Risk factors related to postoperative recurrence of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A retrospective study and literature review
Jian-Xia Xiong, Tao Cai, Li Hu, Xiao-Li Chen, Kun Huang, Ai-Jun Chen, Ping Wang
Jian-Xia Xiong, Tao Cai, Li Hu, Xiao-Li Chen, Kun Huang, Ai-Jun Chen, Ping Wang, Department of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400010, China
Abstract BACKGROUND Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare low-grade malignant soft tissue tumor characterized by rosette-like infiltrative growth. Postoperative recurrence of this tumor is very common.AIM To evaluate the risk factors related to recurrence after wide local excision (WLE)of DFSP and to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment.METHODS The medical records of 44 DFSP patients confirmed by pathology at our hospital from 2012 to 2019 were retrospectively reviewed. The relationship between clinical features, tumor characteristics, treatment, and recurrence risk were analyzed, and the possible risk factors for postoperative tumor recurrence were evaluated.RESULTS There were 44 patients in total, including 21 males and 23 females. The median progression free survival was 36 mo (range, 1-240 mo). Twenty patients were treated for the first time, while 24 had previous treatment experience. Forty-two cases were followed for 25.76 ± 22.0 mo, among whom four (9.52%) experienced recurrence after WLE (rate was 9.52%). The recurrence rate in the recurrent group was higher than that in the patients with primary tumor (19.05% vs 0%, P = 0.028).Eighteen cases had a history of misdiagnosis (rate was 40.91%). The recurrence rate among patients with previous experience of misdiagnosis was significantly higher than in patients without (68% vs 36.84%, P = 0.04). The tumor diameter in patients with a history of treatment was larger than in patients treated for the first time (4.75 ± 0.70 cm vs 2.25 ± 0.36 cm, P = 0.004).CONCLUSION To sum up, the clinical manifestations of DFSP are not specific and are easily misdiagnosed, thus commonly causing the recurrence of DFSP. After incomplete resection, the tumor may rapidly grow. Previous recurrence history may be a risk factor for postoperative recurrence, and tumor location may have an indirect effect on postoperative recurrence; however, we found no significant correlation between sex, age, course of the disease, or tumor size and postoperative recurrence.
Key Words: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans; Recurrence; Clinical features; Wide local excision; Surgery; Retrospective research
INTRODUCTION
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare skin and soft tissue malignant tumor with low grade, accounting for 1% of all soft tissue malignant tumors[1,2]. DFSP is most commonly found in young and middle-aged patients. It is frequently found in the trunk. The tumor size may be different across races, genders, ages, and locations[3]. At present, the cause and mechanism leading to DFSP are not clear. About 10% of DFSP patients have a history of trauma, surgery, vaccination, or burn[4]. More than 90% of patients have 17q22 and 22q13 chromosome translocation, which fuses the geneCOL1A1with platelet-derived growth factor β (PDGF β) to form a circular chromosome[5,6].
DFSP has a slow progression in the early stage, characterized by isolated plaques with a hard texture and red, brown, or normal skin around it. Delays in diagnosis are common because of the benign appearance and its rarity. Clinically, about 52% of the patients have been misdiagnosed as having epidermal cyst, lipoma, benign fibroma,keloid, and other diseases[7]. The tumor infiltrates the surrounding tissue as a pseudopod; therefore, the invasive growth of tumor cells makes it very difficult to determine operation’s scope. Some scholars have proposed that the high recurrence rate is related to its unclear clinical and pathological boundaries[8,9].
In recent years, the number of DFSP patients at our hospital has been steady increasing. Among them, more than 50% have treatment experience. In order to further evaluate the risk factors for tumor recurrence after wide local excision (WLE),we reviewed and retrospectively analyzed the clinical and pathological features,treatment, and recurrence in 44 DFSP patients treated at our hospital between 2012 and 2019.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
The medical records of patients with pathologically confirmed DFSP who were treated at the Department of Dermatology and Department of Plastic Surgery of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University between 2012 and 2019 were retrospectively reviewed. Primary DFSP was defined as a tumor diagnosed at the first visit or the time from the first biopsy conducted to operation less than 3 mo, and recurrent DFSP was defined as tumor regrowth at the original tumor site at least 3 mo after the resection or biopsy[10]. The medical records of patients with DFSP were examined to obtain medical information, including the clinical and tumor characteristics as well as the surgical methods and prognosis. In the process of statistical analysis, two cases were excluded due to loss to follow-up. Consequently, 42 patients with complete medical records and follow-up information were included in the final analysis, and the recurrence rate was compared between the two groups. The followup information mainly came from telephone interviews.
Treatment
The goal of WLE of DFSP is to remove the tumor completely and keep the resection margins negative. Due to the difference in the tumor location, size, and frozen biopsy result, the distance between the surgical margin and the edge of the tumor was 1-15 cm (if the tumor is located in the head, palm, sole,etc., the extent of resection is smaller than that of the trunk), and the depth of surgical resection ranged from the subcutaneous fat layer to the periosteal layer. Some patients underwent radiotherapy after the operation. Before reconstruction, a frozen biopsy revealed negative resection margins; if the incision was positive, it was expanded 1 cm along the corresponding direction until the freezing result was negative.
Statistical analysis
A descriptive analysis was performed on 44 patients. All the data in this study were analyzed with SPSS 21.0 statistical software.Count data were analyzed by chi-square test ort-test, and measurement data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. In all statistical analyses,P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Clinical characteristics
Among the 44 patients (21 males and 23 females), 20 had a primary tumor, and 24 had a history of treatment (before the WLE operation was performed at our hospital, all these patients had treatment experience, including surgery, injection, and laser). The average age at the presentation of DFSP was 31.82 ± 1.64 years; 41 patients were younger than 50 years. The average duration from onset to surgery was 82.09 ± 12.19 mo, and the median progression free survival (PFS) was 36 mo (range, 1-240 mo). The trunk (26 patients) was the most common site involved. The mean diameter of the tumor was 3.61 ± 0.46 cm.
Twenty-four patients were defined as a recurrent group. All of these patients had simple excision at other institutions, and all of them demonstrated local recurrence after resection. Twenty patients were initially diagnosed as having DFSP (primary group). In the primary group, the median PFS was 33 mo (rang, 1-240 mo), the mean onset age was 30.90 ± 2.34 years, the mean course was 54.50 ± 15.40 mo, and the mean diameter of the tumor was 2.25 ± 0.36 cm. In the recurrent group, the onset age was 32.58 ± 2.24 years, Preoperative duration ranged from 2 to 240 mo (average 105.08 mo),and the mean tumor diameter was 4.75 ± 0.70 cm. The tumor size was significantly different between the two groups (P< 0.004) (Table 1).
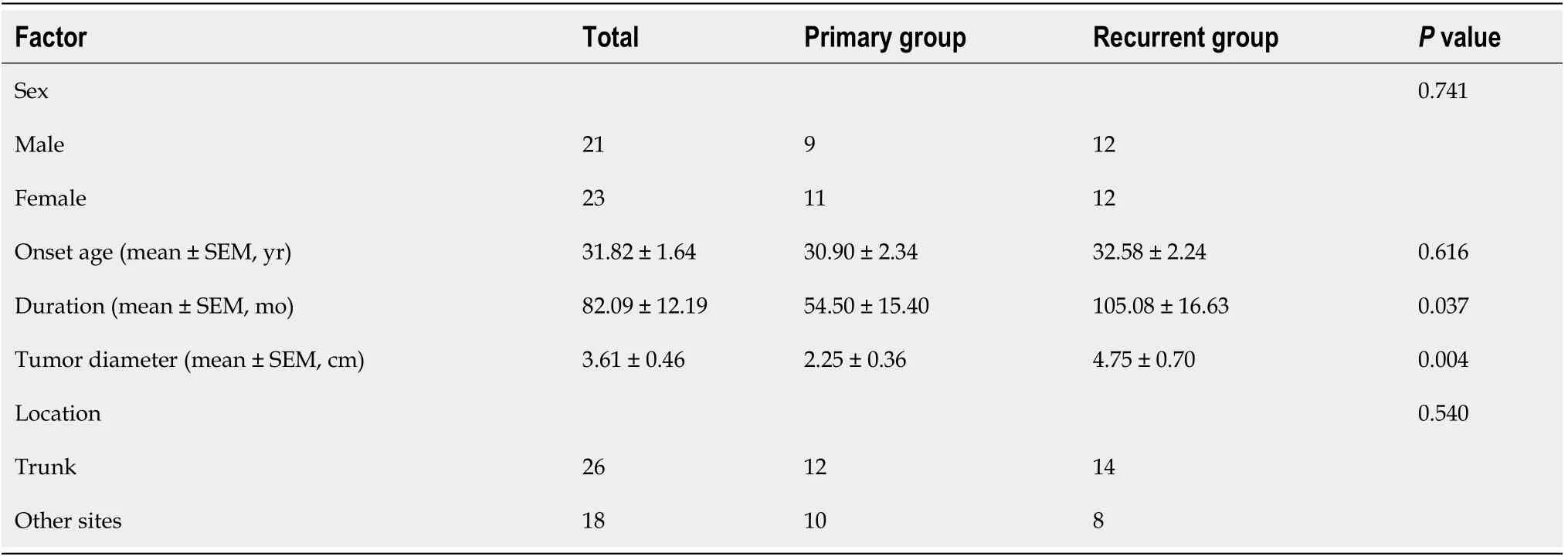
Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 44 patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Clinical misdiagnosis related with local recurrence
The overall recurrence rate in patients with clinical misdiagnosis was 68.00% (17/25).Only seven cases experienced relapse in patients without the experience; their recurrence rate was 36.84%. There was a statistical difference in the recurrence rate between the two groups (P =0.04) (Table 2).

Table 2 Detailed information of misdiagnosed patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Pathological and immunohistochemical results
All patients underwent pathological examinations. DFSP typically presents a storiformor fascicular proliferation of bland spindled cells extending from the dermis into the subcutis on routine hematoxylin-eosin staining. The distribution of tumor cells in the superficial dermis was sparse and dense in the deep dermis. An immunohistochemical examination was performed for 42 patients. The positive rate of CD34 was 97.56%(40/42), and 92.86% of patients were positive for vimentin. Fourteen patients were positive for BCL-2, and there was no significant difference in the positive rate between the primary and recurrent groups (positive rate 66.7%vs75%,P =0.480). There was no difference in the expression of BCL-2 between tumors with a diameter larger than 3 cm and those with a diameter smaller than 3 cm (70%vs75%,P =0.852). The positive expression rate of Ki-67 was 8.5% ± 2.11% in the primary group and 8.72% ± 2.28% in the recurrent group (P =0.943). There was no correlation between tumor size, disease course, and the expression of β-catenin and STAT-6 (Supplementary Tables 1-3).
Follow-up
Up to May 2020, two patients were lost to follow-up. Of the 42 patients who were followed, four had experienced a local recurrence, with a recurrence rate of 9.52%.Among all the 42 patients followed, there was no significant difference in sex, location,or age of onset between the primary and the recurrent groups. The mean lateral resection margin was 3.13 cm (rang, 2-5 cm) in the four locally recurrent patients. Most of them (3/4) had a course exceeding 5 years and tumor size exceeding 3 cm. The recurrence rate in the recurrent patients was higher than that in the primary patients(19.05%vs0%,P =0.028). With the increase in the treatment times, the local relapse risk increased; when the treatment times exceeded 3, the recurrence rate increased to 100% (Table 3).
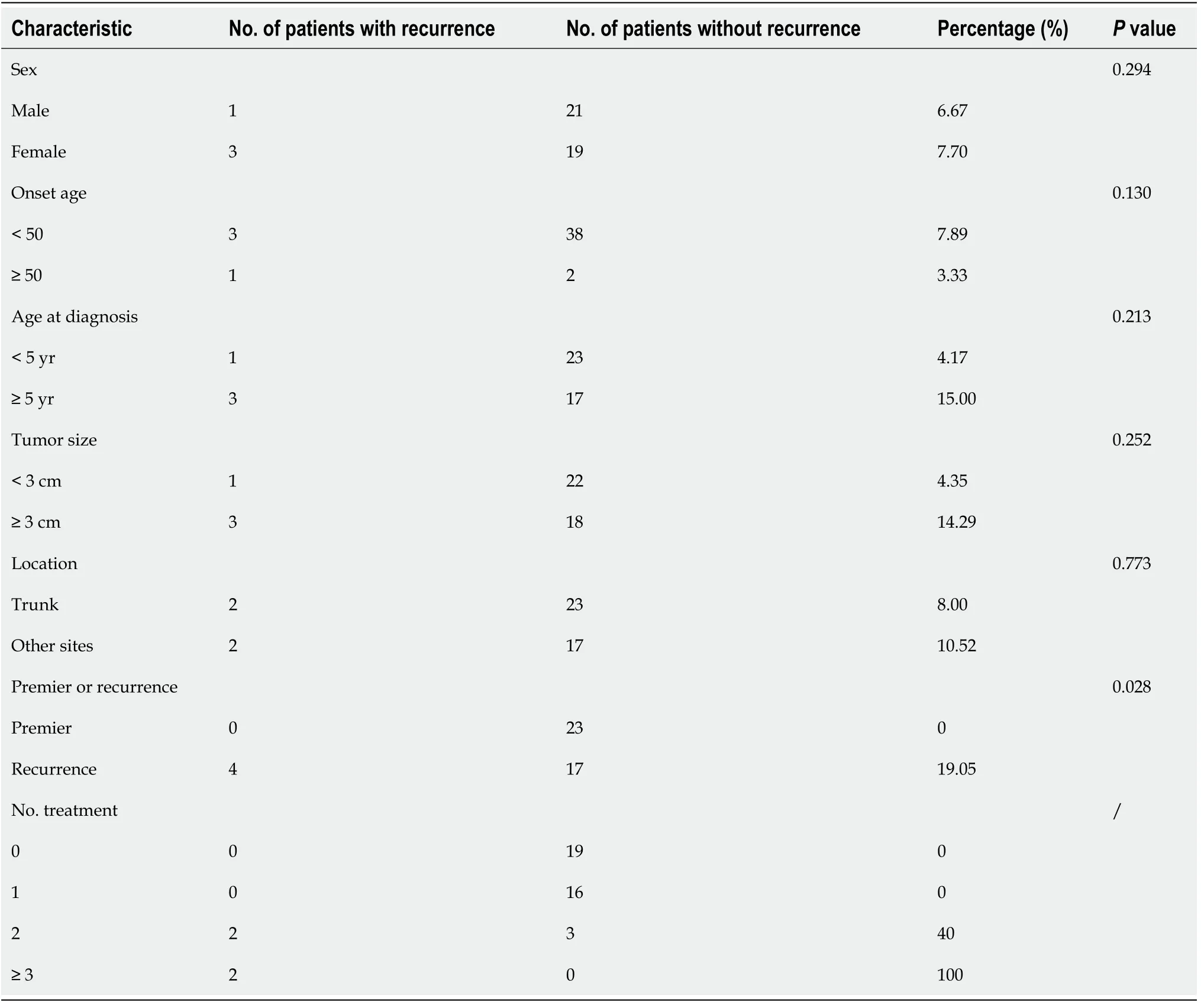
Table 3 Recurrence details
Among the 42 patients, the depth of surgical resection could not be obtained for one patient. In 16 patients, the tumor was resected including the deep muscle layer in order to obtain adequate deep margins, and three patient experienced recurrence.Recurrence occurred in 1 of the 25 patients who were resected above the fascia(Table 4). In addition, two of five patients who received radiotherapy after tumor excision experienced relapse (Table 5).
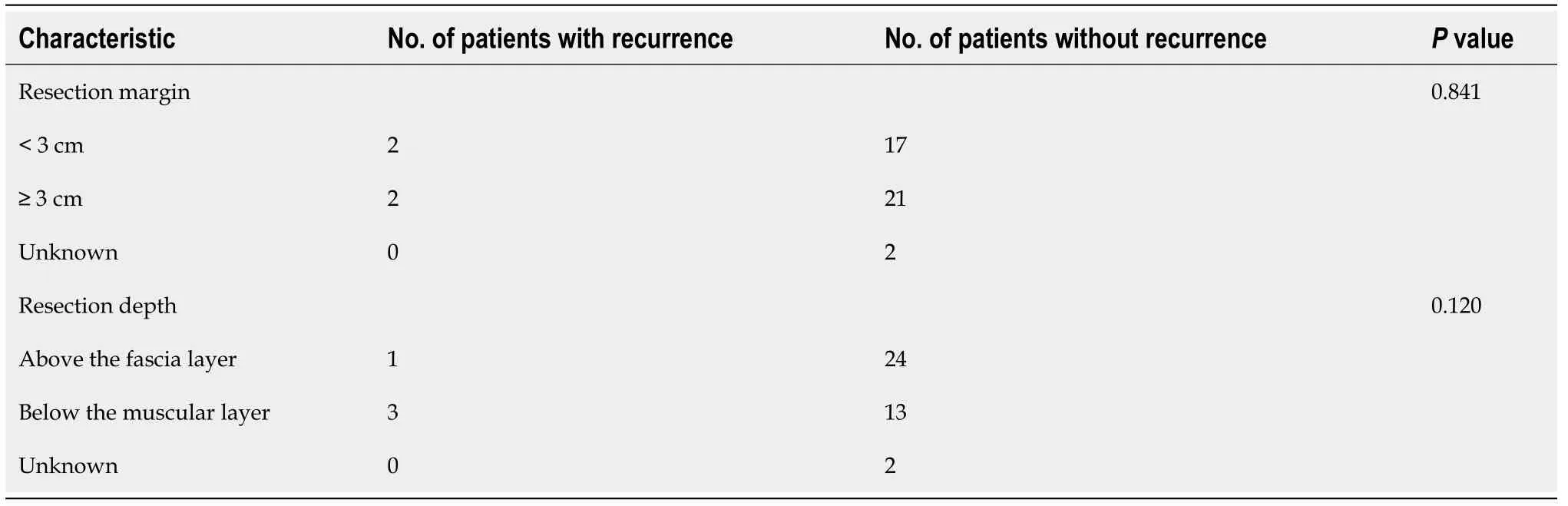
Table 4 Surgical characteristics of patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans

Table 5 Radiotherapy of patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
DISCUSSION
Relationship between clinical features and disease recurrence
In the present study, 93.02% (41/44) of the patients were younger than 50 years old.The trunk was the most commonly involved site, and there was no definite predominance in sex distribution, which is consistent with the previous studies[11]. The tumor size was larger in patients with previous treatment history than in those who were treated for the first time (2.25 ± 0.36 cmvs4.75 ± 0.70 cm,P =0.004). The deep analysisrevealed no significant difference in tumor size between the two groups at the time of onset. Hayakawaet al[12] reported a high correlation between tumor diameter and sarcoma transformation. Inadequate resection may stimulate residual tumor cells,resulting in uncontrolled tumor growth and transformation, increased atypia and mitosis of tumor cells, and sarcoma transformation in tumor tissue. Fibrosarcomatous DFSP (FS-DFSP) is a special subtype of DFSP, which is more malignant than ordinary DFSP; thus, tumor cells tend to grow faster[12,13]. In other words, the increase of tumor size in patients with previous treatment history is the result of disease recurrence, not the cause.
Our results did not reveal gender and age as risk factors for disease recurrence.Phanet al[14] conducted a systematic review of 1777 patients with fibrosarcoma protuberans in 2019, after controlling for confounding factors such as age, race,location, size, average household income, and treatment. They found that the mortality rate in males was higher than that in females. However, they did not clarify the exact reason. Some studies have pointed out that this may be because women are more likely to actively seek medical treatment and because their range of tumor invasion is smaller than in men, thus, it is easier to achieve a satisfactory range of surgery[15].Currently, there have been few studies to support the above hypothesis. Another study also suggested that for every 1-year increase in age, the risk of death increased by 9.0%[16]. Consequently, a longer follow-up time is needed to analyze the relationship between sex, age, and mortality.
Our study showed that more than 40% of patients with tumors located in the head,neck, palmoplantar, and perineal areas were recurrent cases, although the postoperative recurrence rate in these areas was higher than that in the trunk; yet, the difference was not statistically significant (10.52%vs8.0%,P =0.773). Malanet al[17]concluded in their meta-analysis that the recurrence rate after extended resection of the head and neck was nearly three times higher than that of the trunk and limbs(38.19%vs13.34%), thus proving that tumor location does affect local recurrence. The difference in the recurrence rate between sites may be related to the characteristics of the site itself. Lesions with poor skin mobility such as head/face/neck lesions were more likely to present challenges for surgeons to achieve adequate margins than lesions of extremities because of their functionally and cosmetically sensitive anatomic locations[18]. That is to say, the disease’s location is not the direct cause of local tumor relapse.
Our data suggested that sex and age have do nothing to do with local recurrence after excision; the risk of recurrence in patients with an inadequate previous resection was likely higher than that in patients who were treated for the first time; of note, the tumor location indirectly affects the recurrence.
Misdiagnosis and patient status are closely related to recurrence
DFSP is characterized by slow-growing plaques or nodules, a long course with no pain, and itching in the early stage, all of which do not easily attract attention until the above-mentioned symptoms appear locally or the tumor grows rapidly. Some patients were initially misdiagnosed as having benign lesions due to a lack of typical lesions.Studies have shown that the time for delayed diagnosis of DFSP patients is 3-5 years[19], and these patients require a larger excision with a mean resection area of 21.7 cm2with Mohs microsurgery to 63.4 cm2with WLE[20].According to a previous study,the most confusing diseases are epidermal cyst (47.2%), lipoma (14%), scar (7.9%), and dermatofibroma (6.1%)[5]. In addition, pathological manifestations of other tumor diseases are indistinguishable from DFSP, such as dermatofibroma, neurofibroma,schwannoma, leiomyosarcoma, xanthosarcoma, and atypical xanthoma[21,22]. Therefore, misdiagnosis in the early stage of DFSP patients is very common. In our study, 25(56.82%) patients had a history of misdiagnosis. Among them, 17 cases relapsed after treatment (recurrence rate was 68.00%). Yet, seven patients relapsed among the patients who did not experience misdiagnosis (recurrence rate was 36.84%), which suggested a close connection between misdiagnosis and DFSP local relapse. The misdiagnosis will affect the patient’s choice of treatment, thus affecting the prognosis.There were three choices for them: (1) Surgery without biopsy; (2) Biopsy first and then choosing the mode of treatment according to the results of biopsy; and (3) Clinical observation and follow-up. Those without biopsy tend to have a higher risk of recurrence after tumor resection, and the tumor tend to grow up gradually in those patients under clinical observation. Some of them were misdiagnosed after biopsy(pathologic misdiagnosis), which will affect the scope of surgical resection. Therefore,misdiagnosis will affect patients’ choice of treatment, prolong the preoperative duration, require a larger scope of excision, and increase the difficulty of operation.When dermatofibroma, lipoma, keloid, sebaceous gland cyst, and other lesions are highly suspected, surgical resection is necessary, and pathological examination is very important for the prognosis of disease[23].
In the present study, all four relapsed patients underwent excision at another clinic(Table 4). Previous studies have concluded that the local recurrence risk is increasing with the number of previous treatment times, which probably happens due to an incomplete cutoff. The remaining tumor cells are stimulated and rapidly increase,resulting in greater local damage. In such cases, tumors are more likely to transform and invade deeper tissues such as fascia, the surgical margin is more difficult to judge,and postoperative recurrence risk increases[23,24]. However, our study results were different, which may be due to the interaction between previous relapses history and operation mode. In general, surgeons tend to enlarge the diameter and depth of surgical resection for patients with multiple previous relapses, which is important for reducing the recurrence risk.
Relationship between histopathological features and recurrence
Pathology is important for the diagnosis of DFSP. The typical histological feature of DFSP is that fusiform tumor cells grow uniformly, are arranged in flakes, and infiltrate into subcutaneous fat layer like a honeycomb, and some of them show typical mat-like arrangement structure[23]. Asymmetrical pseudopod growth pattern and unclear clinical boundaries commonly found in DFSP make it difficult to determine the operation’s scope. Some patients can show high-grade histopathological features,i.e.,more abundant tumor cells and high atypical and mitotic activity, which are typical of FS-DFSP. At present, a large number of studies have pointed out that FS-DSFP has a poor prognosis and a high risk of local recurrence[25].
Positive CD34 is one of the diagnostic markers for DFSP. Pathologically, the diffuse positive expression of CD34 helps distinguish atypical dermatofibroma from DFSP.Still, in a previous study, 9.1% of DFSP patients were CD34 negative, especially FSDFSP, while CD34 were positive for some myofibrosarcomas, epithelioid sarcomas,and other tumors[12]. Except CD34, PDGF β, and nestin, these markers are also beneficial for the pathological diagnosis of DFSP; nonetheless, these markers are not specific enough to distinguish DFSP from other types of skin tumors[26]. BCL-2 is an important regulator of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway with an anti-apoptotic effect[27]. Theoretically, BCL-2 can inhibit the apoptosis of tumor cells, thus leading to tumor cell proliferation. The positive expression of BCL-2 may be a risk factor for postoperative recurrence. β-catenin is an important regulatory protein in the Wnt/βcatenin signaling pathway. When the Wnt pathway is activated, the degradation pathway of β-catenin is blocked, and β-catenin accumulates in the cytoplasm, after which it enters the nucleus to promote the expression of target genes[28]. Therefore,when β-catenin is positive, the replication and transcriptional metabolism of tumor cells are exuberant, the tumor may grow faster, and the diameter of the tumor becomes larger. However, in our study, the overall positive rate of BCL-2 was 71.43%(10/14), and there was no statistical difference between the primary group and recurrence group (40%vs22.22%,P= 0.480). The overall positive rate of β-catenin was 71.43% (10/14). The positive expression of β-catenin had no difference in patients with different tumor sizes, which may be explained by the small sample size in the present study. In 33 patients with pathologically marked Ki-67, the positive rate varied from 1% to 30%; the positive rate in the primary group was slightly lower than that in the recurrence group, and there was no significant difference between the two groups(8.50%vs8.72%,P =0.943).
In short, pathological and immunohistochemistry are the means for diagnosing DFSP, while positive CD34 is not the only criterion for the diagnosis of DFSP. No immune marks related to the prognosis of the disease have been found[29].
Relationship between treatment and disease recurrence
Effect of WLE on local relapse:At present, the local recurrence rate after tumor resection is as high as 26%-60%. WLE can reduce the recurrence rate to 0%-41%, and Morse microsurgery can control the recurrence rate at 0%-8.3%[30]. Although Morse microsurgery can significantly reduce the recurrence rate, it is complex, timeconsuming, and expensive and requires a combination of surgery and pathology.Tumor cells in frozen sections can be easily confused with spindle cells in the normal dermis, while CD34 staining variability tends to be large, thus requiring surgeons to have higher pathological knowledge. There are still doubts about the reliability of this technique[2,31]. Clinically, extended resection is more often used. The distance between the resection margin and the edge of the tumor of 2 cm is generally recommended. The scope of Morse microsurgery is to make the distance between the cutting edge and the edge of the tumor exceed 1 cm[32]. Nevertheless, Caiet al[33]analyzed the treatment of 260 patients with DFSP and found that the recurrence rate was highest in the patients with an incisal margin ranging from 1.5-2.5 cm. In contrast,with the incisal margin extending above 3 cm, the recurrence rate significantly decreased (13.6%vs5.7%,P =0.043). Through reviewing the medical records and telephone return interviews, we found that most patients in the recurrent group received tumor resection for the first time, and the distance from the excision edge to the tumor was less than 2 cm. Although the recurrence rate in patients with an incisal margin exceeding 3 cm was higher than that of patients with an incisal margin less than 3 cm in our study, the difference was not statistically significant (14.29%vs4.35%,P =0.252).
Except for the width, the depth of tumor invasion should also be taken into account.Histopathology of DFSP showed honeycomb infiltrating tumor cells in the fat layer. A small number of tumor cells in patients could reach the fascia and muscle layer, and even infiltrate the periosteum. The depth of invasion was proportional to the difficulty of operation. The deeper the invasion, the greater the possibility of remaining tumor cells, and the higher the risk of recurrence. Through the follow-up of 244 DFSP patients, Fieldset al[34] found that the disease-free survival of patients with shallow invasion was significantly better than that of patients with deeper invasion (hazard ratio = 3.14, 95%CI: 1.18-8.32,P= 0.022). However, all four relapsed patients in our study had resection to the fascia layer or even the muscle layer, but their recurrence rate was higher compared to patients who had resection above the fascia layer (18.75%vs4.00%,P= 0.120), which is contrary to the results of Fieldset al[34]. It may be that recurrence of DFSP is affected by many factors. The effect of resection depth on tumor recurrence should be analyzed after controlling for other confounding factors (such as surgical diameter, tumor size, course of disease, and previous recurrence). However,our sample size was small, and only four cases experienced postoperative recurrence,so the above analysis was not carried out. Nonetheless, we still cannot deny the effect of resection depth on the recurrence rate.
Effect of radiotherapy on recurrence rate
Of five patients who underwent postoperative radiotherapy after tumor excision, two had relapse again after radiotherapy (recurrence rate, 40%). Among the remaining 19 recurrent patients who did not undergo radiotherapy, two relapsed (recurrence rate,5.41%). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P< 0.013),which suggested that radiotherapy does not reduce the recurrence risk but may increase it. According to a meta-analysis conducted by Chenet al[35], there is no difference in the recurrence rate between postoperative radiotherapy and simple surgery; however, there was a trend that postoperative radiotherapy was associated with a lower recurrence rate than surgery alone, which was inconsistent with our results. Further analysis showed that the five patients who received postoperative radiotherapy had repeated treatment experiences in the past. Tumor recurrence is related to various factors, including the existence of sarcoma transformation, positive surgical margin, history of recurrence, and so on. Therefore, radiotherapy may not be a risk factor for recurrence. The relapse in patients after radiotherapy may be associated with other risk factors mentioned above. Still, complications such as flap necrosis,edema, and poor healing may occur after radiotherapy[33]. Clinically, whether patients need radiotherapy should be evaluated according to the specific conditions.
CONCLUSION
To sum up, the clinical manifestations of DFSP are not specific and it is easily misdiagnosed, which is one of the common causes of recurrence of DFSP. The risk of recurrence increases with the increases in the number of treatments.
In this study, we found that the risk of recurrence in patients with tumors located in the head and neck, perineum, and palmoplantar region is higher than that in patients with tumors located in the trunk.The above factors mainly affect the prognosis of the disease by affecting the range of surgical resection. Moreover, the effect of radiotherapy on prognosis remains controversial. At present, there are no immune molecules related to prognosis. Repeated incomplete treatment may lead to the rapid growth of the tumor and the significant increase in tumor diameter; however, there is no significant correlation between the diameter of the tumor and the prognosis of the disease.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare skin and soft tissue malignant tumor with low grade, accounting for 1% of all soft tissue malignant tumors. The tumor has a high recurrence rate after operation.
Research motivation
To evaluate the clinical manifestations, pathological features, and immune molecules of DFSP, and identify risk factors that may be related to prognosis.
Research objectives
To clarity whether there are some clinical or pathological features related to prognosis of DFSP.
Research methods
This study is a retrospective analysis. We analyzed the tumor size, treatment experience, operation scope, and other dimensions, and quantified the relevant information. SPSS21.0 statistical software was adopted for statistical analyses.
Research results
A total of 44 patients with DFSP were included and 42 cases were followed, of whom four experienced relapse, with a recurrence rate of 9.52%. For patients with a previous history of recurrence, the recurrence risk was higher than that in the patients with primary tumor (19.05%vs0%P= 0.028). The recurrence risk in those patients with misdiagnosis experience was higher than that in the patients without (68%vs36.84%,P= 0.04). The tumor diameter in patients with treatment history was larger than that in patients treated for the first time (4.75 ± 0.70 cmvs2.25 ± 0.36 cm,P= 0.004).
Research conclusions
Tumor location and previous treatment history have an impact on the prognosis of the disease. However, the above factors indirectly affect the prognosis by affecting the extent of surgical resection. Repeated and incomplete treatment can lead to the enlargement of the tumor, which in turn affects the scope of surgical resection. In addition, no immune markers related to postoperative recurrence was found.
Research perspectives
In the future, we will continue to follow all patients to analyze the causes of death and the risk factors that may lead to death. And we will devote ourselves to finding immune markers related to the prognosis of patients with DFSP.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2021年20期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2021年20期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Obesity in people with diabetes in COVID-19 times: Important considerations and precautions to be taken
- Revisiting delayed appendectomy in patients with acute appendicitis
- Detection of short stature homeobox 2 and RAS-associated domain family 1 subtype A DNA methylation in interventional pulmonology
- Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer and vascular resections in the era of neoadjuvant therapy
- Esophageal manifestation in patients with scleroderma
- Exploration of transmission chain and prevention of the recurrence of coronavirus disease 2019 in Heilongjiang Province due to inhospital transmission
