七氟烷静吸复合麻醉与丙泊酚静脉麻醉在老年冠心病患者腹腔镜手术中的应用
殷占君 蔡展飞 庄丽丽


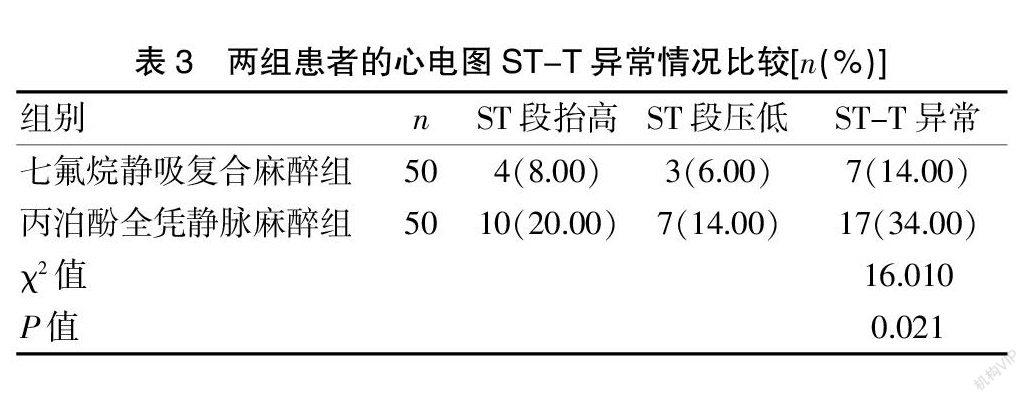
[摘要] 目的 探討接受腹腔镜手术治疗的老年冠心病患者麻醉维持中丙泊酚全凭静脉麻醉与七氟烷静吸复合麻醉的应用。 方法 回顾性选取2019年1月至2020年1月本院接受腹腔镜手术治疗的老年冠心病患者100例,依据麻醉维持方法分为七氟烷静吸复合麻醉组与丙泊酚全凭静脉麻醉组,每组各50例,统计分析两组患者的血流动力学、血管活性药物应用情况、心电图ST-T异常情况、心律失常发生情况、麻醉时间、术后恢复时间、补液量、尿量、认知功能。 结果 T2、T3、T4时七氟烷静吸复合麻醉组患者的心率、平均动脉压均低于丙泊酚全凭静脉麻醉组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。七氟烷静吸复合麻醉组患者的多巴胺、阿托品、去甲肾上腺素应用率均低于丙泊酚全凭静脉麻醉组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。七氟烷静吸复合麻醉组患者的心电图ST-T异常率为14.00%(7/50),低于丙泊酚全凭静脉麻醉组的34.00%(17/50),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。七氟烷静吸复合麻醉组患者的心律失常发生率为4.00%(2/50),低于丙泊酚全凭静脉麻醉组的18.00%(9/50),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 接受腹腔镜手术治疗的老年冠心病患者麻醉维持中七氟烷静吸复合麻醉的应用效果较丙泊酚全凭静脉麻醉好。
[关键词] 腹腔镜手术;老年;冠心病;丙泊酚静脉麻醉;七氟烷静吸复合麻醉;血流动力学;认知功能
[中图分类号] R541.4 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)24-0141-04
Application of sevoflurane intravenous-inhalation anesthesia and propofol intravenous anesthesia in elderly patients with coronary heart disease undergoing laparoscopic surgery
YIN Zhanjun CAI Zhanfei ZHUANG Lili
Department of Anesthesiology, Tianjin Ninghe District Hospital, Tianjin 300000, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the application of propofol intravenous anesthesia and sevoflurane intravenous-inhalation anesthesia in the maintenance of anesthesia in elderly patients with coronary heart disease undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Methods A total of 100 elderly patients with coronary heart disease who received laparoscopic surgery in our hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 were retrospectively selected and divided into sevoflurane intravenous-inhalation anesthesia group and propofol total intravenous anesthesia group according to anesthesia maintenance method, 50 cases in each group. The hemodynamics, application of vasoactive drugs, ECG ST-T abnormalities,the occurrence of arrhythmia,anesthesia time,postoperative recovery time,fluid volume,urine volume,and cognitive function were statistically analyzed between the two groups. Results The heart rate and mean arterial pressure of the sevoflurane intravenous-inhalation anesthesia group were lower than those of the propofol intravenous anesthesia group at T2, T3 and T4, and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). The application rates of dopamine,atropine,and norepinephrine in the sevoflurane intravenous-inhalation anesthesia group were lower than those in the propofol intravenous anesthesia group, and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). The abnormal rate of ST-T in ECG was 14.00%(7/50) in the sevoflurane intravenous-inhalation anesthesia group, which was lower than 34.00% (17/50) in the propofol intravenous anesthesia group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). The incidence of arrhythmia in patients in the sevoflurane intravenous-inhalation anesthesia group was 4.00%(2/50) lower than 18.00% (9/50) in the propofol intravenous anesthesia group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion Sevoflurane intravenous-inhalation anesthesia is more effective than propofol intravenous anesthesia in the maintenance of anesthesia in elderly patients with coronary heart disease undergoing laparoscopic surgery.

