Analysis of the Influence of the Self-efficacy of College Students on Their Response Behaviors Toward COVID-19
Ju-Hua Liu,Yan-Ni Mao,Yu He,Pei-Pei Bai,Jing Ouyang,2,Jing Zhang,2,*
1School of Humanities Management,Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine,Xianyang,China;2The New Style Think Tank of Shaanxi Universities:‘The Belt and Road’Research Center for Health Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Xianyang,China.
Abstract
Objective:This study aims to investigate the self-efficacy of college students during the Coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19)pandemic and to conduct an empirical analysis on its influence mechanism on decision-making and coping skills to provide reference for decision support to improve the coping behavior of college students during public health emergencies.
Methods:The study recruited a total of 1,346 college students in Shaanxi.Data were collected via a questionnaire and analyzed using SPSS 22.0 and AMOS 22.0.
Result:The self-efficacy of the college students exerted a significantly positive impact on their coping decisions(β=0.754)and coping skills(β=0.822)during the COVID-19 pandemic.Both passed the significance test at a 99.9% confidence interval(99%CI).
Conclusion:During the COVID-19 pandemic,improving the self-efficacy of college students can significantly positively influence their coping behaviors.Therefore,providing effective interventions that target the self-efficacy of college students and encouraging them to adopt positive coping behaviors is necessary.
Keywords:COVID-19,Self-efficacy,Coping decisions,Coping skills,Structural equation model
Background
At the end of December 2019,a case of unexplained pneumonia was recorded in Wuhan,China,which attracted the attention of health authorities.The case was later confirmed as an infection caused by a novel coronavirus whose resultant disease was named coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19)[1].On January 30,2020,the World Health Organization(WHO)announced that COVID-19 was listed as a public health emergency of international concern whose causative virus,SARS-CoV-2,was more contagious than SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV [2-3].The COVID-19 outbreak became a global pandemic,as announced by the WHO on March 11.Studies at home and abroad demonstrated that people undergo psychological panic in the face of major public health emergencies,where self-efficacy and coping behavior are two important factors that play a role in mental health.Specifically,they exert an intermediary effect on the process of psychological hyperactivity[4-6].As one of the important concepts of social cognitive theory,self-efficacy refers to the degree of confidence to which people use their skills to complete a task[7].In other words,when faced with specific tasks,self-efficacy determines whether people believe in themselves or the extent to which they believe that they possess the sufficient ability to complete a task[8].After the concept of self-efficacy was put forward,scholars conducted various studies on the correlation between self-efficacy and coping behavior.Results from a large body of research presented a common direction,that is,individuals with high levels of self-efficacy exhibit a positive attitude in addressing sudden stressful events and tend to address these events effectively.Devonport et al.[9]confirmed that positive coping behaviors are related to high levels of self-efficacy and high scores in examinations.The authors conducted a research on college students majoring in physical education and confirmed the significant positive correlation between high levels of self-efficacy and positive coping behaviors[10].In a study on undergraduate nursing students,Jiang[11]found a close relationship between general self-efficacy and coping style with significant differences in this relationship by year level.Moreover,Lu[12]proposed significant differences in regional coping styles according to the locations of schools.The authors examined general self-efficacy,coping style,and the relationship between them.The results pointed to an extremely significant positive correlation between the self-efficacy of students with problem-solving and help-seeking as coping styles.Moreover,self-efficacy was significantly negatively correlated with patience,withdrawal,and venting.The results indicated that self-efficacy in students could predict the coping style adopted.In addition,the study found that an improvement in self-efficacy improves the students’ability to cope with public health emergencies.When engaged in complex activities,people with high levels of self-efficacy can conduct a strategic analysis of problems and search for the best solutions, whereas those with low levels of self-efficacy may experience difficulty in adopting suitable strategies to solve problems,which leads to repetitive ineffectiveness[7].In summary,although the literature presents extensive and in-depth discussions on the relationship between self-efficacy and coping behavior,studies that focused on public health emergencies remain lacking.Specifically,no study was conducted on the influence of the self-efficacy of college students on coping behaviors toward the COVID-19 pandemic.As a key group in the process of prevention and control during epidemics, the psychological vulnerability of college students is undeniable.Thus, this study investigates the self-efficacy of college students,especially during the COVID-19 pandemic,and conducts an empirical analysis on the influence of self-efficacy on their coping decisions and skills.In this manner,decision support can be provided to improve their coping behaviors during public health emergencies.
Self-efficacy is the intermediary between cognition and behavior,the decisive factor of individual behavior,and a prerequisite for whether an individual actively participates in an activity[13].The construct is widely used in the field of health to predict and analyze health behaviors,that is,one’s belief in one’s ability to control environmental events that influence health.Coping behavior refers to behaviors adopted by individuals in stressful environments and events[14].This study mainly refers to the self-coping behaviors of college students in the face of public health emergencies,and whether they possess certain coping skills during the COVID-19 pandemic.Self-efficacy is characterized by two dimensions,namely,coping decisions and coping skills.During the COVID-19 pandemic,improving the sense of self-efficacy of college students is considered crucial to improve their coping decisions and coping skills in relation to the prevention and control of the pandemic.Self-efficacy meets different situational needs through the belief that one possesses the ability to mobilize cognitive resources and behaviors[15],which reflects the belief or confidence needed by individuals to achieve a particular behavior or goal.Moreover,self-efficacy is the basis of individual initiative[16].Specifically,this paper embodies the belief of the self-efficacy of college students in relation to their ability to ensure personal protection during prevention and control efforts related to COVID-19.Self-efficacy influences thoughts and choices,which,in turn,influence decisions and skills.Therefore,this study puts forward two research hypotheses.
H1: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the self-efficacy of college students exerts a significantly positive impact on their coping decisions.
H2: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the self-efficacy of college students exerts a significant positively impact on their coping skills.
Data and methods
Object of the study
Data for this study were collected via a questionnaire survey.Using stratified cluster sampling,the study conducted a survey on colleges and universities(including medical and non-medical colleges)in Shaanxi province.Two trainers for the survey were selected from each university to conduct online training before the survey and to share a link to the questionnaire on the social networking sites of their universities.The questionnaire was disseminated in a random manner,and filling out with instructions.Participation was voluntarily,and the respondents provided written consent.The Medical Ethics Committee of Jining Medical College(JNMC-2020-KY-001)approved the study.The survey lasted for one week from February 25 to March 2,2020,with a total of 1,346 questionnaires distributed.After screening,68 questionnaires with missing key information,contradictory answers,and obvious regular answers were excluded due to the normative requirements of the questionnaire.A total of 1,278 questionnaires were recovered for a response rate of 94.95%.
Questionnaire design
The questionnaire consists of two parts.The first collects the basic information of college students(i.e.,gender,nationality,type of hukou,grade,and major).The second focuses on self-efficacy,coping decisions,and coping skills with a total of eight questions.The items are rated using a five-point Likert-type scale(1=Extremely Inconsistent;5=Extremely Consistent).College students tend to make consistent choices according to their recent psychological feelings.Thus,the higher the score,higher is the degree of compliance.Table 1 presents the variables and their definitions.
Statistical methods
SPSS 20.0 was used for data input and management and statistical analysis.Furthermore,Amos 22 was used to construct a theoretical model,whereas a structural equation was used for analysis.
Results
The structural equation model was used to estimate the influence of the self-efficacy of college students on coping behaviors toward COVID-19.Given the parameter estimation method,the maximum likelihood estimation(MLE)distribution is an asymptotic normal distribution that is unbiased,consistent,and an asymptotically effective estimation method.Furthermore,it displays scale invariance.Therefore,the study selected the MLE method for parameter estimation and for the path analysis of the structural equation model.Harman’s single-factor test was used to conduct principal component analysis.When the principal component is not rotated,the contribution rate of the first principal component is 28.640%,which is less than 40%.This rate indicates the absence of a serious common method deviation in the survey.
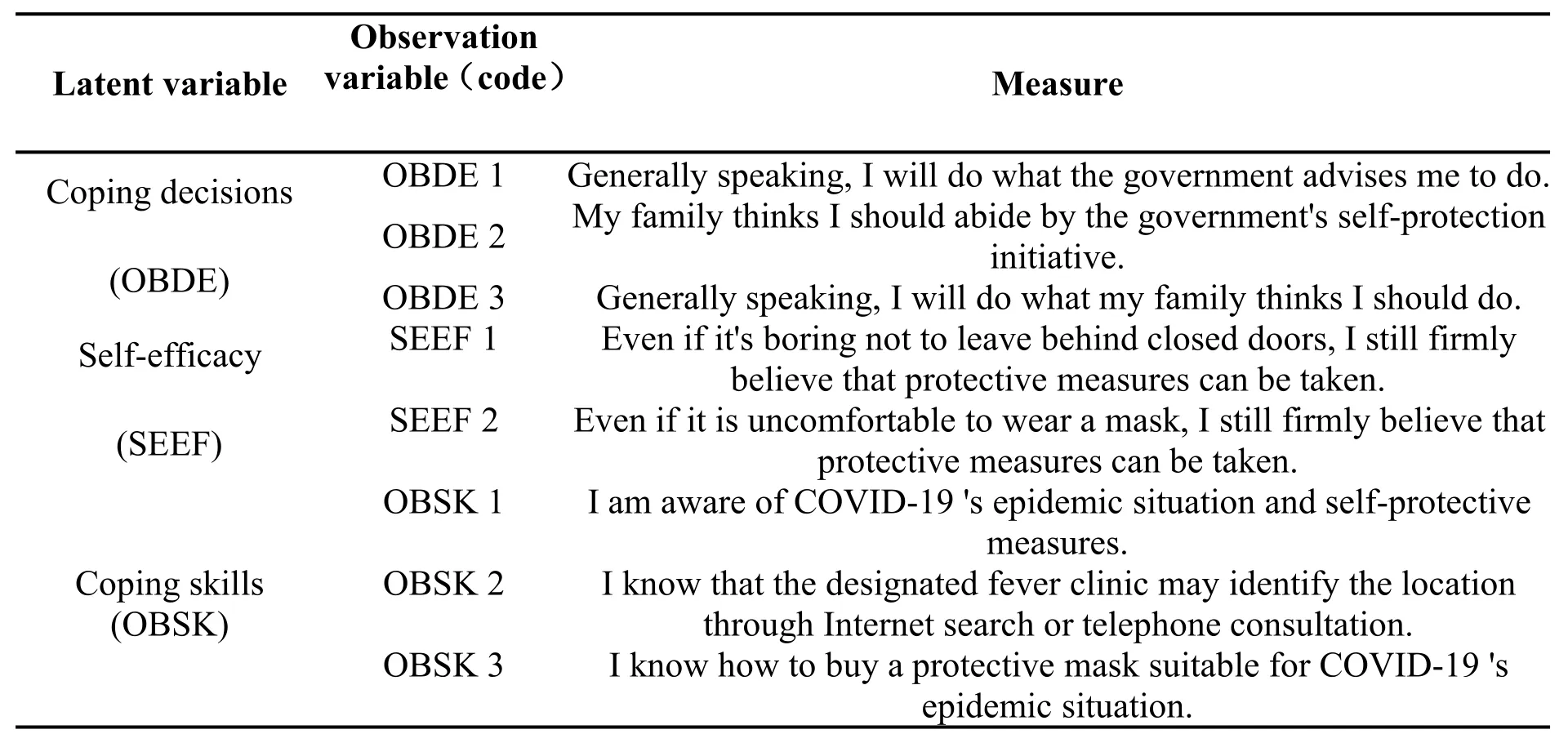
Table 1 Meaning and measure of variables
Correlation analysis of the measured variables
Table 2 presents Pearson’s correlation coefficients,which mainly reflects the correlation among variables.The results indicated a significantly positive correlation between self-efficacy and coping skills(r=0.672,P<0.001)and between self-efficacy and coping skills(r=0.801,P<0.001).No conflict with the research hypothesis was observed,which proved that the hypothesis was reliable.
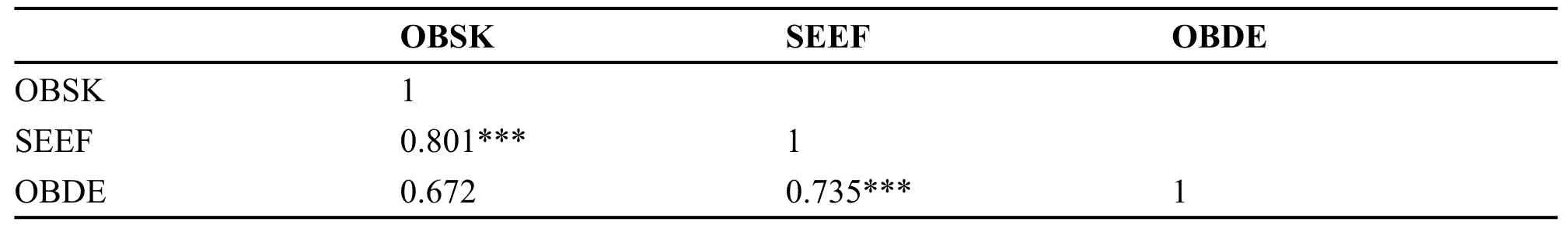
Table 2 The correlation matrix for variables
Reliability test of the measurement model
To measure the reliability of the results,that is,whether the interviewees honestly answered the items of the scale,SPSS 22.0 was used to analyze the internal consistency reliability of the sample data.In general,a Cronbach's α coefficient of more than 0.8 indicates that the reliability of the scale is very good.The results demonstrate that the Cronbach's α coefficients of the total table and each latent variable are above 0.80(Table 3),which indicates that the reliability of the questionnaire is very good.Therefore,the results are very reliable.
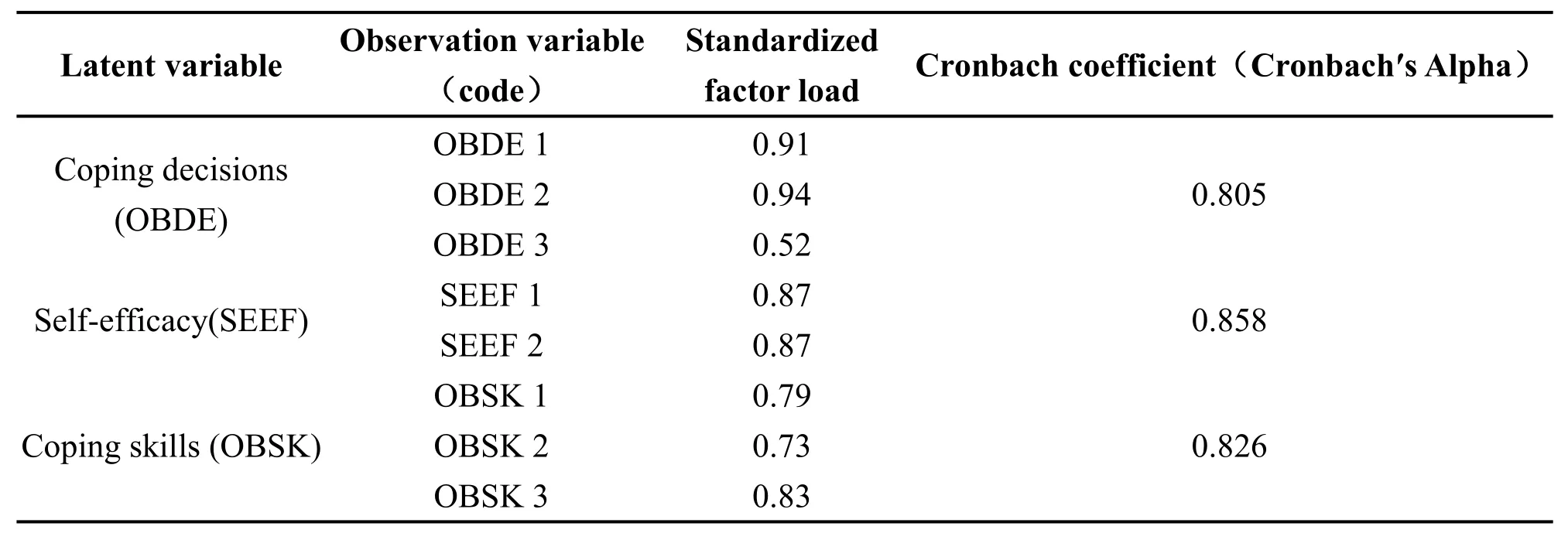
Table 3 Reliability test of self-efficacy,coping decisions and coping skills
Validity test of the measurement model
To test the effectiveness of the measurement tool,that is,whether the scale indeed measured the target it wants to measure,the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin(KMO)value and Bartlett’s sphericity test were used to verify the sample data.The results produced a KMO value of 0.5%,whereas P-value of 870 Bartlett sphericity test is less than 0.001(Table 4).This finding indicates that the correlation between variables is high,whereas the degree of validity is good.Thus,the study can proceed to the next step of structural equation model identification.
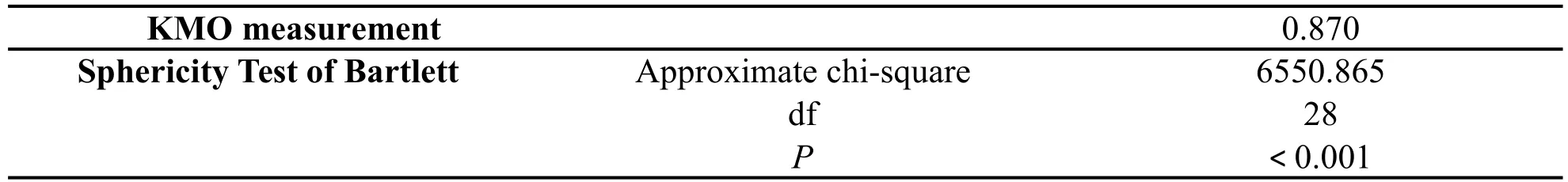
Table 4 Inspection of Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin(KMO)and Bartlett
Evaluation of the goodness-of-fit of the structural model
The goodness-of-fit test of the structural equation model is generally tested using two indexes,namely,absolute and value-added fit indexes.The higher the degree of the fit of the model,the higher the availability of the model,and the more the parameter estimation bears meaning.The fitness index mainly adopts the Chi-square degree of freedom ratio(χ2/df),root mean square error of approximation(RMSEA)under the absolute fitness index,whereas the goodness-of-fit index(GFI),adjusted goodness-of-fit index,comparative fit index(CFI),normed fit index,and increasing fitness degree are under the value-added fitness index.The fitness criteria or critical values of these indicators refer to the recommendation of Wu[17].
Table 5 presents the estimated values and reference standards of the model fitness indicators.The results demonstrate that the overall fitting index of the structural equation model is good(χ2/df=2.535,GFI=0.993,CFI=0.997,RMSEA=0.034).The fitness indexes basically reached the critical standards,which indicates that the model fit the data well and that the goodness-of-fit of the model is acceptable.The results illustrate that the theoretical model constructed by this study fits the actual data well and can be further tested.Given the estimation operation of the model,figure 1 provides a detailed path analysis,whereas table 6 displays the detailed parameter estimation and the test results of the hypotheses.The self-efficacy of college students exerted a significantly positive impact on their response to COVID-19 in terms of coping decisions(β=0.754,P<0.001)and passed the significance test at 99%CI.Therefore,the results supported H1.Moreover,the self-efficacy of college students exerted a significantly positive impact on their response to the COVID-19 pandemic in terms of coping skills(β=0.822,P<0.001)and passed the significance test at 99%CI.As such,the results also supported H2.
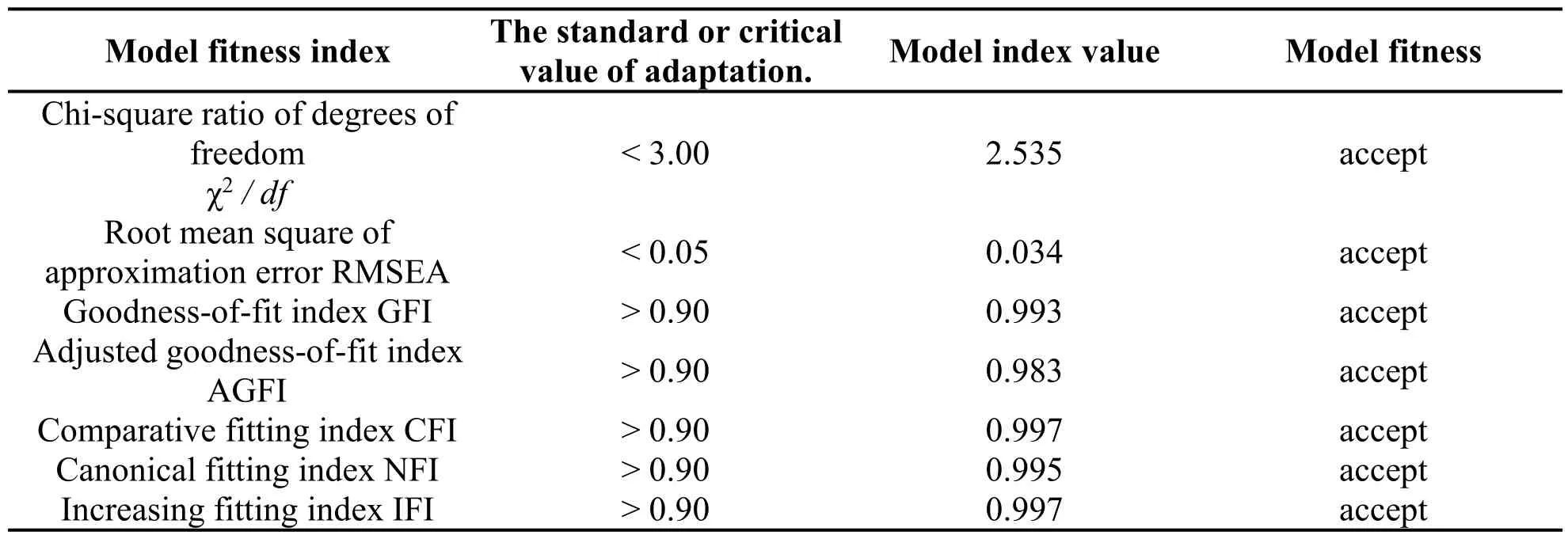
Table 5 Goodness-of-fit index of structural equation model
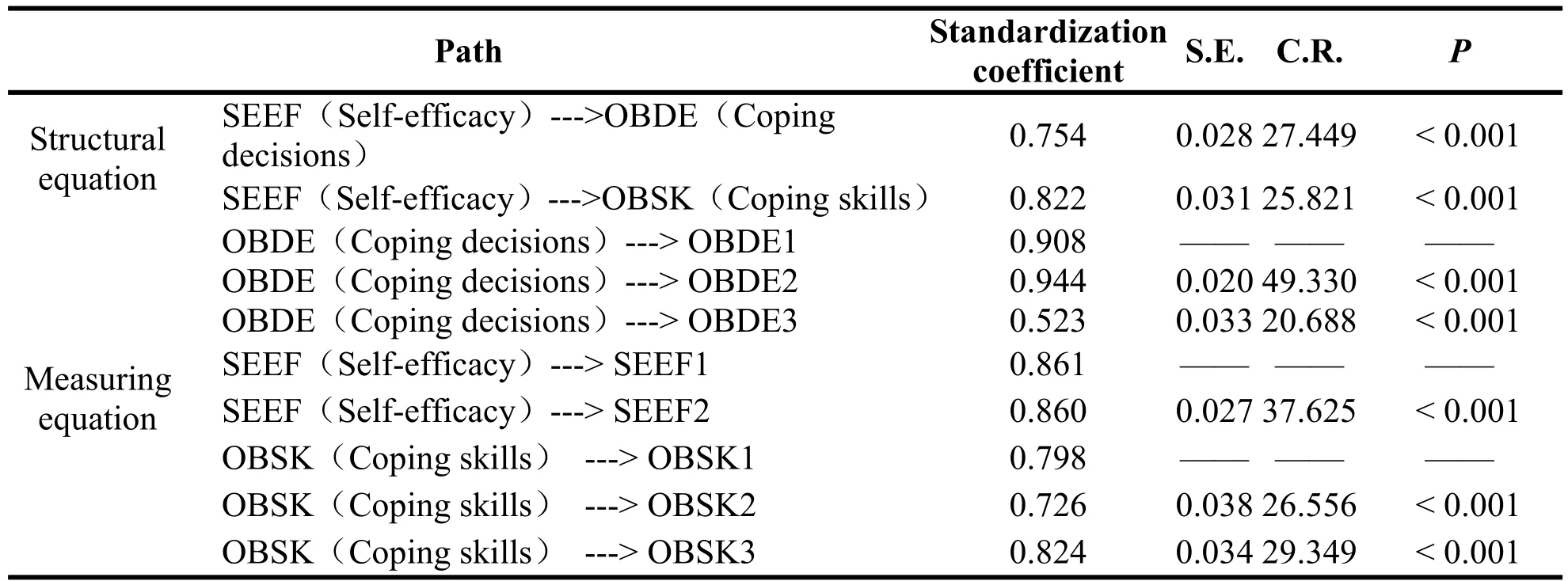
Table 6 Path coefficient and hypothesis test results
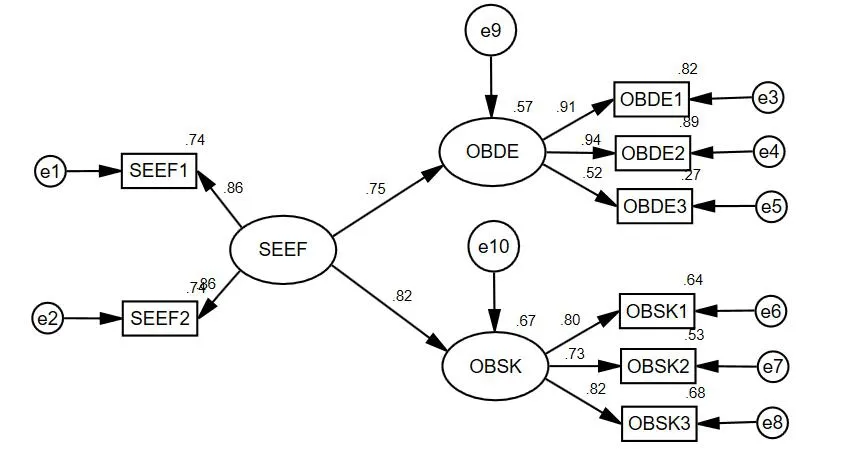
Figure 1 The path of the influence of college students' self-efficacy on COVID-19's epidemic coping behavior
Discussion
This study considers the influence of the self-efficacy of college students on their response to the COVID-19 pandemic in terms of coping decisions and skills.The study establishes a structural equation model and verifies the data.The results demonstrate that the self-efficacy of college students exerted a significantly positive impact on their coping decisions(β=0.754)and skills(β=0.822).Both variables passed the significance test(99.9%CI).This result is consistent with those of relevant studies.Many studies argued that the general self-efficacy of college students is positively and negatively correlated with positive and negative coping styles,respectively.Thus,improving general self-efficacy among this group will contribute to their positive coping styles[18].Yi et al.[19]conducted an empirical study on the correlation between general self-efficacy and the coping style of the elderly in nursing homes in Guangzhou of China.The authors found that the general self-efficacy of the subjects is positively correlated with problem-solving and help-seeking,which is consistent with the results of the current study.Therefore,self-efficacy is an important factor of coping style.By cultivating and improving the self-efficacy of college students,good coping decisions and skills in the face of public health emergencies can be promoted.However,how to improve the self-efficacy of college students is a very important topic,such that numerous studies have been conducted in the relevant literature.
The majority of the results have been obtained through social practice[20],attribution training[21],group counseling[22-23],cognitive reconstruction,and computer-aided systems[24].First,to encourage the participation of college students in the social practice of addressing public health emergencies,they should be immersed in community epidemic prevention and control on the premise of professional knowledge and protection.To accumulate practical experience in dealing with public health emergencies,successful practical experiences will provide students with knowledge and belief in their ability,which could improve their sense of self-efficacy.Second,students should be guided about correct attribution.Weiner's attribution theory holds that people mainly tend to explain the results of their behavior from two dimensions and four aspects,namely,internal and external and controllable and uncontrollable[25].Studies at home and abroad have demonstrated that the non-use of attribution directly influences not only one’s judgment about self-efficacy but also coping behavior[26-27].Therefore,college teachers should guide college students in making internal controllable attribution when they encounter pressure and problems.This strategy is helpful for students in controlling their emotions and actively preparing for epidemics.Third,colleges and universities can establish an online self-protection training system for college students as a form of group counseling that targets epidemic prevention.Counseling can be conducted in a timely,efficient,and strict manner via online teaching,instructional videos,and prevention and control guidance.During the COVID-19 pandemic,online self-training can not only overcome the limitations of traditional teaching in terms of the number of attendees,but also enhance the role of teaching resources.In this manner,the ability and confidence of college students in dealing with public health emergencies and their coping skills in response to the pandemic can be improved.Fourth,the supervision of public opinion related to the pandemic can be reinforced through cognitive reconstruction and computer-aided systems.During the pandemic,access to relevant information among college students is mainly derived from the network media[28].However,its quality is unstable and with several shortcomings in the accuracy and scientific nature of the information transmitted.Through the supervision of public opinion related to the epidemic,the government can improve the quality of relevant network information to ensure the accuracy and access to relevant information.Furthermore,the government can actively use public opinion management to improve the self-efficacy of college students and enhance the quality of their coping decisions.
Conclusion
During the COVID-19pandemic,improving the self-efficacy of college students can significantly positively influence their coping behavior.Thus,providing effective intervention is necessary to encourage them to adopt positive coping behaviors,which can improve their coping decisions and skills.
 Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch2021年4期
Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch2021年4期
- Psychosomatic Medicine Resesrch的其它文章
- Advances in the Pathogenesis of Vascular Cognitive Impairment
- A Commentary of the Queer People of Color Identity Affirmation Scale for Positive Attitudes
- Left Temporal Lobe Arachnoid Cyst Presenting with Symptoms of Psychosis
- Intervention Study on Hypnotherapy of Primary Dysmenorrhea in Female College Students
- An Assessment of the Relationship Between Mizaj and Happiness in College Students During and After Complete Lockdown
