EU Real-World Evidence Supports New Drug Research and Development Decisions and Its Implications for China
Yang Lingling,Xu Fengxiang
(1.School of Business Administration,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang110016,China;2.Research Institute of Drug Regulatory Science,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang110016,China)
Abstract Objective To analyze the application of EU real-world evidence in the decision-making of new drug research and development (R&D),and to provide policy recommendations for China’s government to make new drug R&D decisions.Methods The relevant policy documents of the EU on the development of new drugs and other domestic and foreign literature on the real-world evidence were analyzed to obtain the role and application of the current EU real-world evidence in the implementation of new drug development policies.Results and Conclusion At present,the EU is carrying out the national synchronous scientific advisory policy,urging the formation of a European innovation framework,and providing decision-making for new drug R&D selection and program design based on real-world evidence.It is recommended that China build a real-world medical database and design a new drug screening platform to help companies,scientific research institutions assess target drugs.In addition,a national scientific advisory platform should be set up to integrate scientific research strength and provide technical support for new drug R&D institutions.
Keywords:EU;real-world evidence;R&D decision-making;R&D policy
1 Introduction
Real-world evidence refers to the analysis of data collected outside of routine randomized clinical trials to obtain clinical evidence of drug use and potential benefits-risks.These sources include primary and secondary patient care records,such as electronic health records,insurance claims data,daily administrative data,product and disease registries,and emerging sources of observation such as data collected by social media,mobile devices,and apps[1-5].At present,the EU has conducted in-depth studies in drug-related fields based on real-world evidence,which provides good data support for the decision of new drug R&D.In recent years,more and more attention has been paid to the development of realworld evidence based medicine in China.National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) issued the“Guiding Principles for Drug R&D and Evaluation Supported by Real-World Evidence (Trial)” in January 2020.Given the current demand for quality of health,there is a high degree of attention paid to the R&D of new drugs both at home and abroad.Since the data from the real-world clinical diagnosis and treatment contain medical theoretical knowledge and innovative thinking of doctors,they have important reference value for the R&D of new drugs.Therefore,how to support the decision of new drug R&D based on the real-world evidence becomes a hot research area with theoretical value and practical significance.
Nowadays,there are some research results on drugs in the real world.For example,Sun Xin,et al.[6]formulated the first technical specifications on realworld data and research.Fu Yu[7]proposed that realworld research conformed to the characteristics of individualized diagnosis,treatment,and curative effect evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM),which could open up a new path for the overall evaluation of TCM.Sang Yanlei,et al.[8]conducted a comparative study on the targeted treatment of colorectal cancer based on real-world samples.Wei Xu[9]analyzed the clinical application of non-drug therapy for cervical spondylotic radiculopathy based on real-world research.Sun Xin,et al.[10]proposed a technical framework system for using real-world data in post-marketing drug research and evaluation from the perspective of drug supervision and clinical decision-making.Liang Wenna[11]based on real-world data,studied the methods to solve the computational problems of the four-diagnostic clinical participation model of TCM,taking health status identification as the core,and using artificial intelligence technology to realize the intelligence of TCM health management.Li Man[12]explored the way of mining valuable information from clinical data of TCM by using realworld research,which was of great significance to the R&D of TCM.Wang Jinbo’s[13]interpreted the“Guiding Principles for Drug R&D and Evaluation Supported by Real-World Evidence (Trial)” published by the NMPA,and studied ways of applying realworld research to support dietary supplement regulatory decisions.Zhang Hao[14]interpreted the background and main points of the “Technical Guidance for Real-World Study to Support Children’s Drug R&D and Evaluation (Trial)”.Liao Yingfen[15]briefly reviewed the accessibility and development of applying real-world evidence to support drug R&D and regulatory decisions.
Significant contributions have been made to realworld research on all aspects of medicine.Most of the existing studies focus on the rationality and safety of clinical drug use and the evaluation of real-world data on post-marketing.However,with the growth of world’s wealth and the aging of population,people pay more attention to their health.The existing medicines are far from meeting the needs of the society.Therefore,it is important to develop new drugs that can cure some human diseases according to people’s needs.Real-world research is a study that assesses the safety and effectiveness of new drugs in real clinical practice,and its data are of great significance for decision support in drug R&D.Now,some studies based on real-world evidence have greatly supported the decision of drug R&D.For example,Dai Liang[12],based on the interpretation of the core content of FDA’s “Real-World Evidence Program Framework”,carried out an analysis on the common points of real-world clinical research and TCM intervention.However,there are few relevant studies on the EU’s realworld research supporting new drug R&D decisions.Therefore,this paper will provide policy suggestions for the development of China’s new drug R&D by analyzing the relevant policies and cases supported by the EU’s real-world evidence for drug R&D decisions.
2 How real-world evidence supports new drug R&D decisions
2.1 The task of forming an European innovation network [17]
The Innovation Task Force (ITF) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the National Competent Authorities (NCAs) play an important role in supporting the early stage of new drug development by promoting awareness,dialogue and understanding of regulatory requirements in business,hospitals and academia.
Since 2011,ITF and NCAs of EMA have held regular conference calls to share information and discuss new drug development,in an unofficial collaboration known as the EU-IN.The EU Medicines Agency Network Strategy for 2020 recognizes the important role of the EMA’s ITF and NCAs,and urges all interested NCAs to join EU-IN voluntarily and to seek a larger EU-IN from more countries.Its aim is to promote drug innovation across the EU by strengthening small and medium-sized enterprises and academia to obtain new drug R&D technical support from the ITF and NCAs of EMA.
2.2 Trial implementation of the national synchronous scientific advisory policy [18]
On 1 February 2020,the EU began to pilot the simultaneous national scientific advice (SNSA)provided by the national authorities,which means the new drug R&D units can draw on the new drug R&D recommendations of the two national NCAs simultaneously through the coordination of EMA.The pilot project aims to help new drug R&D units to formulate the best drug R&D model,which can promote the sharing and application of expertise in EU countries and drug-related industries.Besides,it can integrate the recommendations of participating countries on drug R&D to facilitate early cooperation among EU member states to complete the R&D of new drugs.
The specific implementation procedures are as follows.First,the applicant submits an application to the two NCAs they hope to cooperate with according to the list of national innovation offices of SNSA member states.If a certain NCAs cannot participate in the scientific guidance,the applicant can re-select another NCAs.After that,the three parties will jointly select a contact person (one of the NCAs will serve)to coordinate the process of follow-up research.Then,the applicant sends a briefing document and a list of questions according to the requirements of the NCAs of the two countries.After that,the three cooperative parties will conduct seminars and discussions on related issues.It should be pointed out that the applicant must not add new issues or changes after the beginning of the discussion.Finally,the applicant who has received scientific guidance pays corresponding fees to the partner and fills out a questionnaire to provide feedback.The flowchart is shown in Fig.1.
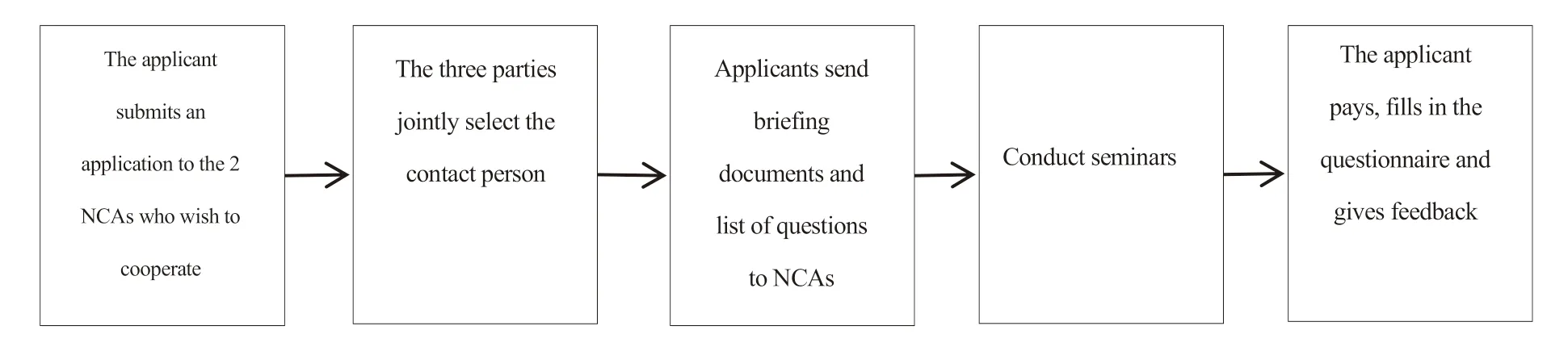
Fig.1 National synchronous scientific consulting advisory implementation process
2.3 Real-world evidence helps R&D decision-making
In 2013,EMA issued the “Opinions on a New Data-Driven Model Method for Alzheimer’s Disease Progression and Clinical Trial Evaluation”,which proposed the use of observational data in the real world to build disease progression models to help drug R&D.That is,the historical clinical data of Alzheimer’s disease could be used to simulate clinical trials.Meanwhile,hypothetical parameters to simulate the effects of drugs in “real” conditions could be used to evaluate different drug characteristics.For instance.how pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics can affect test performance.Analysis of real-world evidence is used to adjust the drug R&D plan[19].
In addition,the EU proposed that NCAs could use real-world evidence to clarify the frequency and distribution of diseases,identify unmet medical needs,determine the population to be treated and whether the disease affects high-risk populations,such as pediatrics[20].Then it can provide applicants with proposal for scientific R&D.The process is shown in Fig.2.According to the data provided by the EU in previous years,based on real-world data,the project team will meet to discuss drug R&D plans every month,and provide more than 600 new drug R&D decision-making recommendations every year,which are about issues of quality (~20%),preclinical (~25%)and clinical (~55%).
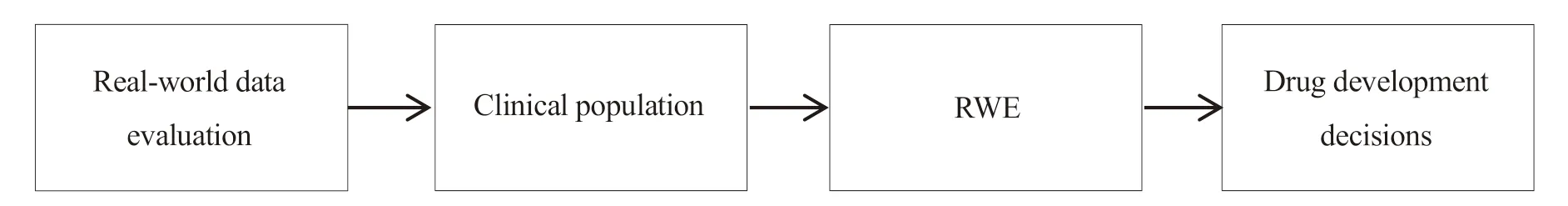
Fig.2 Flow chart of real-world evidence supporting R&D decision-making
3 Enlightenment and suggestions
3.1 Establishing a real-world medical database
The availability of real-world medical big data is a prerequisite for the development of real-world research.A good real-world database not only has a large amount of data with a wide range of disease types,but also has comprehensive and long-term traceable data of patients.The tracked data is used to evaluate long-term efficacy indicators and provide decision-making support for the development of new drugs.
3.1.1 Data sources for the database
According to the NMPA’s announcement on the release of the “Guiding Principles for Drug R&D and Evaluation Supported by Real-World Evidence (Trial)”,real-world database should be established based on real time capture of clinical data from hospitals with direct entry,which should include all kinds of disease and the information of the departments.In addition,the health care system,the disease registration system and the medication of patients should also have the real-time entry into the real-world database.
3.1.2 Data processing in the database
High-quality real-world databases should clean and structure the accessed data in accordance with international generic diagnostic and classification standards.All raw data from hospitals have to be cleaned and desensitized to remove patients’ privacy before the study.All variables need to be standardized and structured,such as the drug anatomical therapeutic chemical (ATC) code.
3.1.3 Integration of data
The establishment of real-world database needs to integrate all medication and medical records of the same patient.It means based on an individual patient,long-term and longitudinal tracking data can be accumulated to support evidence-based medicine research.The database shall contain the following information:patient demographic data and insurance information,diagnostic results,complications,treatment results,laboratory examination details,prescription information,hospitalization details,surgical information,utilization of all health resources and cost,and other clinical and administrative information.
3.2 Building a national synchronous scientific consulting platform
A drug R&D discussion platform should be established.Besides,various universities should form joint expert associations,and expert groups in different provinces and regions should be set up to facilitate companies to apply for or consult related R&D issues.The R&D of major diseases and rare diseases can be discussed by all the experts in China.The discussion content and time can be reasonably arranged according to the different stages of drug development and the development process.For example,in the early stage of R&D,the drug R&D plan can be discussed.In the middle of the R&D process,the problems arise in the drug R&D process can be discussed in a timely manner.
All in all,through the establishment of a national synchronous scientific advisory platform,applicants,especially the small and medium-sized enterprises,scientific research institutions can communicate with hospitals as soon as possible to understand the drugs that are currently in urgent need and provide timely technical support to solve the difficulties in the R&D process.This will improve the R&D plan and increase the success rate of new drug R&D.
3.3 Designing a new drug discovery and screening platform based on real-world database
3.3.1 Designing a new drug screening project based on real-world database
The screening platform starts from the entry of clinical raw data into the system.After processing the data,various process-based confirmatory screening analyses can be made.In addition,assistance is provided in the platform system in the screening of new drug R&D.A variety of tools,such as AI,visualization and other technologies can be used to evaluate the necessity of new drug R&D.
3.3.2 Designing a new drug R&D information sharing project based on real-world database
China has attached great importance to the construction of new drug R&D platforms and made great achievements,such as the technical platform for clinical evaluation and research of new psychotropic drugs.However,at present,the relevant platforms are only a pure academic collaboration network,which has limited data[21].Therefore,building real database to design new drug R&D information sharing project can improve the success rate of new drug R&D.The project should include the screening of drug structure in new drug R&D process,the testing of drug experiment scheme,and the screening of drug clinical experiment subjects.The use of big data to better pharmaceutical enterprises and R&D institutions to provide data support,improve the speed and success rate of new drug R&D.
4 Conclusion
This article analyzes the EU’s current policies and methods in the R&D of new drugs,which include the formation of the European innovation network,the national synchronous scientific consultation policy,and the role of real-world evidence in the two new drug R&D policies.Meanwhile,the enlightenment of EU’s experience in real-world evidence supporting the new drug decision-making can provide policy recommendations for the innovative model of new drug R&D in China.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Research on Retrospective Studies of Real-World Study and Its Selection Bias
- Research on the Pragmatic Clinical Trial Design Based on Real-World Study
- How Real-World Evidence Supports Healthcare Decisions in EU and Its Enlightment to China
- Application of Real-World Evidence in Regulatory Decision-Making for Medical Devices
- Research on Real-World Evidence and Application in EU and Its Enlightment to China
- EU Real-World Evidence Supports the Expansion Indications for Drugs and Its Enlightenment to China

