栀子苷对双酚A致鲤鱼肝毒性的保护作用
顾郑琰 贾睿 何勤 曹丽萍 杜金梁 徐跑 殷国俊

摘要:【目的】探究不同浓度栀子苷对双酚A(BPA)致鲤鱼(Cyprinus carpio)肝毒性的影响,为鱼类保肝药物的筛选提供依据。【方法】以75条鲤鱼为试验材料,设5个处理组,即空白对照组、模型组(0.5 mg/L BPA暴露)及栀子苷处理组(BPA+栀子苷),其中,栀子苷设低(1.25 g/kg)、中(2.50 g/kg)、高(5.00 g/kg)3个浓度,养殖70 d后,检测血清中谷丙转氨酶(GPT)、谷草转氨酶(GOT)、碱性磷酸酶(AKP)、甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)的水平,肝组织中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、谷胱甘肽(GSH)、丙二醛(MDA)和总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)的水平,以及肝脏中fatp1、fas、ppar-α、nrf2、keap1、ho-1、tlr1、myd88、il-1β、il-6和il-10基因的表达量,来评价栀子苷对鲤鱼肝毒性的治疗效果。【结果】与对照组相比,模型组鲤鱼的特定生长率显著降低,饵料系数显著增高(P<0.05,下同),而联合投喂3种浓度的栀子苷可显著提高特定生长率,降低饵料系数,改善鲤鱼的生长情况。与模型组相比,饲喂中、高浓度的栀子苷显著降低鲤鱼血清中GPT、GOT和AKP活性,緩解鲤鱼肝损伤的程度。饲喂低、中浓度的栀子苷显著降低血清中TG和LDL-C的水平和肝组织中fatp1和ppar-α基因的表达量,增加血清中HDL-C的含量,改善了鲤鱼肝脏脂质代谢紊乱。同时,经过3种浓度的栀子苷处理后,肝组织中SOD活性和nrf2、ho-1基因的表达量显著升高,keap1基因的表达量显著降低,表明栀子苷对双酚A引起的肝脏氧化应激有缓解作用。此外,饲喂3种浓度的栀子苷较模型组显著下调了myd88、il-1β和il-6基因的表达量,但显著上调了il-10基因的表达,抑制了鲤鱼肝脏的炎症反应。【结论】栀子苷可不同程度缓解双酚A引起的鲤鱼肝毒性,并通过改善肝脏脂质异常代谢,增强抗氧化能力,抑制炎症反应等,减轻鲤鱼肝损伤程度。考虑到实际生产成本,推荐以中浓度(2.50 g/kg)的栀子苷作为保肝药物的筛选依据。
关键词: 栀子苷;双酚A;保肝作用;肝毒性;鲤鱼
中图分类号: S948 文献标志码: A 文章编号:2095-1191(2021)02-0501-08
Abstract:【Objective】Explored the effects of different concentrations of geniposide on the hepatotoxicity of bisphenol A(BPA) in common carp(Cyprinus carpio), and provided a reference for screening hepatoprotective drug in fish. 【Method】In this study, 75 common carps were divided into five treatment groups: blank control group, model group(0.5 mg/L BPA exposure) and geniposide treatment group (BPA+geniposide). Geniposide was set at low (1.25 g/kg), medium(2.50 g/kg) and high(5.00 g/kg) concentrations for 70 d. Then detected glutamic-pyruvic transaminase(GPT), glutamic oxalacetic transaminase(GOT), alkaline phosphatase(AKP), triglycerides(TG), total cholesterol(TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol(HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol(LDL-C) levels in the serum, super oxide dismutase(SOD), catalase(CAT), glutathione(GSH), malondialdehyde(MDA) and total antioxidant capacity(T-AOC) levels, as well as the expression levels of fatp1, fas, ppar-α, nrf2, keap1, ho-1, tlr1, myd88, il-1β, il-6 and il-10 genes in the liver to evaluate the therapeutic effects of geniposide on hepatotoxicity in common carp. 【Result】Compared with the control group, the specific growth rate of common carp in the model group was significantly reduced, and the feed coefficient was significantly increased(P<0.05, the same below). The combined feeding of three concentrations of geniposide could significantly increase the specific growth rate, reduce the feedcoefficient, and improve the growth of carp. Compared with model group, geniposide at middleandhighconcentrations significantly reduced the activities of GPT, GOT and AKP in common carp serum, and alleviated the degree of liver injury in common carp. Lowor middle concentrations of geniposide significantly reduced the levels of TG and LDL-C in serum and the gene expressions of fatp1 and ppar-α in liver tissue, and increased the content of HDL-C in serum, which improved common carp liver lipid metabolism disorder. At the same time, after three concentrations of geniposide treatment, the activity of SOD and the gene expressions of nrf2 and ho-1 in liver tissues were significantly increased, and the expression levels of keap1 gene was significantly decreased, indicating that geniposide could relieve liver oxidative stress caused by BPA. In addition, compared with model group, feeding three concentrations of geniposide significantly down-regulated the gene expressions of myd88, il-1β and il-6, significantly up-regulated the gene expression of il-10, which inhibited the inflammatory response in liver of common carp. 【Conclusion】In summary,geniposide can alleviate common carp hepatotoxicity caused by BPA to varying degrees, and reduce hepatotoxicity by improving liver lipid metabolism, enhancing antioxidant capacity, and inhibiting inflammation. Taking into account the actual production cost, it is recommended to use geniposide at middle concentration(2.50 g/kg) as the basis for screening hepatoprotective drugs.
Key words: geniposide; bisphenol A; liver protection; hepatotoxicity; common carp
Foundation item:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31702318); Basal Research Fund of Freshwater Fisheries Research Center, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences(2021JBFM09)
0 引言
【研究意义】双酚A(Bisphenol A,BPA)是合成聚碳酸酯和环氧树脂等的原材料,其在水环境中的分布十分廣泛(石健等,2009;Ibrahim et al.,2015)。BPA能干扰鱼类的生长和发育,对其内分泌系统和免疫系统也有不利影响,给水产养殖业带来了很大的危害(Kim et al.,2018)。肝脏是鱼体最主要的代谢器官,大多数有毒物质都要经肝脏分解代谢(初晓红等,2010)。研究表明,长期的BPA暴露对鲤鱼(Cyprinus carpio)肝脏具有明显的毒性作用,可引起氧化应激,以及脂质代谢功能异常等(庄惠生和杨光,2005;吴雪菲,2014)。因此,研发能有效缓解或治疗BPA致肝毒性的药物,对提升鱼类健康水平具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】据报道,中草药因其成分天然、毒副作用小、不易在鱼体富集等优点,在水产养殖业中应用广泛,对鱼类疾病的预防及治疗发挥着重大作用(Galina et al.,2009;贾睿等,2013)。栀子苷(Geniposide)又名京尼平苷,是从茜草科植物栀子(Gardenia jasminoides Ellis)的干燥成熟果实中提取的一种环烯醚萜苷类化合物,被认为是保肝利胆的良药,且已广泛应用于肝脏疾病的治疗中(刘益华等,2012;Kim et al.,2013;代亚萍等,2019)。在对哺乳动物的研究中发现,一定浓度的栀子苷对四氯化碳(CCl4)诱导的大鼠慢性肝损伤有保护作用,可以提高受损伤肝脏的抗氧化水平,缓解肝脏的炎症反应及纤维化(尚新涛等,2012;Chen et al.,2016)。同时,栀子苷可有效改善大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝,明显降低大鼠血清中的游离脂肪酸水平,改善肝脏的病理表现(Ma et al.,2011;Liang et al.,2016)。另外,栀子苷能通过缓解氧化应激、调节细胞凋亡等途径,发挥对小鼠肝脏缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用(Kim et al.,2013)。【本研究切入点】目前,在水产动物中,关于栀子苷对鱼类肝脏保护作用的研究几乎未见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】以BPA诱导的鲤鱼肝毒性模型为基础,通过检测相关生化指标及基因表达水平的变化,探究不同浓度栀子苷对BPA致鲤鱼肝脏毒性的治疗效果,为栀子苷在鱼类肝病防治中的应用提供理论参考。
1 材料与方法
1. 1 试验材料
试验用鲤鱼选自中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心渔场,体重为50±5 g,体表无伤,体质健康。将75条鲤鱼随机分到5个养殖箱,每个养殖箱15条鱼,每天定时投喂2次基础颗粒饲料(28%粗蛋白、11.6%粗纤维、4%粗脂肪、15%粗灰分),每日投喂量约为鱼体总重的2%;暂养7 d,适应养殖环境(溶氧量>6 mg/L,pH 7.4~8.1,温度28~32 ℃)之后开始试验。主要试剂:栀子苷(纯度≥98%)购自上海源叶生物科技有限公司;BPA(纯度≥99%)和二甲基亚砜(DMSO)购自美国Sigma公司。
1. 2 试验设计
根据前期研究结果,本研究以0.5 mg/L BPA作为暴露浓度(Gu et al.,2020)。基于预试验结果及在草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idella)、小鼠和大鼠中的使用剂量(尚新涛等,2012;Sun et al. 2017),本研究选取3种不同剂量的栀子苷添加入基础饲料中,栀子苷浓度分别为1.25、2.50和5.00 g/kg。将养殖箱中的鲤鱼分为5组,分别为空白对照组、模型组(BPA)及低、中、高3个浓度的栀子苷处理组(BPA+栀子苷),每组15条鱼。除空白对照组外,其余4组鲤鱼均暴露在0.5 mg/L BPA中。空白对照组和模型组投喂基础颗粒饲料,栀子苷处理组分别投喂含对应剂量栀子苷的饲料。每天定时吸取残饵和粪便,并更换1/2养殖用水,确保水质健康及BPA浓度稳定。每7 d称量1次各组鱼的总重,并及时更新饲料投喂量。养殖70 d后停喂24 h,给所有鱼称重并记录后,分别从每个养殖箱中随机选取8条鲤鱼,采集血液和肝脏组织进行后续分析。
1. 3 血清及肝脏组织匀浆的制备
将采集好的新鲜血液室温放置一段时间,析出透明液体后4000 r/min离心10 min,吸取上清液(血清)备用。将100 mg肝组织用生理盐水漂洗干净,用滤纸吸干表面水分,放入1.5 mL的离心管中,加入9倍体积的western及IP细胞裂解液,用匀浆器进行匀浆,之后10000 r/min离心3 min,吸取上清液备用。
1. 4 生化指标检测
谷丙转氨酶(GPT)、谷草转氨酶(GOT)、碱性磷酸酶(AKP)、甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、谷胱甘肽(GSH)、总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)和总蛋白(TP)检测试剂盒购自南京建成生物工程研究所有限公司。丙二醛(MDA)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)检测试剂盒购自上海碧云天生物技术有限公司。按照试剂盒的操作说明检测血清生化指标GOT、GPT、AKP、TG、TC、HDL-C和LDL-C,以及肝组织生化指标SOD、GSH、CAT、MDA、T-AOC和TP。
1. 5 基因转录水平分析
用RNAiso Plus试剂盒提取鲤鱼肝脏中的总RNA,酶标仪测定OD260/280值(1.8~2.1),并计算RNA浓度。取1 μg RNA,用PrimeScriptTM RT reagent反转录试剂盒合成cDNA。根据TB GreenTM Premix Ex TaqTM II试剂盒的操作说明,在实时荧光定量PCR(qPCR)仪上对cDNA进行qPCR检测。以β-actin为内参基因,根据2-ΔΔCq法(Livak and Schmittgen,2001),计算目的基因的相对表达量。上述所用试剂盒均购自宝生物工程(大连)有限公司(TaKaRa)。目的基因的特异性引物由宝生物工程(大连)有限公司(TaKaRa)合成,序列如表1所示。
1. 6 生长指标计算公式
特定生长率(%)=100×(lnW末?lnW初)/t
饵料系数=F/(W末?W初)
式中,W初为养殖试验初的鱼体总重(g),W末为养殖试验末的鱼体总重(g),W末为养殖试验初的鱼体均重(g),W初为养殖试验末的鱼体均重(g),t为养殖试验天数(d),F为饲料消耗量(g)。
1. 7 统计分析
采用SPASS 19.0的单因素方差法(One-way ANOVA)进行数据分析。用LSD检验进行组间多重比较(P<0.05)。采用GraphPad Prism 8制图。
2 结果与分析
2. 1 生长指标分析
试验期间未发现鱼体死亡,各组鱼的存活率均为100%。鱼的生长指标如表2所示,模型组的特定生长率与其他各组相比显著降低(P<0.05,下同),饵料系数与其他各组相比显著增加。
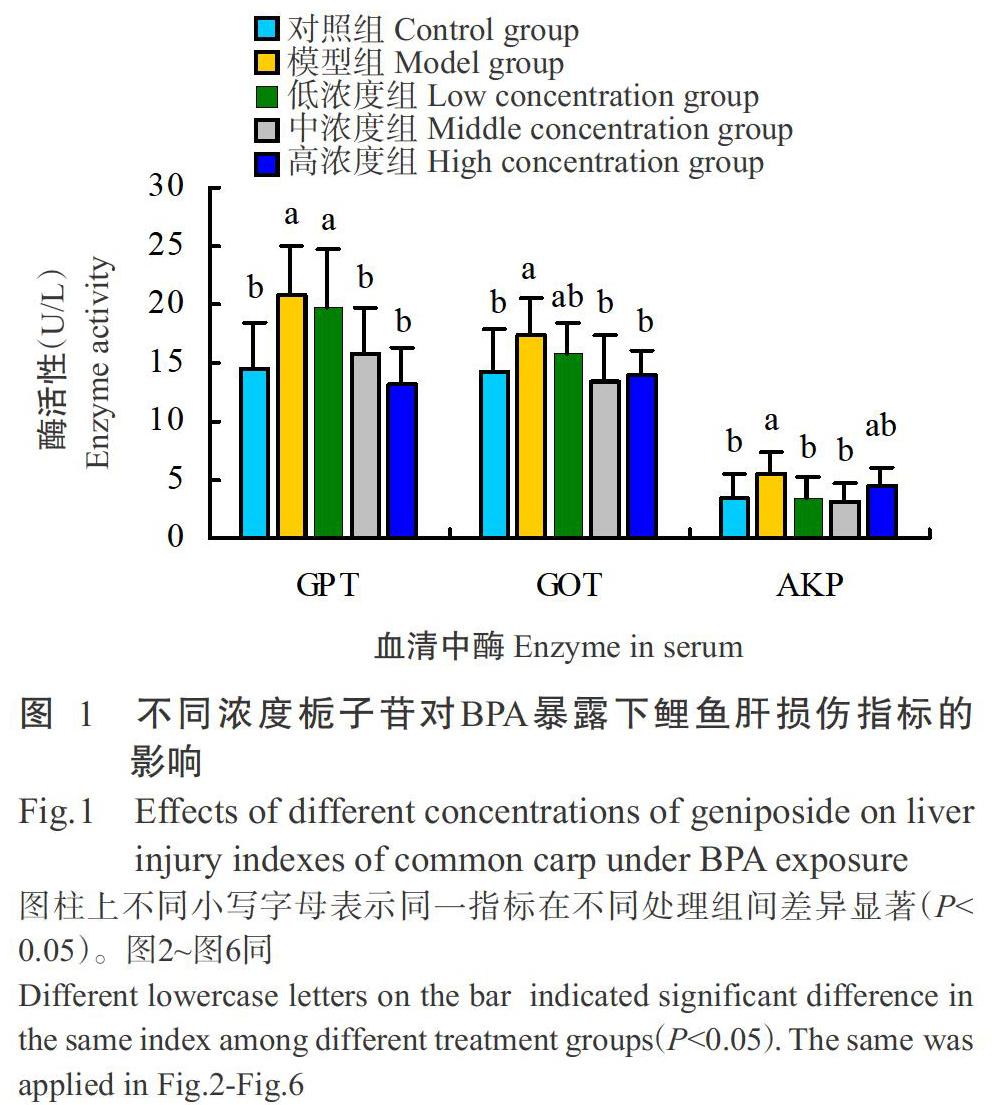
2. 2 不同浓度栀子苷对BPA暴露下鲤鱼肝损伤指标的影响
如图1所示,与对照组相比,模型组的鲤鱼血清中GPT、GOT和AKP活性均显著升高;联合投喂栀子苷后,这些指標的活性均较模型组有所降低,其中,GPT和GOT的活性在中、高浓度组显著降低,AKP的活性在中、低浓度组显著降低。
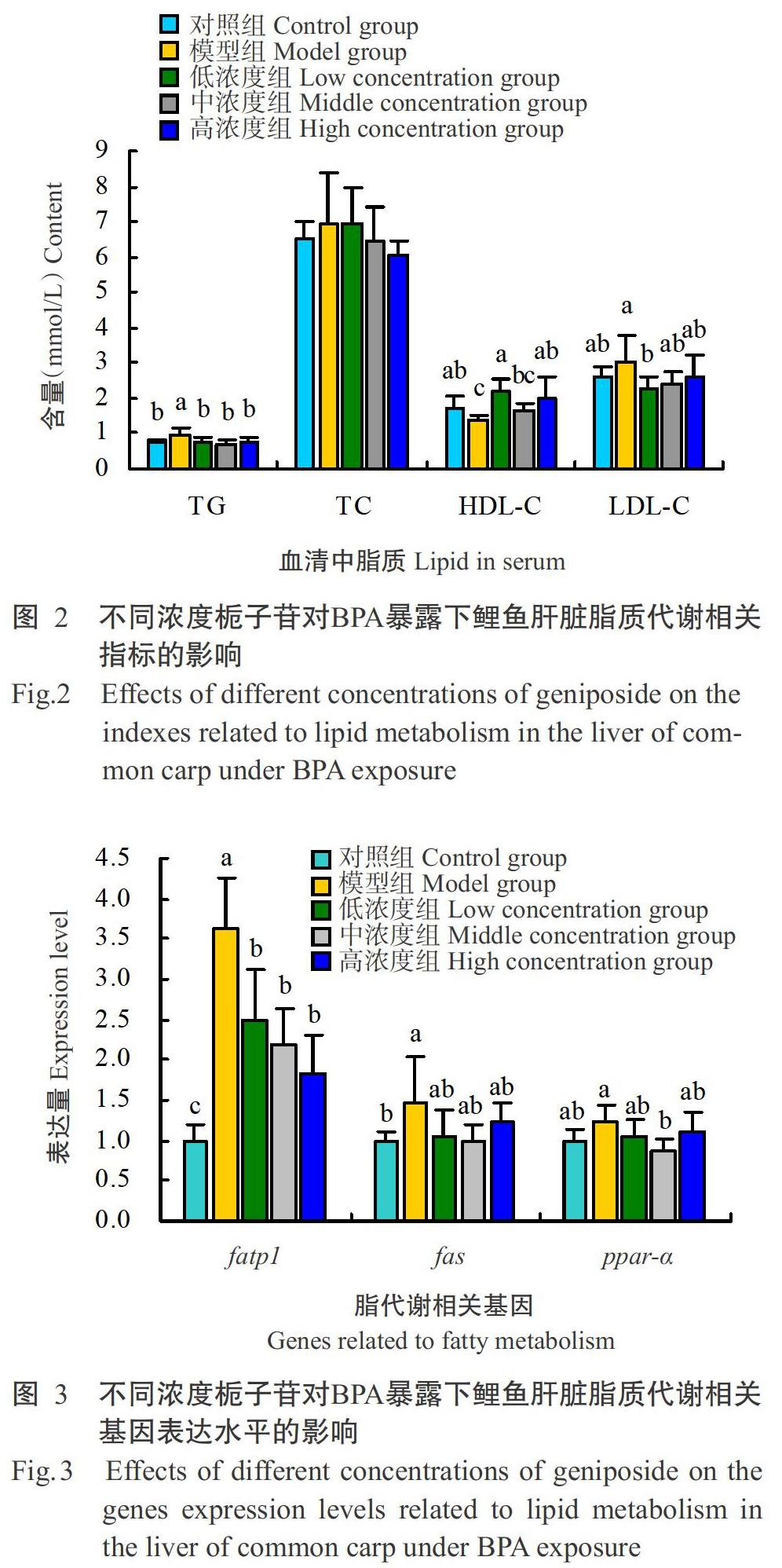
2. 3 不同浓度栀子苷对BPA暴露下鲤鱼肝脏脂质代谢相关指标的影响
如图2所示,与对照组相比,模型组的鲤鱼血清中TG、TC和LDL-C含量有所增加,其中TG含量显著增加;联合投喂栀子苷后,与模型组相比,上述3个指标含量均呈下降趋势,其中TG含量在3个浓度组中均显著降低,LDL-C含量在低浓度组显著降低。与对照组相比,HDL-C含量在模型组显著降低;HDL-C的含量在低、高浓度组比模型组显著增加。
2. 4 不同浓度栀子苷对BPA暴露下鲤鱼肝脏脂质代谢相关基因表达量的影响
从图3可看出,与对照组相比,模型组的fatp1、fas和ppar-α基因表达量均有所上调,其中fatp1和fas的表达量显著上调;与模型组相比,fatp1基因的表达量在3个栀子苷浓度组中均显著下调,ppar-α基因的表达量在中浓度组显著下调。
2. 5 不同浓度栀子苷对BPA暴露后鲤鱼肝脏氧化应激相关指标的影响
如图4所示,与对照组相比,模型组的SOD、GSH、CAT和T-AOC水平均显著降低,联合投喂栀子苷之后,上述4个指标的水平较模型组均有所提高,其中SOD活力在3个浓度组中均显著增加,GSH的在低浓度组显著提高。MDA的水平在模型组升高,在3个栀子苷浓度组降低,但差异均不显著(P>0.05)。
2. 6 不同浓度栀子苷对BPA暴露后鲤鱼肝脏氧化应激相关基因表达量的影响
如图5所示,nrf2和ho-1基因的表达量在模型组比对照组显著下调,3个栀子苷浓度组比模型组显著上调;keap1基因的表达量在模型组比对照组显著上调,3个栀子苷浓度组比模型组显著下调。
2. 7 不同浓度栀子苷对BPA暴露下肝脏免疫功能的影响
从图6可看出,与对照组相比,tlr1、myd88、il-1β和il-6基因的表达量在模型组均显著上调,联合投喂栀子苷后,这些基因的表达量较模型组均有所下调,其中tlr1的表达量在高浓度组下调显著,myd88、il-1β和il-6基因的表达量在3个浓度组均显著下调。il-10基因的表达量在模型组比对照组显著下调,在3个栀子苷浓度组比模型组显著上调。
3 讨论
BPA是分布十分广泛的环境雌激素,能对机体生长、发育、代谢和免疫等多个方面产生不良影响(Kim et al.,2018)。本研究中,BPA单独暴露显著降低了鲤鱼的特定生长率,且明显提高了投喂饲料的饵料系数(饵料系数越高,饲料转化率越低,饲料使用效果越差);而联合投喂栀子苷后,3个浓度组中的特定生长率和饵料系数均恢复到正常水平(与对照组相比),表明栀子苷投喂可改善BPA引起的鲤鱼生长抑制。
肝脏是鱼体代谢有毒物质的关键器官,也最先受到许多外源性化学品的毒性影响(初晓红等,2010;端正花等,2015)。GPT、GOT和AKP活性的变化是反映肝损伤的重要指标,一定浓度的BPA暴露可导致肝功能受损,引起血清GPT活性升高(Lee et al.,2006)。在对小鼠和斑马鱼的(Danio rerio)研究中显示,BPA可扰乱肝脏脂质代谢,上调fatp1、fas和ppar-α等基因的表达,干扰脂肪酸的转运、合成及代谢,以及加重肝内TG沉积(Srivastava et al.,2015;李丹婷等,2016;姚亚运,2016)。同时,BPA暴露可引起机体TC代谢出现异常,改变血清中HDL-C和LDL-C的水平(冯丹和杨岚,2015);BPA暴露还会产生过多的活性氧自由基(Abdel-Wahab,2014),诱导小鼠肝脏细胞发生脂质过氧化,促进MDA形成。此外,多余的活性氧自由基可消耗抗氧化酶和非酶抗氧化物质(SOD、GSH和CAT等),严重影响肝脏的抗氧化能力,导致氧化还原状态失衡(Korkmaz et al.,2010;Battisti et al.,2011)。Nrf2、keap1和ho-1是调节氧化应激的关键基因,而BPA暴露会下调nrf2和ho-1基因的表达,上调keap1基因的表达,进一步降低小鼠肝脏的抗氧化能力(Müller et al.,2018)。有报道称,BPA暴露会影响机体的免疫功能,诱发炎症反应。Toll样受体信号通路在免疫炎症调节中发挥着重要作用(Rauta et al.,2014),BPA暴露能激活此通路,使斑马鱼胚胎中tlr3、myd88和促炎因子il-1β基因的表达上调(Xu et al.,2013),也能使小鼠心肌组织中促炎因子il-6基因的表达上调,抗炎因子il-10基因的表达下调(洪燕,2013),促进炎症反应的发生。
本研究用0.5 mg/L的BPA对鲤鱼进行70 d的暴露试验,结果显示,鲤鱼血清中GPT、GOT和AKP活性显著提高,说明BPA暴露引起鲤鱼肝脏损伤。在BPA暴露后,肝组织中fatp1、fas和ppar-α基因的表达量也显著上调,血清中TG含量明显增加,HDL-C含量显著减少,表明BPA引起鲤鱼肝脏脂代谢功能发生紊乱。此外,BPA明显降低了肝组织中SOD、CAT、GSH和T-AOC的水平,下调了nrf2和ho-1基因的表达,上调了keap1基因的表达,诱导鲤鱼肝脏发生了严重的氧化应激反应。同时,暴露后tlr1、il-1β和il-6基因的表达量上调,il-10基因的表达量下调,说明BPA还会使鲤鱼肝脏的免疫功能失调,诱发炎症反应。
栀子苷具有保肝利胆、镇痛抗炎及抗氧化等作用(刘益华等,2012)。研究表明,栀子苷可有效缓解由CCl4引起的小鼠肝损伤,显著抑制血清中GPT、GOT和AKP的活性,提高肝组织中SOD、CAT和GSH等抗氧化指标的水平(尚新涛等,2012)。栀子苷还可通过对Toll样受体通路的调节,抑制tlr2和tlr4基因的表达,提高败血症小鼠的抗炎能力(Kim et al.,2012)。在脂多糖诱导的大鼠巨噬细胞损伤的模型中,栀子苷的处理显著降低了炎症因子il-1β和il-6基因的表达量,改善了大鼠巨噬细胞的炎症反应(Fu et al.,2012)。另外,在探究栀子苷对脂质代谢影响的研究中发现,栀子苷可降低非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠血清中TG和游离脂肪酸的含量,提高HDL-C的水平,明显改善非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠的脂质代谢功能(林曼婷,2015)。本研究结果显示,联合投喂栀子苷后,与模型组相比,鲤鱼血清中GPT、GOT和AKP这3种酶活性升高被抑制,表明栀子苷可缓解BPA诱导的鲤鱼肝损伤。栀子苷处理组中TG、TC和LDL-C含量降低,HDL-C含量增加,肝脏中脂代谢有关基因fatp1、fas和ppar-α基因的表达量下调,表明栀子苷可改善鲤鱼肝脏脂质代谢紊乱;SOD、CAT、GSH和T-AOC的水平升高,MDA含量减少,nrf2和ho-1基因的表达量上调,keap1基因的表达量下调,表明栀子苷的保肝机制与其抗氧化作用相关。同时,投喂栀子苷抑制了与炎症相关的tlr1、myd88、il-1β和il-6基因的表达,表明栀子苷可有效抑制BPA引起的肝脏炎症反应。
4 结论
栀子苷可不同程度缓解双酚A引起的鲤鱼肝毒性,并通过改善肝脏脂质异常代谢,增强抗氧化能力,抑制炎症反应等,减轻鲤鱼肝损伤程度。考虑到实际生产成本,推荐以中浓度(2.5 g/kg)的栀子苷作为保肝药物的筛选依据。
参考文献:
初晓红,濮俊毅,包慧君,胡建华,高诚,姚一琳,徐春生,覃君慧,陈秋生. 2010. 斑马鱼正常肝脏显微形态和超微结构的初步观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学,30(1): 17-23. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2010.01.005. [Chu X H,Pu J Y,Bao H J,Hu J H,Gao C,Yao Y L,Xu C S,Qin J H,Chen Q S. 2010. Observation on micro- and ultra-structures of the liver in zebrafish(Brachydanio rerio)[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine,30(1): 17-23.]
代亚萍,邓凯波,周伟,李积华,曹玉坡. 2019. 栀子果功能成分及干燥技术研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,40(21): 300-306. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.21.049. [Dai Y P,Deng K B,Zhou W,Li J H,Cao Y P. 2019. Research progress in functional components and drying technology in the fruit of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,40(21): 300-306.]
端正花,陈晓欧,刘灵丽,宫知远,李彩霞. 2015. 苯并三唑和镉对斑马鱼肝脏的联合毒性效应[J]. 中国环境科学,35(6): 1872-1876. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.06.033. [Duan Z H,Chen X O,Liu L L,Gong Z Y,Li C X. 2015. Joint toxicity of benzotriazole and cadmium on zebrafish liver[J]. China Environmental Science,35(6): 1872-1876.]
冯丹,杨岚. 2015. 双酚A对成年小鼠血清胆固醇和炎症因子水平的影响[J]. 环境与健康杂志,32(11): 962-964. doi:10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2015.11.006. [Feng D,Yang L. 2015. Effects of bisphenol A on levels of serum cholesterol and inflammatory cytokines in adult mice[J]. Journal of Environment and Health,32(11): 962-964.]
洪燕. 2013. 雙酚A对小鼠心脏毒性及其机制初步探讨[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学. [Hong Y. 2013. Preliminary study on the toxicity of bisphenol A to the heart of mice[D]. Hengyang: South China.]
賈睿,曹丽萍,杜金梁,徐跑,殷国俊. 2013. 水飞蓟素对四氯化碳致鲫肝(细胞)损伤的保护和抗氧化作用[J]. 中国水产科学,20(3): 551-560. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1118.2013. 00551. [Jia R,Cao L P,Du J L,Xu P,Yin G J. 2013. In vitro and in vivo hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of sily-marin against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatocyte damage in crucian carp Carassius auratus[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China,20(3): 551-560.]
李丹婷,刘露路,高茹菲,彭川,杨淑敏,胡金波,肖晓秋,李启富. 2016. 内质网应激参与双酚A导致小鼠的肝脏脂质沉积[J]. 基础医学与临床,36(7): 886-890. [Li D T,Liu L L,Gao R F,Peng C,Yang S M,Hu J B,Xiao X Q,Li Q F. 2016. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in bisphenol A-induced hepatic lipid deposition of mice[J]. Basic & Clinical Medicine,36(7): 886-890.]
林曼婷. 2015. 栀子苷改善大鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病游离脂肪酸代谢的机制研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学. [Lin M T. 2015. Study on the mechanism of geniposide on impro-ving free fatty acid metabolism in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University.]
刘益华,李晶,林曼婷,周海虹,陈少东. 2012. 栀子有效成分栀子苷的现代研究进展[J]. 中国药学杂志,47(6): 406-409. [Liu Y H,Li J,Lin M T,Zhou H H,Chen S D. 2012. Modern research progress of geniposide,an effective ingredient in gardenia[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,47(6): 406-409.]
尚新涛,张琳,祖元刚,曹姗. 2012. 京尼平苷对CCl4诱导的大鼠慢性肝损伤保护作用研究[J]. 中药药理与临床,28(4): 29-31. [Shang X T,Zhang L,Zu Y G,Cao S. 2012. Therapeutic effects of geniposide on chronic liver injury induced by CCl4 in rats[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,28(4): 29-31.]
石健,高美芳,刘云,严勇,杨仪. 2009. 典型环境激素双酚A的环境行为简述[J]. 广东化工,36(9): 71-72. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2009.09.031. [Shi J,Gao M F,Liu Y,Yan Y,Yang Y. 2009. A review of the famous environmental hormon matter BPA enviroment ehavior[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,36(9): 71-72.]
吴雪菲. 2014. 环境内分泌干扰物对鱼组织中脂肪酸的影响[D]. 太原: 山西大学. [Wu X F. 2014. Effects of endocrine disrupting compounds on fatty acids in carps tissues[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University.]
姚亚运. 2016. 双酚A对雄性斑马鱼(Danio rerio)脂肪代谢影响的研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学. [Yao Y Y. 2016. Effects of Bisphenol A exposure on lipid fat metabolism in male zebrafish(Danio rerio)[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University.]
庄惠生,杨光. 2005. 双酚A对鲤鱼急性和亚急性毒性的研究[J]. 环境化学,24(6): 682-684. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0254- 6108.2005.06.014. [Zhuang H S,Yang G. 2005. Study on acute and subacute toxicity of Bisphenol A on the carp[J]. Environmental Chemistry,24(6): 682-684.]
Abdel-Wahab W M. 2014. Thymoquinone attenuates toxicity and oxidative stress induced by bisphenol A in liver of male rats[J]. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences,17(11): 1152-1160. doi:10.3923/pjbs.2014.1152.1160.
Battisti V,Maders L D K,Bagatini M D,Reetz L G B,Chiesa J,Battisti I E,Goncalves J F,Duarte M M F,Sche-tinger M R C,Morsch V M. 2011. Oxidative stress and antioxidant status in prostate cancer patients: Relation to Gleason score,treatment and bone metastasis[J]. Biome-dicine & Pharmacotherapy,65(7): 516-524. doi:10.1016/ j.biopha.2011.06.003.
Chen P,Chen Y,Wang Y R,Cai S N,Deng L,Liu J,Zhang H. 2016. Comparative evaluation of hepatoprotective activities of geniposide,crocins and crocetin by CCl4-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Biomolecules and Therapeutics,24: 156-162. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2015.094.
Fu Y H,Liu B,Liu J H,Liu Z C,Liang D J,Li F Y,Li D P,Cao Y G,Zhang X C,Zhang N S,Yang Z T. 2012. Geniposide,from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis,inhibits the inflammatory response in the primary mouse macrophages and mouse models[J]. International Immunopharmacology,14: 792-798. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2012.07.006.
Galina J,Yin G,Ardó L,Jeney Z. 2009. The use of immunostimulating herbs in fish. An overview of research[J]. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry,35: 669-676. doi:10.1007/s10695-009-9304-z.
Gu Z Y,Jia R,He Q,Cao L P,Yin G J. 2020. Oxidative stress,ion concentration change and immune response in gills of common carp(Cyprinus carpio) under long-term exposure to bisphenol A[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C Toxicology & Pharmacology,230: 108711. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108711.
Ibrahim J,Eissa S,El-Ghor A A. 2015. Bisphenol A induces oxidative stress and DNA damage in hepatic tissue of female rat offspring[J]. The Journal of Basic & Applied Zoology,71: 10-19. doi:10.1016/j.jobaz.2015.01.006.
Kim B M,Jo Y J,Lee N,Lee N,Woo S,Rhee J S,Yum S. 2018. Bisphenol A induces a distinct transcriptome profile in the male fish of the marine medaka(Oryzias javanicus)[J]. BioChip Journal,12: 25-37. doi:10.1007/s13206- 017-2104-0.
Kim J,Kim H-Y R,Lee S M. 2013. Protective effects of geniposide and genipin against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice[J]. Biomolecules and Therapeutics,21(2): 132-137. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2013.005.
Kim T H,Yoon S J,Lee S M. 2012. Genipin attenuates sepsis by inhibiting toll-like receptor signaling[J]. Molecular Me-dicine,18(1): 455-465. doi:10.2119/molmed.2011.00308.
Korkmaz A,Ahbab M A,Kolankaya D,Barlas N. 2010. Influence of vitamin C on bisphenol A,nonylphenol and octylphenol induced oxidative damages in liver of male rats[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,48(10): 2865-2871. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.019.
Lee C Y,Peng W H,Cheng H Y,Chen F N,Lai M Ts,Chiu T H. 2006. Hepatoprotective effect of phyllanthus in Taiwan on acute liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride[J]. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine,34(3): 471-482. doi:10.1142/S0192415X06004004.
Liang H Q,Lin M T,Zhao X,Zhou H H,Wang H G,Li G H,Wang Y J,Zhang L M,Wang Y Y,Chen S D. 2016. Me-chanism of geniposide in improving free fatty acid metabo-lism in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,41(3): 470-475. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20160319.
Livak K J,Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method[J]. Methods,25(4): 402-408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Ma T T,Huang C,Zong G J,Zha D J,Meng X M,Li J,Tang W J. 2011. Hepatoprotective effects of geniposide in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology,63(4): 587-593. doi:10.1111/ j.2042-7158.2011.01256.x.
Müller S G,Jardim N S,Quines C B,Nogueira C W. 2018. Diphenyl diselenide regulates Nrf2/Keap-1 signaling pathway and counteracts hepatic oxidative stress induced by bisphenol A in male mice[J]. Environmental Research,164: 280-287. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2018.03.006.
Rauta P R,Samanta M,Dash H R,Nayak B,Das S. 2014. Toll-like receptors(TLRs) in aquatic animals: Signaling pathways,expressions and immune responses[J]. Immunology Letters,158(1-2): 14-24. doi:10.1016/j.imlet. 2013.11.013.
Srivastava S,Gupta P,Chandolia A,Alam I. 2015. Bisphenol A: A threat to human health?[J]. Journal of Environmental,77(6): 20-26.
Sun W T,Li X Q,Xu H B,Chen J N,Xu X Y,Leng X J. 2017. Effects of dietary geniposide on growth,flesh quality,and lipid metabolism of grass carp,ctenopharyngodon idella[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society,48(6): 927-937. doi:10.1111/jwas.12412.
Xu H,Yang M,Qiu W H,Pan C Y,Wu M H. 2013. The impact of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on oxidative stress and innate immune response in zebrafish embryos[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry,32(8): 1793-1799. doi:10.1002/etc.2245.
Zhao J,Feng L,Liu Y,Jiang W D,Wu P,Jiang J,Zhang Y A,Zhou X Q. 2014. Effect of dietary isoleucine on the immunity,antioxidant status,tight junctions and microflora in the intestine of juvenile Jian carp(Cyprinus carpio var. Jian)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,41(2): 663-673. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2014.10.002.
(責任编辑 邓慧灵)

