Enlightenment and Reference of Vaccine Clinical Trial Design Based on Immunological Surrogate Endpoints in the United States
Gu Jinmeng,Yang Yue,Xing Hua
(School of Business Administration,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China)
Abstract Objectives To explore the optimization method of vaccine clinical trial design based on immunological surrogate endpoint to improve the quality and efficiency of vaccine clinical research and development.Methods As to the problems in the vaccine clinical research in China,the relevant guidelines and literatures of FDA and WHO were used to analyze and summarize the methods of optimizing the design of vaccine clinical trials.Results and Conclusion The adaptive design guidelines are established to guide clinical trial design,encourage the development and application of immunological surrogate endpoints,establish qualification process for drug development tools and information disclosure procedures to improve vaccine development efficiency.
Keywords:vaccine; immunological surrogate endpoint; adaptive design
In order to optimize the design of clinical trials for preventive vaccines (hereinafter referred to as “vaccines”),improve vaccine research and development efficiency,and reduce research and development costs,the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) encourages the use of immunological surrogate endpoints for vaccine research and development.The WHO defines an immunological surrogate endpoint as a vaccine-induced response that predicts protection against clinical endpoints after vaccination[1].Traditionally designed clinical trials often use the incidence of clinical endpoints as an indicator of effectiveness evaluation,while clinical trials based on immunological surrogate endpoints can directly apply established immunological surrogate endpoints to evaluate the efficacy of vaccines,shorten the time of clinical trials and improve the efficiency of vaccine development.
The immunological surrogate endpoint of enterovirus 71 (EV71) vaccine is the first immunology surrogate endpoint developed in China[2].According to the problems in the development and application of immunological surrogate endpoints,the optimal design methods of vaccine clinical trials based on immunological surrogate endpoints in the United States were explored so that we could give some suggestions on China’s vaccine clinical trials.
1 Relevant regulations for optimal design of vaccine clinical trials and immunological surrogate endpoints in the United States
Immunological surrogate endpoints are essentially used in vaccines.After the mid-1980s,research on surrogate endpoints continued to develop in the United States,and the FDA promoted the development and application of surrogate endpoints.According to 21CFR 601.41,the FDA is allowed to approve biologics license applications (BLA) based on surrogate endpoints or on clinical endpoints affecting survival or irreversible morbidity.This determines the rationality of the development and application of surrogate endpoints at the regulatory level[3].
As a research and development (R&D) tool,immunological surrogate endpoints can improve the development efficiency of vaccine.According to Article 507 of the Federal Food,Drug,and Cosmetic Act (FD&CA),the US FDA has established a“Qualification Process for Drug Development Tools”,and FDA needs to publish the “Table of Surrogate Endpoints That were the Basis of Drug Approval or Licensure”[4].Through the identification of immunological surrogate endpoints and information disclosure,it can promote the development and application of immunological surrogate endpoints,reduce the waste of R&D resources,and improve vaccines R&D efficiency.
By September 30,2019,the FDA announced the immunological surrogate endpoints for 18 vaccines(Table 1[5]),some of which have been applied to biologics license application (BLA) for vaccines and have been approved for marketing.Some of them may be eligible for BLA,but the vaccine has not yet been approved for marketing.
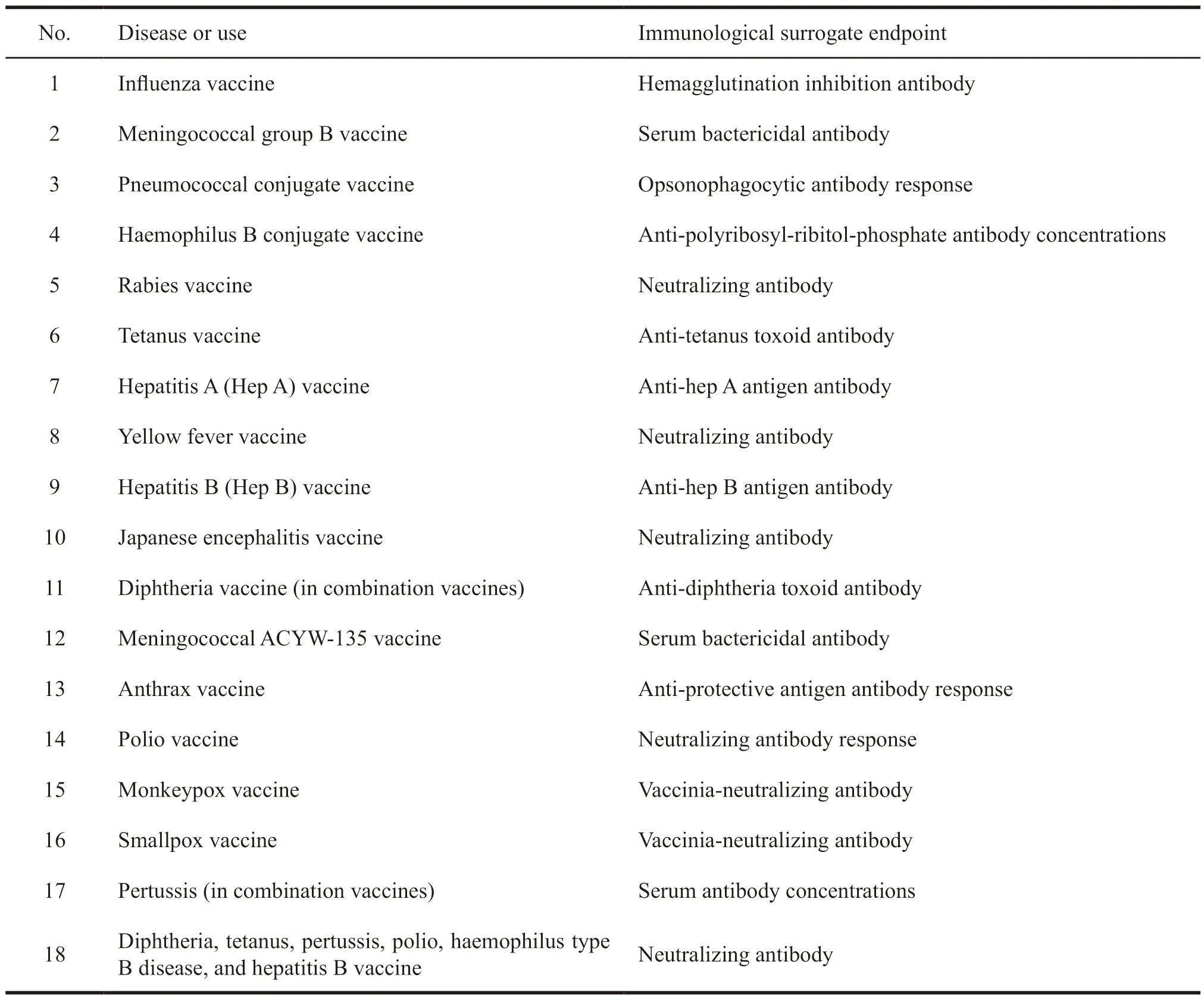
Table 1 Immunological surrogate endpoints published by the US FDA
In the United States,clinical endpoint adaptive selection is taken as a type of adaptive design for clinical trials.Adaptive design of clinical trial refers to a design that allows advance planning to improve one or more aspects of the clinical trials based on accumulated data.In November 2019,the US FDA issued the “Industry Guidance for Adaptive Designs of Clinical Trials for Drugs and Biologics”[6],which described a variety of adaptive design types,including the adaptations to endpoint selection,adaptations to patient allocation,etc.The guidance was applicable to vaccines.
2 Optimized design of clinical trials based on surrogate endpoints in the United States
The adaptive design of clinical trials and the choice of immunological surrogate endpoints will affect the quality,timeliness and integrity of vaccine clinical trials.
2.1 Adaptive design of vaccine clinical trials
The adaptive design includes group sequential design,sample size reevaluation,adaptive selection of subjects,selection of treatment groups,patient allocation,endpoint selection and multiple design features.In the adaptive design of clinical trials,researchers need to coordinate clinical trial plans,improve corresponding parts of clinical trial plans by analyzing the accumulated data,such as changing clinical endpoints or immunological replacement endpoints,sample size,etc.These can rationalize the setting of clinical trials,shorten the time of clinical trials,improve the efficiency of the trials,reduce the cost of R&D,and ensure the efficiency,flexibility and feasibility of clinical trials.
2.2 Adaptive selection of vaccine clinical endpoints
The premise of adaptive selection of clinical endpoints is to identify clinical endpoints or immunological surrogate endpoints related to clinical outcomes and to determine the relationship between different clinical endpoints or immunological surrogate endpoints and clinical outcomes.In a word,it is to determine immunological surrogate endpoints or new clinical endpoints.The adaptive selection of clinical endpoints is often used to expand clinical trials for specific populations and individualized treatments[7].
The adaptive selection of clinical endpoints allows adjustment of trial endpoints,which has advantages in clinical trial flexibility,ethical compliance,and judgment of clinical efficacy of vaccines.But it may also introduce the bias.The use of adaptive selection of endpoints and other adaptive designs at the same time will increase the complexity of clinical trials and make it difficult to predict the error rate of type I and the problems that may be encountered in trials.Therefore,clinical trial simulations can be implemented to evaluate clinical trials.
2.3 Development and application of immunological surrogate endpoints
2.3.1 Advantages of clinical trial design based on immunological surrogate endpoints
In this they did very well for him, for the Fairy was as kind as she was powerful, and she spared no pains in teaching the little Prince everything it was good for him to know, and even imparted to him some of her own Fairy lore5
In vaccine clinical research,the use of immunological surrogate endpoints can significantly reduce the sample size of clinical trials,shorten the time of clinical trial,reduce the costs of R&D,and promote the development,evaluation,approval and application of new vaccines[8].In addition,the immunological surrogate endpoint can be used to assess the individual’s immunity after vaccination.It can also provide a reference for expanding clinical research to specific populations[9].From the perspective of clinical trial implementation effect,the traditionally designed clinical trials are compared with those designed based on immunological surrogate endpoints,as shown in Table 2.
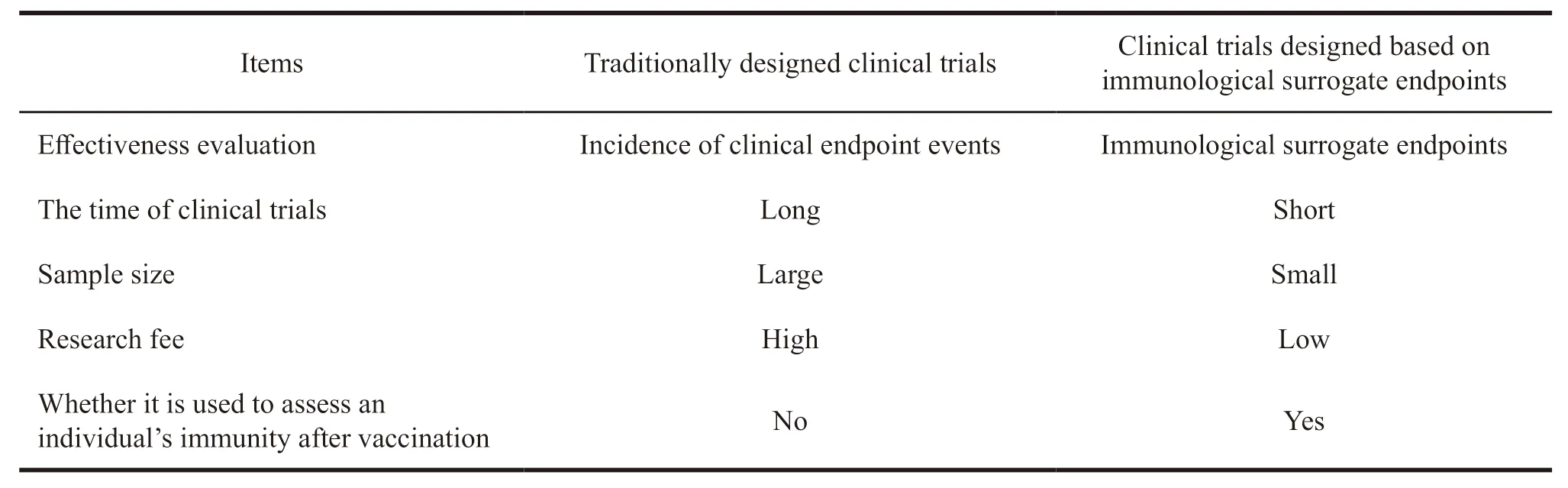

Table 2 Comparison of traditionally designed clinical trials and clinical trials based on immunological surrogate endpoints
2.3.2 The development of immunological surrogate endpoints
In the development of immunological surrogate endpoints,researchers need to determine the factors related to the clinical endpoint according to the data,and then determine the immunological surrogate endpoints with the help of statistical research.
Gilbert et al.[10]determined the immune related factors of the immunological surrogate endpoints,including correlate of risk (CoR),surrogate of protection at validation level 1 (level 1 SoP) and surrogate of protection at validation level 2 (level 2 SoP).SoP is an immune response (including humoral and cellular immunity) that can effectively predict vaccine efficacy to evaluate clinical event endpoints[11]. Table 3 briefly introduces the factors related to immunological protection.
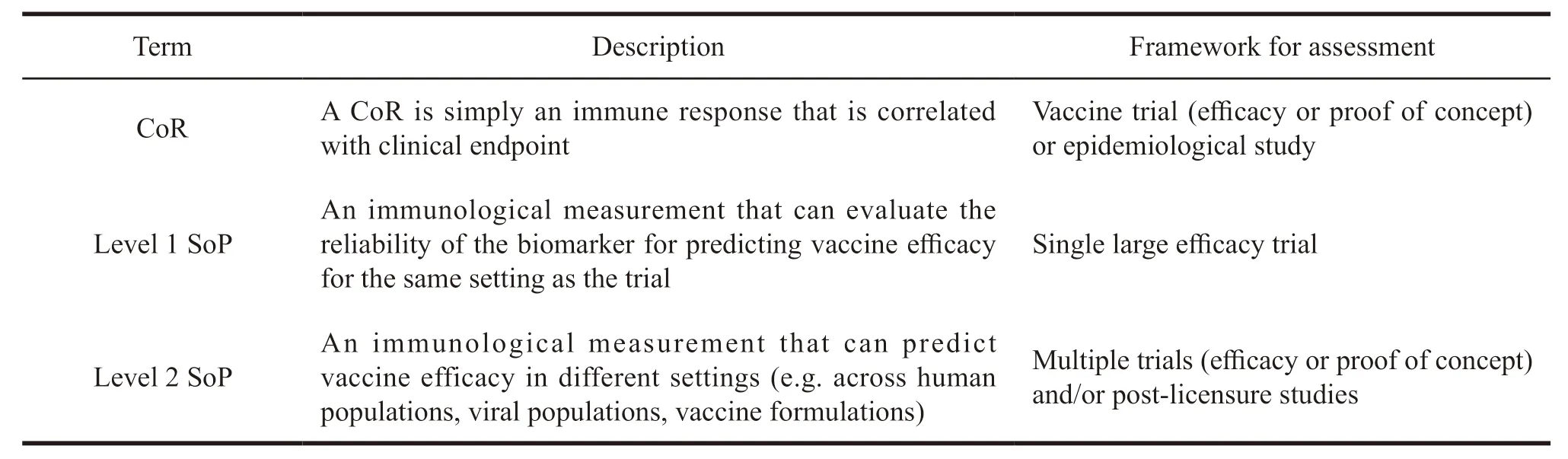
Table 3 Brief introduction of factors related to immunological protection
A CoR is simply an immune response that is correlated with the rate or level of a clinical endpoint.In the epidemiological studies and clinical trials of many diseases,biomarkers are generally regarded as CoRs.After the CoR is determined,the level 1 SoP and then level 2 SoP need to be screened out gradually in statistical methods based on clinical data.The screening step from CoR to level 1 SoP to level 2 SoP is a process that continuously narrows the target range until the final endpoint is determined.
After determining the CoR,there are two statistical methods that can be used to develop and evaluate level 1 SoP.The first,namely the Prentice criteria,was proposed by professor Prentice to evaluate surrogate endpoints for vaccine clinical trials in 1989[12].CoRs conforming to Prentice criteria can be screened as level 1 SoP,and Prentice criteria is the method widely used at present.The Prentice criteria believe the vaccine can effectively prevent the occurrence of clinical endpoints.The CoR is related to the level of vaccination and it is also related to the occurrence of clinical endpoint events.The CoR can fully explain the protective effect of the vaccine on the occurrence of clinical endpoint events[13].The second way is to use vaccine efficacy curve based on clinical data and causal inference to obtain level 1 SoP.
Level 2 SoP was evaluated and screened in different clinical settings and finally determined to be the surrogate endpoint.In this process,the following statistical methods were used,including threshold method,receiver operating characteristic curve method and continuous method.

Fig.1 Development process of immunological surrogate endpoint
2.3.3 Application of immunological surrogate endpoints
Currently,18 immunological surrogate endpoints have been established in the United States.The qualification of immunological surrogate endpoint is still in the initial stage in China.The Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention has developed an immunological surrogate endpoint for EV71 vaccine,which is the first one in China[14].Compared with the use of traditional clinical endpoints,the use of immunological surrogate endpoints for the same vaccines can shorten the time of clinical trial by more than 60% and save more than 80% of the costs[15].
3 Regulations and issues related to optimized design of vaccine clinical trials and immunological surrogate endpoints in China
3.1 The flexibility of clinical trial is not enough,and there is a lack of guidelines for adaptive design of vaccine
At present,there is a lack of relevant guidelines for the adaptive design of vaccines in clinical trials.For example,China’s “Drug Administration Law”and “Vaccine Administration Law” didn’t include the relevant content of adaptive design of clinical trials.On June 3,2016,the former Food and Drug Administration issued the “Biological Guidelines for Drug Clinical Trials”,which were applicable to confirmatory clinical trials of biologics (including vaccines) for the purpose of registration.Besides,it is also significant to exploratory clinical trials and post-marketing clinical trials.The guidelines involve three types of adaptive design in clinical trials:sequential design of groups,recalculation of sample sizes under blind conditions,and enrichment design.But not all types of adaptive design and their related regulations are detailed.
On January 20,2017,the former Food and Drug Administration issued the “Guidelines for General Considerations of Drug Clinical Trials”,which allowed to make clinical trial decisions by phase.It can improve the flexibility of clinical trial to a certain extent.That is,clinical trials are continuous decisionmaking processes.When the clinical trial at every stage is over,the risk assessment should be conducted timely to decide the termination or continuation.The clinical R&D plan should also be adjusted appropriately with the results of the study.Although the guidelines enhance the flexibility and adaptability of clinical trials,they only apply to chemical drugs and therapeutic biologics,not for vaccines.
At present,the adaptive design of clinical trials in China is in its infancy.Enterprises and institutions need to standardize the design of clinical trials and improve its flexibility in accordance with specific guidelines.
3.2 The development capabilities of immunological surrogate endpoint need to be improved
On December 3,2004,the former Food and Drug Administration issued the “Technical Guidelines for Vaccine Clinical Trials”,which stipulated that surrogate endpoints can be used in clinical trials to replace clinical endpoints to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of vaccines.However,the guidelines did not include the development process of surrogate endpoints.On October 8,2017,the General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the General Office of the State Council issued the “Opinions on Deepening the Reform of the Review and Approval System and Encouraging the Innovation of Drugs and Medical Devices” (Tingzi[2017] No.42),which aimed to promote the new drug R&D including vaccines.The guidelines allow scientific research institutions and researchers to apply for clinical trials under the premise of bearing relevant legal responsibilities.And then they can carry out R&D of new drugs and related technology to promote the transfer of scientific and technological achievements.
In the context that the government encourages innovation and clinical research,only the EV71 vaccine has established immunological surrogate endpoint in China due to the difficulty in the development of immunological surrogate endpoints and the time cost.Therefore,the development capability of immunological surrogate endpoints needs to be further improved.
3.3 The qualification of immunological surrogate endpoints and information disclosure procedures should be enhanced
China has not yet established the qualification of immunological surrogate endpoints and information disclosure procedures.As a tool,immunological surrogate endpoints can improve the efficiency of vaccine development and review.As a government platform,the qualification and information disclosure procedures for immunological surrogate endpoints can connect companies,scientific research institutions,and drug regulatory departments.Immunological surrogate endpoints can be further optimized through continuous collection of real-world evidence related to the research and application of immunological surrogate endpoints.
4 Suggestions on optimizing the design of vaccine clinical trials based on immunological surrogate endpoints in China
4.1 Establishing adaptive design guidelines for clinical trial designs
It is recommended that drug regulatory agencies should issue relevant guidelines for the adaptive design of biologics such as vaccines as soon as possible.The adoption of adaptive clinical trial designs must be encouraged for vaccines that are needed for prevention.Meanwhile,immunological surrogate endpoints should be introduced to accelerate the development and marketing of vaccines.Besides,post-market monitoring and evaluation of the use of surrogate endpoint vaccines should be strengthened to control the risk.
4.2 Encouraging the development of immunological surrogate endpoints
The development of immunological surrogate endpoints is difficult due to the complex immune response and the diversity of individual immune protection effects.It is suggested that the comprehensive guidelines should be formulated to promote the understanding of immunological surrogate endpoints by the industry,medical research institutes to facilitate their development and application[16].As different vaccines will encounter different problems during the research process,drug administration departments should communicate actively with stakeholders to help them get more guidance.At the same time,it is recommended to continuously optimize the existing surrogate endpoints through clinical research,improve the development level of immunological surrogate endpoints,and promote the development of vaccine clinical research.
4.3 Establishing R&D qualification and information disclosure procedures to improve efficiency
The application of immunological surrogate endpoints should be based on regulations.It is recommended to formulate a procedure for the qualification of R&D in the “Implementation Regulations of the Drug Administration Law”to ensure the legality and rationality of the use of surrogate endpoints.In order to promote the application and development of immunological surrogate endpoints in the field of vaccine R&D,it is recommended to regularly disclose surrogate endpoint information.The qualification and information disclosure procedures can avoid repeated research and save resources.By publishing the development results of immunological surrogate endpoints,it can promote the optimization and upgrade of existing surrogate endpoints,realize positive interactions,and improve the efficiency of vaccine R&D.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Research on the Construction of Pharmacy Organization and the Development of Pharmaceutical Services in China’s Primary Medical and Health Institutions— Based on the Survey of 5 Provinces
- DRG Payment System in the United States and Its Enlightenment to China
- Research on the World’s Most Valuable Antihypertensive Drugs Based on Patent Analysis
- Literature Review on the Development of New Drugs Based on TRIZ
- Research on the Relationship between Export Orientation and R&D lnvestment of China’s Pharmaceutical lndustry in Different Regions
- SWOT Analysis and Countermeasures Study on TCM Industry in Hainan Free Trade Port

