Analysis of Drug Use in Outpatients with Hypertension Based on Real-World Study
Wang Lili
(Medical and Nursing Branch,Panjin Vocational and Technical College,Panjin 124000,China)
Abstract Objective To explore the situation and trend of drug use in the treatment of hypertension in outpatient department of a hospital,and to provide reference for clinical rational drug use.Methods The data of 833 outpatients with hypertension in a hospital from July to December in 2020 were retrospectively analyzed.Results and Conclusion Among the 833 cases,calcium channel blocker (CCB) was the most frequently used drug (38.54%),followed by angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) (13.81%),β-receptor blockers (β-RB) (10.44%),angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) (5.52%),and diuretics (0.72%).The combination rate was 37.09% (including single-pill combination,SPC).The highest rate was the combination of two drugs (28.21%),followed by the combination of three drugs (8.64%) and four drugs (1.20%).The DDDs and DDC of SPC were the highest among the six kinds of drugs.The use of antihypertensive drugs in outpatient department of the hospital is in line with the medication guidelines,but a small number of drugs are used irrationally,which needs further supervision and management.
Keywords:hypertension;antihypertensive drugs;combined use
Hypertension is a common chronic disease in clinic,which is mainly manifested by the continuous increase of blood pressure in the systemic circulation,and it is an important cause and risk factor of many cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases[1].The total number of hypertension patients in the world has exceeded 1 billion,and there are 270 million hypertensive patients in China[2].The main purpose of hypertension treatment is to minimize the occurrence and death of cardiovascular complications[3].The reason for the high rate of disability and death of hypertension is the unreasonable treatment of hypertension patients.Normally,non-drug intervention is the basis of controlling blood pressure,drug intervention is the key to control blood pressure.Once diagnosed,it needs to take antihypertensive drugs for a long time.Therefore,reasonable selection of antihypertensive drugs and standardized treatment of hypertension can effectively reduce the blood pressure of patients and lessen target organ damage.Besides,the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events will be reduced[4].
Real-world study is to collect data related to patients in real world settings,and it can help us to obtain clinical value and potential benefits or risks of the medical products through analysis[5].In order to further grasp the situation of the use of hypertensive drugs in the real clinical environment,find out the rule of medication and promote the rational drug use,the real-world studies carried out based on the medical electronic medical records of 833 patients with hypertension.
1 Data,methods and diagnostic criteria
1.1 General information
1.1.1 Data source
The data were from 833 patients with hypertension in the information system of a Grade-A hospital from July to December in 2020.In this study,the real-world data were used for retrospective analysis,and the single and combined use of five kinds of first-line antihypertensive drugs in clinic were statistically analyzed.
1.1.2 The classification of antihypertensive drugs
The classification of antihypertensive drugs was classified according to the 2018 edition of the “Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension in China”[6].The antihypertensive drugs include calcium channel blocker (CCB),angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI),angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB),diuretics,β-receptor blocker(β-RB) and single-pill combination (SPC).The guidelines suggested that six kinds of antihypertensive drugs could be used as the initial and maintenance drugs.According to the risk factors of patients,subclinical target organ damage and the combined clinical diseases,rational use of drugs should be given priority to certain antihypertensive drugs.
1.1.3 Inclusion criteria
The patients were clinically diagnosed as hypertension.
1.1.4 Exclusion criteria
Patients without basic information and medication information were not included.
1.1.5 Data standardization research
Disease diagnosis referred to 2018 edition of the “Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension in China”[6].Disease name and drugs name referred to “Pharmacopoeia of the people’s Republic of China” for proofreading,standard coding,and standardized treatment.Meanwhile,repetition,error,and abnormal data were deleted[7,8].
1.2 Methods
The basic information of 833 prescriptions and the use of antihypertensive drugs were analyzed by SPSS23 software.The amount recommended by WHO and the ranking method of frequency of drug use were applied to judge drug use.According to the adult routine dose recommended in the “Notice on Clinical Medication” (2010 version)[9]and “New Pharmacy” (17th edition)[10],the drugs not included in the literature were comprehensively determined by referring to the drug specification.DDDs meant the total consumption of the drug/ the defined daily dose (DDD) of the drug.The greater the DDDs,the more the frequency of the drug use was[11].DDC meant the total consumption amount of a drug/DDDs of the drug.DDC represented the total price level of the drug,showing the average daily cost of the drug application by the patient.The larger the DDC,the more the economic burden would be.
1.3 The diagnosis standard of hypertension
It was conducted according to the standards in the 2018 “Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension in China”.Hypertension was defined as:in the absence of antihypertensive drugs,the blood pressure of the patient was measured three times on different days,and the systolic blood pressure (SBP)≥ 140 mmHg and/or diastole blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mmHg.
2 Results
2.1 Basic information of patients
Among the 833 prescription data,the male patients were 458,accounting for 54.98%,the female patients were 375,accounting for 45.02%,and the ratio of male and female was 1.22:1.The maximum age of the patients was 91 years old,the minimum was 23 years old,the average age was 61.07 years old,among which 94 patients under the age of 40 accounted for 11.26%,297 patients aged 40– 59 years old,accounting for 35.57%,and 444 patients ≥ 60 years old,accounting for 53.17%.Table 1 and Table 2 were the distribution of gender and age of patients.
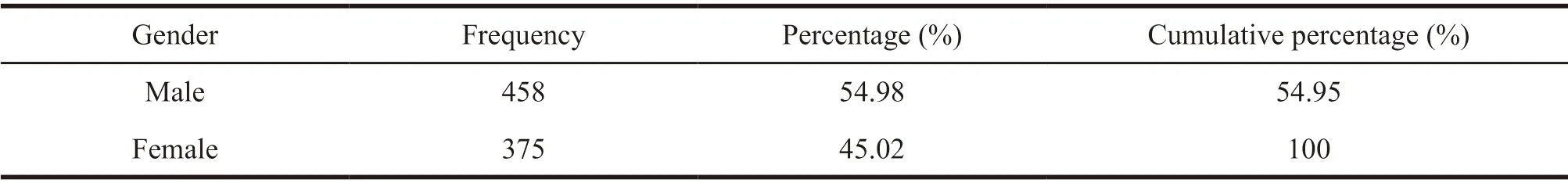
Table 1 Gender distribution of patients with hypertension
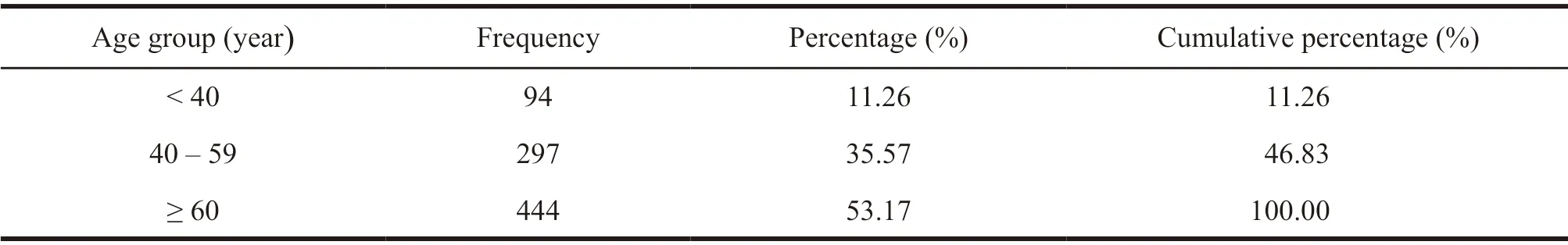
Table 2 Age distribution of patients with hypertension
2.2 Use of antihypertensive drugs alone
Among the 833 prescriptions,there were 733 prescriptions of five first-line antihypertensive drugs,accounting for 88.00%.Among the five first-line antihypertensive drugs,the number of CCB drugs was 321,accounting for 38.54%.The number of ARB drugs was 115,accounting for 13.81%.The number ofβ-RB drugs was 87,accounting for 10.44%.The number of prescriptions for ACEI drugs was 46,accounting for 5.52%.The number of prescriptions for the drugs of diuretics was 6,accounting for 0.72%.The number of prescriptions of SPC was 100,accounting for 12.00%.There were 27 kinds of antihypertensive drugs,including 7 kinds of CCB,6 kinds of ARB,6 kinds of SPC,4 kinds of ACEI,2 kinds ofβ-RB and diuretics,respectively.Table 3 was the use of various antihypertensive drugs alone.
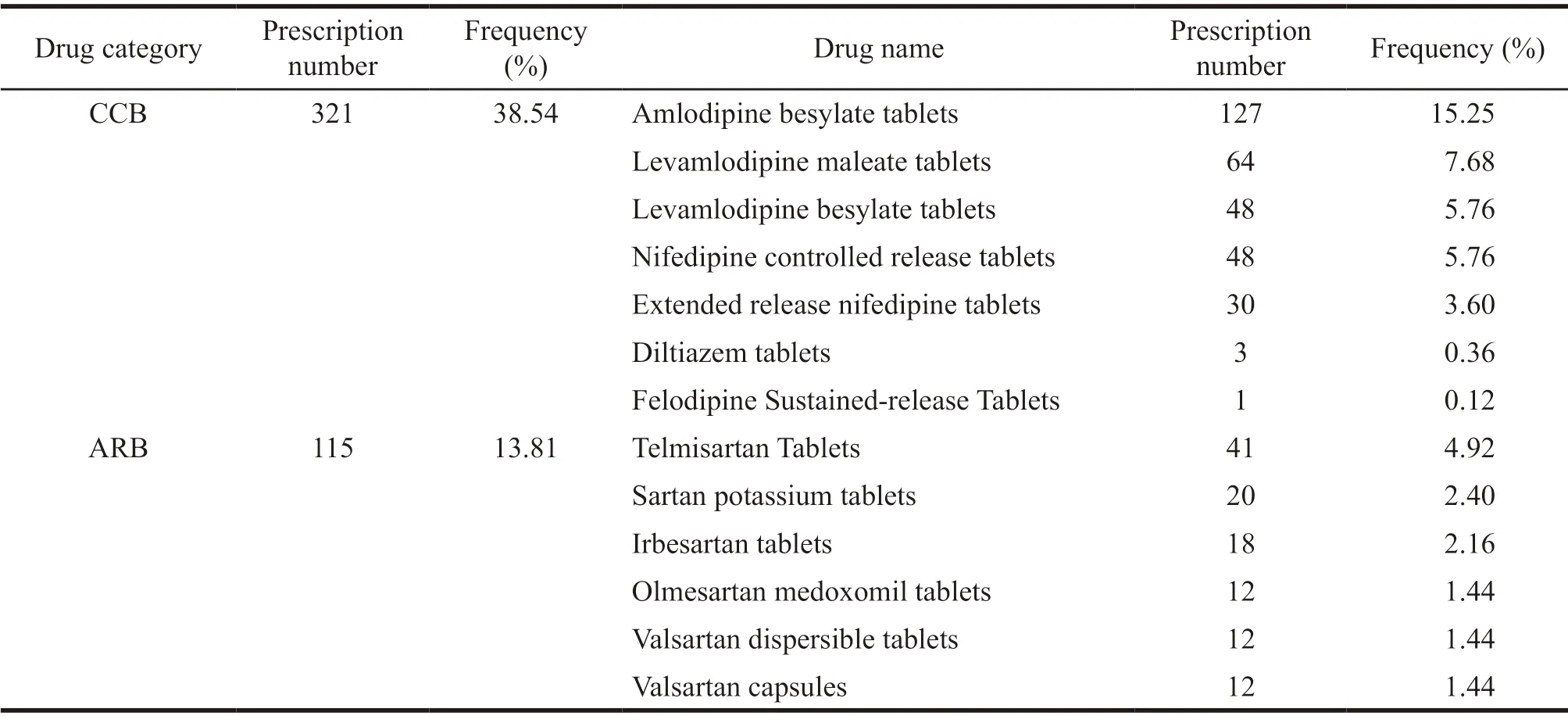
Table 3 Use of antihypertensive drugs alone
(to be continued)
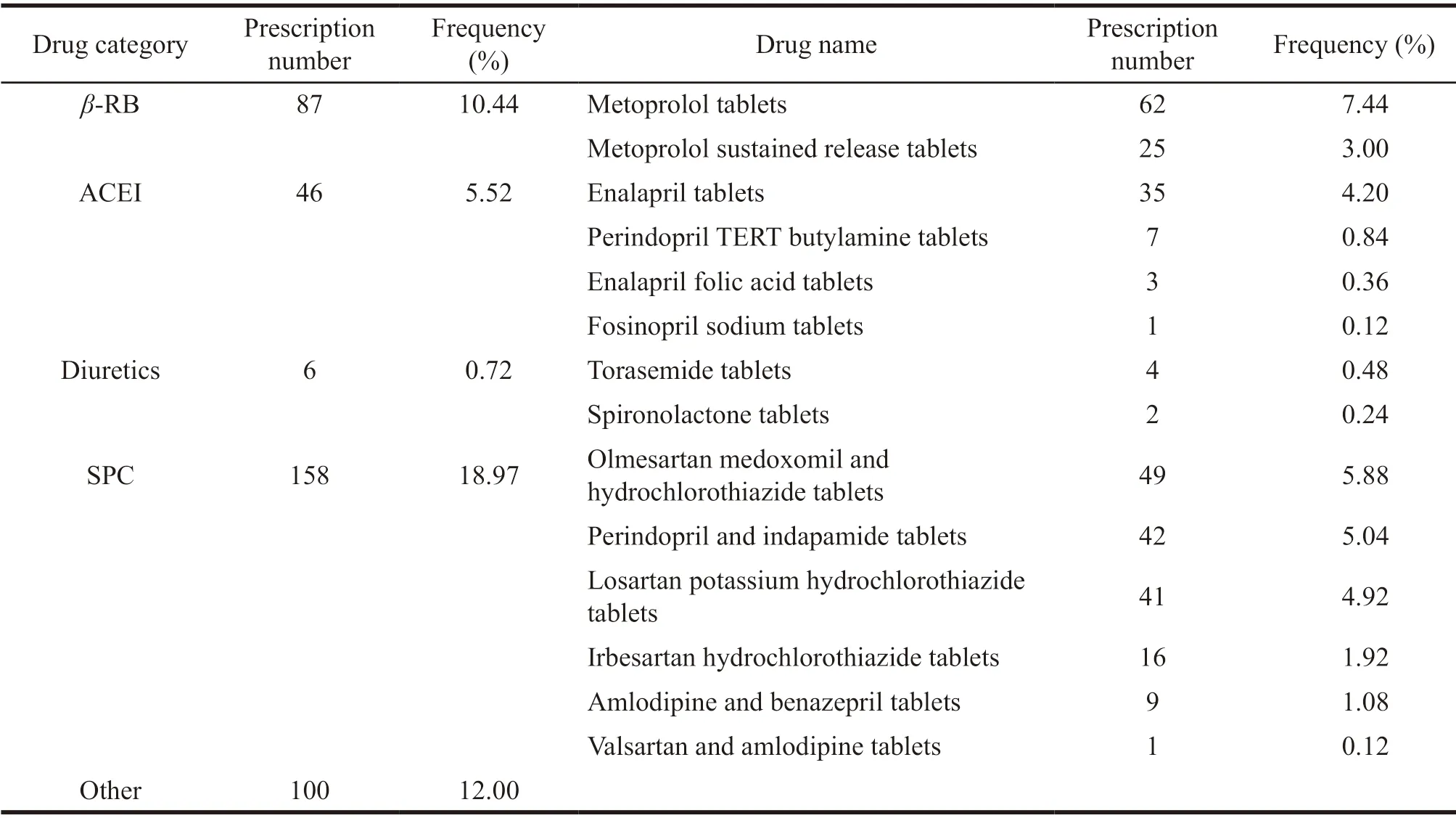
Continued Table 3
2.3 Combined use of antihypertensive drugs
Among the data of 833 hypertension prescriptions,309 prescriptions were used in combination,accounting for 37.09%.The combination of two drugs was the most,which was 235,accounting for 28.21%.The second was triple-combination therapy,it was 72,accounting for 8.64%.The minimum of the quadruple-combination therapy was 10,accounting for 1.2%.The various joint programs were shown in Table 4.

Table 4 Combined use of antihypertensive drugs
(to be continued)
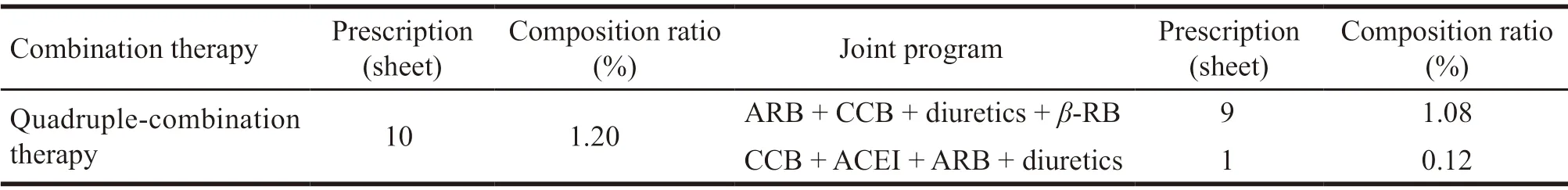
Continued Table 4
2.4 DDDs and DDC of various antihypertensive drugs
Among the data of 833 hypertension prescriptions,the total cost of drugs was 118 129.46 yuan.The cost of five first-line antihypertensive drugs was 57 299.5 yuan,accounting for 48.51%,and the remaining drugs amounted to 60 829.96 yuan,accounting for 51.49%.The ranking of DDDs and DDC of various hypertension drugs were shown in Table 5.
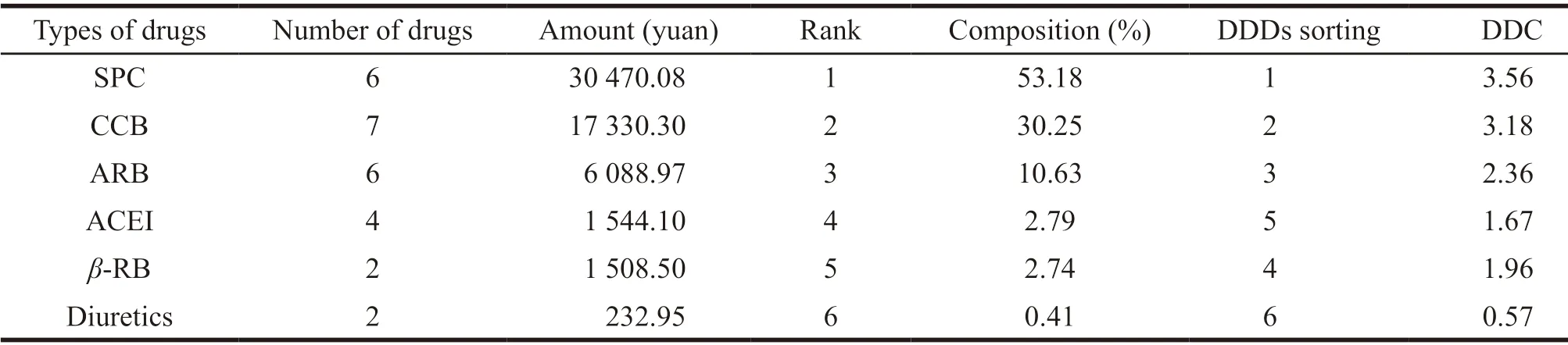
Table 5 The ranking of various DDDs and DDC drugs
3 Discussion
The number of people suffering from hypertension in the world is more than 1 billion[12].The number of people with hypertension in China has exceeded 200 million.Hypertension has posed a serious threat to human health.Besides,hypertension is an important factor leading to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.Effective control of blood pressure can reduce the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events and death.Therefore,it is necessary to prevent and control hypertension reasonably and effectively.It is significant to explore the current situation of antihypertensive drugs in outpatient clinics and to avoid unreasonable use of drugs.Only in this way can it improve the compliance of drug use[12].
3.1 Analysis of the distribution of hypertension patients
In this study,the sex ratio of male and female patients with hypertension was 1.22:1.A total of 53.71% of the people who were over 60 years old suffered from high blood pressure.So,the age was proportional to the prevalence of hypertension,which was consistent with the “Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension in China” and previous related literature reports[13].
3.2 Analysis of CCB antihypertensive drugs
Among the 833 prescriptions,321 were CCB drugs used alone,accounting for 38.54% of the total prescriptions.It was the most used antihypertensive drug in outpatient clinics of the hospital,which was in line with the recommendation of the clinical application of CCB in Asia.7 drugs were involved in single prescription,6 were dihydropyridine,among which Amlodipine Besylate was the most widely used.127 drugs were for single prescription,accounting for 15.25%.Amlodipine is a third generation CCB drug,which can keep blood pressure stable with a long half-life.The concentration of the drug in the blood is stable for 24 hours,which improves the compliance of the patients.
3.3 Analysis of ARB antihypertensive drugs
Among the 833 prescriptions,115 prescriptions were CCB drugs used alone,accounting for 13.81%of the total prescriptions.Its utilization rate was second to CCB drugs.The single prescription involved 6 drugs,of which the most used were Telmisartan tablets,41 prescriptions were used alone,accounting for 4.92% of the total prescriptions.ARB antihypertensive drugs could reverse myocardial remodeling and improve heart conditions.Meanwhile,they could delay the progress of renal dysfunction and retinopathy in patients with primary hypertension and diabetes mellitus,reducing the risk of dialysis in diabetic patients with normal blood pressure.Moreover,there were no adverse reactions such as itching and coughing.ACEI had gradually replaced by ARB as primary hypertension with diabetes.They became an important antihypertensive drug for heart failure and other diseases.
3.4 Analysis of β-RB antihypertensive drugs
Among the 833 prescriptions,87 prescriptions wereβ-RB drugs,accounting for 10.44%.Metoprolol was a commonly used drug inβ-RB,which had fast and strong antihypertensive effect,and was suitable for hypertensive patients with fast heart rate.However,its use rate was low because it could lead to adverse events such as bradycardia,atrioventricular block,and bronchospasm[14].The use of antihypertensive drugs in outpatient department was significantly lower than that of the first two drugs.
3.5 Analysis of ACEI antihypertensive drugs
Among the 833 prescriptions,46 were ACEI drugs that were used alone,accounting for 5.52% of the total prescriptions.Enalapril tablet was one of the ACEI drugs,which was often used as first-aid drugs.Because of its adverse reactions such as dry cough,it was not often used.However,some data show that ACEI was more suitable for patients with coronary heart disease complicated with heart failure,hypertension,diabetes,and chronic kidney disease than ARB[15].Besides,the DDC value of ACEI was small,which indicated that the price was low and could reduce the economic burden of patients with hypertension.Therefore,it was suggested to increase the use of ACEI appropriately,and those who could not tolerate adverse reactions such as dry cough should consider switching to ARB drugs.
3.6 Analysis of the use of diuretics
Among the 833 prescriptions,6 were diuretics which were used alone,accounting for 0.72%.Diuretics had mild hypotensive effect,and the diuretic intensity was positively correlated with the dose.When the hypotensive intensity reached the maximum concentration with the increase of dose,the hypotensive effect didn’t rise,but it could cause serious adverse reactions.Therefore,large dose diuretics were rarely used alone in clinic,and they were often used in combination.
3.7 Analysis of combined use of antihypertensive drugs
Combined use of antihypertensive drugs had become the basic method of antihypertensive treatment.To achieve the target blood pressure level,most patients with hypertension needed to use two or more antihypertensive drugs[6].309 prescriptions of antihypertensive drugs were used in combination,accounting for 37.09%.The combination of ACEI/ARB and diuretics was took up the most.ACEI or ARB could make up for the electrolyte disorder and metabolic disorder caused by diuretics,such as hypokalemia,hyperuricemia,and insulin resistance.It could inhibit the hyperglycemia and new onset diabetes caused by diuretics alone.There were 72 prescriptions of triple combination therapy,accounting for 8.64%.The most used regimen was the combination of ACEI or ARB,diuretics with CCB drugs.This regimen was a combination of antihypertensive drugs with complementary mechanism,which was more effective and safer,and it was commonly used in the first line.The total number of quadruple prescriptions was 10,accounting for 1.2%.Among the CCB+ACEI+ARB+diuretics regimens,ACEI+ARB was not recommended or used cautiously in the guidelines.Although they were sometimes effective for patients with proteinuria or heart failure symptoms,the ongoing clinical trials of telmisartan alone and combined with ramipril showed that,compared with monotherapy,patients receiving combination therapy had lower blood pressure but no improvement in cardiovascular events and many other adverse reactions.This combination was inefficient[16].
3.8 Analysis of DDDs and DDC of various antihypertensive drugs
The order of all kinds of antihypertensive drugs in the amount of drug use was as follows,SPC >CCB >ARB >ACEI >β-RB >diuretics.The ranking of DDDs was SPC >CCB>ARB>ACEI >β-RB >diuretics,and the ranking of DDC was SPC >CCB >ARB >β-RB >ACEI >diuretics.It showed that the two components in SPC had synergistic effect.Compared with the single use of either component,the hypotension range of the drug was greater,and it was easier to be selected and used by doctors and patients.However,the overall price level of compound preparation was relatively high.Since it was difficult to adjust the dosage,it was hard to implement individualized treatment.It was only suitable for patients with stable condition,which was also likely to limit its large-scale clinical use.
4 Conclusion
There are some limitations in this article,such as the data included in this paper is limited,there are errors in the collection of the original data,the proportion of the results have certain limitations,and the prediction results may have errors.
From the above data analysis,the use of antihypertensive drugs in the outpatient department of our hospital is reasonable,and the clinical prescriptions are in line with the national drug use standards.However,we still need to continue to improve the drug use.When using drugs,we should try our best to choose drugs with low price and high efficacy in combination with the patient’s condition to reduce the frequency of drug use in patients with hypertension.In addition,the combination of drugs shows a strong advantage in the treatment of hypertension,it is reasonable and worthy of clinical promotion.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Research on Retrospective Studies of Real-World Study and Its Selection Bias
- Research on the Pragmatic Clinical Trial Design Based on Real-World Study
- How Real-World Evidence Supports Healthcare Decisions in EU and Its Enlightment to China
- Application of Real-World Evidence in Regulatory Decision-Making for Medical Devices
- Research on Real-World Evidence and Application in EU and Its Enlightment to China
- EU Real-World Evidence Supports the Expansion Indications for Drugs and Its Enlightenment to China

