Laryngeal myxoma: A case report
Ting-Ting Yu, Hong Yu, Yu Cui, Wei Liu, Xiang-Yan Cui, Xin Wang
Ting-Ting Yu, Hong Yu, Yu Cui, Xiang-Yan Cui, Xin Wang, Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Jilin University, Changchun 130000, Jilin Province, China
Wei Liu, First Operation Room, Jilin University, Changchun 130000, Jilin Province, China
Abstract BACKGROUND Myxomas are benign tumors of mesenchymal origin that rarely occur in the larynx.CASE SUMMARY We report a case of a laryngeal myxoma that presented as a right vocal cord mass in a 54-year-old man.CONCLUSION Laryngeal myxoma is a rare benign tumor in the larynx. It is difficult to distinguish glottis myxoma from vocal cord polyps on laryngoscopy. We recommend that otolaryngologists acquire a better understanding of this disease. If a laryngeal myxoma is suspected, dynamic laryngoscopy, acoustic voice analysis, and pathological biopsy should be performed.
Key Words: Laryngeal myxoma; Mesenchymal; Glottis; Hoarseness; Dyspnea;Laryngoscopy; Case report
INTRODUCTION
A myxoma is a benign mucinous tumor of mesenchymal origin. These tumors occur in the heart, bones, skin, subcutaneous and aponeurotic tissues, urogenital system, and skeletal muscles[1]. Myxomas can locally invade tissues despite their benign nature[2,3].The term “myxoma” was first proposed by Virchow in 1871 and described as aggregation of a mucinous substance of the umbilical cord[4]. The diagnostic criteria for myxomas were refined by Stout in 1948 as “a true mesenchymal neoplasm consists of undifferentiated stellate cells in the loose myxoid stroma that do not metastasize”[5].
Myxomas can occur in the head and neck, especially the facial bones, such as the mandible and maxilla, with these locations accounting for 3%-6% of myxomas[6].Laryngeal myxoma, however, is very rare, with only 22 cases reported in the English literature. The clinical presentations of laryngeal myxomas are highly similar to those of common benign laryngeal lesions such as laryngeal polyps, and thus, they are difficult to diagnose through physical examination.
Here, we report a case of laryngeal myxoma treated in our center. We also review and summarize the clinical characteristics of reported laryngeal myxomas to help clinicians obtain a better understanding of laryngeal myxomas and improve the diagnosis, treatment, and patients’ postoperative recovery.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 54-year-old man was admitted to the hospital because of progressive hoarseness and dyspnea. He had no cough, sputum, or sore throat.
History of present illness
He had a history of hoarseness lasting 7 years, which persisted and gradually worsened. The patient had been stable until 10 d earlier, when hoarseness significantly worsened and dyspnea presented. The patient was treated with penicillin at the local hospital, which provided no relief, then he was referred to our hospital.
History of past illness
The patient had a free previous medical history.
Physical examination
The patient presented with moderate inspiratory dyspnea; however, vital signs were stable. There were no other abnormal findings.
Laboratory examinations
The results of laboratory examinations were normal.
Imaging examinations
Laryngoscopy revealed a smooth laryngeal mass.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
After admission, the patient was diagnosed with throat obstruction, degree II dyspnea,a right vocal cord mass (myxoma), and mild anemia.
TREATMENT
We performed resection of the right vocal cord mass with the assistance of an endoscope.
During the operation, a smooth mass with a pedicle was observed on the front end of the right vocal cord, with a size of about 1.5 cm × 1.4 cm × 1 cm, without invasion of the vocal cord muscle (Figure 1). The tumor extended below the glottis, and the glottis was narrow. We removed the vocal cord mass completely without damaging the vocal ligament (Figure 2). Pathological examination (Figure 3) of the excised vocal cord mass showed that it was a mesenchymal tumor. The results of immunohistochemistry revealed that it was a myxoma. The tumor had no envelope and showed expansive growth. It was composed of well-differentiated phyllodes mucinous tumors separated by fibroid tissues. There was no obvious atypia, mitosis, or necrosis. Part of the epithelium was missing, and mucosal ulcers were formed (Figure 3A). The immunohistochemical results were as follows: Ki-67 (+ < 5%), calponin (-), cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31) (+), CD34 (weak +), cytokeratin pan (-), desmin (-),neurofilament (-), S-100 (-), and glial fibrillary acidic protein (-) (Figure 3B). After the operation, the patient received budesonide inhalation suspension and supportive care.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
The patient will be followed up every 3 mo and should be checked by laryngoscopy at each visit.
DISCUSSION
We searched the PubMed and Geenmedical databases using laryngeal myxoma as a keyword, and analyzed the search results (Table 1). All of the literature contained information about the patient’s medical history, symptoms, lesion location,pathological diagnosis,etc.A total of 24 cases have been reported in the literature or admitted to our center to date (Table 1). Among them, the incidence in men was higher than that in women (91.67%vs8.33%). The average patient age was 53.29 years (range:25-77 years). Tumors were commonly found in the glottis (79.17%), and most of them were unilateral. Therefore, hoarseness was the most common symptom. Most patients had a history of smoking. Myxomas in the supraglottic area were mostly larger than tumors in the glottal area, and there are two possible reasons. First, the small space in the glottis restricts tumor growth. Second, tumors in the glottis are prone to cause obvious symptoms, which prompts patients to see a doctor, leading to early detection.Due to the large space in the supraglottic area, myxomas in this area have no specific symptoms in the early stage. After the tumor grows, the patient may experience foreign body sensation during swallowing and snoring during sleep. The tumor is usually found during on physical examination by a doctor at this time. The clinical presentation of the present case is consistent with the above characteristics.
We summarize the characteristics of laryngeal myxomas in the glottis in Table 2.Among the 19 cases of laryngeal myxoma in the glottis, 11 occurred in the right vocal cord (57.89%), 7 in the left vocal cord (36.84%), and 1 in the anterior commissure of the larynx. There were 17 male patients (89.47%) and 2 female patients (10.53%). The tumor size ranged from 0.4-2.5 cm. Theoretically, breathing difficulties will occur if the maximum diameter of the tumor exceeds the front two-thirds of the vocal cords (1.4 cm in males and 1.0 cm in females). Other factors such as the location and texture of the tumor also affect the occurrence of laryngeal obstruction. A back location and dense texture are related to a higher risk of laryngeal obstruction. We found that very few reports provided the results for patient acoustic voice indicators. Only Imaizumiet al[7]reported the preoperative and postoperative dynamic laryngoscopic and voice analysis indicators. They found that the fundamental frequency, fundamental frequency perturbation (jitter), and amplitude perturbation (shimmer) of the vocal cord mucosa were significantly improved after surgical treatment, suggesting that surgery can effectively improve the voice quality of patients with a myxoma in the glottis. We propose that dynamic laryngoscopy and acoustic voice testing should be performed for patients with benign laryngeal tumors, as this information can not only help us make a differential diagnosis, but also evaluate the effect of surgery.
The differential diagnoses of myxoma include myxoid liposarcoma, myxoid chondrosarcoma, and laryngeal polyp[8]. S-100 protein is indicative of lipoblasts and chondroblasts, while CD34 protein is commonly used as a marker for myxomas. The present case showed negative staining for S-100 and positive staining for CD34[9]. In summary, histopathological examination is the main method for the differential diagnosis of benign laryngeal tumors. When clinicians cannot differentiate anddiagnose glottal benign tumors under laryngoscopy, a pathological biopsy is recommended to avoid misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis and reduce the tumor recurrence rate.

Table 1 Systematic review of all cases of laryngeal myxoma
Laryngeal microsurgical resection is the first choice for the treatment of laryngeal myxoma[10]. It should be noted that during the operation, gross-total resection should be performed and the marginal tissue of the tumor should be removed to prevent recurrence. This is different from the recommendations for vocal cord polyp removal.Total resection of laryngeal myxoma is necessary to prevent recurrence[11]. Follow-up should be done within 3 years after surgery, because recurrence usually occurs within the first 3 years after surgery[12]. The present patient will be followed up closely.
CONCLUSION
Laryngeal myxoma is a rare benign tumor in the larynx. It is difficult to distinguish glottis myxoma from vocal cord polyps on laryngoscopy. We recommend that otolaryngologists acquire a better understanding of this disease. If a laryngeal myxoma is suspected, dynamic laryngoscopy, acoustic voice analysis, and pathological biopsy should be performed.

Table 2 Systematic review of cases of laryngeal myxoma in the glottis

Figure 1 Preoperative laryngoscopic image. A smooth mass was seen on the left vocal cord with a broad base. The tumor was so large that it blocked the throat cavity.

Figure 2 Intraoperative image. The multiple layers of the vocal folds remained intact after mass removal.
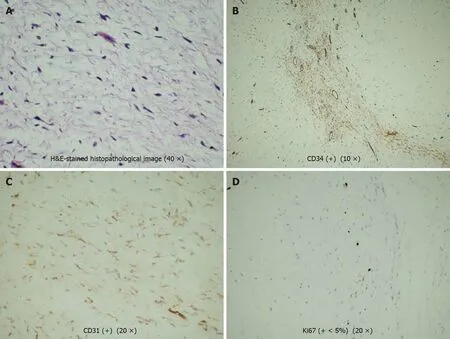
Figure 3 Hematoxylin & eosin-stained histopathological image (40 ×). A: Hematoxylin & eosin (H&E)-stained histopathological image; B:Immunohistochemical staining of cluster of differentiation 34 (CD34) (+) (10 ×); C: Immunohistochemical staining of CD31 (+) (20 ×); D: Immunohistochemical staining of Ki67 (+ < 5%) (20 ×). The tumor had no envelope and showed expansive growth. It was composed of well-differentiated phyllodes mucinous tumors separated by fibroid tissues. There was no obvious atypia, mitosis, or necrosis. Part of the epithelium was missing, and mucosal ulcers were formed. The immunohistochemical results were as follows: Ki-67 (+ < 5%), CD31 (+), and CD34 (weak +).
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2021年12期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2021年12期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Management and implementation strategies of pre-screening triage in children during coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Guangzhou, China
- Separated root tip formation associated with a fractured tubercle of dens evaginatus: A case report
- Budd-Chiari syndrome associated with liver cirrhosis: A case report
- Sclerosing polycystic adenosis of the submandibular gland: Two case reports
- Congenital bilateral cryptorchidism in an infant conceived after maternal breast cancer treatment: A case report
- Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a 3-year-old boy with congenital pyruvate kinase deficiency: A case report
