An Investigation on College Students’U-campus Learning under OBE
——Taking Minjiang University as an Example
School of Foreign Languages,Minjiang University,Fuzhou,China Email:279348910@qq.com
[Abstract]OBE advocates utilizing students’previous successful learning to promote further successful learning.To assist college English learning,U-campus learning is widely adopted.This paper investigates the use of U-campus learning by non-English major undergraduates and finds that the degree of students’interest in English significantly influences the overall recognition of U-campus learning; there is greater recognition of U-campus learning among students with higher English proficiency;there is low recognition in reading practice and convenience of U-campus.It is suggested that U-campus platform should be adjusted and improved incessantly,taking into account the practicality and interest to meet the needs of students of different levels,so as to be widely accepted by users and to realize the favorable outcome under OBE.
[Keywords]OBE;U-campus learning;interest;English proficiency
Introduction
“Outcome Based Education”(OBE),first proposed by Spady in 1981,is an educational philosophy oriented to students’learning outcomes,focusing and organizing everything in an educational system around what is essential for all students to be able to do successfully at the end of their learning experiences(Spady,1994,p.1).Since then,the global education community has begun to discuss and practice it extensively.OBE can be summed up as“resultsorientated thinking”and is the opposite of“input-based education”where the emphasis is on the educational process and where we are happy to accept whatever is the result(Harden,Crosby & Davis,1999).The“outcome”in OBE is a collection of students’learning results,covering different modules such as knowledge,skills,emotions and attitudes,and it is generated top-down from the school-level to the specific learning results in class(Shen & Shen,2018).OBE takes goal realization as its guiding direction,and pays attention to how to design teaching and how to measure in order to realize the goal.It has three basic premises:All students can learn and succeed,but not on the same day in the same way.Successful learning promotes even more successful learning.Schools control the conditions that directly affect successful school learning(Spady,1994,p.10).In terms of classroom design,its model is to determine the expected classroom teaching results;design teaching activities;design a reasonable evaluation system;and formulate evaluation criteria(Chen&Yin,2011).
Under the guidance of OBE,in order to promote students’English learning,numerous universities began to apply various platforms to assist English teaching,among which is U-campus online English learning platform(U-campus),presented by“Unipus”of Foreign Language Teaching and Research Press,which aims to provide a one-stop foreign language teaching solution with blended teaching,including teaching,learning,evaluating,testing,and researching in colleges and universities.When setting course learning,homework and tests,teachers can preset the minimum standard for students to reach,the method of recording scores and the learning duration,so that students can learn and practice anytime and anywhere independently according to their own situation and the instant results shown on the platform to achieve satisfactory results.Meanwhile,teachers can check on students’learning through the teacher terminal at any time,remind and supervise students to study independently after class,and find common problems of students in time to discuss,explain,and solve in class to promote learning and teaching.U-campus is in line with the focus of outcome in OBE in theory,but in reality,students’recognition of U-campus learning differs a lot,and students’recognition of different items is also different,which call for a related investigation.
Investigation
Research Questions
How is U-campus learning recognized among different types of students?
What factors affect students'recognition of U-campus learning?
How are different items on U-campus recognized by students?
Research Tools
The questionnaire of this investigation is composed of three parts.The first part is basic personal information about the subject,including gender,level of the English class(Class A or Class B),and degree of interest in English.The second part is a survey of 6 items of the recognition of U campus,including the recognition of course learning,listening practice,speaking practice,reading practice,learning effect,and convenience.The questions of the first two parts are multiple choices and the answers are rated on a Linkert rank-type five-point scale except gender and level of the English class.The third part is other information about U-campus learning including the way often used(mobile phone or computer)and whether the tasks are often forgotten(yes or no)and students’optional opinions or suggestions about U-campus learning in writing word.A total of 665 valid questionnaires are collected and SPSS20 is used for data analysis.
Research Subject
The research subject of this article is the non-English major sophomores who have conducted U-campus learning for one year in Minjiang College.There are 665 students in total,including 238 males and 427 females from various majors so they are widely representative.
Research Results
First,reliability analysis.The reliability of the research data is of high quality(α =0.906); second,the validity analysis shows that the commonness value corresponding to the research items is higher than 0.4,indicating that the research item information can be effectively extracted.In addition,the KMO value is 0.894,which means that the data is valid; afterwards,a factor analysis is processed to extract a factor that is the overall recognition of U-campus learning.
Difference measurement
In order to explore whether there are significant differences of the 7 items of U-campus learning among subjects of different class levels,genders,and interest degrees,relevant data has been processed.
Differences among subjects of different class levels
Through non-parametric T test,it is found that there exist differences among subjects of different class levels in 5 items,including recognition of course learning,listening practice,oral practice,learning effect,and overall recognition but not in the recognition of reading practice and convenience,as shown in Table 1.
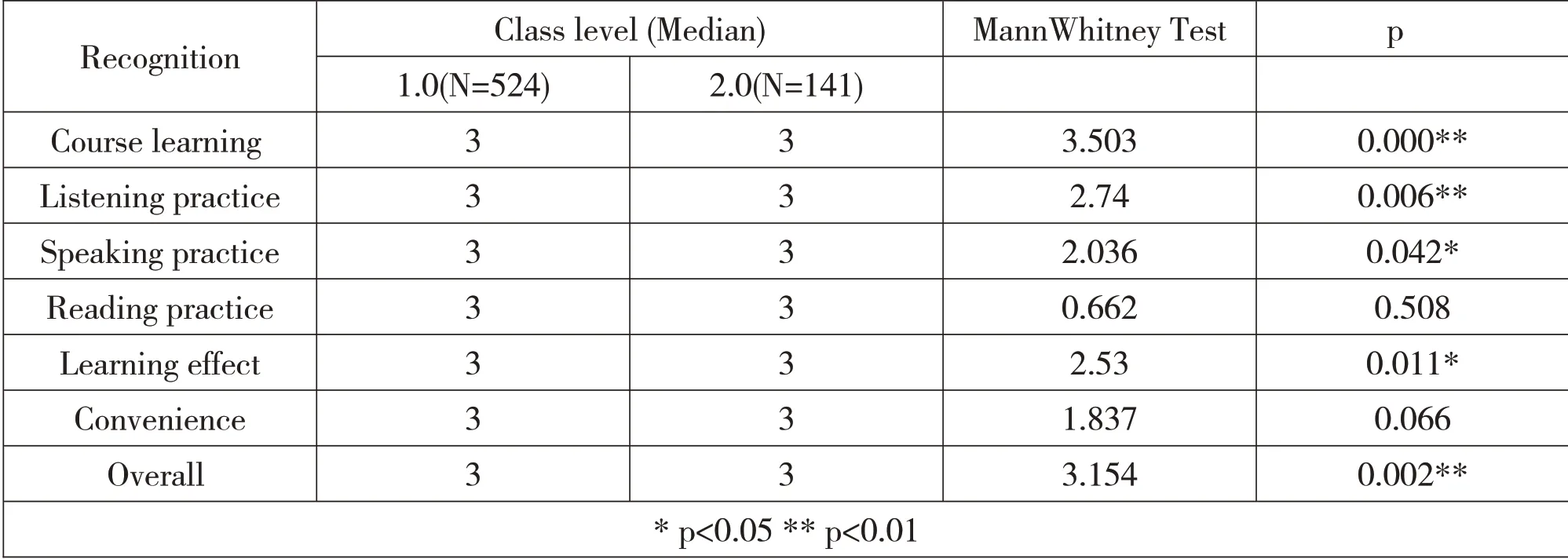
Table 1.Result of non-parametric T test
Differences among subjects of different genders
Through non-parametric T test,it is found there exists a significant difference among subjects of different genders in the recognition of course learning on U campus,as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.Non-parametric T test
Differences among subjects of different degrees of interest
Through analysis of variance,it is found that there exist significant differences among subjects of different levels of interest in English in all the 7 items,including the recognition of course learning,listening practice,course learning,reading practice,speaking practice,learning effect,convenience,and overall recognition,as shown in Table 3.
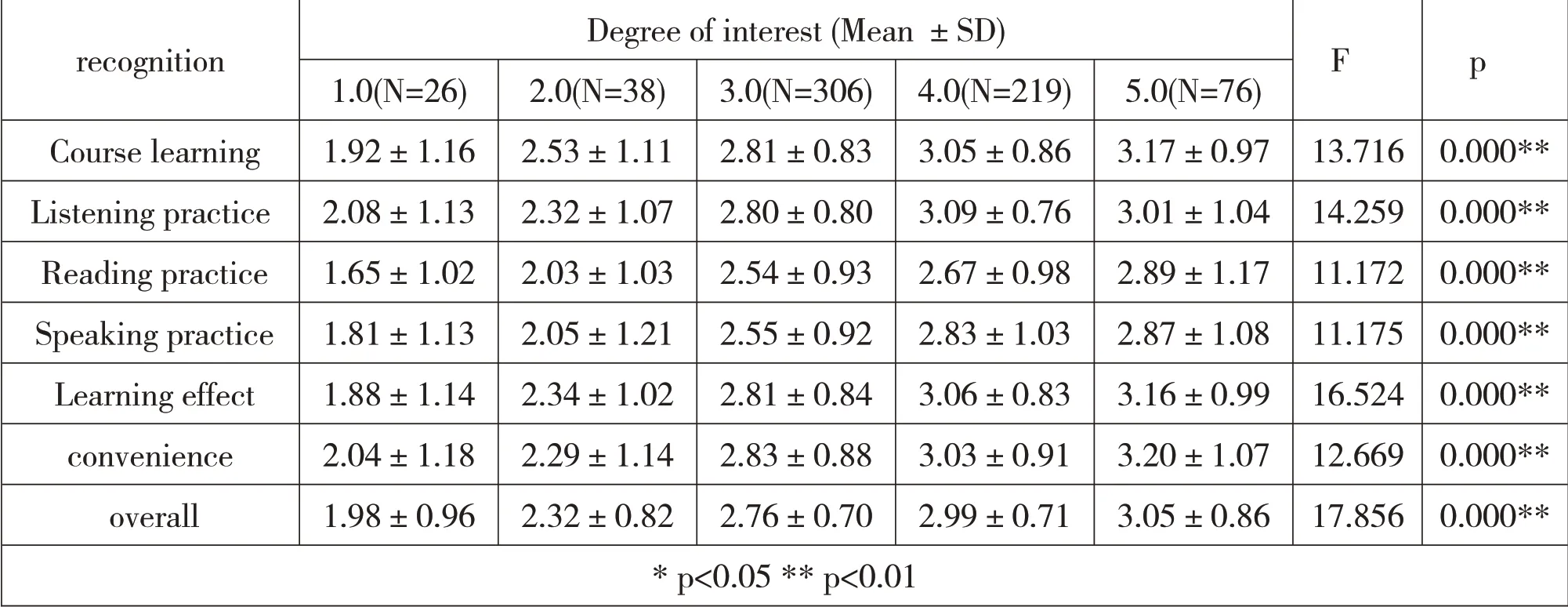
Table 3.Variance analysis
Correlation analysis
In order to further study whether the 3 items showing significant differences above are related to U-campus learning items,a correlation analysis is carried out,and it is found that there exist significant positive correlations between the gender difference and the recognition of course learning,between the class level and the five items including recognition of course learning,listening practice,speaking practice,learning effect and overall recognition,and between the interest degree and all of the seven items,as shown in Table 4.
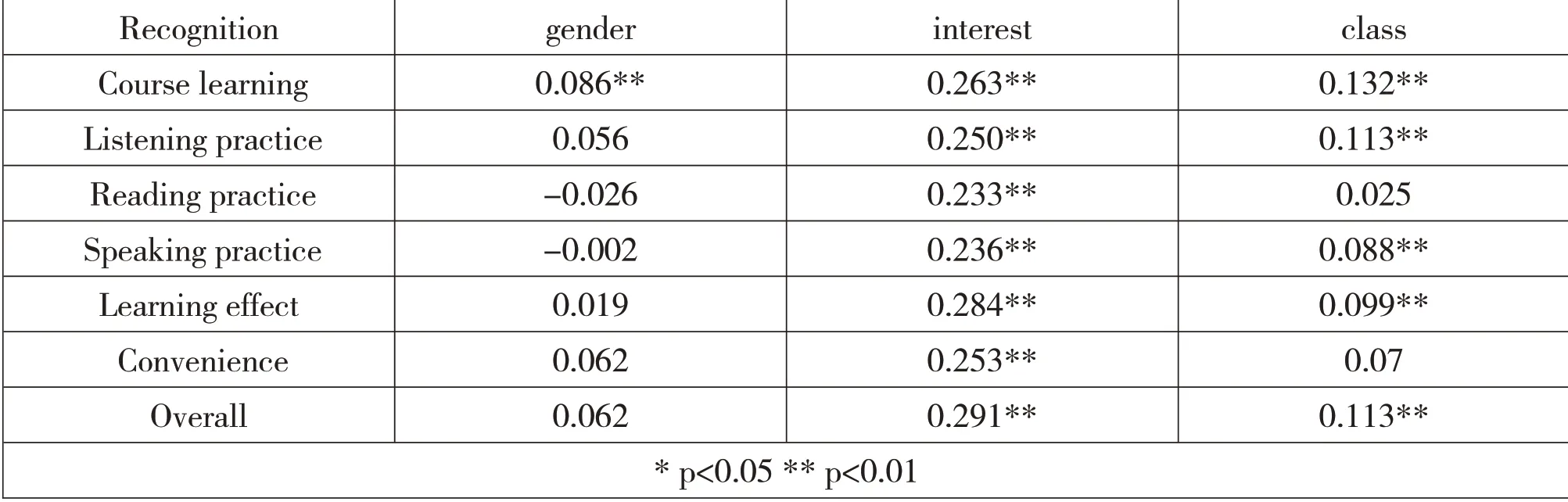
Table 4.Pearson correlation analysis
Regression analysis
In order to further explore whether different interest degrees and class levels have an impact on the overall recognition of U campus learning,linear regression analysis is processed with the interest degree and English class level as independent variables,and the overall recognition of U campus learning as the dependent variable.It is shown that the degree of interest has a significant positive impact on the overall recognition of U campus(R²=0.084,F=20.274,P<0.01),but the English class level doesn’t have a significant influence on the overall acceptance of U campus,as shown in Table 5.
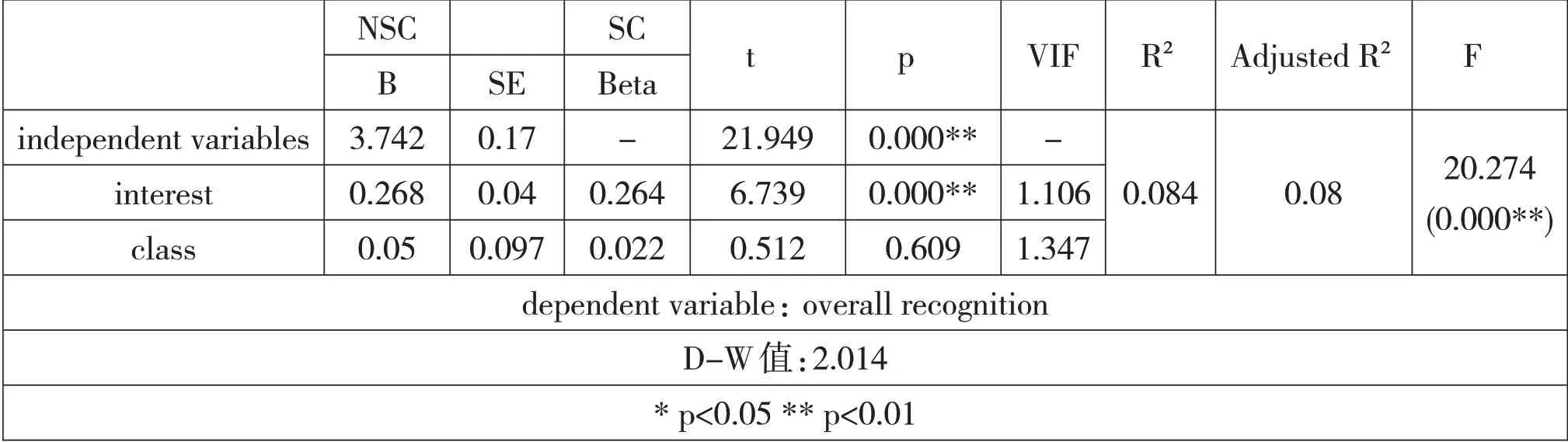
Table 5.linear regression analysis
Discussion
Above all,it is found in the investigation that the degree of subjects’interest in English significantly affects the overall recognition of U-campus learning.Whether students are interested in English has a significant impact on their autonomous learning on U-campus.However,it is found in the investigation that the subjects who are interested in English only account for 44.36%of the total subjects.Among them,66.8%of the subjects from Class A and only 37.97%of the subjects from Class B are interested in English.The subjects who are not interested in English account for up to 62.03%in Class B.In addition to teachers’efforts to promote students’interest in English learning,how to increasing students'interest in U-campus learning is an important issue that the platform needs to consider.It is proposed that the platform should provide attractive and practical learning materials,including more audio and video materials,as well as more extracurricular knowledge items,to expand the richness and practicality of U-campus learning so as to increase students'interest in it.
Secondly,it is also found that the level of the English class is positively correlated with five items of recognition of U-campus learning,including the recognition of course learning,listening practice,speaking practice,learning effect and overall recognition.Subjects from class A,with higher English proficiency,accept U-campus learning better.This is consistent with the results of a study conducted by Fan and Guan who find in oral English teaching under OBE the students with high English proficiency are more willing to improve through autonomous learning(Fan & Guan,2017).It is also found that there is lower acceptance of U-Campus learning in Class B,because subjects with limited English proficiency believe that a large majority of tasks on U campus are too difficult,plus they don’t have the right to choose the compulsory items personally,so they can’t experience success even with much effort.Since U-campus tasks can only be assigned to the whole class but not to individuals,while the gap in English proficiency among students in Class B is relatively large,it is recommended that with more tasks of different levels,U-campus platform should improve the function of the platform to provide students with some independent options so that students with low English proficiency can gradually experience the success model advocated by the OBE,utilizing previous success to promote ultimate success(Xia&Fang,2011).
In addition,it is found that female subjects have higher recognition of course learning on U-campus,which is a necessary supplement to in-class text learning,therefore,it is suggested that teachers should encourage and supervise male students to place more emphasis on course learning to strengthen the foundation of their English.Furthermore,with 91.71%of the subjects using U-campus on mobile phones,only 22.86%of the subjects recognize the convenience of U- campus learning,so it is highly recommended that the design and stability of the U- campus should be updated and strengthened to be more convenient for users on mobile phones.What’s more,it is found that the recognition of reading practice is the lowest with 85.56%of the subjects disapproving of the convenience and efficiency of it,partly because most students use U-campus on mobile phones,and partly because most students have been accustomed to doing reading practice in paper.Teachers may suggest that students should complete more reading practice by computer but not by mobile phone,so that students can become more used to on-line reading practice.Apart from those,39.7% of the subjects often forget to complete U-campus tasks before deadlines,so it is advised that the platform should remind users for task submission in a more apparent way.
In short,OBE advocates product should define process(Harden,Crosby&Davis,1999),utilizing students'successful learning experience to promote further successful learning(Xia&Fang,2011).How to build appropriate evaluation system which will encourage students’success output is also a crucial issue under OBE.The operating method of OBE is to allow students to improve step by step to achieve peak results,and to measure the value-added"outcomes" formed at each stage(Shen & Shen,2018).If students with low English proficiency can’t achieve expected outcome gradually from U-campus learning,which is one of the most important tools of students’autonomous learning,they will not experience the outcome of improvement,which is the last result any educator wishes to see and which also goes against the principles of OBE.U-campus platform can be an advisable tool for English teaching and learning only if it is incessantly adjusted to meet the interests and needs of students of different levels so as to realize the functions of tasks under OBE,that is all students can experience successful English learning step by step so as to achieve ultimate successful learning in future.
 Proceedings of Northeast Asia International Symposium on Linguistics,Literature and Teaching2020年0期
Proceedings of Northeast Asia International Symposium on Linguistics,Literature and Teaching2020年0期
- Proceedings of Northeast Asia International Symposium on Linguistics,Literature and Teaching的其它文章
- Language Assessment Literacy and the Influential Factors:Evidence from a Survey of Middle School English Teachers in Chongqing
- Case Study:Interviewing,Assessing,and Analyzing a Second Language Learner
- A Comparative Study on the Effects of Two Modes of Internet-based Feedback in EFL Writing Settings
- A Corpus-based Study on Conceptual Metaphor in T.S.Eliot’s Four Quartets
- Exploration of the SPOC-based Blended Teaching Model:Case Study of Business English Course
- The Study on CET-4 Writing and Writing Teaching Strategies Based on the Survey of CET-4 Writing Marking Teachers
