Exploring the mechanism of Xiaopi Hewei capsule in treating functional dyspepsia based on network pharmacology
Runhua Liu,Yu Sun,Shiting Ni,Jiaqi Wang,Hao Wu,Yuxia Qu,Chenning Zhang*,Yikun Sun*
1 School of Chinese Materia Medica,Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing,China.
Abstract
Key words:Xiaopi Hewei capsule,Function dyspepsia,Network Pharmacology
Background
Function dyspepsia (FD) is a clinical syndrome with epigastric pain and/or burning, early fullness and/or postprandial fullness according to the Rome IV criteria, which cannot be explained by organic or metabolic disease [1].Patients are grouped and diagnosed according to symptoms, with those accompanying only epigastric pain or burning considered as epigastric pain syndrome (EPS), those having early fullness or postprandial fullness identified as postprandial distress syndrome (PDS)and those with both types of symptoms seemed as overlap of EPS and PDS [2].According to the results of epidemiological investigation, the global prevalence rate of FD is 11.5%-14.5%,which not only affects people's quality of life,but also consumes a lot of medical resources [3].Currently, there are many approaches to treat FD, but they do have pros and cons.Clinically, the treatment strategies for FD mainly focus on promoting gastrointestinal wriggle,applying central action drugs,regulating gastrointestinal immune function, and eradicating of HP,etc [4].However, a single drug has the limitations of single target, large side effects and short course of treatment [5], so it is difficult to meet the treatment needs of its complex pathogenesis.Therefore, more effective therapeutic measures are urgently needed for FD treatment.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been playing an important part in curing disease and improving the people’s wellbeing.In recent years,much more attention has been paid to the treatment of FD with TCM, with some superiority of shorting the duration of symptoms, reducing the recurrence rate and minimizing side effects [6].XHC, a Miao medicine prescription medicine,has been proven to be effective in treating FD.Moreover, clinical trials have shown that XHC can effectively improve the EPS and PDS by acting on alleviating epigastric pain and relaxing fullness via reducing the gastric emptying time [7].XHC is consisted of four herbs which corresponding to the rule of“Jun,Chen,Zuo and Shi”.Specifically, Geshanxiao (Cynanchum wilfordii(Maxim.) Hemsl.) is defined as Jun herb in this prescription with the effects of immune regulation,digestion improvement,tumor inhibition,anti-oxidation and liver protection; Chen herb is cili(Rosa roxbunghii), which existing the effect of curing food retention and fullness; As Zuo herbs, Liuzhi(Salix babylonica L.) serves as assistant to alleviate pain and help digestion; Sanqi (Panax notoginseng(Burkill) F.H.Chen ex C.H.) is the Shi herb with function of hemostasis, dispersing blood and pain relief[8].However,the molecular mechanism of XHC in treating FD has ever been addressed.Therefore, the study of the active components, targets and possible mechanisms of XHC will further reveal the scientific significance of XHC in treating FD and promote its clinical application.
On account of multiple components and multiple targets of TCM, it is a complicated task to identify potential bioactive molecules and mechanisms of combinations[9].Network pharmacology is applied to the analysis of TCM increasingly, which is a promising approach to illustrate the mechanisms of TCM in treatment and elucidate the complex interactions between drugs and complex diseases [10,11].Hence, in this study, the network pharmacology was used to expound the potential mechanism of XHC in treating FD, which lays the foundation for further research of XHC.
Methods
Data preparation
Collection Targets of FD.Related targets of FD were collected with the help of the integration of multi-source databases.The following is databases resources used in our study: The GeneCards(https://www.genecards.org/) is a whole bioinformatics database including transcriptomics,genomics, proteomics and etc [12].The Therapeutic Target Database (TTD, http://db.idrblab.net/ttd/ ) is known for providing information related to the explored targets of therapeutic protein and diseases[13].Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM,https://omim.org/) is a representative online database presenting continuously updated resources of genetic disorders and human genes.By searching these databases with the keyword ‘functional dyspepsia’,all the screened targets were list as FD-targets.And the names of targets were corrected to gene symbol through UniProt website (https://www.uniprot.org/),and removed duplicate genes meanwhile[14].
Collection Bioactive Compounds of XHCIn this paper, chemical compounds of XHC were acquired from Chemistry Database, TCMSP and literature mining [15-21].Chemistry Database(http://www.organchem.csdb.cn/) is one of the important scientific databases of the Chinese Academy of Sciences [17], which provides the retrieval service of chemical information for the whole scholars.The traditional Chinese medicine system pharmacology database and analysis platform Database (TCMSP, http://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php.), a Chinese medicine pharmacology database, includes information of herbs used in TCM, and characteristics of the individual compounds, and their targets, related diseases,and pathways[22].
ADME Screening of Bioactive Compounds
Recently, early assessment of absorption, distribution,metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of bioactive compounds has become a popular choice to give priorities to those components having good pharmacokinetic properties.To ensure that we got meaningful results, OB, DL (RO5), GI absorption as ADME-related models were exploited to screen the active compounds from XHC in the present work.
The convergence of the ADME process is displayed by OB (%F), which elucidated the percentage of an orally administered dose of the chemical compounds that reaches the systemic circulation [9].Compounds with OB ≧ 30% were selected as candidate components for next step.
The “drug-like” prospective of compounds was estimated by DL an established concept for drug design.Furthermore, Lipinski's rule of five (RO5) is applied to evaluate DL or determines if a chemical compound has chemical and physical properties [23].The rule is composed of relative molecular mass(MW),number of hydrogen bond donors(HBD),fatty water partition coefficient (LogP), rotatable Bonds(RB) and number of hydrogen bond acceptors (HBA).Candidate compounds that accord with the RO5 tend to have an increased chance of reaching the market.In this process,compounds with MW ≤500,HBD ≤5,LogP ≤5,RB≤10 and HBA ≤10 were selected as the active compounds for next step.
GI absorption,a pharmacokinetic behavior of drugs,is significant to supervision at various stages of the drug discovery processes [24].In this study, the GI absorption value of the components in XHC was obtained through SwissADME website(http://www.swissadme.ch/index.php) [25].The screening criterion of GI absorption was defined as high.
Finally, herbal compounds were chosen as the candidate ingredients for further analysis when they meet three criteria.
Collection Predicted Targets of Bioactive CompoundsThe active compounds of drugs exert related biological functions via targets.Related targets were located by target collection according to aforementioned included active ingredients.After obtaining the micromolecular structure information about the active compounds of XHC by retrieving Pubchem database(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), all the screened targets were collect as predicted targets based on Swiss Target Prediction(http://swisstargetprediction.ch/).At last, the overlapping targets were chosen as the related targets of XHC in treating FD through matching the targets of bioactive compounds of XHC and the related targets of FD based on Draw Venn diagrams website(http://jvenn.toulouse.inra.fr/app/example.html)[26].
Construction of PPI Network and Topological Analysis
PPI network was completed based on String database(https://string-db.org/) and Cytoscape 3.7.1 platform.String database covered most of functional interactions between the proteins reported.The parameters were frequently set as follows during data preprocessing: Homo sapiens; minimum required interaction score: 0.9; display simplifications: hide disconnected nodes in the network [27].Moreover,Cytoscape 3.7.1 platform, an open source bioinformatics software platform, was available for visualization and analysis of interconnection network.Three parameters, betweenness centrality (BC),closeness centrality (CC) and degree centrality (DC),were employed to evaluate topological features of PPI network.The corresponding median values of each parameter were deemed to be the threshold values of the hub genes in the network analysis[26].
Construction of “compounds-hub genes-pathways”Network
The network construction, analysis and visualization were carried out using the Cytoscape 3.7.1 platform(https://cytoscape.org/) [28].The pathway information of targets was obtained according to the result of KEGG pathway enrichment.In the network diagram,compounds, hub genes and pathways present in the form of nodes, and intermolecular interactions among them were indicated by edges.Meanwhile, “network analysis”was used to analyze the whole network.
GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses
The Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery [29](DAVID,https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) was usually preferred to accomplish GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.Ordinarily, the composition of Go analysis includes three parts: biological process (BP),molecular function (MF) and cell component (CC).Moreover, the KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were used for identifying the biological functions and candidate targets.In this research, the results of GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were processed with R package.
Molecular docking stimulation
CB-Dock (http://cao.labshare.cn/cb-dock/), a friendly online molecular docking tool, predicts the binding sites of a given protein and calculates the center and size of the pocket, which was performed with AutoDock Vina.PDB files of the top 5 compounds in“compounds-hub genes-pathways” network and ligand files in SDF formats in the top 5 targets in PPI network were processed with CB-Dock to evaluate the binding behaviors.[30].
Results
Identification of Active compounds
In the current work, a total of 232 chemical constituents were identified from Chemistry Database,TCMSP and literature mining.Even if any TCM formulation contains a variety of components, only a few components have the characteristics of pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic.Therefore,62 active compounds were filtered out via three ADME-related models indicated above.The detail information was shown in Table 1 and the herbs-compounds network was built as Figure 1.
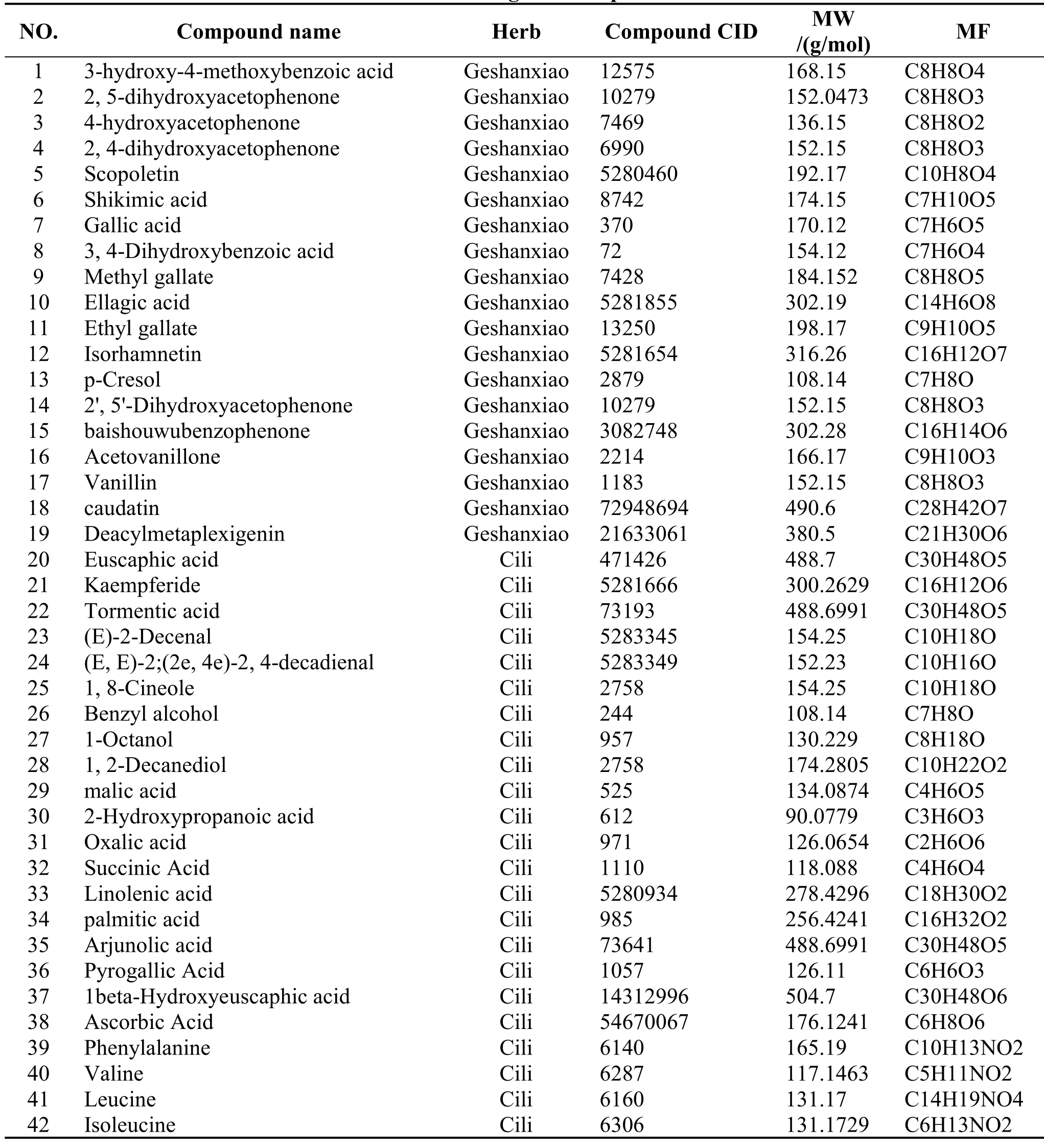
Table 1 Pharmaceutical ingredients specific information.
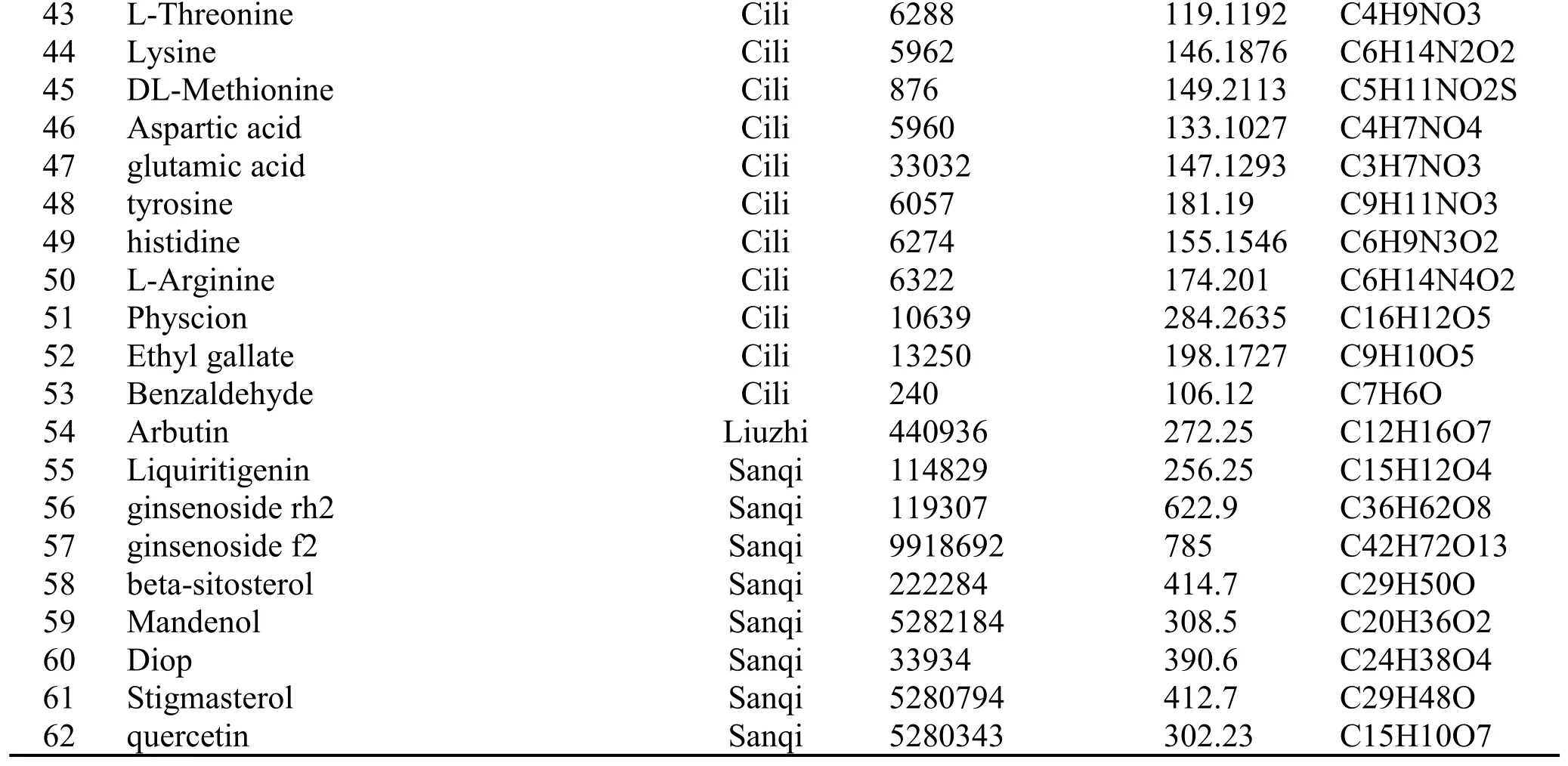
43 L-Threonine Cili 6288 119.1192 C4H9NO3 44 Lysine Cili 5962 146.1876 C6H14N2O2 45 DL-Methionine Cili 876 149.2113 C5H11NO2S 46 Aspartic acid Cili 5960 133.1027 C4H7NO4 47 glutamic acid Cili 33032 147.1293 C3H7NO3 48 tyrosine Cili 6057 181.19 C9H11NO3 49 histidine Cili 6274 155.1546 C6H9N3O2 50 L-Arginine Cili 6322 174.201 C6H14N4O2 51 Physcion Cili 10639 284.2635 C16H12O5 52 Ethyl gallate Cili 13250 198.1727 C9H10O5 53 Benzaldehyde Cili 240 106.12 C7H6O 54 Arbutin Liuzhi 440936 272.25 C12H16O7 55 Liquiritigenin Sanqi 114829 256.25 C15H12O4 56 ginsenoside rh2 Sanqi 119307 622.9 C36H62O8 57 ginsenoside f2 Sanqi 9918692 785 C42H72O13 58 beta-sitosterol Sanqi 222284 414.7 C29H50O 59 Mandenol Sanqi 5282184 308.5 C20H36O2 60 Diop Sanqi 33934 390.6 C24H38O4 61 Stigmasterol Sanqi 5280794 412.7 C29H48O 62 quercetin Sanqi 5280343 302.23 C15H10O7
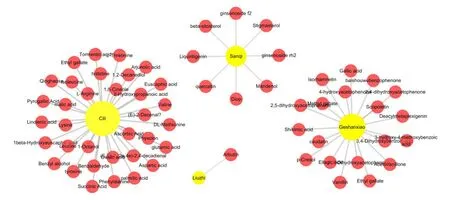
Figure 1 Herbs-Compounds network.The yellow nodes represent herbs in XHC, and the red nodes represent active compounds.The edges represent the relationship between them.
PPI Network for XHC in Treating FD
2817 targets associated with FD coming from the OMIM, GeneCards and TTD databases, and 547 related targets of the 62 chemical components were selected for preparation of 241 common targets (see the supplement for more information), which were regarded as the related targets of XHC in treating FD(see Figure 2).
241 common targets were early screened by string website with 233 nodes and 1711 edges remained.Subsequently, PPI network of those 233 nodes established in STRING database was later processed to screen key targets based on three major parameters of BC,CC and DC.The third screening ended up with 14 big hub nodes and 72 edges (Figure 3), which included AKT1, MAPK1, STAT3, EGFR, IL6,MAPK3, VEGFA, SRC, MAPK8, PIK3R1, PIK3CA,JUN, TNF and CCND1 (Table 2).When the 14 hub nodes and the other 219 nodes are sorted in descending order and viewed in the network, AKT1(degree=43),MAPK1 (degree=42),STAT3(degree=41), EGFR (degree=40), IL6 (degree=39),MAPK3 (degree=37), VEGFA (degree=37) and SRC(degree=36) were key targets in this network (Figure 4).
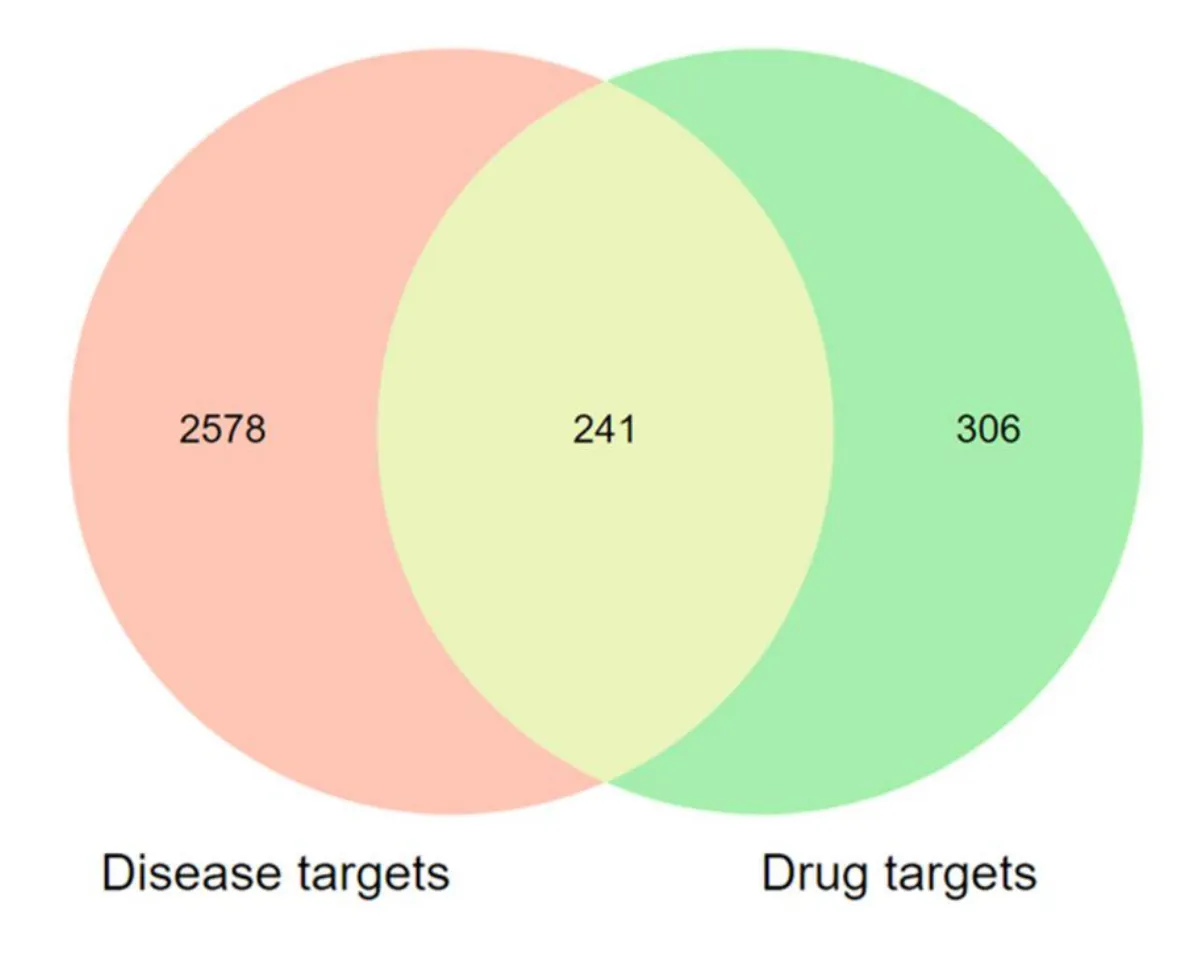
Figure 2 The venn diagram of the targets both in functional dyspepsia targets and Xiaopi Hewei Capsule targets.
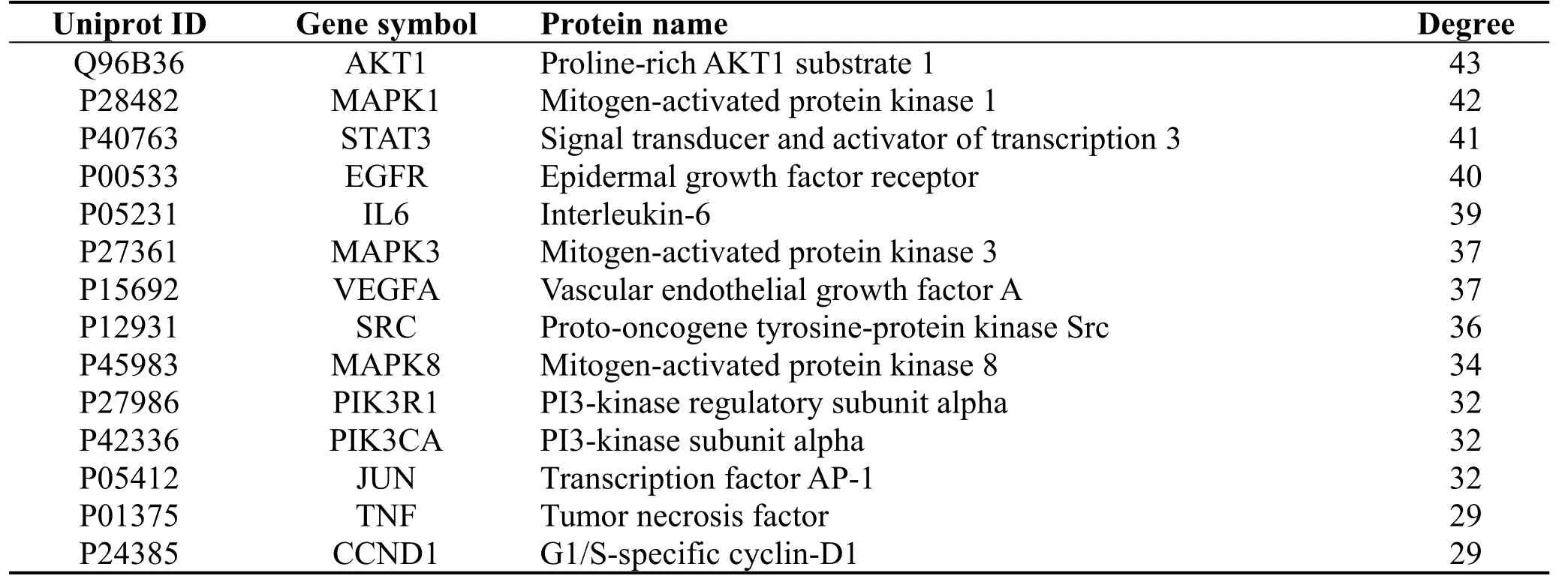
Table 2 Information of 14 hub targrts
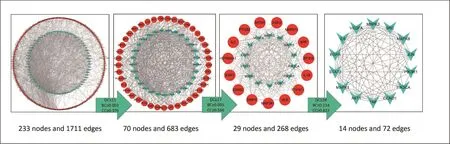
Figure 3 The process of topological screening for the PPI network
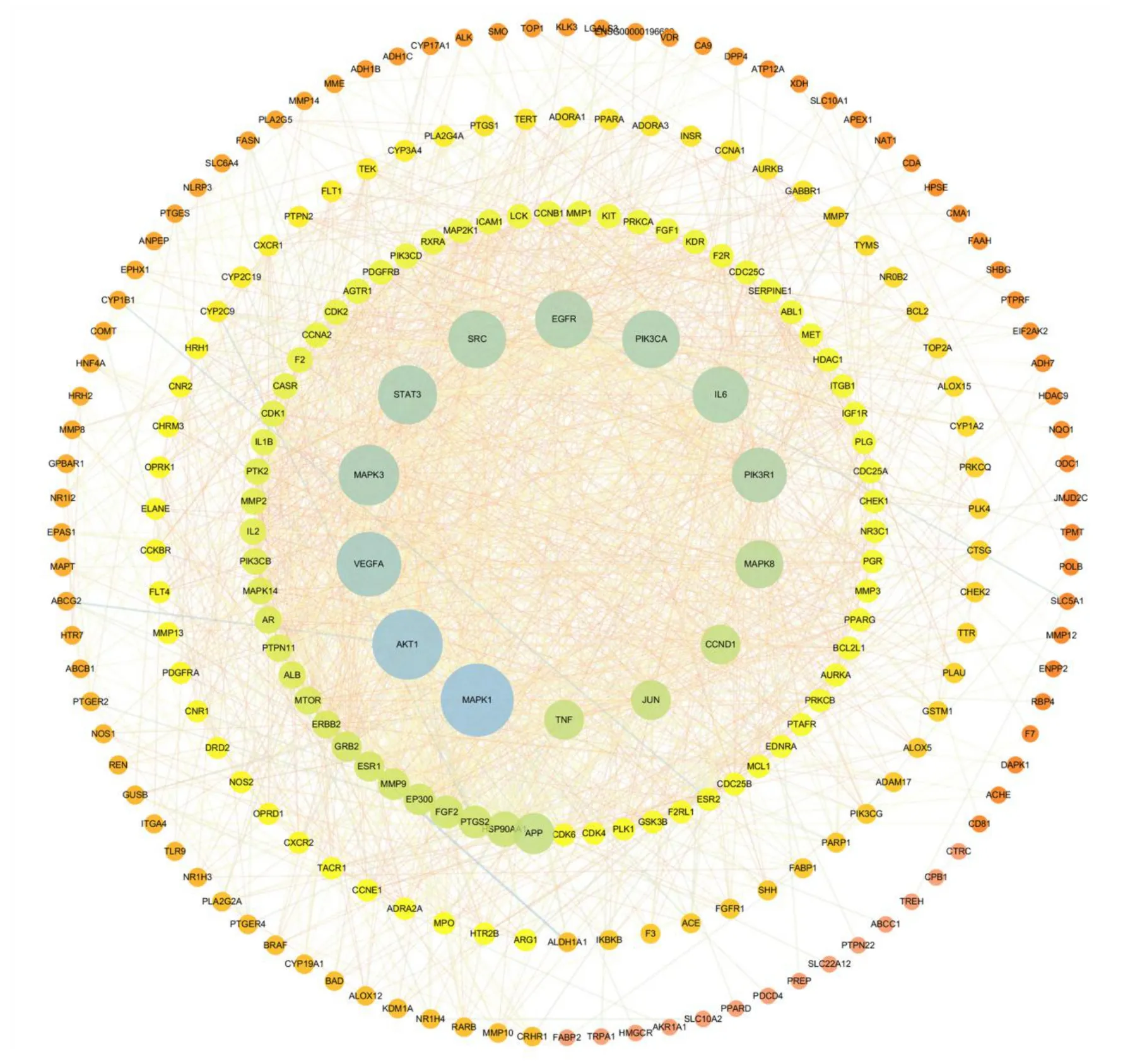
Figure 4 The PPI network.The node color changes from orange to blue reflect the degree value changes from low to high in the network.
GO and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analyses
GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of selected 233 targets were carry out in the DAVID system, which end up with 893 GO terms (BP: 652;CC: 75; MF: 166) and 131 KEGG pathways.The results were visualized by R package (Figure 5).Biological process (BP) mainly included oxidation-reduction process, inflammatory response,protein phosphorylation, positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade, etc.Cell composition (CC) was composed of plasma membrane, cytosol, integral component of plasma membrane, extracellular exosome,cell membrane,etc.The results of molecular function (MF) suggested these targets were mostly involved receptor activity, kinase activity, RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, protein binding,drug binding,etc.
In addition, KEGG enrichment analysis has identified much pathways of potential target genes,such as, FOXO signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, cAMP signaling pathway and Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.Meanwhile, 15 pathways were screened out based on the threshold of FDR<0.05 to establish the “compounds-hub genes-pathways”network.
“compounds-hub genes-pathways”Network
The “compounds-hub genes-pathways” network map of XHC was established using Cytoscape, which shows the relationship among 28 active components,14 hub nodes and 15 key pathways(Figure 6).The top five compounds were caudatin, kaempferide,quercetin, isorhamnetin, and ellagic acid in descending order of degree, indicating the crucial roles of these components in treating FD.
Docking stimulation verification
The top 5 compounds in “compounds-hub genes-pathways” network were docked with the respective top 5 targets in PPI network, respectively.Ligands and proteins were represented by licorices and a cartoon chains respectively.It is generally assumed that the highest cavities’size and the lowest Vina score indicate a strong binding ability between a protein and a compound.Thus, the Vina scores and cavities’ sizes from CB-Dock were selected as the group representative (Table 3 and Table 4).According to the Figure 7, all the bioactive components of XHC showed a good binding with the hub genes,suggesting that the process of treating FD with XHC may be achieved by these hub genes,namely,AKT1,MAPK1,STAT3,EGFR and IL-6.
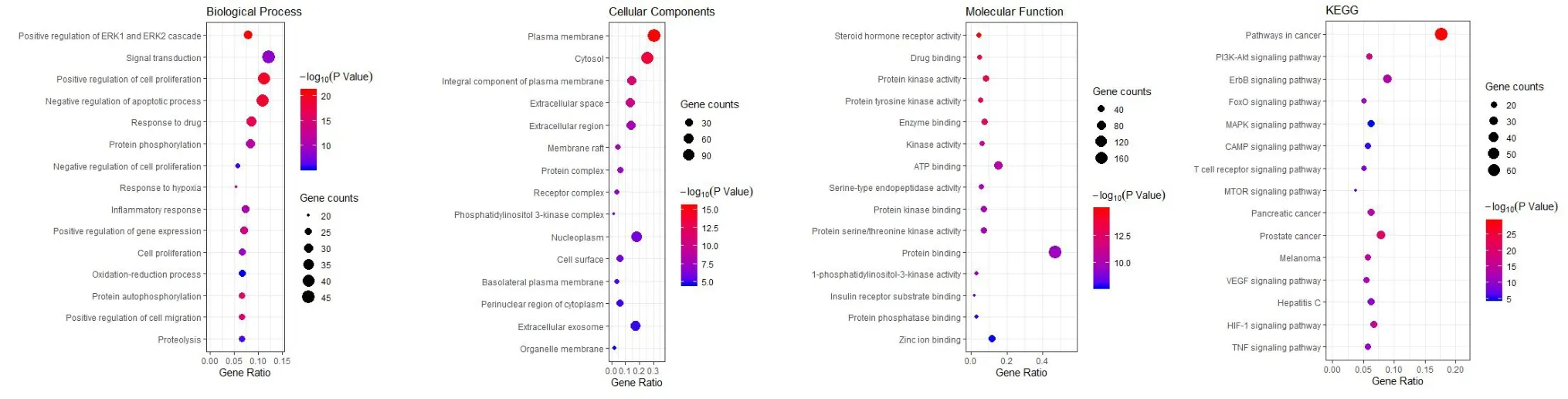
Figure 5 GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses.
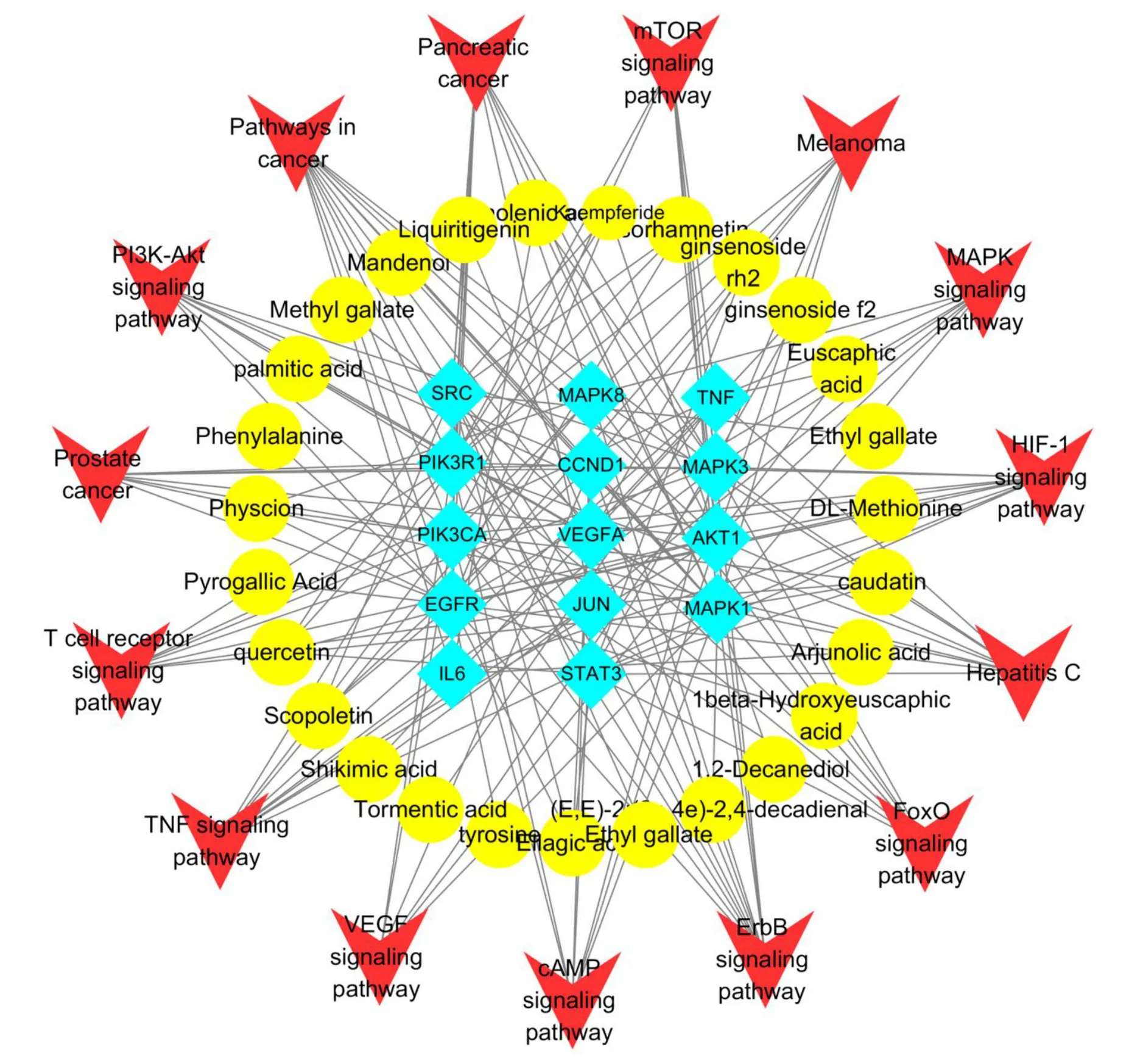
Figure 6 The “compounds-hub genes-pathways” network.The blue diamonds represent the hub genes, the yellow round nodes represent the active compounds,and the red nodes represent the related pathways
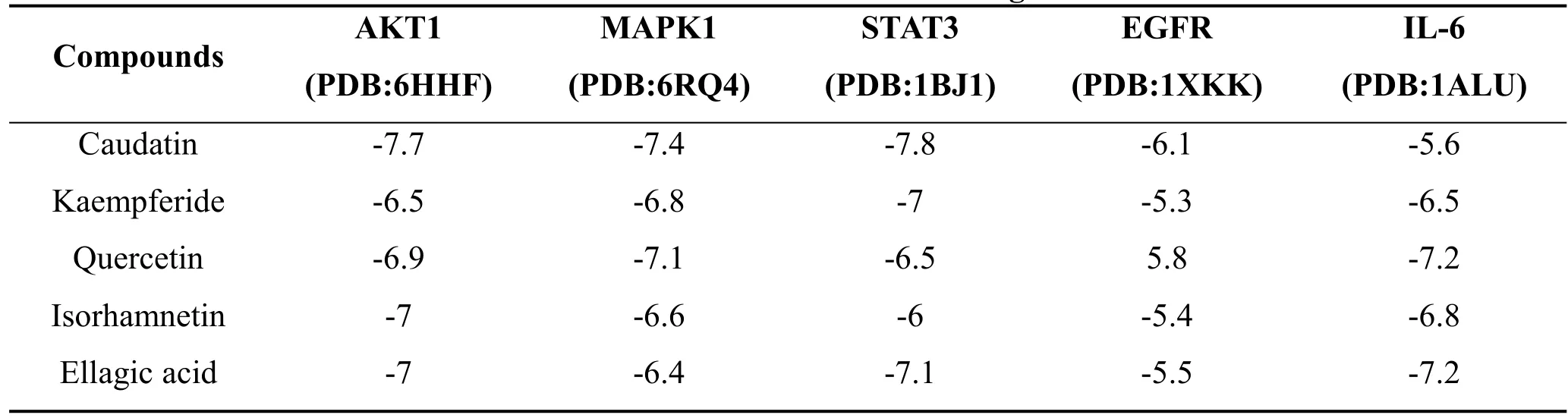
Table 3 Vina scores of molecular docking studies
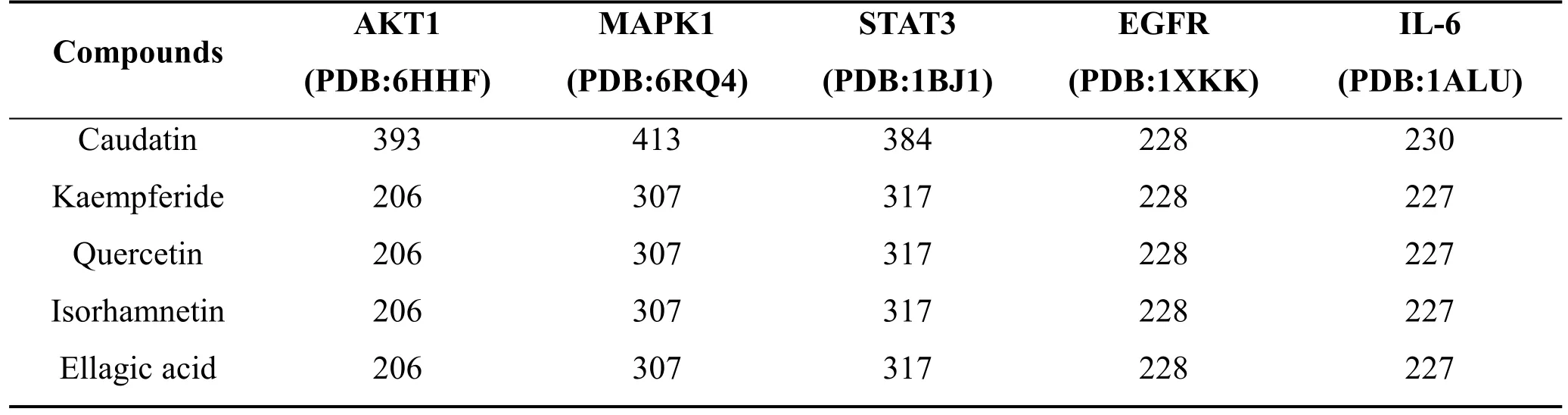
Table 4 Cavities’sizes of molecular docking studies
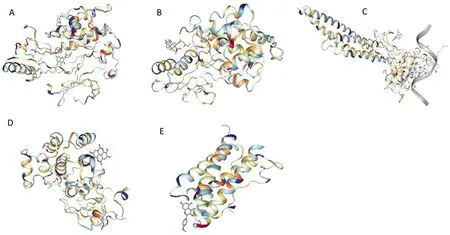
Figure 7 Molecular docking stimulation of active compound-hub gene.(A)Quercetin to AKT1;(B)caudatin to MAPK1;(C)isorhamnetin to STAT3;(D)ellagic acid to EGFR;(E)kaempferide to IL-6.
Discussion
At present, the incidence of FD is increasing year by year, which seriously threatens people's health and quality of life [31].XHC has been used in the treatment of FD, but its mechanism is still unclear.Therefore, it is of great significance to study the molecular mechanism of XHC in the treatment of FD.
The causes of FD mainly include dyspepsia,Helicobacter pylori infection, depression, etc [32],which can generate inflammation, gastrointestinal movement dysfunction,etc.According the analyses of biological process, we found the oxidation-reduction process has previously been shown to correlate with the pathogenesis of depression [33] and inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (such as H.pylori infection and IBD) [34].Moreover, the role of inflammatory response in FD is extensive, such as anti-depression [35], eradicating HP infection and improving dyspepsia [36].The abnormalities of ERK1/2 signaling may be crucial to the vulnerability of depression, moreover, the ERK activity continuously or transiently may serve as a negative regulator of vascular inflammation by suppressing endothelial NF-κB activation, and play an anti-inflammatory role[37].
Based on the results of KEGG pathway enrichment analyses, we known MAPK signaling pathway and cAMP signaling pathway were closely related to emotional regulation.ErbB signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the inflammatory reaction process, and epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection was related to HP infection and therapy.
According the “compounds-hub genes-pathways”network, five active compounds with the highest degree value were screened out.Among them,caudatin exhibits antioxidants, neuroprotective [38],immunoregulation and inhibition of angiogenesis actions [39].Quercetin has anti-depression [40],anti-inflammatory effect [41].Kaempferide exhibits antioxidants and neuroprotective activities [42].Ellagic acid exhibits strong activity at eradication of HP, protection of stomach and reduction of the secretion of gastric acid [43].Isorhamnetin plays a role in anti-inflammatory and antibacterial [44].To conclude, these active ingredients are the material basis of XHC in treating functional dyspepsia.
Therefore, the results certificated that the potential mechanism of treating functional dyspepsia of XHC is probably connected to its participant in anti-depression,inflammatory reaction and eradicating HP infection.
Anti-depression
Previous research showed that psychiatric factors may increase the likelihood of FD, and eighty percent of patients with FD have anxiety and depressive mood[45].MAPK1, mitogen activated protein kinase 1, is an important molecule in MAPK signaling pathway[46].Experimental verification showed that the occurrence of depression may be concerned with activation of MAPK signaling pathway, and MAPK1 pathway is closely related to the pathological mechanism of depression [47].Furthermore,inflammatory cytokines play an important role in the development of depression [48].Clinical studies also showed that the expression of IL-1β and IL-6 was up-regulated in patients with depression[49].Besides,AKT1 gene is associated with antidepressant treatment response in patients with depressive disorders[50].
XHC’s regulative effect on depression is possibly achieved by the inhibitory effect of caudatin,quercetin and kaempferide.For instance, caudatin participates in MAPK signaling pathway and down-regulate MAPK1 directly or indirectly, so as to achieve the purpose of antidepressant.Also, quercetin and kaempferol inhibit the expression of AKT1 to affect downstream targets, which further regulate the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.Besides, quercetin is capable of intervening RAS -MAPK pathway via acting on MAPK1, further participating in regulation of anti-depression[51,52].
Inflammation reaction
In the pathogenesis of FD, inflammatory cells will proliferate and differentiate on account of the damage of gut barrier function.The research suggested that SRC may promote the occurrence of intestinal inflammation by mediating the release of inflammatory factors, inducing the homing and activation of inflammatory cells, and angiogenesis[53].Meanwhile, VEGFA contributes significantly in the pathogenesis of FD, and overexpression of VEGFA will mediate inflammation and promote angiogenesis [54].A further investigation showed that SRC can increased VEGFA expression in a mechanism that implicates the EGFR/ErbB signal pathway [55].Jun participates in inflammation reaction through ErbB signal pathway by regulating angiogenesis [56].It is suggested that stimulation of Jun gene may consequently activate the expression of VEGFA [57].Furthermore, AKT1 plays an important role in cell survival, growth and proliferation, which was controled by PI3K directly through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway that participates in the release of inflammatory mediators and the proliferation of inflammatory cells[58].
These results suggest that targets could produce a combination effect on inflammation reaction.It is possible that the formula of XHC can exert the effect on inflammatory of FD by inhibiting the expression level of SRC and JUN and then regulating negatively the activation of VEGFA.Also, quercetin and isorhamnetin inhibit the expression of AKT1, thus realize the alleviation of inflammatory reaction.
Eradicating HP infection
HP was overexpressed in the gastric mucosa of patients with FD [59].Several studies have demonstrated that the changes of gastric motility and sensory function caused by HP infection are one of the crucial pathological foundations of FD.EGF(epidermal growth factor) can promote the proliferation and migration of epithelial cells, which plays a functional role in the reconstruction of the basal surface of ulcer and the filling of mucosal defects[60].Moreover,EGFR,also known as receptor tyrosine-protein kinase (RPTK), has the activity of tyrosine-protein kinase (PTK).Vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA), an exocrine protein of HP, can in some degrees stop the up-regulation effect of EGF on the EGFR expression, and affect the proliferation and repair of gastric mucosal cells[61].
In XHC, compounds that act on EGFR and EGF include: kaempferide, ellagic acid, isorhamnetin,phenylalanine and tyrosine.Among them, ellagic acid and isorhamnetin can not only act on inflammatory,but also the eradicator of HP.Phenylalanine and tyrosine, as aromatic amino acids, can regulate the proliferation and differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells and promate the secretion of gastrointestinal hormones [62].Hence, bioactive compounds of XHC participate in treating FD by up-regulating of the EGFR via Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection, and then promoting the proliferation and repairing of gastric mucosal cells[63].
Conclusion
In summary, the study highlights that XHC has significant effects on FD via various bioactive targets and compounds.The mechanism of XHC in treating FD connecting to the process of anti-depression,inflammatory reaction and HP eradication was revealed by the approach of network pharmacology and molecular docking.It has a significant value to provide theoretical basis for clinical treatment of FD and promote the development of XHC.Regrettably,Liuzhi (Salix babylonica L.), as an adjuvant of prescription, has few active ingredients and been excluded by molecular docking, which may be due to limited literatures and complicated screening conditions and will be discussed further.
Supporting Information
Additional supporting information will be found online in the Supporting Information section.
Acknowledgments
RHL and YKS conceived and designed the whole study and obtained funding.YS, STN, JQW, HW and CNZ performed the data analysis.RHL and YXQ wrote the manuscript.All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2020年4期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2020年4期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Network-pharmacology and molecular docking-based investigation of mechanism of Sophora flavescens on cancer and inflammation
- Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on diabetic retinopathy: a meta-analysis and systematic review
- Efficacy and safety of Shen Zhi Ling oral liquid (a Chinese patent) for Alzheimer's disease:A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- A new sesquiterpenoidal glucoside from the roots of Paeonia lactiflora
- Efficacy and safety of the combination of Liushen capsules and Arbidol in the treatment of COVID-19:protocol for a randomized,multi-center pilot study
