机器类通信中集中式与分布式Q学习的资源分配算法研究
余云河,孙君
机器类通信中集中式与分布式Q学习的资源分配算法研究
余云河,孙君
(南京邮电大学通信与信息工程学院,江苏 南京 210023)
针对海量机器类通信(massive machine type communication,mMTC)场景,以最大化系统吞吐量为目标,且在保证部分机器类通信设备(machine type communication device,MTCD)的服务质量(quality of service,QoS)要求前提下,提出两种基于Q学习的资源分配算法:集中式Q学习算法(team-Q)和分布式Q学习算法(dis-Q)。首先基于余弦相似度(cosine similarity,CS)聚类算法,考虑到MTCD地理位置和多级别QoS要求,构造代表MTCD和数据聚合器(data aggregator,DA)的多维向量,根据向量间CS值完成分组。然后分别利用team-Q学习算法和dis-Q学习算法为MTCD分配资源块(resource block,RB)和功率。吞吐量性能上,team-Q和dis-Q算法相较于动态资源分配算法、贪婪算法分别平均提高了16%、23%;复杂度性能上,dis-Q算法仅为team-Q算法的25%及以下,收敛速度则提高了近40%。
资源分配;集中式Q学习;分布式Q学习;余弦相似度;多维向量
1 引言
机器型通信(machine type communication,MTC)允许智能物体在没有人为干预情况下实现相互通信,3GPP(3rd Generation Partnership Project)认为MTC将会对物联网(internet of things,IoT)的发展起到关键作用[1-2]。随着IoT的普及,对“物”之间的通信具有很高的需求,即使5G也不能保证满足未来新业务的所有需求,因此在B5G(beyond 5G)和6G网络中,MTC将会是研究人员关注的重点[3-4]。思科预测到2022年各行业中将会有39亿个MTC设备连接到网络中[5],而海量机器类通信设备(machine type communication device,MTCD)连接不仅导致频谱资源匮乏,还会造成网络拥塞,给基站(base station,BS)带来沉重负担。
在部署了高密度MTCD的mMTC网络中,将MTCD分组为较小集群被视为一种有助于缓解MTC网络拥塞,提高MTCD接入成功率,进而促进吞吐量提升的技术[6]。为此,国内外学者提出了一系列关于MTCD分组聚类算法。文献[6-7]分别依据设备的QoS要求、地理位置进行分组,文献[8]为了延长网络寿命,依据MTCD剩余能量以及与BS间的距离进行聚类。文献[9-10]在传统-means算法基础上作出改进,分别针对MTCD能量效率与MTC网络传输时延要求,对MTCD进行聚类。然而,上述研究中提出的MTCD聚类策略,有的仅考虑了地理位置和QoS要求中的单个因素,并未充分发掘MTCD之间的关联性,导致在MTCD聚簇内不能很好地协调干扰,潜在影响系统吞吐量;有的仅针对特定优化目标进行聚类,不具有普遍适用性。
文献[11-12]均考虑H2H(human to human)与M2M(machine to machine)共存场景中系统用户过载情况下的资源分配问题。然而,文献[11]未考虑时延敏感M2M业务的传输需求,导致无法满足此类M2M业务的QoS要求,文献[12]则利用基于背包模型的资源分配算法,保证了时延敏感M2M通信业务的QoS,但在文献[12]中仅将所提算法同传统的优先为H2H终端分配资源的算法进行性能比较,无法充分验证该算法的优越性。文献[13]提出了一种动态资源分配策略用于解决MTCD间的资源分配问题,虽然考虑了MTCD请求过载的情况,但并不允许资源复用,导致频谱利用率较低,同时由于接入网络的MTCD数量较少,也造成系统吞吐量下降。文献[14]针对多输入多输出系统中动态资源分配问题,提出了一种确保用户最低QoS要求的资源分配算法,能获得较高的系统吞吐量,然而该方法是在用户功率等分配的前提下执行的,并不符合实际,具有一定的局限性。文献[15]讨论了在频谱资源匮乏条件下,基于设备到设备(device to device,D2D)分簇的车通信资源分配问题,在保证车用户正常通信下,最大化蜂窝用户的吞吐量。文献[16]研究了基于容量最大化地mMTC场景的资源分配问题,但使用的是传统粒子群算法,该算法对容量提升作用有限,且没有考虑MTCD分组问题。在功率有限、频谱资源匮乏的MTC网络中,传统资源分配方法难以满足MTCD不断增长的QoS要求。近年来研究表明基于机器学习的资源分配策略已经优于传统的方法[17-18],而Q学习作为一种著名无模型强化学习(reinforcement learning,RL)算法引起了人们的关注。
基于以上分析,本文在确保承担高信噪比传输任务的MTCD最低QoS要求前提下,提出两种Q学习算法:team-Q学习算法和dis-Q学习算法,解决网络内MTCD之间的资源块和功率联合分配问题。该资源分配算法分为两个阶段:第一阶段设计一种基于CS的聚类方案,即借鉴商品推荐系统中求取用户之间相似度的做法,分别为MTCD、DA构造多维向量,再利用向量之间余弦相似度进行分组。第二阶段中,针对分组后的MTC网络上行链路资源块和功率分配问题,提出了两种基于Q学习的分配算法:team-Q学习和dis-Q学习,其中dis-Q算法在team-Q算法基础上改进了Q值表和奖励函数。最后,通过仿真验证了所提算法能在复杂性、收敛速度以及对系统吞吐量促进作用等方面的有效性。
2 系统模型
本文研究的系统模型如图1所示,随机分布的MTCD经过聚类后形成MTCD聚簇,每个聚簇内含有一个数据聚合器DA,构成MTC网络。在MTC网络中,MTCD通过稀疏码分多址技术[19]与DA连接,DA充当数据接收和转发的角色,即负责接收MTCD数据并转发至BS,使得整个网络变成双层架构,可以减轻BS的接入负担。假定聚簇与聚簇间使用正交的频谱资源,而聚簇内的MTCD之间以非正交多址方式共用资源块。因此,在MTC网络内由于资源块的复用会产生多址干扰,在接收端则可采用串行干扰消除(successive interference cancellation,SIC)技术进行正确解调。

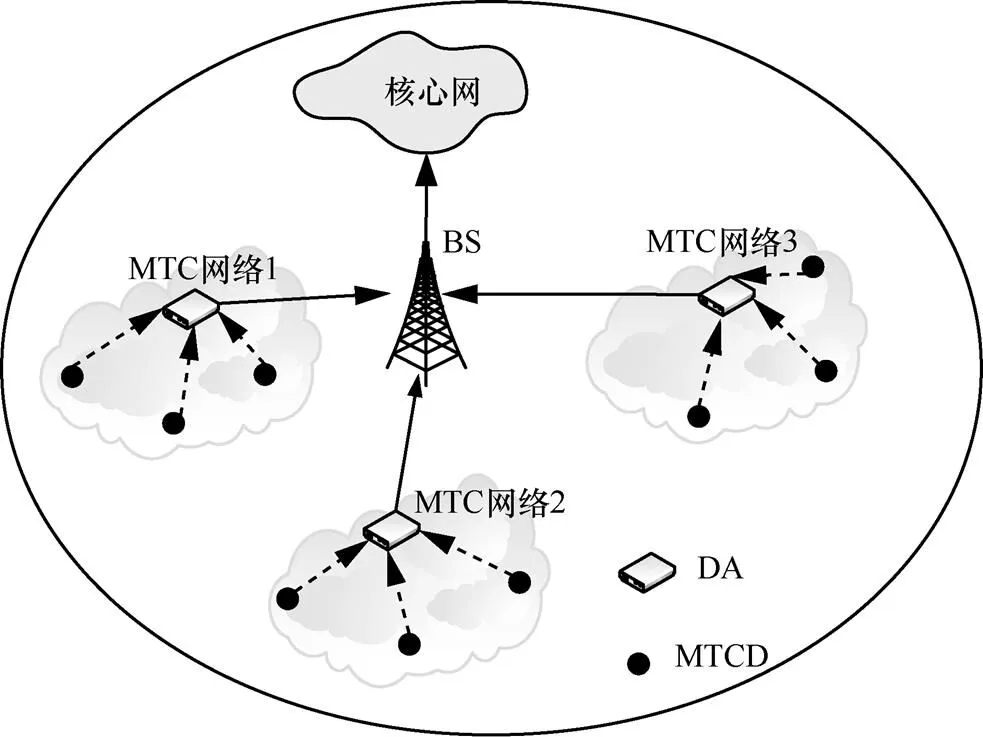
图1 系统模型
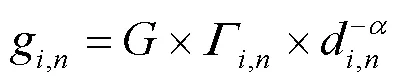
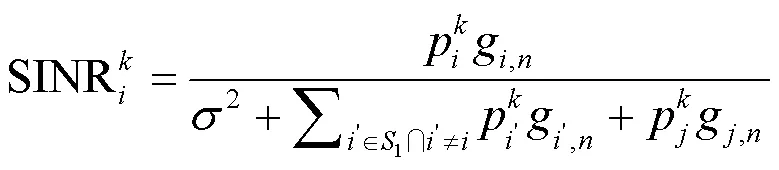
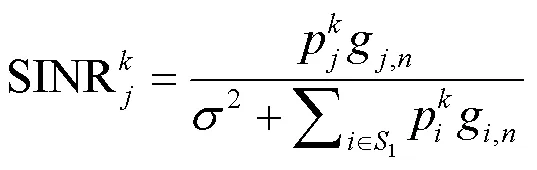
所以针对使得整个MTC网络吞吐量最大化的目标,根据香农信道容量计算公式可以构造出如下最优化问题:

上述问题属于混合整数非线性规划(mixed integer nonlinear programming,MINLP)问题,通常是NP难[17]的,很难直接求解,在本文中使用Q学习算法解决。
3 算法的提出
3.1 MTCD聚簇形成
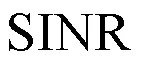





算法1 基于余弦相似度的MTCD聚类算法
初始化:
循环:
3.2 MTC网络内部资源分配
(1)基于team-Q学习算法的资源分配策略




(2)基于dis-Q学习算法的资源分配策略


算法2 dis-Q学习资源分配算法
初始化:
迭代:
根据式(10)更新Q值表;
4 仿真结果与性能分析
本节主要对本文所提算法的性能进行分析验证,包括收敛性、复杂度和系统吞吐量等,仿真平台是MATLAB工具,仿真参数见表1[12,20]。

表1 仿真参数
首先对比两种Q学习算法的收敛速度。如图2所示,可以得到team-Q算法和dis-Q算法随着迭代次数增加都趋向于收敛,但从迭代次数角度出发,dis-Q学习算法的收敛速度相比team-Q学习算法提高了近40%。这是由于在team-Q学习算法中,Q值表的维度远大于dis-Q学习算法,当动作空间和智能体agent数量都增大时,team-Q算法复杂度会呈现指数级增长,最终导致dis-Q学习算法的收敛速度快于team-Q学习算法。

图2 两种Q学习算法收敛性分析

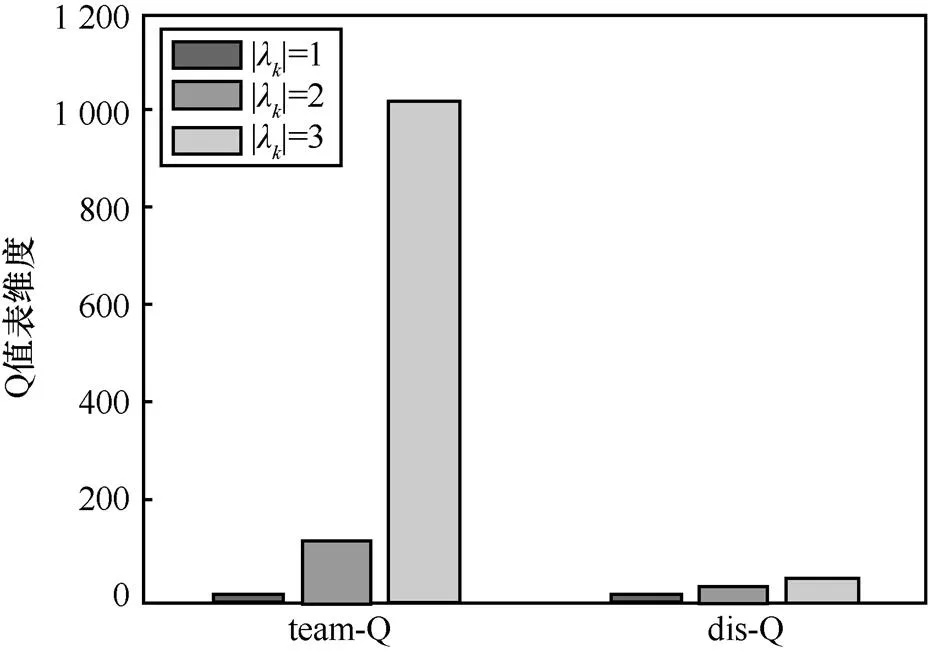
图3 不同下team-Q、dis-Q算法中Q值表维度对比


图4 不同算法下系统吞吐量对比

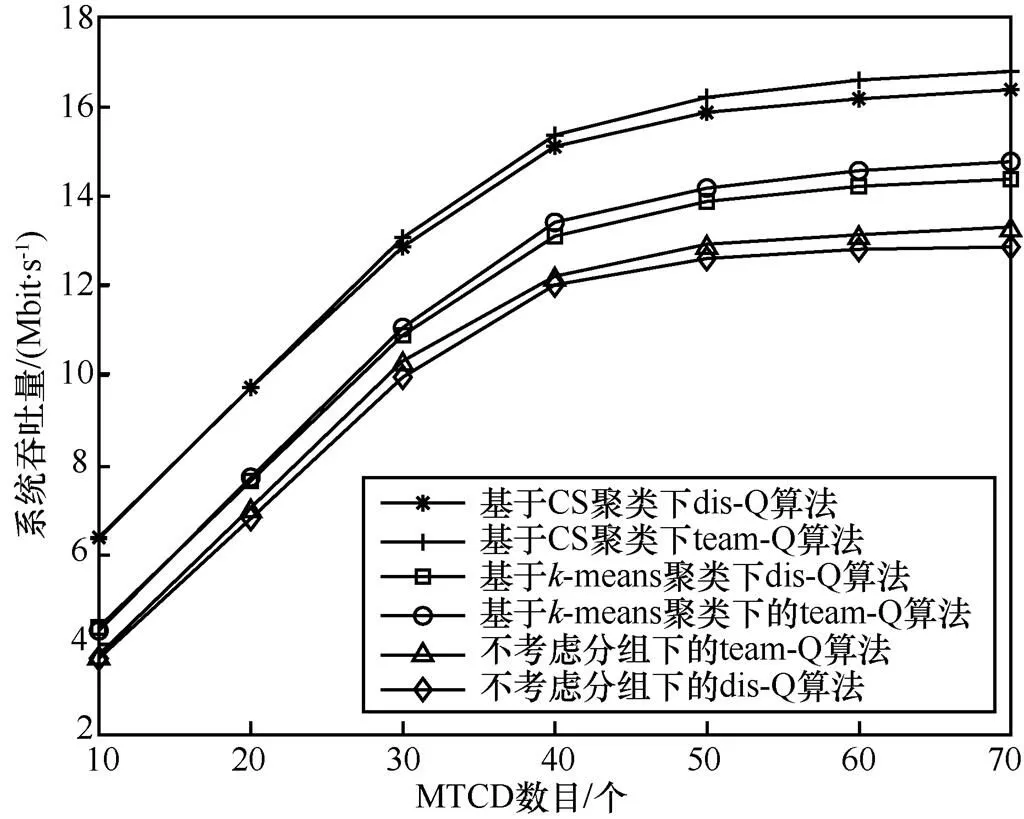
图5 不同聚类算法下系统吞吐量对比
5 结束语
本文研究了在mMTC场景中以系统吞吐量最优化为目标的资源分配问题。首先,提出了一种基于余弦相似度的聚类算法,根据MTCD与DA之间的相对位置和QoS要求,将MTCD分组。该算法能充分发掘出MTCD之间的关联性,能更好地协调MTC聚簇内的干扰,有利于提升系统性能。此外,针对MTC网络中的资源分配问题,提出了team-Q学习算法和dis-Q学习算法。仿真结果表明,两种Q学习算法对系统吞吐量的提升作用相较于对比算法均有较大幅度的提高,其中team-Q算法在系统吞吐量性能上略优于dis-Q算法,但是dis-Q算法在信令消耗、收敛速度方面明显优于team-Q算法,这也更加符合“绿色通信”的理念。
[1] CHEN S Y, MA R F, CHEN H H, et al. Machine-to-machine communications in ultra-dense networks—A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(3): 1478-1503.
[2] 钱志鸿, 王义君. 物联网技术与应用研究[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(5): 1023-1029.
QIAN Z H, WANG Y J. IoT technology and application[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(5): 1023-1029.
[3] Service-aware transport network: opportunities and chanenges[J]. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2005.
[4] ZHOU Y Q, TIAN L, LIU L, et al. Fog computing enabled future mobile communication networks: a convergence of communication and computing[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(5): 20-27.
[5] Cisco visual networking index: global mobile data traffic forecast update 2014-2019[EB]. 2014.
[6] LIANG L, XU L, CAO B, et al. A cluster-based congestion-mitigating access scheme for massive M2M communications in internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(3): 2200-2211.
[7] GHAVIMI F, LU Y W, CHEN H H. Uplink scheduling and power allocation for M2M communications in SC-FDMA-based LTE-A networks with QoS guarantees[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(7): 6160-6170.
[8] GAO H, XU X D, HAN S J. Homogeneous clustering algorithm based on average residual energy for energy-efficient MTC networks[C]//Proceedings of 2018 24th Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 28-33.
[9] HUSSAIN F, HUSSAIN R, ANPALAGAN A, et al. A new block-based reinforcement learning approach for distributed resource allocation in clustered IoT networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(3): 2891-2904.
[10] XU Y Q, FENG G, LIANG L, et al. MTC data aggregation for 5G network slicing[C]//Proceedings of 2017 23rd Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6.
[11] 王鑫, 邱玲. H2H与M2M共存场景的准入控制及资源分配[J].中国科学院大学学报, 2016, 33(3): 427-432.
WANG X, QIU L. Admission control and resource allocation of H2H & M2M co-existence scenario[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016, 33(3): 427-432.
[12] 蒋继胜, 朱晓荣. H2H与M2M共存场景下的上行资源分配算法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(5): 1259-1264.
JIANG J S, ZHU X R. An uplink resource allocation algorithm under the scenario of coexistence of H2H & M2M based on knapsack model[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(5): 1259-1264.
[13] SALAM T, REHMAN W U, TAO X F. Cooperative data aggregation and dynamic resource allocation for massive machine type communication[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 4145-4158.
[14] 郭涛, 李有明, 雷鹏, 等. MIMO中继系统中一种基于用户QoS的资源分配方法[J]. 电信科学, 2015, 31(4): 121-126.
GUO T, LI Y M, LEI P, et al. A resource allocation scheme based on user’s QoS in MIMO relay system[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2015, 31(4): 121-126.
[15] 张海波, 向煜, 刘开健, 等. 基于D2D通信的V2X资源分配方案[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2017, 40(5): 92-97.
ZHANG H B, XIANG Y, LIU K J, et al. V2X resource allocation scheme based on D2D communication[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017, 40(5): 92-97.
[16] 刘佳言, 秦鹏, 赵雄文, 等. 基于容量最大化的mMTC场景的资源分配问题研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2020, 18(12): 17-22.
LIU J Y, QIN P, ZHAO X W, et al. Research on resource allocation of m MTC scenario based on capacity maximization[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2020, 18(12): 17-22.
[17] SHARMA S K, WANG X B. Toward massive machine type communications in ultra-dense cellular IoT networks: current issues and machine learning-assisted solutions[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(1): 426-471.
[18] HUSSAIN F, HASSAN S A, HUSSAIN R, et al. Machine learning for resource management in cellular and IoT networks: potentials, current solutions, and open challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(2): 1251-1275.
[19] NIKOPOUR H, BALIGH H. Sparse code multiple access[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 332-336.
[20] KAI C H, LI H, XU L, et al. Joint subcarrier assignment with power allocation for sum rate maximization of D2D communications in wireless cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 4748-4759.
Research on resource allocation algorithm of centralized and distributed Q-learning in machine communication
YU Yunhe, SUN Jun
College of Telecommunications and Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
Under the premise of ensuring partial machine type communication device (MTCD)’s quality of service (QoS) requirements, the resource allocation problem was studied with the goal of maximizing system throughput in the massive machine type communication (mMTC) scenario. Two resource allocation algorithms based on Q-learning were proposed: centralized Q-learning algorithm (team-Q) and distributed Q-learning algorithm (dis-Q). Firstly, taking into account MTCD’s geographic location and multi-level QoS requirements, a clustering algorithm based on cosine similarity (CS) was designed. In the clustering algorithm, multi-dimensional vectors that represent MTCD and data aggregator (DA) were constructed, and MTCDs can be grouped according to the CS value between multi-dimensional vectors. Then in the MTC network, the team-Q learning algorithm and dis-Q learning algorithm were used to allocate resource blocks and power for the MTCD. In terms of throughput performance, team-Q and dis-Q algorithms have an average increase of 16% and 23% compared to the dynamic resource allocation algorithm and the greedy algorithm, respectively. In terms of complexity performance, the dis-Q algorithm is only 25% of team-Q algorithm and even below, the convergence speed is increased by nearly 40%.
resource allocation, centralized Q-learning, distributed Q-learning, consine similarity, multi-dimensional vector
TP929.5
A
10.11959/j.issn.1000−0801.2021244

余云河(1995− ),男,南京邮电大学通信与信息工程学院硕士生,主要研究方向为大规模机器类通信网络中的资源分配。
孙君(1980− ),女,南京邮电大学硕士生导师,主要研究方向为无线网络资源管理。
s: The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61771255), Open Project of Key Laboratory of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No.20190904)
2021−04−30;
2021−10−20
孙君,sunjun@njupt.edu.cn
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No.61771255);中国科学院重点实验室开放课题(No.20190904)

