏信号进行1000次恢复实验, 取每次实验所得误差值的算术平均值与恢复时间的算术平均值.
实验结果见表4.
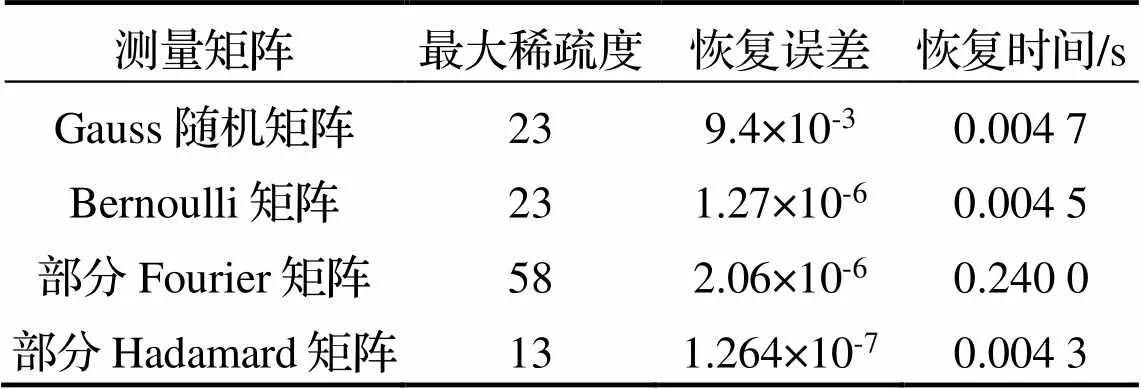
表4 4种测量矩阵的恢复参数
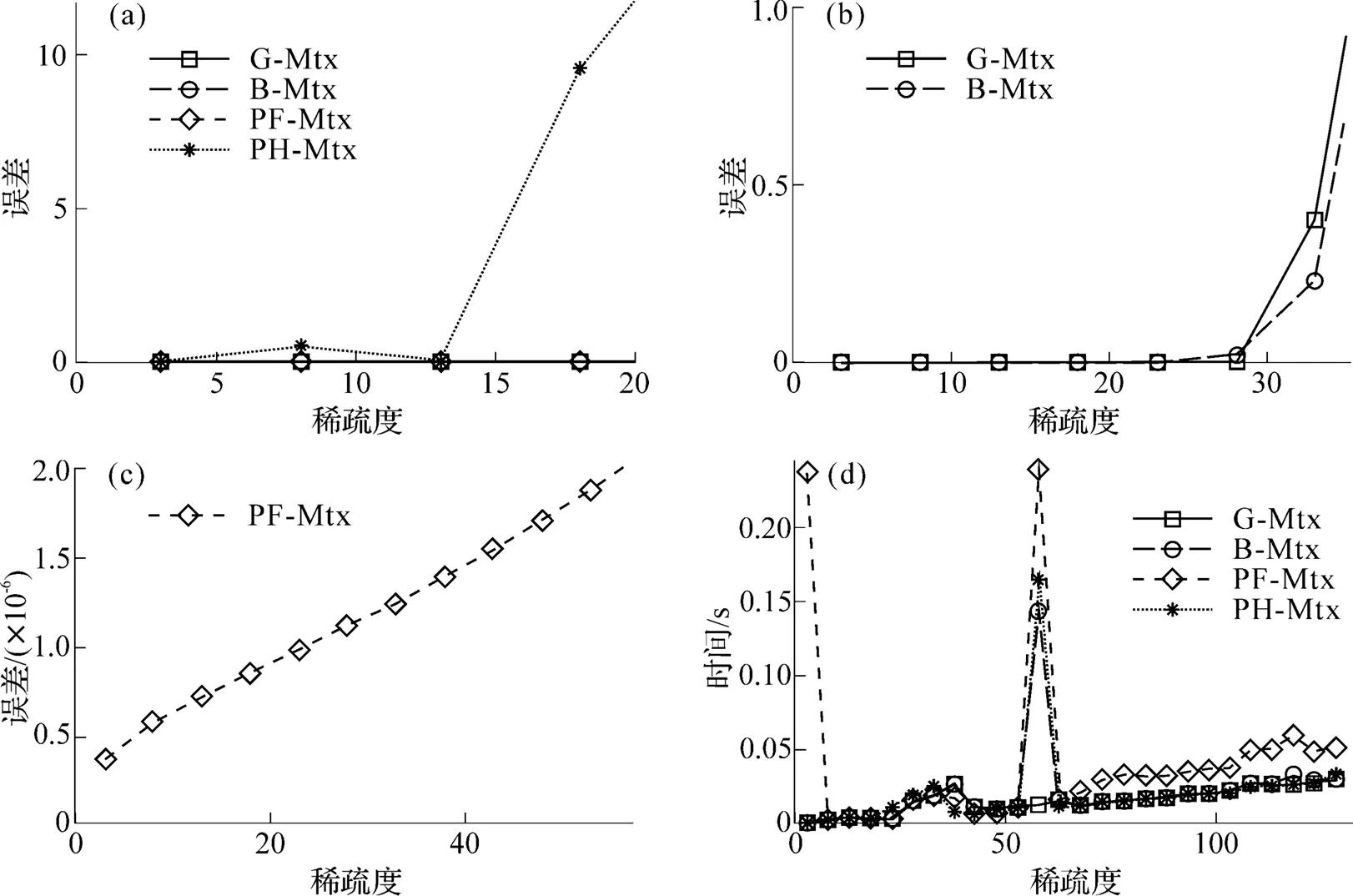
图4 4种测量矩阵的恢复误差与时间
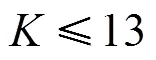
4 结论
本文通过将SP算法与共轭梯度法相结合对SP算法加以改进提出了CGSP算法, 并使用几种常见的测量矩阵对此算法的有效性加以验证, 实验证明此算法确实可行. 在此基础上, 本文设计实验讨论了算法在无噪声条件下应用各测量矩阵时对稀疏信号的重构效果. 结果表明, 算法在测量矩阵为部分Fourier矩阵时效果最好, 表现在两方面: 首先, 以稀疏度为变量, 算法在部分Fourier矩阵下所需测量数最少; 其次, 以测量数为变量, 算法能够重构的稀疏度区间最广. 限于篇幅, 本文只选取了较为常见的几种测量矩阵测试并给出了仿真结果, 其他的测量矩阵均可以同上述方法讨论. 此外, 本文只给出了算法在不同测量矩阵下的相关实验结果, 并未对算法进行理论分析, 这是下一阶段研究的目标.
[1] Jerri A J. The Shannon sampling theorem—Its various extensions and applications: A tutorial review[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1977, 65(11):1565-1596.
[2] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4):1289-1306.
[3] Trop J A, Gilbert A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12):4655- 4666.
[4] Needell D, Vershynin R. Signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements via regularized orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2):310-316.
[5] Needell D, Tropp J A. CoSaMP: Iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2009, 26(3):301-321.
[6] Dai W, Milenkovic O. Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(5):2230-2249.
[7] Donoho D L, Tsaig Y, Drori I, et al. Sparse solution of underdetermined systems of linear equations by stagewise orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2012, 58(2):1094-1121.
[8] Blumensath T, Davies M E. Iterative hard thresholding for compressed sensing[J]. Applied and computational harmonic analysis, 2009, 27(3):265-274.
[9] Foucart S. Hard thresholding pursuit: an algorithm for compressive sensing[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2011, 49(6):2543-2563.
[10] Blanchard J D, Tanner J, Wei K. CGIHT: conjugate gradient iterative hard thresholding for compressed sensing and matrix completion[J]. Information and Inference: A Journal of the IMA, 2015, 4(4):289-327.
[11] Zhang Y, Huang Y, Li H, et al. Conjugate gradient hard thresholding pursuit algorithm for sparse signal recovery [J]. Algorithms, 2019, 12(2):36.
[12] Zhu Z, Ma J, Zhang B. A new conjugate gradient hard thresholding pursuit algorithm for sparse signal recovery [J]. Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2020, 39(4): 1-20.
[13] Candès E J, Romberg J K, Tao T. Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 2006, 59(8):1207-1223.
[14] Tur R, Eldar Y C, Friedman Z. Innovation rate sampling of pulse streams with application to ultrasound imaging [J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(4): 1827-1842.
[15] 李小波. 基于压缩感知的测量矩阵研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2010.
[16] Gilbert A, Indyk P. Sparse recovery using sparse matrices [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(6):937-947.
[17] Bajwa W U, Haupt J D, Raz G M, et al. Toeplitz- structured compressed sensing matrices[C]//2007 IEEE/ SP 14th Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing, IEEE, 2007:294-298.
[18] Fletcher R. Conjugate gradient methods for indefinite systems[M]//Watson G A. Numerical Analysis. Berlin: Springer, 1976:73-89.
Conjugate gradient subspace pursuit algorithm and related results
HAO Jiajun, ZHANG Xiwen, WANG Jinping*
( Schoolof Mathematics and Statistics, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China )
Compressed sensing can accurately recover sparse signals below Nyquist sampling rate. Reconstruction algorithm is one of the main research contents of compressed sensing. Based on the backtracking notion of subspace pursuit algorithm and conjugate gradient method, a conjugate gradient subspace pursuit algorithm is proposed in this paper. The effectiveness of the algorithm is verified through simulations, and the reconstruction effect of the algorithm on sparse signals is discussed using several common measurement matrices. The results show that the algorithm has the best reconstruction effect when the measurement matrix is a partial Fourier matrix.
compressed sensing; measurement matrix; conjugate gradient; iterative algorithm
O177.92
A
1001-5132(2022)01-0098-07
2021−09−05.
宁波大学学报(理工版)网址: http://journallg. nbu. edu. cn/
国家自然科学基金(62071262).
郝嘉骏(1992-), 男, 山西长治人, 在读硕士研究生, 主要研究方向: 积分变换与图像处理. E-mail: 825821801@qq.com
王金平(1962-), 男, 湖北武汉人, 教授, 主要研究方向: 积分变换与图像处理. E-mail: wangjinping@nbu.edu.cn
(责任编辑 韩 超)

