Study on pharmacodynamic mechanism of compound Shuanghuanglian in prevention and treatment of pneumonia based on network pharmacology and association analysis
Xiao-Lin Zhang, Cao Di, Long Zhang, Chao-Chao Hua , De-Hui Ma, Hui-Hui Liu, Ming-Jun Liu *
Study on pharmacodynamic mechanism of compound Shuanghuanglian in prevention and treatment of pneumonia based on network pharmacology and association analysis
Xiao-Lin Zhang1, Cao Di2, Long Zhang1, Chao-Chao Hua1, De-Hui Ma1, Hui-Hui Liu3, Ming-Jun Liu1 *
1Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130117, China.2Changchun Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130000, China.3Chifeng University School of Basic Medical Sciences, Chifeng 024000, China.
Platform for prediction and analysis of Chinese medicine against coronavirus disease 2019 (TCMAntiCOVID-19 V1.0) was used to explore the active ingredients, key targets and mechanisms of the compound coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), It will provide a reference for the clinical application of this prescription as a broad-spectrum agent in the prevention and treatment of pneumonia. It will also win valuable time for finding symptomatic Chinese medicine prescriptions and vaccine research and development.Set Banxia Tianma Baizhu decoction as the negative control. Qingfei Paidu decoction as the positive control, and use TCMAntiCOVID-19 V1.0 platform to predict the potential efficacy of compound Shuanghuanglian. We used the quantitative evaluation algorithm of multi-target drugs for the network disturbance of disease, by comparing the changes of network topological characteristics before and after drug intervention, and using the disturbance rate to evaluate the drug’s dryness for disease prediction. Using batman-TCM, the credibility card value of the target sets 20, then the target of traditional Chinese medicine composition is predicted, the heterogeneous network of traditional Chinese medicine composition-drug target-disease target is established. The interaction of related network is realized by JavaScript Visualization is realized, and cycloscape is edited. The average connectivity, the average shortest path length, the centrality of connectivity and the centrality of network compactness are calculated by using R’s iGraph package, and nulldistribution is used as the overall distribution to correct the disturbance rate of drugs to the real network, so as to evaluate the stability of network topology and explore its mechanism.The key targets of COVID-19 were Aif1, Ccl2, Cdc20, Cxcl13, Fcer1g, Ido1, Ifng, Il10, Il1rnIl6, Ncf4, Ptger4, Spi1, Tnf, Xcl1; after the intervention, the average connectivity, the average shortest path length, the network connectivity centrality and the network tightness centrality were (2.31e+1), (2.41e+0), (6.21e−1), (1.68e−2) respectively; the total scores of network stability evaluation of drug intervention diseases were 18.29, 12.59 and 19.10 respectively.Compound Shuanghuanglian can effectively break the stability of the disease network of COVID-19, and the overall effect of prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is close to that of the positive control Qingfei Paidu decoction, which is significantly better than that of the negative control Banxia Tianma Baizhu decoction. That is because compound Shuanghuanglian mainly acts on Aif1, Ccl2, Cdc20, Cxcl13, Fcer1g and other key targets. Compound Shuanghuanglian plays important role of inhibiting the inflammatory response of patients with COVID-19 and alleviating lung injury, so as to achieve the purpose of treating COVID-19. At the same time, in the initial stage of COVID-19 and other sudden infectious pneumoniausing compound Shuanghuanglian can win valuable time before finding symptomatic Chinese medicine prescription and vaccine research.
Compound Shuanghuanglian, Coronavirus disease 2019, TCMAntiCOVID-19, Network pharmacology, Pharmacodynamic mechanism
Background
Novel coronavirus pneumonia broke out in the whole world. At 8am on April 10th 2020, there are 465,329 confirmed cases in USA and 18,279 deaths in Italy. The mortality is up to 12.73%. 1519702 cases of novel coronavirus pneumonia were identified, 92384 cases died and 277250 cases were cured globally [1]. According to statistics from the, as of February 17th,2020, there were a total of 60,107 confirmed cases of COVID-19 involved in rescue by traditional Chinese medicine in China, accounting for more than 80% [2]. Among them, utilization rate of Chinese medicine is83.3% in 225 fixed-point hospitals in Hubei Province. The 9 shelter hospitals developed and opened to the outside world basically take all traditional Chinese medicine. The involvement of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of diagnosed cases in areas other than Hubei with curative discharge and symptom improvement accounted for 87% [3]. Traditional Chinese medicine has had remarkable success in combating COVID-19, and the experience of integrated traditional and western medicine provides a demonstration and reference worldwide.
Emerging coronaviruses are surgically spreading through many routes, including droplets, contacts, and so on, and because of their infectious and rapid spread, they have become seriously detrimental to people’s health, public safety, and public property [4].No specific agent has been investigated for the treatment of COVID-19. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) because of its unique holistic view and syndrome differentiation makes TCM and TCM become “specific medicines” for the prevention of COVID-19 worldwide, and in February the national anti plague related department recommended the compound Shuanghuanglian as one of the optional medicines for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, and the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica combined with Wuhan virus institute successively confirmed that Shuanghuanglian has a certain inhibitory effect on this virus [5].
The compound Shanghuanglian is derived from the practice of “Yinqingsan” herbal formula recorded in, written by Wu Tang in Qing Dynasty (218 BC). Prepared from a combination of three herbs (Jinyinhua (), Lianqiao (), and Huangqin ()) [6]. The long-term clinical practice of TCM has proved that these three herbs have good efficacy in clearing away ShangJiao pulmonary heat and resolving pharyngeal and laryngeal heat toxins (Shangjiao is named after the human body in Chinese medicine. It refers to the part from the throat to the chest and diaphragm, mainly including the heart and lung). It is confirmed by modern research that the compound Shuanghuanglian has the effects of broad-spectrum antiviral, bacteriostatic, and improving the body’s immunity [7]. After more than 20 years of clinical practice, it has been shown that this drug can significantly treat bacterial respiratory infections in the clinic, and the clinical application scope is not only limited to those diagnosed and treated by respiratory diseases, but also extended to other systemic diseases, and the clinical efficacy for common diseases is exact.
In this study, we initially investigated the pharmacodynamic mechanism of the compound Radix Rehmanniae in treating COVID-19 by network pharmacology based on a novel pharmacodynamic prediction analysis platform of traditional Chinese medicine against coronavirus pneumonia (TCMAntiCOVID-19 V1.0) [8]. This method effectively integrates the aspects of “drug-target-disease-signal pathway” analysis by multi-level bioinformatic network [9]. It will provide a theoretical basis for further development of the compound Shuanghuanglian treatment on the pharmacological mechanism of COVID-19. It will also d identify the active ingredients and to explore the mechanism of action, a TCM formula treating COVID-19 with clinical feedback of the compound Shuanghuanglian, which will provide a reference for further clinical practice and efficacy evaluation, and to win valuable time for searching for symptomatic TCM formula and vaccine development in the face of sudden infectious pneumonia such as COVID-19 in the initial onset period.
Methods
Disease network setup
The disease network is constituted by differentially expressed proteins from Severe Acute Respiratory Syndromes model mice as well as cytokines specific for COVID-19. Significantly changed cytokines in critically ill patients using COVID-19: IL2, Il7, IL10, GSCF, IP10, MCP1, MIP1A, TNF-α. Protein interaction network constructed with differential genes in animal model of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndromes inoculated mice to model the pneumonia disease network specific to COVID-19 to model the involvement of drug pharmacophore in “response to bacteria and viruses”, “cytokine production”, and other biological signaling pathways associated with cytokine storm [8]. At the same time, Banxia Tianma Baizhu decoction was set as the negative control compound, and Qingfei detoxification decoction was set as the positive control. The TCM compound pharmacophore action COVID-19 occurs to some extent simulated through this disease network.
TCM target prediction
Input of compound Shuanghuanglian compatibility Chinese medicine “Jinyinhua/Lianqiao/Huangqin” in TCMAntiCOVID-19 platform, a total of 82 active compounds were screened out according to the criteria of oral bioavailability (OB ≥ 30%), drug-likeness (DL ≥ 0.18), the basic information is shown in Table 1. The 274 effective drug action targets were obtained by TCMSP combined with UniProt database name annotation conversion. BATMAN-TCM target prediction was set a prediction score greater than 20 when ranking drug target interactions from high to low based on the likelihood score [10].
Prediction of the likelihood of drug target interactions based on the similarity of published and validated known drug target interactions yielded the following for the compound bishuanglian drug targets: Aif1, Ccl2, Cdc20, Cxcl13, Fcer1g, Ido1, Ifng, Il10,I l1rn, Il6,Ncf4, Ptger4,S pi1, Tnf, Xcl1.
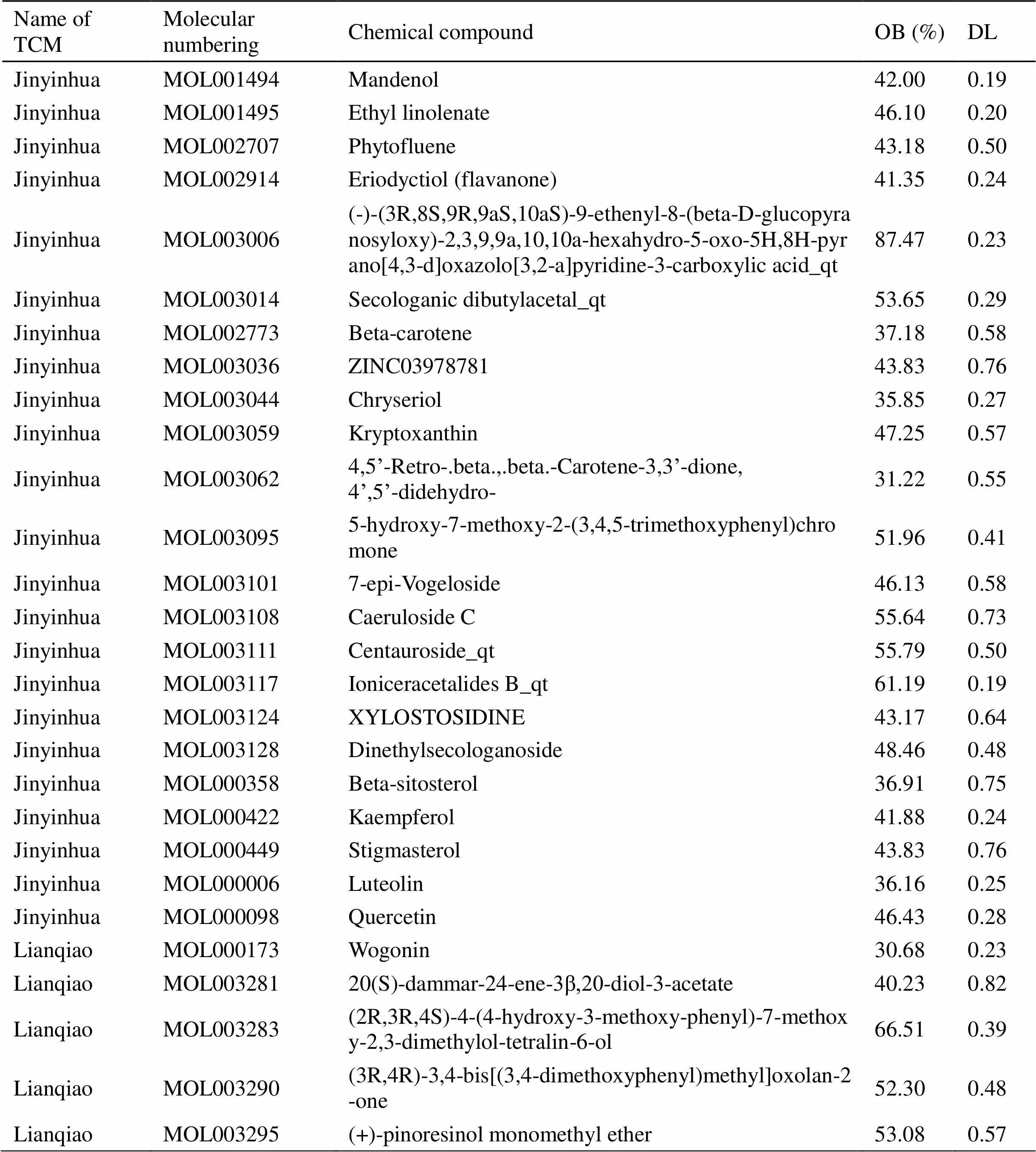
Table 1 Basic information of 161 candidate compounds after screening in compohund Shaunguanglian
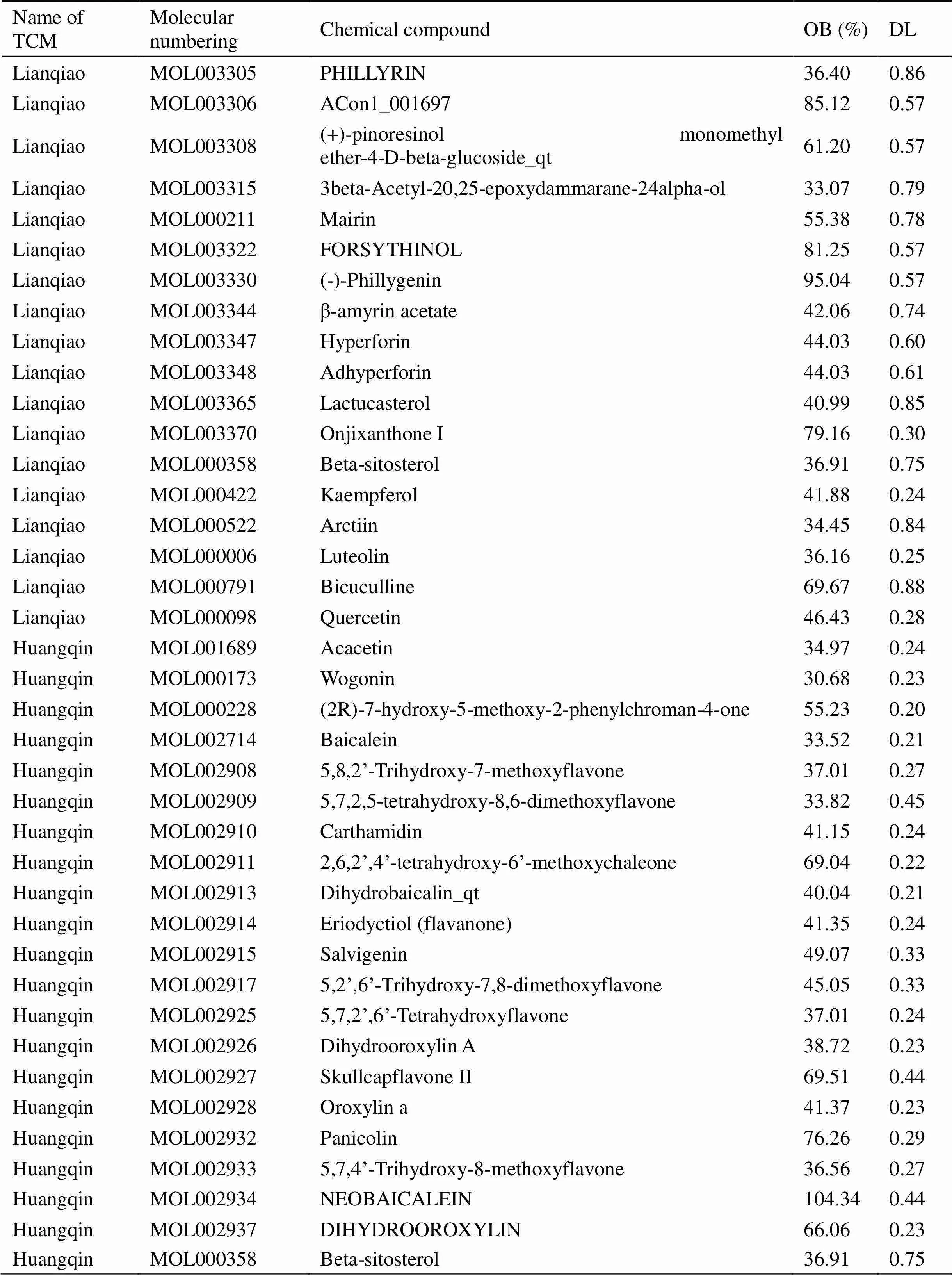
Table 1 Basic information of 161 candidate compounds after screening in compohund Shaunguanglian (Continued)

Table 1 Basic information of 161 candidate compounds after screening in compohund Shaunguanglian (Continued)
TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; OB, oral bioavailability; DL, drug-likeness.
Component-dug-target disease protein interaction network
The confidence score was set to 20, and the relationship between components and drug targets was analyzed by bioinformatics analysis tool of molecular mechanism of TCM (BATMAN-TCM). Set the confidence score to 0.5, and use the STRING website to analyze the Protein-Protein Interaction relationship between drug targets and disease proteins [11]. After comprehensive analysis and editing with Cytoscape, the following component drug target disease protein interaction network is obtained, as shown in Figure 1.
The influence of drugs on the disturbance of network topology
Through quantitative evaluation algorithm, the platform predicts the potential efficacy based on the disturbance effect of multi-target drugs on the disease network. By constructing a random network, it simulates the overall distribution of the influence of deleting nodes on the random network robustness (permutation test), observes the position of drugs in the overall distribution of the real network disturbance, and analyzes the disturbance rate after calculation and correction, objective to evaluate the disturbance intensity of drugs to the real network. The disturbance rate is corrected by null distribution of random network [8]. The average connectivity was (3.61e+1) vs. before intervention, after intervention (2.31e+1), the disturbance rate was −35.96%, and the corrected disturbance rate was −3.63, as shown in Figure 2A. The mean shortest path intervention (2.15e+0) vs. dry prognosis (2.41e+0), disturbance rate 11.95%, corrected disturbance rate 7.83, see Figure 2B. Connectivity centrality, before intervention (8.81e−1), after intervention (6.21e−1), the disturbance rate was −29.51%, and the corrected disturbance rate was −0.94, as shown in Figure 2C. The tightness and centrality was (4.43e−1) vs. before intervention, after intervention (1.68e−2), the disturbance rate is −96.21%, and the corrected disturbance rate is −5.89, as shown in Figure 2D.
Evaluation of the robustness of drug intervention network
On the premise of preserving the number of nodes and edges of real network, the topological characteristics of random network are generated to form null distribution of disease network. By observing the different changes of network topological characteristics after removing drug targets, and then comparing the drug effect of real disease network with null distribution composed of random network, to study whether there are significant differences in network robustness between real network and random network after the same drug disturbance. The corrected disturbance rate of topological characteristics, the corrected disturbance rate of topological characteristics, the average network connectivity, the average shortest path, the centrality of connectivity and the centrality of compactness are shown in Table 3.
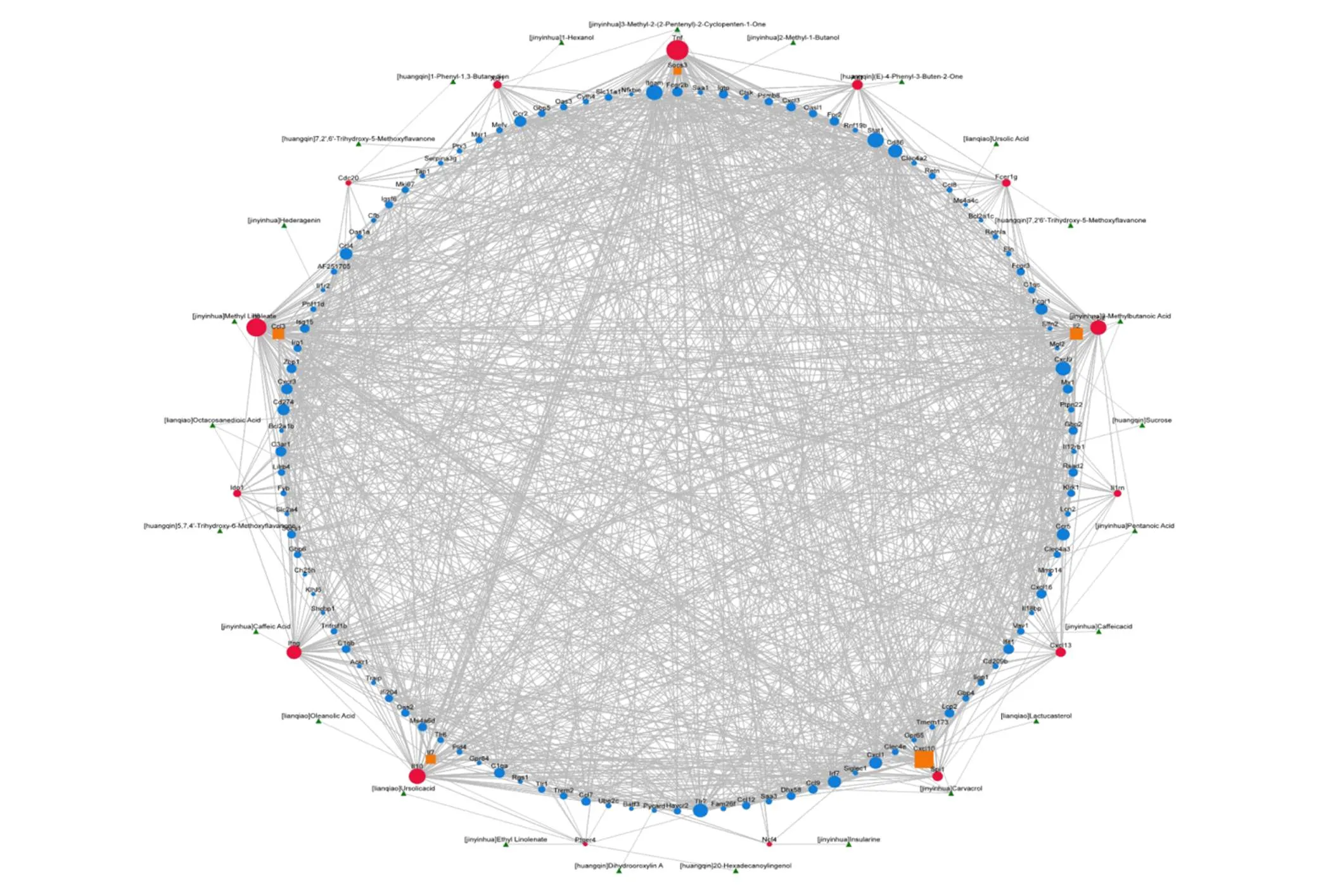
Figure 1 Component-drug-target disease protein interaction network
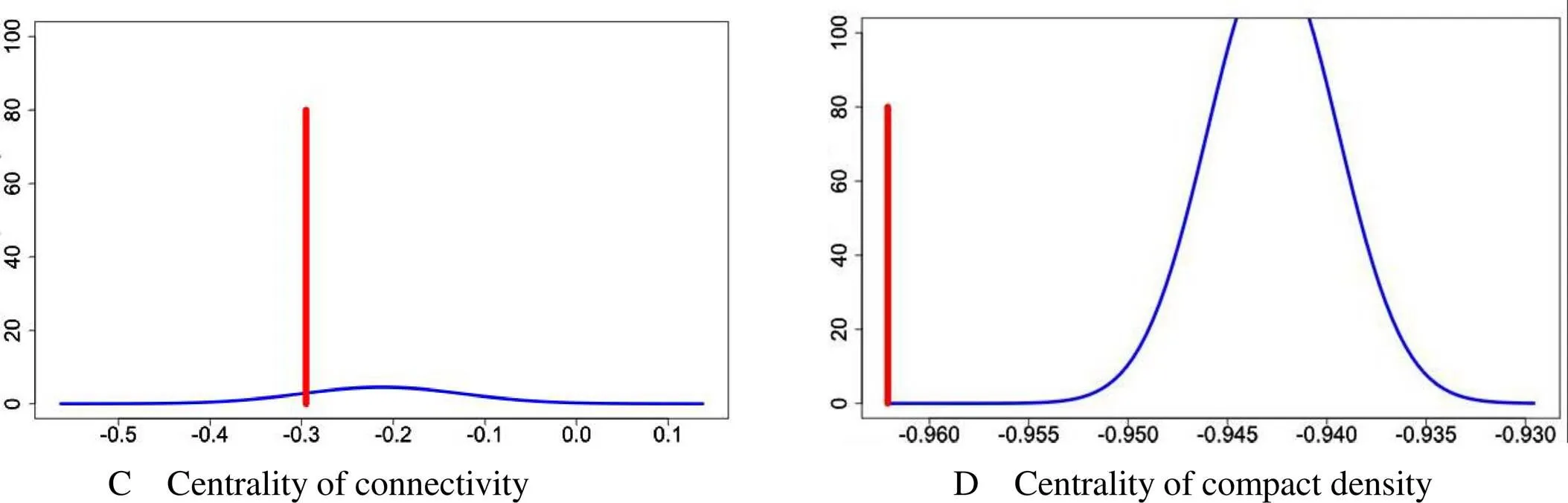
Figure 2 The influence of drugs on the disturbance of network topology

Table 3 Topological characteristic disturbance rate after correction of compound Shuanghuanglian and control
Results
TCMAntiCOVID-19 platform combined with BATMAN-TCM was used to predict the target of compound Shuanghuanglian. The results showed that the target of compound Shuanghuanglian were Aif1, Ccl2, Cdc20, Cxcl13, Fcer1g, Ido1, Ifng, IL10, Il1rn, IL6, Ncf4, Ptger4, Spi1, Tnf, Xcl1.
The quantitative evaluation algorithm of multi-target drugs for the disturbance of disease network was used. The results showed that the average connectivity decreased by 1.31e, the negative disturbance rate reached −35.96%, and the disturbance rate after correction was −3.63. The average shortest path increases by 0.26e, the disturbance rate is 11.95%, and the corrected positive disturbance rate is 7.83. The centrality of connectivity decreases by 2.60e, and the disturbance rate reaches −29.51%. After correction, the disturbance rate is −0.94. The centrality of compactness decreases by 2.75e, and the disturbance rate reaches −96.21%. After correction, the disturbance rate is −5.89.
Discussion
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, TCM has gained great attention because of its unique way of thinking, diagnosis and treatment, and remarkable clinical effect. Team of Burli Zhang of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine comprehensively collated and analyzed the diagnostic and therapeutic regimens of TCM in 24 regions of China, and concluded that the COVID-19 pathomechanism is “Wet, Hot, Toxic, Stasis, and Deficiency”, in which TCM formula focused on Shanghuanglian class is recommended [12, 13]. TCM compound Shanghuanglian is one of the long-standing clinical classic formulas for TCM, which consists of three herbs, Jinyinhua, Huangqin and Lianqiao [14], and has the characteristics of relieving wind and relieving exterior, clearing heat and detoxification, and clearing both exterior and interior. Jinyinhua is the “Jun drug” and the auxiliary ingredients Huangqin and Lianqiao are “Chen drugs”, and the compound Shuanghuanglian can “Clear Heat and Detoxify”, “Clear Evil Out”, and effectively inhibits the progression of the disease [15]. It was found that the compound Shanghuanglian can achieve the effect of inhibiting inflammatory responses by neutralizing the endotoxin produced by bacteria, and by promoting the body production instant file name search α, improve the body’s own immunity and thus enhance the body’s antiviral effect [16]. Studies have confirmed that Jinyinhua has the effects of broad-spectrum antibacterial [17], inhibiting influenza associated virus replication due to multiple active components [18]. The active ingredient of Lianqiao glycosides in Lianqiao can inhibit the expression of nucleoprotein of influenza A virus [19]. Huangqin glycoside is anti alphavirus, herpes simplex virus and coxsackievirus [20, 21], while the compound Shuanghuanglian can down regulate interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α. The levels of other inflammatory factors have obvious down-regulation efficacy and inhibit nuclear factor-κ-gene binding in lung tissue-κ. The B signaling pathway gets overexpressed, thus alleviating the inflammation of the lung in pneumonia patients and improving the symptoms such as shortness of breath and chest tightness, which has a better promoting effect on the lung tissue to gradually recover the normal morphology and physiological function [22]. Related studies have shown that baicalein can obviously inhibit Staphylococcus aureus [21], and studies from Xiuhua Wu confirmed that Huangqin can significantly increase lung index and survival rate of mice with pneumonia, and can obviously improve their lung tissue inflammatory mutations, and found that Huangqin has some in vivo anti influenza A virus effects [23]. Wogonin is a common active ingredient shared by Lianqiao and Huangqin, and studies by Wuying et al found that Huangqin could significantly inhibit the expression levels of various inflammation related factors in alveolar macrophages after influenza virus infection such as pneumonia and had better anti-inflammatory effects [24]. Modern studies have found that lutelin inhibits the effect of influenza virus H1NI under in vitro settings. Kaempferol is a shared compound between Jinyinhua and Lianqiao, betasitosterol is a chemical shared among three herbs of Jinyinhua, Lianqiao and Huangqin, and both kaempferol and betasitosterol have better anti-inflammatory effects [25, 26]. It is widely used clinically in diseases such as pneumonia, acute pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis and other respiratory infections [27–34]. Prediction by big data, network pharmacology techniques, and entropy cluster association analysis can provide pharmacodynamic mechanism related data support for the evaluation of TCM formulas, effectively promoting the rapid and widespread clinical use of TCM Formulas, so that they can be used as broad-spectrum prevention and treatment drugs with well-defined effects in times of strong infectious pneumonia outbreaks.
This study applies the robustness of networks to perturbations in network science as a metric. The effect of multi-target drugs on disease network was evaluated by network pharmacology and association analysis [35], the effect of targets on network stability was evaluated by compound Shuanghuanglian pair to evaluate the topological characteristics of the acting targets in disease network, and the change of overall network topological characteristics after target removal [8, 17]. And compared with the standard target effect control of negative reference Banxia Tianma Baizhu decoction and positive reference Qingfei detoxin decoction, the potential pharmacodynamic effect of the compound Shuanghuanglian for diseases was finally quantitatively evaluated.
Target prediction of ingredients from TCM using the TCMAntiCOVID-19 platform combined with BATMAN-TCM yielded compound Shuanghuanglian drug targets as Aif1, Ccl2, Cdc20, Cxcl13, Fcer1g, Ido1, Ifng, IL10, Il1rn, IL6, Ncf4, Ptger4, Spi1, Tnf, Xcl1. Among them, AIF1, a calcium binding scaffold protein mainly expressed in immune cells, is a surface marker of monocytes/macrophages and microglia [36, 37], and it is involved in inflammatory response and immunoregulation in the prevention and treatment of pneumonia by Shuanghuanglian [38]. AIF1 can activate monocytes/macrophages, microglia, lymphocytes and other immune cells and promote the expression of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines (such as IL6, IL10), chemokines (such as CCL2, CXCL13) inducible nitric oxide synthase [39].
Research using the quantitative evaluation algorithm of the effect of multi-target drugs for disease network perturbation, the quantitative evaluation algorithm of the effect of multi-target drugs for disease network perturbation concluded that after compound Shuanghuanglian action, the average connectivity decreased by 1.31e, the negative perturbation rate reached −35.96%, and the corrected perturbation rate −3.63;The average shortest path rose by 0.26e, the perturbation rate was 11.95%, and the positive perturbation rate reached 7.83 after correction;Connectivity centrality decreased by 2.60e, achieving a perturbation rate of −29.51% with a corrected perturbation rate of −0.94;The closeness centrality decreased by 2.75e with a high perturbation rate of −96.21% and a corrected perturbation rate of −5.89. It indicated that the compound bishuanglian could strongly break the stability of the ring breaking COVID-19 disease network. For drug intervention disease network robustness evaluation, the total perturbation score of compound Shuanghuanglian compared with the negative control of Banxia Tianma Baizhu decoction and the positive control of Qingfei detoxification decoction was 18.29 in between. Mean connectivity was −3.63 lower than control, and disruptions were stronger than control. The average shortest circuit was 7.83 which was slightly lower than the positive control Qingfei detoxification decoction 8.30. Connectivity centrality of −0.94 was less negatively perturbed than both sets of controls. The closeness centrality was −5.89, and the ring breaking intensity was slightly lower than that of the positive control Qingfei detoxification decoction −6.76. It is indicated that the overall effect of combined Shuanghuanglian prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is close to that of the positive control Qingfei detoxification decoction, which is significantly better than that of the negative control Banxia Tianma Baizhu decoction, which may play a spectral type prevention and treatment effect on COVID-19 and other related pneumonia in the period without “specific medicine”.
Limitations
This study applied network pharmacology and association analysis to evaluate the effects of multi-target drugs on the disease network, and compared with the target effect control of negative reference Banxia Tianma Baizhu decoction and positive reference Qingfei detoxification decoction, to finally quantitatively evaluate the potential pharmacodynamic effect of the compound Shuanghuanglian for disease.
Several limitations exist. ① The related results are based on database analysis because the research subjects are special and can’t be experimentally verified. ② Contrast positive and negative drugs are traditional Chinese medicine formulas, because there is no specific western medicine, and no clear positive drug control can be obtained. ③ The establishment of relevant databases is shorter because COVID-19 is an epidemic of temporal plague and there are fewer relevant studies.
Conclusion
In this study, from the perspective of disease network perturbation, integrating multi-level data, using multi compound contrast and targeting key protein analysis to evaluate the potential effectiveness of compound Shuanghuanglian, which can provide pharmacodynamic relevant reference data for the next relevant experiments or clinical validation. At the same time, based on the pharmacodynamic target and overall network topological characteristics, it provides evidence for rational and practical use of compound Shuanghuanglian to prevent the progress of related pneumonia such as COVID-19, and at the same time, for facing sudden infectious pneumonia such as COVID-19 in the early onset period, it wins valuable time to find symptomatic Chinese medicine formulas and vaccine development.
1. Liang K. Mathematical model of infection kinetics and its analysis for COVID-19, SARS and MERS.. 2020;82:104306.
2. Beijing Business Today. National Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine: the proportion of confirmed cases in China medicine involved in rescue treatment is 85.20%. https://dy.163.com/ article/F5JOEI740519DFFO.html. Published February 17 2020. Accessed April 28 2021.
3. Health Commission of Hubei Province: the use rate of rescue Chinese medicine for novel coronavirus pneumonia in Hubei province is 83.3% literature. https://m.gmw.cn/baijia/ 2020-02/18/33564341.html?sdkver=ab0abe70l. Published February 20 2020. Accessed April 28 2021.
4. Hhang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China.2020;395(10223): 497–506.
5. Phoenix Net. Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica and Wuhan Institute of Virology: the initial study found that BIS Huanglian oral solution inhibited new coronavirus. https://tech.ifeng.com/c/7tijg7NjEOl. Published February 02 2020. Accessed April 28 2021.
6. Guo J, Song D, Rong J. Pharmacological effects and clinical application and adverse effects of Shuanghuanglian.2017;10(21):161–163.
7. Wang YY, Deng WP, Li XQ. A mechanistic study on the protective effect of Shuanghuanglian oral solution in C57BL/6J nude mice, a model of acute liver failure induced by murine hepatitis 3 virus.2020;29(09):941–944.
8. Guo FF, Zhang YQ, Tang SH, et al. Construction of an anti-COVID-19 pharmacodynamic prediction platform for traditional Chinese medicines and analysis of potential effects of commonly used traditional Chinese medicines.. 2020;45(10):2257–2264.
9. Xu HY, Zhang YQ, Qin YW, et al. Exploring the scientific connotation of TCM syndromes and recommended formulas for the full course of coronavirus disease based on TCMIP 2.0.. 2020;45(07):1488–1498.
10. Peng LH, Liu HY, Ren RL, et al. Prediction of drug target interactions based on multi marker learning.. 2017;53(15): 260–265.
11. Niu M, Wang RL, Wang ZX, et al. Rapid screening mode and application of a Chinese herbal formula for anti novel coronaviruses based on clinical experience and molecular docking techniques.. 2020;45(06):1213–1218
12. Ruan YD, Fan DM, Xie YB, et al. Discussion from the idea of cold dampness disease to treat a coronavirus disease.2020;37(06):1003–1007.
13. Yu MK, Chai QY, Liang CH, et al. A pooled analysis of traditional Chinese medicine prevention and treatment options for coronavirus disease.. 2020;61(05): 383–387.
14. Feng YP, Du GL, Di B, et al. On compatibility of Chinese formula -- metabolic relationship.. 2007;12(10):69–71.
15. Wang H, Xi L. Ultra high pressure assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction of the active components of compound Shuanghuanglian.2019;42(03):628–638.
16. Li JF, Zhang ZD, Qi YF, et al. Protective effect and preliminary mechanism study of Shuanghuanglian oral solution on septic rats. C. 2014;37(01):111–114.
17. Feng XL, Xu QH, ZhaoXY, et al. In vitro antibacterial activity and in vivo anti-inflammatory effect of Jinyinhua and its compound formula.. 2013;30(01):35–39, 62.
18. Zhu LF, Bao XX, Yao Hui, et al. Jinyinhua and Houttuynia cordata inhibit influenza A virus replication in vitro study.. 2018;39(04):485–486.
19. Duan LJ, Zhang Q, Wang NR, et al. Study of the effect of Lianqiao glycoside on the expression of influenza A virus nucleoprotein genes.. 2012;15(18):2082–2084.
20. Nayak MK, Agrawal AS, Bose S, et al. Antiviral activity of baicalin against influenza virus H, Npdm09 is due to modulation of NS1-mediated cellular innate immune re-sponses.. 2014;69(5):1298–1310.
21. Gao L, Chen HS. Inhibition of influenza virus, herpes simplex virus, and coxsackievirus by Huangqin glycoside in vitro.2008;13(06):474–478.
22. Yang F, Liu LB, Su D. Effect of Shuanghuanglian granules on TNF in a rat model of mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia-α, IL-6 and NF-κImpact of B.2020;26(09):4–7.
23. Wu SH, Liu N, Yang L, et al. Study of the in vivo anti influenza A virus effects of Huangqin Xuebao,. 2009;26(02):157–159, 200.
24. Wu Y, Jin YZ, Wu J, et al. Effects of Han Huangqin on inflammation related factors in alveolar macrophages infected with influenza virus.2011;27(03):533–538.
25. Devi KP, Malar DS, Nabavi SF, et al. Kaempferol and in-flammation: from chemistry to medicine.2015;99(17):1–10.
26. Tan MA, Takayama H, Aimi N, et al. Antitubercular triterpenes and phytosterols fromSoland. var..2008;62(14):232–235.
27. Zheng BS, Wu DL. Microwave assisted extraction of active ingredients from a compound bishuanglian recipe.2009;25(05):507–510.
28. Yuan J, Chen JY. A clinical study of Shuanghuanglian oral liquid with ranitidine for the treatment of oral ulcers.. 2020;18(20):35–36.
29. Zhao LJ. Clinical efficacy and pharmaceutical research of penicillin combined with Shuanghuanglian in the treatment of acute respiratory infection.. 2020;14(16):138–139.
30. Li Q. Efficacy and effect on C-reactive protein of Shuanghuanglian powder needle assisted by aerosolized budesonide for the treatment of acute bacterial pneumonia in children.. 2020;36(20):99–101.
31. Zhang X, Xiao WW. Clinical outcomes of Shuanghuanglian assisted functional rhinoscopy surgery for injection in chronic rhinosinusitis.2020;5(19):87–89.
32. Wei PH, Zhang W, Li C, et al. Discovery and validation of an active fraction of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with bishuanglian against colon cancer.. 2020;26(15):69–74.
33. Ma DM, Tao QC, Jiang DH, et al. Inhibition of extensive drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in vitro by a combination of bis Huanglian and antimicrobial agents.. 2020;41(09): 1052–1055, 1059.
34. Liu GQ. Effect of Shuanghuanglian granules combined with amoxicillin clavulanate potassium in the treatment of pediatric pneumonia.. 2020;13(11):94–95.
35. Zheng ZW, Ye WQ, Liu CF. Research on the mechanism based on network pharmacology to explore the oral solution of bishuanglian for the treatment of coronavirus disease.2020;43(06):1515–1522.
36. Yang ZF, Ho DW, Lau CK,et al. Allograft inflammatory factor-1 (AIF-1) is crucial for the survival and pro-inflammatory activity of macrophages.2005;17(11): 1391–1397.
37. Hendrickx DAE, van Eden CG, Schuurman KG, et al. Staining of HLA-DR, Iba1 and CD68 in human microglia reveals partially overlapping expression depending on cellular morphology and pathology.2017;309(19):12–22.
38. Elizondo DM, Andargie TE, Yang D, et al. Inhibition of allograft inflammatory factor-1 in dendritic cells restrains CD4(+) T cell effector responses and induces CD25(+) Foxp3(+) T regulatory subsets.2017;8(19):1502.
Ming-Jun Liu. Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, 1035 Boshuo Road, Jingyue Economic Development Zone, Changchun 130117, China. E-mail: mingjunliu646590@163.com.
:
COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; TCMAntiCOVID-19, prediction and analysis of Chinese medicine against coronavirus disease 2019; OB, oral bioavailability; DL, drug-likeness.
:
The project is jointly suupported by the school construction project of the State Administration of traditional Chinese medicine (LPGZS22012-11).
:
We have read and understood Medical Data Mining policy on declaration of interests and declare that we have no competing interests.
:
Zhang XL, Di C, Zhang L, Ma DH, Liu HH, Liu MJ. Study on pharmacodynamic mechanism of compound Shuanghuanglian in prevention and treatment of pneumonia based on network pharmacology and association analysis.. 2021;4(3):16. doi: 10.53388/MDM2021083012.
:Shan-Shan Lin.
:15 March 2021,
07 June 2021,
:25 September 2021
© 2021 By Authors. Published by TMR Publishing Group Limited. This is an open access article under the CC-BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/BY/4.0/).
- Medical Data Mining的其它文章
- Internet public opinion monitoring in public health emergencies may benefit from artificial intelligence
- Data Mining Method for Exploring the Composition Law and Therapeutic Mechanism of Chinese medicine of macroscopic
- A meta-analysis of the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine alone in the treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease
- A cross-sectional study on traditional Chinese medicine syndromes distribution for chronic atrophic gastritis based on data mining
- Reporting quality of systematic review protocols of interventions for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review protocol

