Development of Medication Literacy Scale for Pediatric Population with Nephrotic Syndrome and Assessment on Reliability and Validity
Yi-Ming Zhao ,Qiang Sun ,Xiao-Lan Mo ,Yuan-Yuan Ma ,Xiao-Lin Xu*
1Pharmacy Department,Beijing Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University,Beijing 100045,China.2Blood purification center,Beijing Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University,Beijing 100045,China.3Pharmacy Department,GuangZhou Women and Children’s Medical Center,Guangzhou 510623,China.4School of Public Health,Shandong University,Shandong 250100,China.
Abstract Objective:To develop a medication literacy scale for the pediatric population with nephrotic syndrome (NS) in order to evaluate its reliability and validity.Methods:According to the medication belief scale,specific medication beliefs,and self-set dimensions,the NS pediatric population health literacy scale was designed to evaluate the medication literacy of 120 children with NS.Items,homogeneity,reliability,and validity of the scale were analyzed.Results:There were statistically significant differences in the Levene F test between the top 27%and the last 27%of the 22 items (P<0.001).The differences in the t-test were statistically significant (P<0.001).Content validity I-CVI:after deletion of item 4,the I-CVI of other items were all higher than 0.91.S-CVI was higher than 0.80,and S-CVI/ AVE was higher than 0.90.The internal consistency coefficient (Cronbach's α) was 0.868.Structural validity:KMO(Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin)statistical value was 0.862,and Bartlett's spherical test value was 1578.172(P<0.001).The extracted 6 common factors explain 70.21%of the variance variation.The loads of 22 items on their main factors are all greater than 0.427 except items 2 and 5.Conclusion:The medication literacy scale for the NS pediatric population has proved its good practicability,but some items of cognition need to be further explored.
Keywords:Nephrotic syndrome,Pediatric population,Medication literacy,Reliability,Validity
Introduction
It has been general acknowledged that the enhancement of medication literacy is one of the most economical and effective public health policies for maintaining national health [1].In “The options of implementation of healthy China initiative(2019-2030)” published by the State Council of China[2],the first major initiative is “Popularization of Health Knowledge”,in which rational medication is identified as the most important health knowledge and skill set mastered by citizens.As for children,adverse drug events are 2.73 times that of adults,due to immature organ development[3].
Medication literacy refers to the necessary cognitive and social abilities to follow through with medication information.Not be restricted to reading medication labels or remembering medication names [4].Medication literacy is an emerging and chronic non-infectious disease closely related factor.Improvement of medication literacy is considered a key factor contributing to the management of chronic non-infectious disease,reducing improper use of medical service resources (unnecessary hospitalization and emergency room visits),reducing medical expenses,and improving the efficiency and sustainability of the medical service system[5,6].
In recent years,the development of standardized and objective measures of medication literacy has become an important step in supporting health providers to plan interventions tailored to a patient’s medication literacy.A variety of measure can be used to evaluate medication literacy in patient.However,specific measurement tools needed by different diseases and patient populations are inadequate.
Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is a common glomerular disease in children,which threatens children’s lives[7].According to some studies,the incidence of primary NS in children is (2-4)/ 100,000 [8,9]and is showing an increasing trend.Children with NS are primarily treated with medicine,especially long term and repeated use of glucocorticoids,which will lead to various adverse reactions such as growth inhibition,hypertension,diabetes,and osteoporosis.
KDIGO (Kidney Disease:Improving Global Outcomes) emphasizes the importance of comprehensive management of children with poor glucocorticoid treatment [10].As documented in studies,about 84.9% of children in China have safety problems with medication at home,among which 72.5% of their parents stop medication without authorization [11,12],leading to prolonged and difficult disease recovery (some children may have end-stage renal disease).This affects the quality of the child’s life,and increases the unexpected expenditure on disease treatment.Therefore,it is vital to improving medication knowledge,while,there is no research tool to evaluate the medication literacy of NS in pediatric.Nutbeam suggested [13] that the evaluation content and development of medication literacy tools depend on the interpretation of mediation literacy.Based on the medication literacy scale from China and abroad,the present study developed a medication literacy scale for the pediatric population with NS based on the results of patient qualitative interviews and primarily analyzes its feasibility to provide a scientific basis for improving rational medication,increasing self-health consciousness,and enhancing health management at home.
Subjects and methods
Subjects
A total of 125 caregivers were selected as research subjects whose children with NS were treated in the nephrology department,Beijing Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University from June to December 2020.
Inclusive criteria.Caregiver of the patient corresponding to NS diagnosis criteria in“Evidence-based guidelines for the management of glucocorticoid-sensitive,relapsed/dependent nephrotic syndrome in children (2016)” (hereafter called‘guideline’) published by nephrology group of pediatrics society of Chinese medical association [14];Patient taking glucocorticoids or other drugs for more than one month;Caregivers with basic communication and comprehension ability confirmed by the doctor.Both caregiver and patient with normal mental condition and memory.
Exclusive criteria.Caregiver of NS patients with other organic lesions;Caregivers with significant intellectual,hearing,and visual impairment;Caregivers unable to complete the scale.
Methods
Sampling method.According to the proportional probability sampling method and standard of HIS system data of hospitalized children patients in 2019,5%~10%of total patients were sampled.A total of 1500 patients were pooled,and of that,a total of 125 caregivers of NS children were involved in this study.
Investigation method.Two trained pharmacists comprised the group,where each acted as the investigator and quality controller for each other.Only if a caregiver signed the informed consent,the investigation was carried out.The investigation was completed independently by the caregiver.If a caregiver were illiterate or unable to write,a pharmacist would read items one by one to help the caregiver choose a corresponding score.
Quality control.This part primarily consisted of investigation and data control.①Before the investigation started,the implementation plan was formulated,the investigator and quality controller were trained together.If a responder did not understand the contents of the questionnaire,they should inquire with the investigator.Investigators were not allowed to answer questions related to the answers of the questionnaire,or give inductive questions or cues.②In the data entry stage,double entry was carried out,and a consistency test was used to ensure the accuracy of the data entry.
Research tool
The authors designed the medication literacy scale based on the principle that medication science popularization education was designed to promote behavior change.In addition to demographic data,two sub-scales were designed as an action possibility and action adoption.The preliminary scale was formed using a semi-structured method,interviewing various professionals including nephrologists,epidemiologists,and statistical experts.After discussing and revising the items,a total of 22 items were eventually accepted in the preliminary scale.Then,the preliminary scale was applied to 125 children for pre-investigation.The formal scale was obtained using item selection and statistical analysis of the pre-investigation data.
Scale design index system.Following the principle of purpose,science,hierarchy,systematisms,operability,and comparability,the scale contained two aspects of “Action possibility “and “Action adoption.”First level indexes consisted of the “Public information,” “Medication cognition and attitude,”“Specific medication belief,” “Influence constraints,”“Medication behavior,” and “Compliance.” On this basis,second level indexes were constructed.The index construction framework is shown in Figure 1.
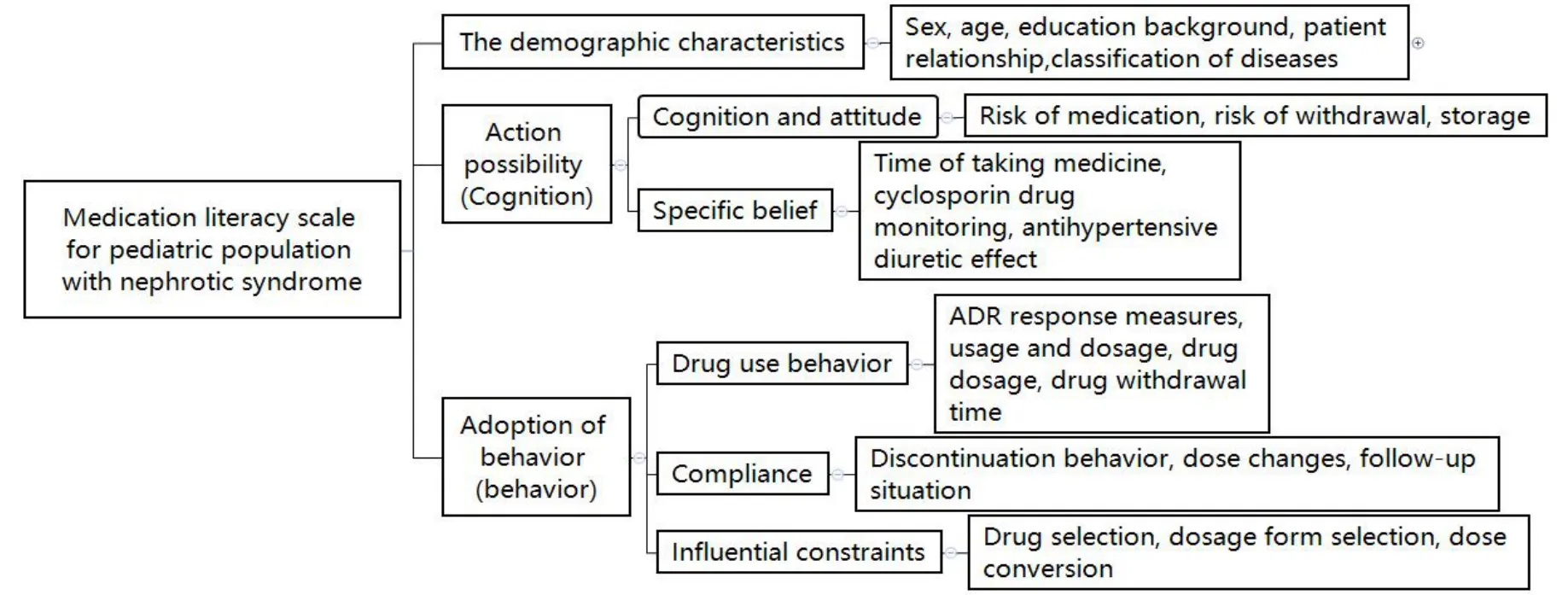
Figure 1 Questionnaire index design
Statistical analysis
The subject’s general data was described as a median and percentage (95% confidence interval).Measurement data were described as x±s,and enumeration data were described as rate.Data base construction was performed using Epi Data 3.1 software;statistical analysis was performed using SPSS.P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
Homogeneity test.Bivariate correlation analysis was used to calculate the product difference correlation coefficient(γ)between each item and the total score in order to indicate the homogeneity of the item and the whole scale.The γ value of the item was deleted if it was not significant or showed a low correlation.
Reliability analysis.The scale’s internal consistency was evaluated using an internal consistency coefficient(Cronbach's α),and two points of "yes/no" were used for items 1 to 11.Likert Five Grade was used for items 12 to 22,each item was graded as 0,0.25,0.50,0.75,and 1 point meaning strongly disagree,disagree,unsure,agree,and strongly agree,respectively.Due to the different measurement units,it was appropriate to adopt the standard Cronbach’s.Rang of Cronbach’s α:<0.60,unacceptable;0.60~0.65,not ideal;0.65~0.70,the minimum acceptable level;0.70~ 0.80,considerable;0.80~ 0.90,very good;>0.90,considering items reduction.
Validity analysis.①Construct validity:Factor analysis (principal component varimax rotation analysis) was used for testing the scale construct validity.Using a Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin test,Bartlett’s test,and Measures of Sampling Adequacy,it was determined whether items were suitable for factor analysis.②Content validity:Expert judgment was used for testing content validity.A total of 10 experts were selected to evaluate questionnaire validity.Their titles consisted of 4 seniors and 6 intermediates from the departments of nephrology and pharmacy.CVI was used for the quantitative index,the higher the CVI was,the better the scale reflected the meaning of the measured concept.
Results
Subjects basic information
A total of 125 questionnaires were collected.Among them,5 questionnaires with a logical error were deleted;namely,120 questionnaires were finally obtained(effective rate 96%).The subjects’general data are shown in Table 1.Of them,81 cases were male,39 cases were female.The gender ratio was similar to the reported literature[15].
Subjects analysis
The results showed that the score of the action possibility was 9.00(8.26,8.96),of which the low,the medium,and the high were 27.5%,38.3%,and 34.2%,respectively.There were statistically significant differences in the Levene's method F test (P<0.001)of the average scores of 11 items of the two extreme groups in the top 27%(n=33)and the bottom 27%(n=41).In addition,there were also statistically significant differences in the t test (P<0.05),indicating that all 11 items in the scale had a good degree of discrimination,which was able to clearly distinguish between high and low groupings.
The score of action adoption was 3.50,3.31,and 4.05,of which the low,the medium,and the high were 25.0%,49.2%,and 25.8%,respectively.Compared with the action possibility,items 3 to 7 were deleted,including item 14:"When half or one-third of a pill is needed,it can be accurately divided";Item 15:“An externally used medication(Kangfuxin ye)can be used as required by the doctor”,item 16:"Peritoneal dialysis tubes or other tubes shall be disinfected as required by the doctor”;Item 17:"glucocorticoids can be taken with meals if gastrointestinal irritation occurs";Item 18:"No more medication should be taken after the child vomits it up.(within 15 minutes)".There was a statistically significant difference in the Levene's method F test(P<0.05)of the average scores of the 11 items of the two extreme groups in the top 27%(n=37)and the bottom 27%(n=32).In addition,there were also statistically significant differences in the t test(P≤0.001),indicating that all 11 items in the scale had a good degree of discrimination,which was clearly able to distinguish between the high and low grouping.The results are shown in Table 2.
Homogeneity test
In the action possibility scale,the γ value of each item and the total score was more than 0.222.There was a statistically significant difference with the total score(P<0.05),indicating a high homogeneity of each item within the action possibility scale.In the action adoption scale,except for the γ value of item 5 the total score was 0.268(P<0.01),the γ value of the rest of each item,and the total score was more 0.353.In addition,there were statistically significant differences with the total score (P<0.001),indicating a high homogeneity of each item in the action adoption scale.
Validity test
Content validity.Expert judgment was used for the evaluation of the content validity of the action possibility scale.The correlation was evaluated on a 4-point scale “1=irrelevant,2=weak correlation,3=strong correlation,and 4=very correlation”.The results showed that except for I-CVI of item 4 was 0.55,meaning there was a problem within this item.The I-CVI of the other items were >0.91,indicating a high correlation between each item and the study concept.Furthermore,S-CVI and S-CVI/Ave of the scale were more than 0.80 and 0.90,respectively,indicating a high degree of experts’recognition for this scale.
Construct validity.Exploratory factor analysis was used for the evaluation of the construct validity of the two sub-scales.The closer the KMO value is to 1,the more common factors there are among the variables.The result showed that the KMO value was 0.862,indicating a good construct of scale.Bartlett’s test value was 1578.172(P<0.001,indicating that there were common factors among the total correlation matrices,which was suitable for factor analysis.The results are shown in Table 3.
Principal component analysis was used to analyze 22 items,and the number of factors was determined as 6.The results showed that the cumulative variance contribution rate of the two factors was 70.2%,and the cumulative variance contribution rate was more than 70%.The maximum variance method was used to analyze the factor loading.The main factor loading of 20 items were more than 0.427,indicating a high loading value,except for item 2 and item 5,which were 0.353 and 0.287,respectively.However,the matching situation of each item and its expected factor showed significant deviation in sub-scale 1 (action possibility),while the matching situation of each item and its expected factor were good in sub-scale 2(action adoption).The data analysis results showed that the common factor 1 included items 1,2,3,7,10,and 12-22;common factor 2 included items 5,6,and 11;common factor 4 included item 9;common factor 5 included item 8,and common factor 6 included item 4.Further adjustments should be made to name and classify factors or deleted related items to improve the degree of discrimination.The result is shown in Table 4.

Table 1 Demographic characteristics of NS patients and their families
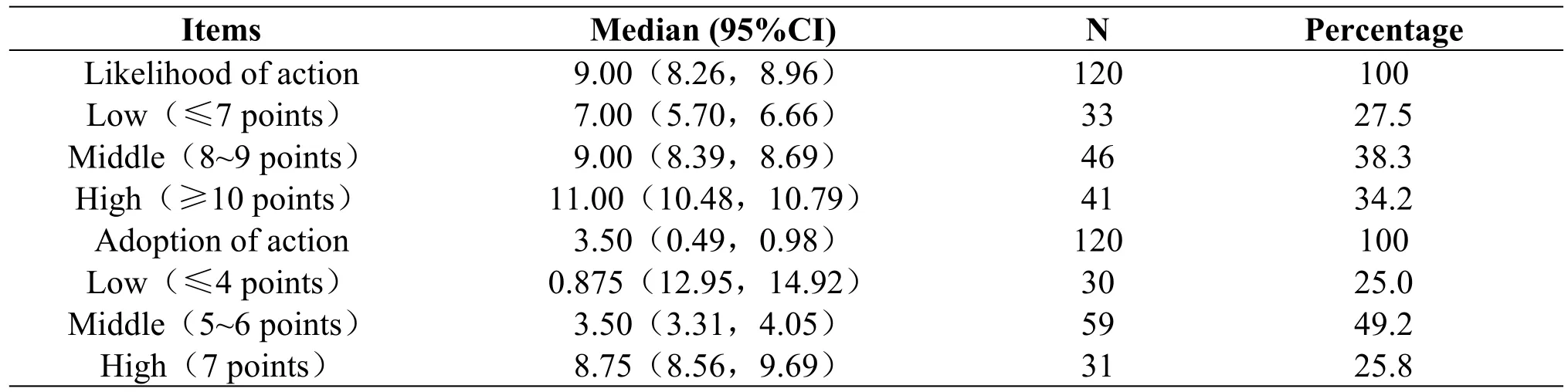
Table 2 The total score for the likelihood of action and the adoption of action

Table 3 Structural validity analysis
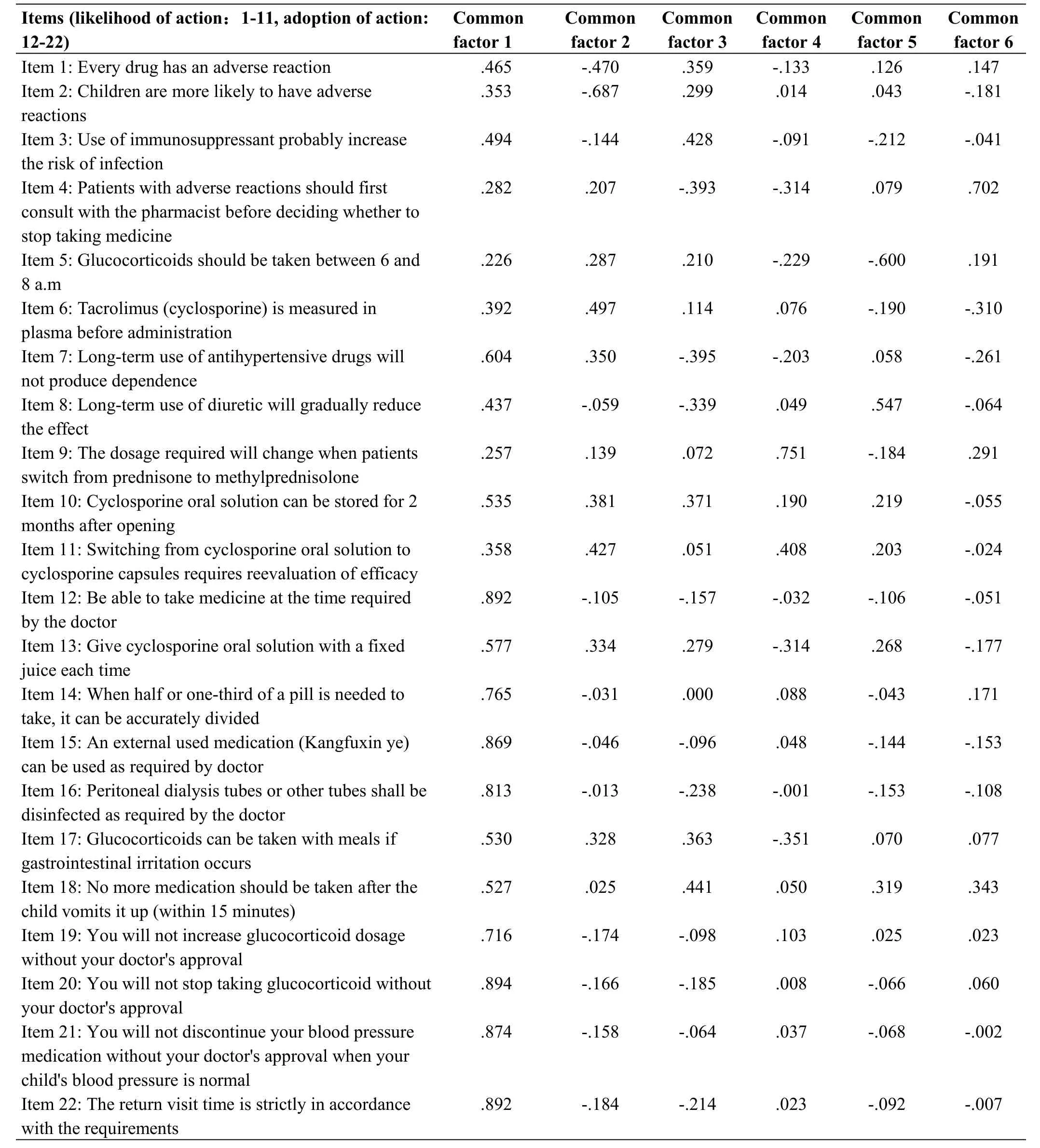
Table 4 Load factors of items of the scale
Reliability test.The α reliability coefficient was used for analyzing internal consistency,Cronbach’s α of the scale was 0.868.The α value of the action possibility sub-scale was 0.581,indicating low reliability,so a further study of the sample expansion was needed.The α value of the action adoption sub-scale was 0.965,indicating high reliability.
Discussion
Design of medication literacy scale
Currently,there are many evaluation tools available.However,we need a specific assessment tool that can make pharmaceutical care more targeted.Based on the theory of the health belief model and belief of the medical questionnaire,the present study comprehensively reflects the connotation of medication literacy that children with NS and their caregivers should possess in 6 dimensions,forming a medication literacy evaluation index system.
Reliability and validity of scale
Reliability and validity are two key factors that reflect scale quality [16].Regarding reliability in the present study,Cronbach's α value was 0.868 in the action adoption sub-scale,indicating an ideal scale.Cronbach's α value was 0.581 in the action possibility sub-scale,indicating low reliability.The reasons for this might be as follows:As for item 5,medication time was described as 6-8 am,but caregivers did not pay attention to the exact time,they only knew to take the medication in the morning with a meal;As for item 7,there was comprehension deviation from caregivers,so it is necessary to optimize the question.
Regarding validity,it primarily reflects if the scale can achieve the accuracy of the measurement index or not.In the context of validity,the I-CVI value of item 4 was dissatisfactory.There were three main reasons for this:The caregivers did not fully understand the meaning of adverse reactions,they generally believed adverse events were all adverse events that occurred after taking the medication [17,18];in terms of adverse action management,caregivers usually choose to stop the medication,which is suitable for conventional medication only [17].However,in this study,all medications referred to immunosuppressants,glucocorticoids,and antihypertensives,so the question was not clearly described;Pharmacists are important members of the medical staff,but the significance of their duties is not understood or recognized by most caregivers in China [19].The I-CVI values of other items were more than 0.91,indicating a high correlation between each item and the research concept.The matching of the 22 items with related factors suggested that matching was ideal for action adoption.At the same time,there was a significant deviation for action possibility,it was necessary to re-name and classify the factors.
Innovations and limitations
In the present study,a self-designed medication literacy scale was adopted for children with NS.The scale is designed to distinguish different levels of medication literacy,making up the related vacancy in China.However,there were some limitations in the present study:①Limited by time and study conditions;only 120 questionnaires were included in this study,so the sample size was small,a larger sample size is needed in the future.② Its general applicability needs to be verified in other types of disease states.③In addition to the items included in the present scale,many other factors may influence medication literacy of children with NS,and should be considered and included in a future study.
In conclusion,the research is still not deep enough on the medication literacy of children with chronic diseases in China.The evaluation systems are insufficient,so developing an evaluation system for children is necessary.More attention will be paid to people's health behavior regarding people’s health awareness in a post-pandemic era [20].Rational medication is one of the important components in chronic disease management.In future educational works and patients with chronic disease,the medication literacy scale can be used to evaluate the medication conditions of children with NS.It can provide information for medical staff to correct the poor cognition of children’s families,relieve parents’anxiety,and improve their care[21].
 Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch2021年3期
Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch2021年3期
- Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch的其它文章
- Discussion on Treatment of Asthenospermia from the Perspective of Psychosomatic Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Psychosomatic Medicine and Evidence-Based Surgery:Reflections and Perspectives
- A Commentary of a Psychological Experience Questionnaire for Screening Non-Psychiatric Inpatients for Violence-Related Mental Health Disorders
- Evidence Based Medicine in Psychosomatics:Prospects and Challenges
- A Case Report:Traditional Chinese Medicine for Curing Psychosomatic Tinnitus Symptoms
- Impacts of Social Media Use on Body Dissatisfaction Among Female College Students in China
