2018-2020年上海某社区慢性乙型病毒性肝炎流行病学特征分析
王丽楠 王通 聂莲莲 尹丹娟
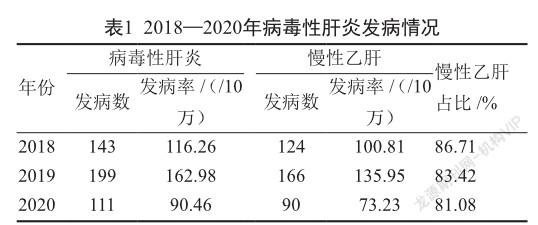
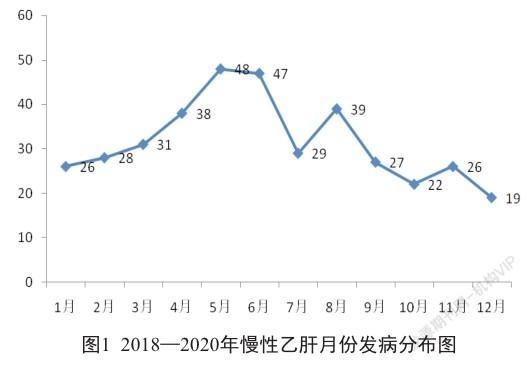
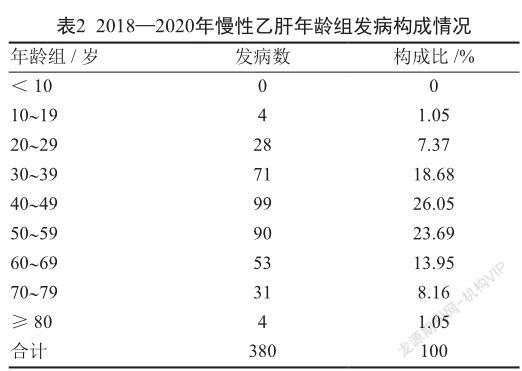
摘 要 目的:分析2018-2020年上海市某社区慢性乙型病毒性肝炎(慢性乙肝)的流行病學特征,为慢性乙肝的精准防控工作提供理论依据。方法:采用描述性流行病学方法,分析2018-2020年中国疾病预防控制信息管理系统上报的上海市某社区慢性乙肝资料。结果:上海某社区2018-2020年累计报告慢性乙肝病例380例,占病毒性肝炎总数的83.89%,年均报告发病率为103.23/10万,2019年报告发病率为135.40/10万,在3年中排首位(χ2=23.47,P<0.05)。农村地区报告发病率大于城市地区(131.70/10万比85.36/10万,χ2=18.20,P<0.05)。男性报告发病率大于女性(男女病例数之比为1.59∶1,χ2=18.90,P<0.05)。全年4季均有病例发生,第二季度呈高发态势。发病主要集中在30~59岁年龄组(68.42%)。职业主要集中在农民、离退人员、家务及待业人员及工人,其中工人在所有职业中所占的比例逐年降低(χ2=15.28,P<0.05)。结论:男性以及农村地区是该社区慢性乙肝的高发人群及地区,各年发病波动较明显,因此应针对特定人群开展针对性的监测、防控、健康教育等工作,并在儿童乙肝疫苗接种工作基础上加大力度提高成人乙肝疫苗接种率,以降低慢性乙肝发病率。
关键词 乙型病毒性肝炎;社区;流行病学特征
中图分类号:R512.62 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2021)20-0050-04
Analysis of epidemiological characteristics of chronic hepatitis B in a community in Shanghai from 2018 to 2020
WANG Linan, WANG Tong, NIE Lianlian, YIN Danjuan(Prevention and Health Care Department of Zhujing Community Health Service Center of Jinshan District, Shanghai 201599, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To analyze the epidemiological characteristics of chronic viral hepatitis B (chronic hepatitis B) in a community in Shanghai from 2018 to 2020, to provide theoretical basis for accurate prevention and control work of chronic hepatitis B. Methods: Descriptive epidemiological methods were used to analyze the data of chronic hepatitis B in a community in Shanghai reported by the Chinese disease control and prevention information management system from 2018 to 2020. Results: A total of 380 cases of chronic hepatitis B were reported from 2018 to 2020 in a community in Shanghai, accounting for 83.89% of the total number of viral hepatitis, the annual incidence rate was 103.23/100 000, and the reported incidence rate was 135.40/100 000 in 2019, ranking the first in 3 years (χ2=23.47, P<0.05). The reported incidence in rural areas was higher than that in urban areas (131.70/100 000 to 85.36/100 000, χ2=18.20, P<0.05). The incidence rate of male reported cases was greater than that of female reported ones (the ratio of male to female cases was 1.59:1, χ2=18.90, P<0.05). There were cases in 4 quarters of the year, and the second quarter showed a trend of high incidence. The incidence was mainly concentrated in the age group of 30~59 years old (68.42%). The occupations were mainly concentrated in farmers, retirees, domestic and unemployed persons and workers, of which the proportion of workers in all occupations decreases year by year (χ2=15.28, P<0.05). Conclusion: Men and rural areas are the high-risk groups and areas of chronic hepatitis B in this community, and the incidence fluctuates significantly from year to year, therefore, targeted monitoring, prevention and control, and health education should be carried out for specific groups of people, and based on the work of hepatitis B vaccination in children, efforts should be made to increase the coverage rate of hepatitis B vaccination in adults.

