带式残膜揉搓打包机设计与试验
王 征,王吉奎,2,唐永飞,罗勇军
带式残膜揉搓打包机设计与试验
王 征1,王吉奎1,2※,唐永飞1,罗勇军1
(1. 石河子大学机械电气工程学院,石河子 832003; 2. 农业农村部西北农业装备重点实验室,石河子 832003)
针对国内现有残膜回收机械作业时不能打包,回收的残膜松散,导致残膜转运和存放不方便、易随风飘散造成二次污染等问题,研究设计了一种带式残膜揉搓打包机。该打包机主要由揉搓机构、浮动式喂入机构、传动系统和液压系统等部分组成。该揉搓机构是带式残膜揉搓打包机的核心部件,在张紧机构和浮动式喂入机构辅助下,将回收的残膜揉搓打包。通过对主要工作部件的设计,确定了揉搓机构和浮动式喂入机构的结构尺寸参数,并对残膜包的形成过程进行分析,确定了影响打包质量的主要因素为打包室方位角和打包带表面形态。田间试验表明:在打包带适度张紧的条件下,打包室方位角为-5.0°~2.5°,打包带表面为波纹面,打包带线速度为2.0 m/s时,残膜成包率为100%,残膜包密度在88.5~92.1 kg/m3之间;在回收残膜含杂相同的情况下,残膜包密度与打包带线速度有关,打包带线速度越大,残膜包密度越大,但打包带线速度超过2.5 m/s以后,残膜包密度增加趋势减缓。带式残膜揉搓打包机结构简单、使用方便、满足残膜打包技术的要求,研究结果对新型残膜打包机的研制提供参考。
农业机械;设计;残膜;打包机;揉搓机构;浮动式喂入机构
0 引 言
中国使用铺膜种植技术已有近40 a时间,铺膜种植面积和地膜使用量均居世界第一,但使用后的地膜一直没能及时有效回收,常年在田间积累,给农业生态环境造成严重的“白色污染”[1-5]。机械化回收地膜是解决农田地膜污染的有效手段,目前已有多种类型残膜回收机,部分残膜回收机已达到较高的残膜回收率[6-10]。然而,现有机型回收的残膜堆集松散、占用空间大、给后续残膜装卸、拉运和存放造成不便,且松散的残膜易随风飘散,造成二次污染[11-15]。若将残膜及时打包,则回收的残膜包裹密实、体积小、且不易松散,可为回收残膜的后续处理带来较大便利[16-21]。因此,在作业过程中对残膜边回收边打包,有助于残膜污染的综合治理,是机械化回收残膜的发展方向。
国外使用的地膜厚度较大,残膜强度较高,回收时大多采用简单缠绕的方式将残膜打成膜辊[22-24]。国内郭笑欢等研制了全膜双垄沟废膜捡拾打捆机,该机采用钢辊打包(捆)装置将残膜打包[25];张海春等在4JLM-1800(A)型残膜回收机的基础上加装钢辊打包(捆)装置,研制成棉田地膜回收打包一体机[26];张爱民等研究了一种能够将残膜和根茬一起回收并打捆的棉田残茬废膜收集打捆机[27];赫鹏亮等研究设计了一种残膜液压打包成型系统[17];新疆农垦科学院机械装备研究所研制了一款CMJY-1500型农田残膜捡拾打包联合作业机,可同时完成残膜捡拾、清理与压缩打包作业[6]。
现有残膜打包机借鉴已有秸秆或牧草打包(捆)技术,存在机具结构复杂、造价高、与现有残膜回收机配套性差等问题。针对国内残膜回收打包作业要求,本文利用残膜易揉搓成辊这一特性,设计了一种带式残膜揉搓打包机,分析了残膜包形成过程,并进行了田间性能试验。
1 整机结构与工作原理
1.1 整机结构
带式残膜揉搓打包机由揉搓机构、浮动式喂入机构、传动系统、连接板、侧板和液压油缸组成,其结构示意图如图1所示。其中揉搓机构由前后2组打包带、支撑辊、张紧机构和侧板组成,2组打包带分别绕在对应的上支撑辊、下支撑辊和张紧辊上。张紧机构将打包带张紧后,在2个打包带之间形成一个V型槽,该V型槽即是打包室。打包室上端开口宽度大,为打包机进料口,下端开口宽度小(作业状态),为打包机出料口。浮动式喂入机构主要由喂入辊、U型支撑架、带滑槽座轴承和压紧弹簧组成,喂入辊压在与上支撑辊相接触的后打包带上侧。液压油缸设在前、后两侧侧板之间。
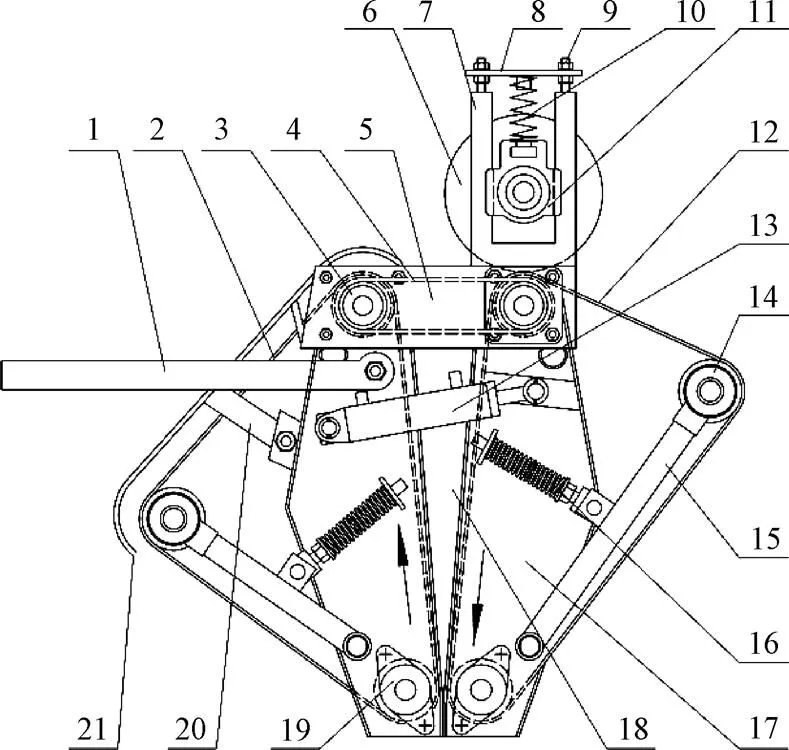
1.拉杆 2.前打包带 3.上支撑辊 4.传动系统 5.连接板 6.喂入辊 7.U型支撑架 8.压板 9.螺杆 10.压紧弹簧 11.带滑槽座轴承 12.后打包带 13.液压油缸 14.张紧辊 15.张紧支架 16.张紧装置 17.侧板 18.打包室 19.下支撑辊 20.支撑杆 21.挡板
1.2 工作原理
作业时,在传动系统带动下,前后打包带绕上、下支撑辊和张紧辊逆时针转动,喂入辊在后打包带摩擦力作用下顺时针转动。回收的残膜落到喂入辊或后打包带上侧,随着后打包带和喂入辊的转动,残膜被夹持在喂入辊和后打包带之间,由打包机进料口进入打包室,沿后打包带下落到打包室底部。在工作状态下,打包机出料口开口宽度较小,残膜被挡在打包室底部,在重力作用下夹在2个打包带之间。由于打包室两侧打包带运动方向相反,在摩擦作用下,前侧打包带带动残膜向上运动,后侧打包带带动残膜向下运动,残膜受到两侧打包带的揉搓作用,并旋转形成圆柱形残膜包芯。随着打包作业的进行,喂入打包室的残膜不断缠绕在包芯上,包芯直径不断增大,最终形成残膜包。在此过程中,残膜包直径的增大使打包带的张紧度变大,从而使打包带对残膜包的挤压揉搓作用增强,残膜包的密度也随之增大。当残膜包的直径达到设定值时,打包带停止转动,通过操作液压系统,使打包机出料口张开,在重力作用下,残膜包从打包室内掉落,完成一次打包。
1.3 主要技术参数
带式残膜揉搓打包机主要技术参数如表1所示。
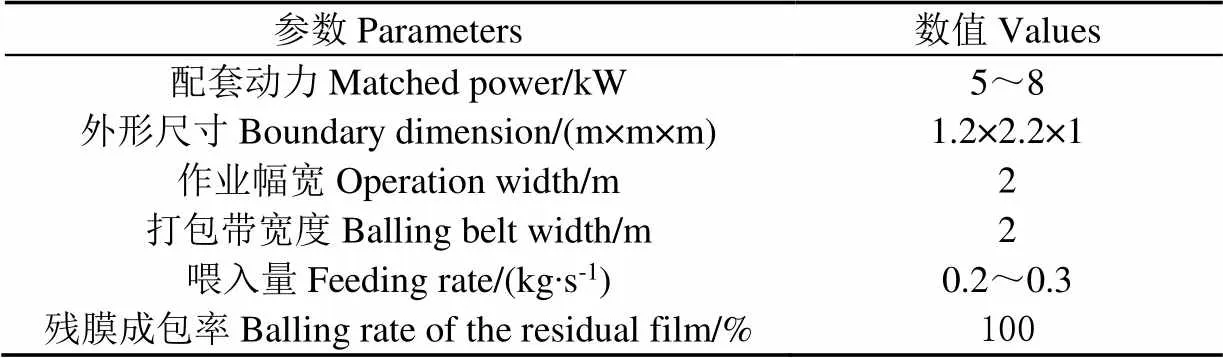
表1 带式残膜揉搓打包机主要技术参数
2 主要部件设计
2.1 揉搓机构
揉搓机构是带式残膜揉搓打包机的核心部件,作业时,进入打包室的残膜在揉搓机构作用下形成残膜包。该机构由前打包带、后打包带、上支撑辊、下支撑辊、侧板和张紧机构组成,张紧机构上有张紧辊。为方便与现有残膜回收机配套和残膜包的搬运,打包机形成的最大残膜包直径=0.5 m。
2.1.1 打包室结构参数的确定
打包室是形成残膜包的空间,作业过程中,残膜进入打包室后在两侧打包带的作用下旋转,形成圆柱状包芯。包芯在打包带的作用下继续旋转,由于残膜具有粘附性,随后进入打包室的残膜不断缠绕在旋转包芯上,形成残膜包。因此,包芯的形成是实现揉搓打包的关键环节,而残膜的受力情况对包芯的形成有直接影响。
开始作业时,残膜由进料口进入V型打包室并堆积在其底部,此时喂入打包室的残膜质量与体积较小,两侧打包带形变可以忽略不计,残膜在打包室底部受力如图2所示。
根据图2,残膜在水平和竖直方向的受力为
由式(1)可得打包带对残膜的压力为

残膜受到的转动力矩为
式中为残膜受到的转动力矩,N/m;为残膜包芯至打包带的距离,m。
将式(2)代入式(3)可得:
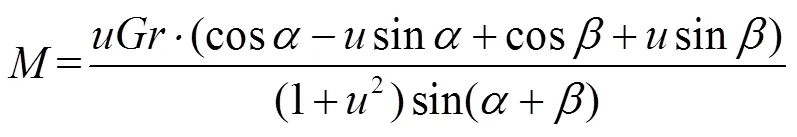
残膜受到的转动力矩越大,堆积在打包室底部的残膜越容易转动形成残膜包芯。由式(4)可知,残膜受到的转动力矩与打包室方位角、打包室夹角以及打包带表面形态有关。由(4)式分别对和求偏导数。通过分析可知当其他参数一定时,力矩随和的减小而增大,且的变化对力矩值影响最大。因此,为增大力矩,首先考虑减小打包室方位角。为方便实际操作,选取打包室方位角=0°(通过横向转动打包机即可改变打包室方位角的大小),即打包室内前打包带呈竖直状态。
当打包室方位角=0°时,由(4)式对求偏导数,通过分析可知转动力矩随摩擦系数值增大而增大。故可通过改变打包带表面形态来增大力矩。
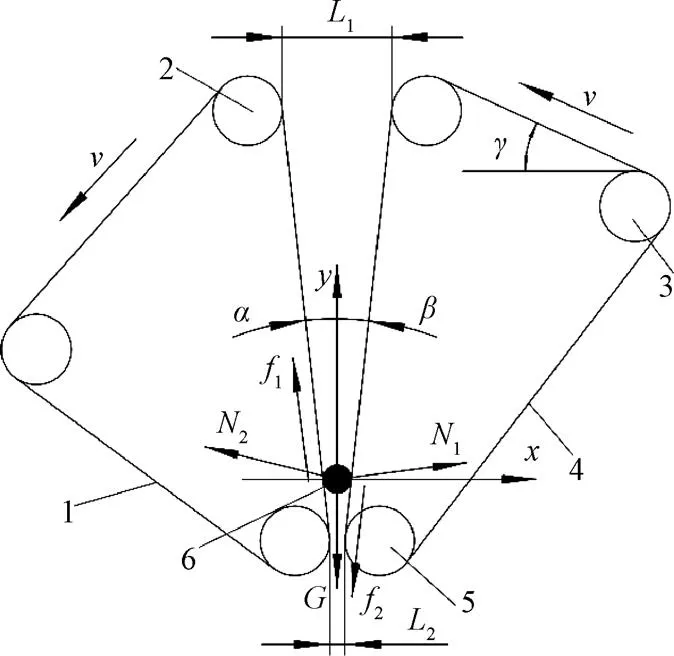
1.前打包带 2.上支撑辊 3.张紧辊 4.后打包带 5.下支撑辊 6.残膜
注:为水平方向;为竖直方向;1为前打包带对残膜的支持力,N;2为后打包带对残膜的支持力,N;1为前打包带与残膜间的摩擦力,N;2为后打包带与残膜间的摩擦力,N;为打包室方位角,(°);为打包室夹角,(°);为残膜的重力,N;1为打包室上端前后打包带间隙;2为打包室底部前后打包带间隙;为后打包带与水平方向的夹角,(°);为打包带线速度,m∙s-1。
1.Front balling belt 2.Upper supporting roller 3. Tensioning roller 4.Back balling belt 5. Lower supporting roller 6.Residual film
Note:is the horizontal direction;is the vertical direction;1is the supporting force of the front balling belt to the residual film, N;2is the supporting force of the back balling belt to the residual film, N;1is the friction force between the front balling belt and the residual film, N;2is the friction force between the back balling belt and the residual film, N;is the azimuth of the balling room, (°);is the angle of the balling room, (°);is the gravity of the residual film, N;1is the gap between the front and back of the upper end of the balling room;2is the gap between the front and back of the bottom of the balling room r;is the angle between the back balling belt and the horizontal direction, (°) ;is the linear speed of the balling belt, m∙s-1.
图2 残膜在打包室底部的受力示意图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of residual film force at the bottom of the baling room
由于残膜包芯的密实度与打包带对包芯的压力有关。由式(2)可知,打包带对残膜的压力随打包室方位角、打包室夹角的减小而增大。因此,为增大残膜包芯的密实度,打包室方位角和打包室夹角的取值应较小。在打包室方位角确定的情况下,打包室夹角的取值与打包机进料口宽度大小有关。为防止残膜在喂入过程中堵塞打包机进料口,结合残膜物料层的厚度,取进料口宽度1=150 mm(打包室上端前、后打包带间隙),则打包室夹角=15°。为防止残膜从打包室底部掉落和前后打包带磨损,作业状态下打包机出料口宽度2=2 mm(打包室底部前、后打包带间隙)。
为防止落在后打包带上的残膜掉落,后打包带与水平方向的夹角应小于残膜与打包带表面的摩擦角,通过试验残膜与光面打包带间的摩擦角在35°~45°之间,残膜与波纹面打包带的摩擦角在40°~50°之间。考虑到实际作业过程中残膜会受到气流作用力的影响,结合试验,取后打包带与水平方向的夹角=25°。
2.1.2 张紧机构
张紧机构的作用是使打包带保持一定的张紧度,一方面防止打包带打滑,另一方面使残膜包持续受压,保证残膜包的密实度。本设计采用弹性张紧机构,该机构由张紧辊和设在张紧辊两侧的张紧辊支架、张紧弹簧、挡板、销轴、导杆和张紧螺母等组成,其结构如图3所示。张紧辊支架一端铰接在打包机侧板下端,另一端通过带座球面轴承联接在张紧辊轴端,张紧弹簧设在张紧支架的中部,通过调整张紧螺母位置来调节弹簧的压缩量,进而调节打包带的张紧度。
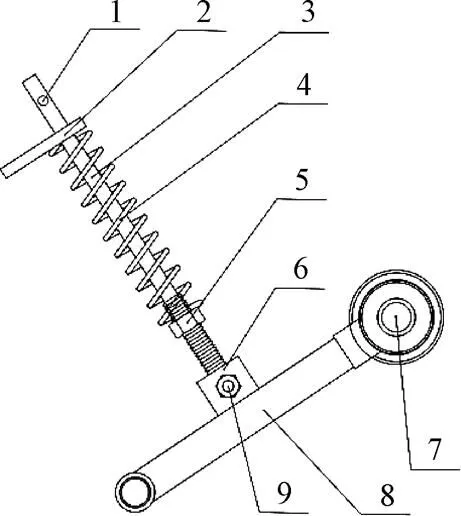
1.销子 2.挡板 3.导杆 4.张紧弹簧 5.张紧螺母 6.耳板 7.张紧辊 8.张紧支架 9.销轴
打包带在上支撑辊与打包带间的摩擦力作用下转动,该摩擦力大小与打包带的张紧度有关,因此,作业前张紧弹簧应有一定的预压缩量,使打包带适度张紧,确保上支撑辊能带动打包带转动。随着打包作业的进行,残膜包直径逐渐增大,打包带受残膜包的挤压而变形,导致打包带对残膜包的包角增大,打包室两侧的打包带长度增加,从而使张紧辊向打包室靠拢,随之带动张紧支架压缩弹簧。经试验分析,形成直径=500 mm的圆柱形残膜包,打包室内前、后打包带的长度变形量各约为200 mm,张紧弹簧的长度依据打包前、后张紧支架的摆动量和弹簧的安装位置确定。弹簧的弹簧系数越大,打包带的张紧度越大,打包带作用于残膜包的压力就越大,形成的残膜包越密实。但打包带受到的张紧力越大,作业中打包带受到的磨损越大,影响打包带的使用寿命。根据打包机整体结构尺寸和田间试验效果,本文设计选用碳素弹簧钢丝Ⅰ类C级弹簧[28],自由长度为250 mm,中径为25 mm,线直径为5 mm,弹簧总圈数为25圈,有效圈数为20圈,当弹簧压缩量为20~35 mm时,作业过程中打包带未出现打滑现象,机具作业效果较好。
2.2 浮动式喂入机构
一般情况下,残膜回收分为起膜、收膜和脱膜3个过程,其中脱膜是将收起的残膜从残膜回收装置上脱取下来。试验中发现,脱下的残膜受脱膜装置和气流等因素的影响,下落位置不确定,残膜有可能在进料口发生堵塞。另外,若残膜被连片收起且残膜片较长,当残膜前段进入打包室并绕在残膜包上而残膜片后段仍在残膜回收装置上未被脱下来时,由于打包带线速度较快,进入打包机的残膜会拉拽未脱下的残膜,在反向作用力下,残膜包直径较小时会被拽出打包室,影响打包效果。浮动式喂入机构的作用是使脱下的残膜强制有序喂入打包室,确保打包作业可靠。
因后打包带转动时将残膜带入打包室,故将浮动式喂入机构设在与上支撑辊相接触的后打包带上侧。该机构主要由喂入辊、U型支撑架、压紧弹簧、带滑槽座的轴承和压板组成,其结构如图4所示。U型支撑架设在打包机两侧连接板上,喂入辊轴端通过带滑槽座轴承安装在U型支撑架内,轴承座上侧有压紧弹簧,压板设在压紧弹簧上端。在压紧弹簧和重力作用下,喂入辊紧贴在后打包带上。上支撑辊为主动辊,转动时带动后打包带运动,进而带动喂入辊转动,喂入辊转动可在后打包带上侧上下浮动。
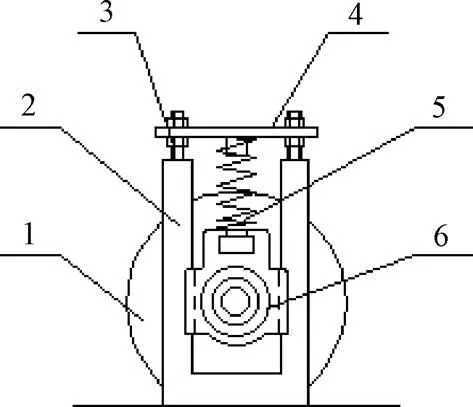
1.喂入辊 2.U型支撑架 3.螺杆 4.压板 5.压紧弹簧 6.带滑槽座轴承
残膜夹在打包带与喂入辊之间进入打包室,故残膜喂入速度与打包带线速度相等。因回收的残膜下落位置不确定,残膜可能掉落在进料口前打包带上,随着前打包带的转动,残膜夹在前打包带与挡板之间,导致残膜不能顺利喂入打包室,造成堵塞。为此,可增大喂入辊的直径,使其在竖直方向遮住打包室入口,掉落在进料口处的残膜落在喂入辊上,并随着喂入辊的转动及时进入打包室。参照打包机进料口宽度和打包带宽度,取喂入辊直径=330 mm,喂入辊长度=2 000 mm。
3 残膜包形成过程分析
残膜包芯形成后,包芯只有在打包带的揉搓作用下转动时,喂入打包室的残膜才能不断缠绕在残膜包芯上,最终形成残膜包。通过残膜包形成过程分析,确定影响残膜包转动的条件。开始作业时,残膜包芯从打包室底部开始形成,初始直径小,残膜包芯的回转中心靠近打包室下侧,随着残膜包芯直径逐渐增大,残膜包芯回转中心由打包室底部向上移动,当包芯的中心与打包室中心重合时,残膜包直径达到最大值。若打包带匀速运动(一般情况下,配套残膜回收机的作业速度为6.0 km/h,考虑到残膜有一定弹性,确定打包带线速度为残膜回收机作业速度的1.2倍),打包室方位角=0°,残膜包为圆柱形且不考虑打包带变形时,残膜包芯的受力分析如图5所示。
由受力分析可知,前、后打包带对残膜包芯的支持力3、4和残膜包的重力相对残膜包芯回转中心点的力矩均为0。若残膜包芯在打包带表面做纯滚动,打包带与残膜包芯间的摩擦力为静摩擦力;若残膜包芯在打包带表面有滑动,则打包带与残膜包芯间的摩擦力为滑动摩擦力。因滑动摩擦力小于最大静摩擦力,结合残膜包实际受力情况,取残膜包芯与打包带间的摩擦力为滑动摩擦力。
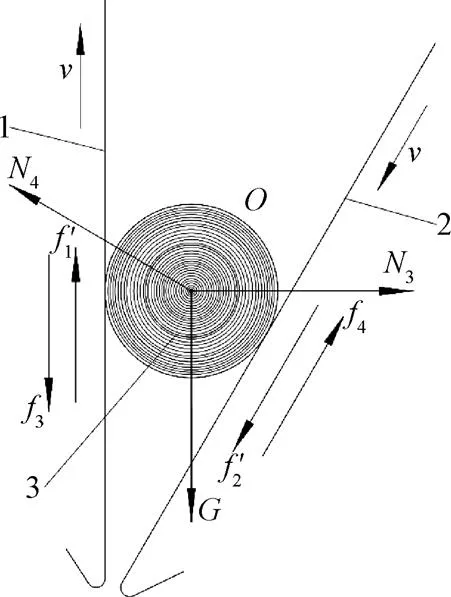
1.前打包带 2.后打包带 3.残膜包芯
注:3为前打包带对残膜包芯的支持力,N;4为后打包带对残膜包芯的支持力,N;3为前打包带对残膜包芯的滚动阻力,N;4为后打包带对残膜包芯的滚动阻力,N;为残膜包芯回转中心;1′为前打包带与残膜包芯间的滑动摩擦力,N;2′为后打包带与残膜包芯间的滑动摩擦力,N。
1. Front balling belt 2. Back balling belt 3. Residual film core
Note:3is the supporting force of the front balling belt to the residual film core, N;4is the supporting force of the back balling belt to the residual film core, N;3is the rolling resistance of the front balling belt to the residual film core, N;4is the rolling resistance of the back balling belt to the residual film core, N;is the rotation center of the residual film core;1′ is the sliding friction force of the front balling belt to the residual film core, N;2′ is the sliding friction force of the back balling belt to the residual film core, N.
图5 残膜包芯受力示意图
Fig. 5 Stress diagram of residual film core
由受力分析得残膜包芯受到的转动力矩1为
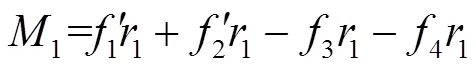
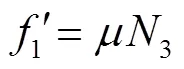
由残膜包芯在水平和竖直方向上受力分析可得:

由式(6)可得打包室内两侧打包带对残膜包芯的压力为
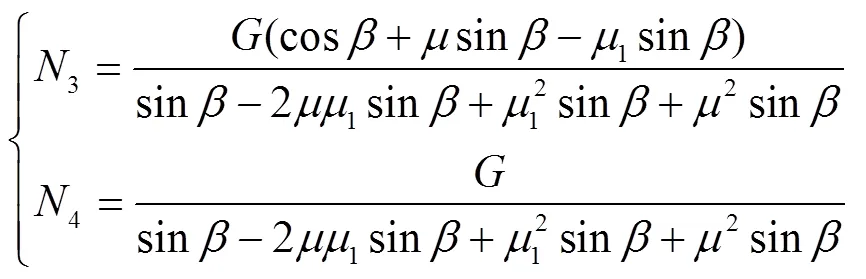
将式(7)代入式(5)得残膜包芯受到的转动力矩:
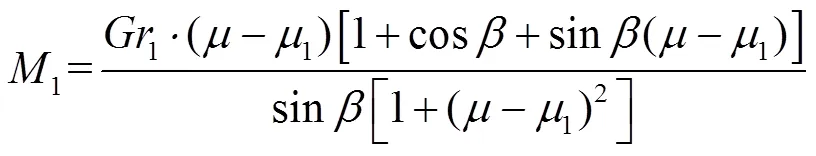
因残膜包芯与打包带间的滑动摩擦系数大于滚动阻力系数[29],即1。由式(8)可知,在前后打包带的揉搓作用下残膜包芯受到的转动力矩1﹥0,即残膜包芯可以在打包带的作用下旋转。由此可知在打包室方位角=0°,残膜包芯受到的转动力矩1﹥0时,可以实现残膜揉搓打包作业。
另外,由于残膜柔软,残膜包芯受压易变形,处于V型打包室的残膜包芯不可能是圆柱形(近似楔形),残膜包芯在打包带上的滚动阻力增大,使残膜包转动力矩减小,影响残膜包芯转动。为确保残膜包芯转动,需增大残膜包芯的转动力矩,分析式(8)可知,在打包室方位角一定时,改变打包带的表面形态可以增大力矩1,提高打包作业可靠性。
4 田间试验
4.1 试验条件
于2019年10月在新疆石河子市143团收获后的棉田进行带式残膜揉搓打包机田间作业性能试验,该打包机与夹指链式残膜回收机[12]配套使用。试验棉田为机采棉的种植模式(660 mm(宽)+100 mm(窄)),地面较为平整,滴灌带已回收,土壤松软,地表土壤含水率为11.23%,单次作业6行(1膜6行种植模式),地膜的厚度为0.008 mm,幅宽为2 050 mm,秸秆高度在700~900 mm,棉株密度为4.5~5.5万株/hm2。考虑到机具作业效率和实际经济效益,机组的作业速度为6.0 km/h,配套动力由约翰迪尔904拖拉机提供。试验场景如图6所示。
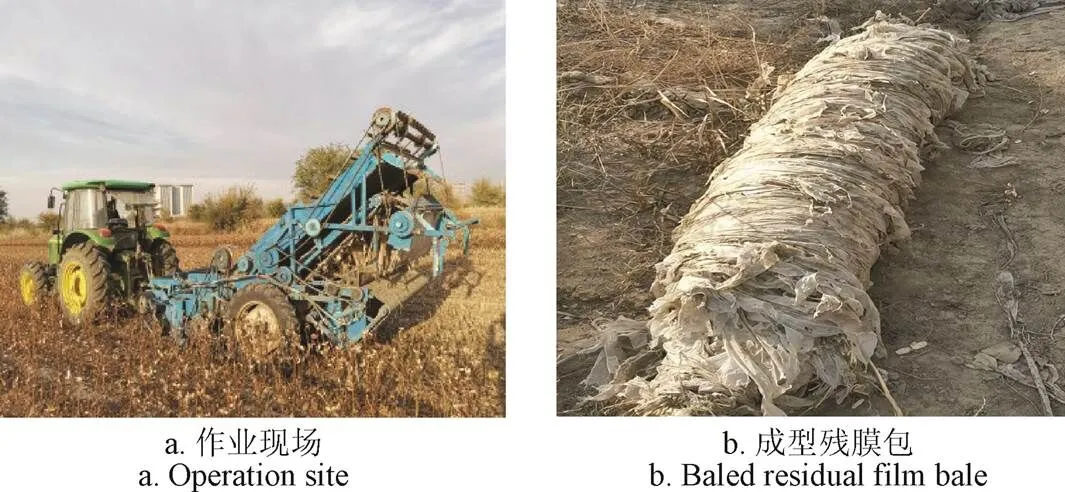
图6 田间试验
4.2 试验方法
受田间试验环境和时间的限制,本试验采用单因素试验方法。根据前文分析和预试验结果,选取打包室方位角、打包带表面形态和打包带线速度为试验因素,残膜成包率和残膜包密度为试验指标。试验过程参考《GB/T 14290-1993 圆草捆打捆机试验方法》进行[30]。
打包带的工作表面分为光面和波纹面,材质为PVC,其与残膜间的摩擦系数分别为0.78和1.1;打包室方位角的取值范围为−5°~5°;打包带线速度取值范围为1.0~3.0 m/s(通过更换传动链轮,改变打包机的传动比实现),适度张紧打包带,使支撑辊能带动打包带转动。依据前期试验结果,试验时固定其中2个因素,改变第3个因素的取值水平,每个水平连续打包5个,采用精密电子秤测其质量,采用米尺测其长度和直径,结果取平均值。
残膜成包率由下式计算:

式中c为残膜成包率,%;c为每个水平内累计形成残膜包数;a为每个水平内累计散包数。
残膜包的密度由下式计算:
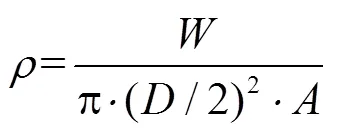
式中为残膜包的密度,kg/m3;为残膜包的长度,m;为残膜包的直径,m。为残膜包的质量,kg。
根据预试验,残膜包直径越大,残膜包越密实。对于不规则的圆柱形残膜包,残膜包两端较小,对试验结果影响较小,因此将其向残膜包中部折叠,分别取残膜包直径最大处和处理后的残膜包长度作为密度试验值。
4.3 试验结果与分析
打包带线速度为2 m/s、打包室方位角为0°时,分别采用光面打包带和波纹打包带面,试验得到残膜包10个,散包0个,残膜成包率为100%;更换打包带前后残膜包的密度变化不大,在88.5~91.2 kg/m3之间,残膜包密度试验结果如表2所示。
打包带线速度为2 m/s、分别采用光面打包带和波纹面打包带、改变打包室方位角,当打包室方位角在−5°~2.5°测试时,得到残膜包40个,散包0个,残膜成包率为100%;当打包室方位角大于2.5°时,出现散包以及不打包现象。这是由于打包室方位角增大,残膜所受的转动力矩减小,导致作业时出现散包或者不打包;残膜包的密度变化范围在89.2~92.1 kg/m3之间,残膜成包率及残膜包密度试验结果如表3所示。
打包室方位角为0°、分别采用光面打包带和波纹面打包带、改变打包带线速度,试验得到残膜包50个,散包0个,残膜成包率为100%。在其他因素不变的情况下,残膜包密度随打包带线速度的增大而增大;当线速度大于2.5 m/s后,残膜包密度增加趋势减缓。残膜包密度试验结果如表4所示。
由试验结果可知,影响残膜成包率的主要因素是打包室方位角,在此试验的条件下,当打包室方位角在−5.0°~2.5°时,成包率为100%。在打包带初始张紧度一定的情况下,残膜包的密度与打包带的线速度有关,线速度越大,残膜包密度越大,但增大到一定值后增幅减小。田间试验表明:当机具作业速度为6.0 km/h、打包室方位角=0°、打包带线速度为2 m/s、采用波纹面打包带时,带式残膜揉搓打包机的残膜成包率为100%,残膜包密度在88.5~92.1 kg/m3之间,满足打包机的田间作业性能要求。机具在田间连续作业过程中性能良好,浮动式喂入机构可确保残膜有序喂入打包室,未出现不打包现象。张紧机构可保证残膜包的密实度,并减少打包带的磨损,各部件功能与作业效果均达到了设计的预期。
因田间情况比较复杂,测试时受风力作用的影响,样机工作过程中有少量残膜飘挂在脱膜装置和打包机外壳上,导致残膜不能喂入打包机,影响了残膜的打包效果。本次试验只在现有的结构参数下对样机进行了性能验证试验,未深入探究打包机在不同结构与作业参数组合下的作业效果,因此在后续的研究中还需进行打包机结构与作业参数的优化试验,进一步提高带式残膜揉搓打包机及整机的作业效果。
5 结 论
1)在打包带张紧、前后打包带线速度相同的情况下,影响带式残膜揉搓打包机成包率的主要因素是打包室方位角,其次是打包带表面形态。为保证试验结果可靠,打包室方位角为0°,打包带选用波纹面打包带。
2)残膜包密度与打包带的张紧度、打包室夹角和打包带的线速度有关,打包带的张紧度越大、打包室夹角越小、打包带线速度越大,则残膜包密度越大。
3)田间试验表明,当机具作业速度为6.0 km/h、打包室方位角为0°、打包带线速度为2 m/s、采用波纹面打包带时,带式残膜揉搓打包机的残膜成包率为100%,形成的残膜包密度在88.5~92.1 kg/m3之间。
带式残膜揉搓打包机与现有残膜回收机配套使用,在边收膜边打包的作业模式下,机具各部件运转良好,工作平稳,未发生堵塞、缠绕问题,残膜打包效果良好,满足对回收残膜打包的田间作业要求。
[1] 赵岩,陈学庚,温浩军,等. 农田残膜污染治理技术研究现状与展望[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(6):1-14.
Zhao Yan, Chen Xuegeng, Wen Haojun, et al. Research status and prospect of residual membrane pollution control technology in farmland[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery (Transactions of the CASM), 2017, 48(6): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 何文清,严昌荣,刘爽,等. 典型棉区地膜应用及污染现状的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2009,28(8):1618-1622.
He Wenqing, Yan Changrong, Liu Shuang, et al. The use of plastic mulch film in typical cotton planting regions and the associated environmental pollution[J]. Journal of Agriculture Environment Science, 2009, 28(8): 1618-1622. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王吉奎. 农田残膜回收技术[M]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学出版社,2012.
[4] 梁荣庆,陈学庚,张炳成,等. 新疆棉田残膜回收方式及资源化再利用现状问题与对策[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(16):1-13.
Liang Rongqing, Chen Xuegeng, Zhang Bingcheng, et al. The current problems and countermeasures of recovery methods and recycling of cotton residual film in Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2019, 35(16): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 严昌荣,何文清,刘恩科,等. 作物地膜覆盖安全期概念和估算方法探讨[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(9):1-4.
Yan Changrong, He Wenqing, Liu Enke, et al. Discussion on the concept and estimation method of crop film mulching safety period[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2015, 31(9): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李斌,王吉奎,蒋蓓. 新疆棉区残膜污染及其治理技术[J]. 新疆农机化,2012(4):60-63.
Li Bin, Wang Jikui, Jiang Bei. Residual membrane pollution and its control technology in Xinjiang cotton area[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Mechanization, 2012(4): 60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 严昌荣,刘恩科,舒帆,等. 我国地膜覆盖和残留污染特点与防控技术[J]. 农业资源与环境学报,2014,31(2):95-102.
Yan Changrong, Liu Enke, Shu Fan, et al. Characteristics and prevention and control technology of mulch and residual pollution in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(2): 95-102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 杨莹,白圣贺,马少腾. 残膜回收机研究综述[J]. 粮食科技与经济,2019,44(1):97-100.
Yang Ying, Bai Shenghe, Ma Shaoteng. Overview of research on residual membrane recycling machine[J]. Grain Science and Technology and Economy, 2019, 44(1): 97-100. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 邢剑飞,王旭峰,王龙,等. 残膜回收机在新疆地区的应用现状研究[J]. 塔里木大学学报,2019,31(3):76-82.
Xing Jianfei, Wang Xufeng, Wang Long, et al. Research on the application status of residual plastic film recycling machine in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Tarim University, 2019, 31(3): 76-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 舒帆. 我国农用地膜利用与回收及其财政支持政策研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院,2014.
Shu Fan. Study on the Utilization and Recovery of Agricultural Mulch Film and Its Financial Support Policy in China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 唐永飞,赵永满,王吉奎,等. 夹指链式残膜回收机脱膜装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(13):11-19.
Tang Yongfei, Zhao Yongman, Wang Jikui, et al. Design and experiment of film removing device for clamping finger-chain type residual film collector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2020, 36(13): 11-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 段文献,王吉奎,李阳,等. 夹指链式残膜回收装置的设计及试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(19):35-42.
Duan Wenxian, Wang Jikui, Li Yang, et al. Design and test of clamp finger chain residual film recovery device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2016, 32(19): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] Li Tianwen, DuanWenxian, Wang Jikui. Design and test of clamping and conveying residual membrane recovery device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2016, 32(24): 18-25. (in English with Chinese abstract)
李天文,段文献,王吉奎. 夹持输送式残膜回收装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(24):18-25.
[14] 由佳翰,陈学庚,张本华,等. 4JSM-2000型棉秆粉碎与残膜回收联合作业机的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(10):10-16.
You Jiahan, Chen Xuegeng, Zhang Benhua, et al. Design and test of 4JSM-2000 cotton stalk crushing and residual film recycling combined machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2017, 33(10): 10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 于云海,陈学庚,温浩军. 秸秆粉碎与残膜集条联合作业机的研制与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(24):1-8.
Yu Yunhai, Chen Xuegeng, Wen Haojun. Development and test of a combined machine for straw crushing and residual film collecting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2016, 32(24): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 牛琪,纪超,赵岩,等. 集条残膜打包机捡拾清理装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(5):101-107.
Niu Qi, Ji Chao, Zhao Yan, et al. Design and test of pick-up and cleaning device of strip and residual film packer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(5): 101-107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 赫鹏亮,纪超,郑炫,等. 集条残膜打包机压包成型系统设计[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2017,22(12):138-145.
He Pengliang, Ji Chao, Zheng Xuan, et al. Design of the press forming system of the strip and residual film packer[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2017, 22(12): 138-145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘进宝,郑炫,赵岩. 残膜捡拾压缩车及其作业工艺设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(19):17-26.
Liu Jinbao, Zheng Xuan, Zhao Yan. Design and test of residual film collecting compression vehicle and its operation process[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2017, 33(19): 17-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 赫鹏亮. 残膜压缩成型的试验研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2017.
He Pengliang. Experimental Study on Compression Molding of Residual Film[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 邓宇玄. 水葫芦压缩打包机的设计与试验研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学,2018.
Deng Yuxuan. Design and Experimental Research of Water Hyacinth Compression Packer[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王德福,蒋亦元,王吉权. 钢辊式圆捆打捆机结构改进与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(12):84-88.
Wang Defu, Jiang Yiyuan, Wang Jiquan. Structural improvement and test of steel roller round baler[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 41(12): 84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 赵岩,陈学庚,温浩军,等. 农田残膜污染治理技术研究现状与展望[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(6):1-14.
Zhao Yan, Chen Xuegeng, Wen Haojun, et al. Research status and Prospect of residual membrane pollution control technology in farmland[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(6): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 罗威,王吉奎,牛海龙,等. 夹指链式残膜回收机清杂装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,40(2):75-79.
Luo Wei, Wang Jikui, Niu Hailong. Design and test on debris clean-up device of clamping finger-chain type device for recycling agricultural plastic film[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 40(2): 75-79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 戚江涛,张涛,蒋德莉,等. 残膜回收机械化技术综述[J]. 安徽农学通报,2013(9):153-155.
Qi Jiangtao, Zhang Tao, Jiang Deli, et al. Study on the plastic film recovery machine technology[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013(9): 153-155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 郭笑欢,戴飞,赵武云,等. 全膜双垄沟废膜捡拾打捆机的设计[J]. 中国农机化学报,2016,37(9):32-36.
Guo Xiaohuan, Dai Fei, Zhao Wuyun, et al. Design of full film double ridge ditch waste film pickup and bundling machine[J]. China Journal of Agricultural Machinery Chemistry, 2016, 37(9): 32-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 张海春,张丽,蒋永新,等. 棉田地膜回收打捆机关键参数设计及试验研究[J]. 中国农机化学报,2017,38(5):28-31.
Zhang Haichun, Zhang Li, Jiang Yongxin, et al. Design and experimental study on key parameters of plastic film recycling and bundling machine used in cotton field[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2017, 38(5): 28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 张爱民,廖培旺,李伟,等. 基于Adams的棉田残茬废膜收集打捆机分析[J]. 农机化研究,2018,40(3):22-27.
Zhang Aimin, Liao Peiwang, Li Wei, et al. Analysis research of cotton stubble collecting waste film bundling machine based on adams[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(3): 22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 秦大同,谢里阳. 弹簧设计[M]. 北京:化工工业出版社,2013:15-54.
[29] 卢克箴. 新编中学物理手册[M]. 西安:陕西人民教育出版社,1987:24.
[30] GB/T 14290-1993圆草捆打捆机试验方法[S]. 北京:高等教育出版社,1993.
Design and test of the belt-type residual film rubbing and baling machine
Wang Zheng1, Wang Jikui1,2※, Tang Yongfei1, Luo Yongjun1
(1.832003,;2.832003,)
There are some problems existing in the domestic residual film recycling machinery, such as unable to bale, recovered film was loose, which leads to inconvenient transportation and storage, and easy to drift with the wind, resulting in secondary pollution and so on. In order to solve these problems, the belt-type residual film rubbing and baling machine was designed. The machine mainly consisted of rubbing mechanism, floating feeding mechanism, transmission system and hydraulic system, etc. The rubbing mechanism mainly consisted of front and back baling belts, support rollers, side plates and tensioning mechanism, etc. The baling belts rotated counterclockwise around the upper and lower support rollers, and the tension roller under the driving of the transmission system. The floating feeding mechanism mainly consisted of feeding roller, U-shaped support frame, bearing with sliding seat, and compression spring, etc. It was fixed to the upper end of the connecting plate, and the feeding roller rotated clockwise under the frictional force of the back baling belt. Through the design of the rubbing mechanism and the force analysis of the residual film, the structural dimension parameters of the baling room were determined, which contained the azimuth of the baling room was 0°, the angle of the baling room was 15°, the gap between the front and back of the upper end of the baling room was 15 mm, the gap between the front and back of the bottom of the baling roomwas 2 mm, the angle between the back baling belt and the horizontal direction was 25°, and the baling belt used PVC conveyor belt. The function of tension mechanism was to make the baling belt keep a certain degree of tension, so as to prevent the belt from slipping, keep the residual film bale baling under continuous pressure, and ensure the compactness of the residual film bale. Through the mechanical analysis of the formation of the residual film bale, the mechanical equation of the residual film core in the baling room was obtained, and then the rotational torque equation of the residual film core was derived. Finally, the field test of the baling machine was carried out. The results showed that the main factors affecting the baling quality were the azimuth of the baling room and the surface morphology of baling belt. The filed test showed that under the conditions of moderate tension of the baling belt, the azimuth angle of the baling room was -5° to 2.5°, the surface of balling belt was corrugated and the linear speed of the baling belt was 2.0 m/s, and the baling rate of the residual film was 100%, the density variation range of the residual film bale was 88.5 to 92.1 kg/m3. When the recovered residual film contained the same impurities, the density of the residual film bale was related to the linear speed of the baling belt, and the higher the linear speed, the higher the density of the residual film bale. However, when the linear speed exceeds 2.5 m/s, the increasing trend of the density slowed down. The research could provide reference for the development of a new type residual film baling machine.
agricultural machinery; design; residual film; baling machine; rubbing mechanism; floating feeding mechanism
王 征,王吉奎,唐永飞,等. 带式残膜揉搓打包机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(19):11-18.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.19.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Wang Zheng, Wang Jikui, Tang Yongfei, et al. Design and test of the belt-type residual film rubbing and baling machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(19): 11-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.19.002 http://www.tcsae.org
2020-05-05
2020-07-20
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51465050);石河子大学成果转化与技术推广计划项目(CGZH201907)
王征,研究方向为农业机械装备创新与性能设计。Email:761065289@qq.com
王吉奎,博士,教授,主要从事农业机械化工程研究。Email:shzwjk@126.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.19.002
S223.5
A
1002-6819(2020)-19-0011-08

