Botulinum toxin type A combined with robot-assisted training for upper limb spasticity and motor function after stroke:a case report
Min Zhang,Hong You*,Yong-Ping Li,Ming-Ming Wen
1Sino-French Department of Neurological Rehabilitation,Gansu Provincial Hospital,Lanzhou 730000,China.
Abstract
Keywords:Botulinum toxin type A,Robot,Spasticity,Motor function,Stroke
Background
Hemiplegia spasticity is one of the most common disability manifestations of stroke patients, which is mainly manifested by increased muscle tension of upper and lower limbs on the affected side,accompanied by symptoms such as pain, muscular atrophy and limb motor dysfunction.It is easy to cause anxiety and depression of patients, which seriously affects the daily life and rehabilitation efficacy of patients[1].
Traditional rehabilitation training (such as Bobath neurodevelopmental techniques, functional mobility training,oral medications,etc.)is the main treatment to help restore the limbs function, while it is also time consuming and labor-intensive processes.Moreover,traditional rehabilitation training is slow-acting and more appropriate for treating chronic ailments, which may lead to miss the best time for treatment [2, 3].At present, in order to improve the upper limb motor function and training enthusiasm of stroke patients,besides relying on therapists to carry out some traditional rehabilitation training, robot-assisted training has been gradually applied to clinical practice,it uses computer virtual software to create a virtual space close to the life environment for patients, and trains stroke patients through sight, hearing and touch,so as to promote the recovery of their upper limb function[4–8].
Studies have shown that Botulinum toxin type A(BTX-A) therapy can improve upper limb spasticity,relieve pain and improve joint mobility after stroke,and at the same time, it takes effect faster and lasts longer than traditional rehabilitation training, and shortens the rehabilitation process [9–11].However,the effect of robot-assisted training in combination with BTX-A therapy on upper limb spasticity and motor function after stroke is not clear.Thus, the purpose of this study is to report a case describing the effects of BTX-A in combination with robot-assisted training on upper limb spasticity and motor function in stroke patient.
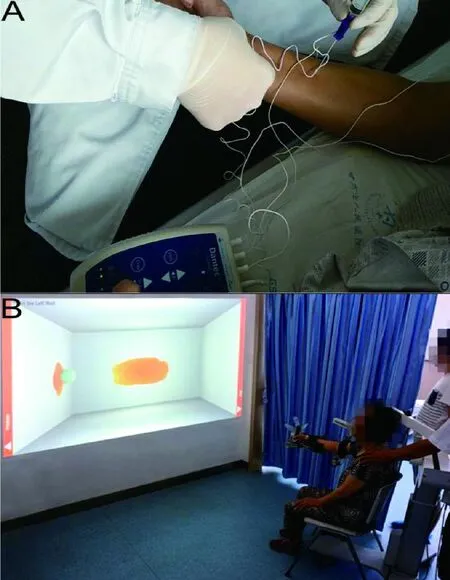
Figure 1 Patient received the combination of BTX-A(A)and robot-assisted training treatment(B)
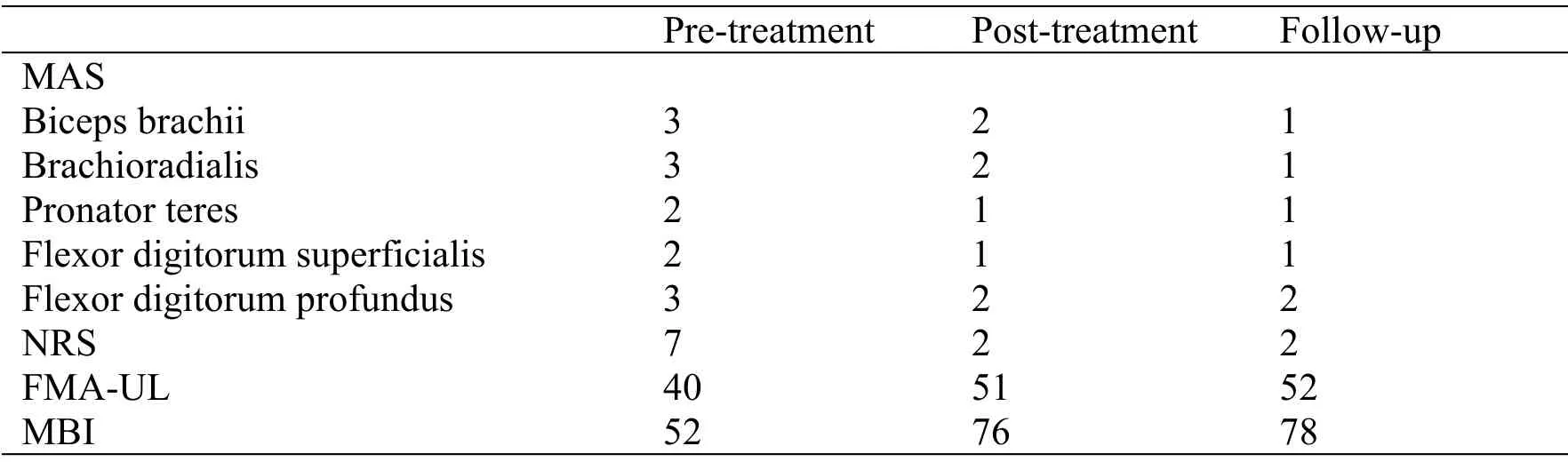
Table 1 The effects of the combination of BTX-A and robot-assisted training treatment
Case description
On May 3, 2018, a 53-year-middle aged man, went to the Sino-French Department of Neurological Rehabilitation of Gansu Provincial Hospital due to right hemiplegia and severe spasticity of the upper limb, presented with left basal ganglia hemorrhage from 3 months ago.
After admission, regular physical examination was conducted, the patient was consciousness but had speech deficient, with T: 36.3℃, P: 93 times/min, R:19 times/min, BP: 158/98 mmHg; both pupils equal in size and diameter about 3 mm, sensitive to light reflexes, bilateral eye movements in all directions freely in place, no nystagmus or diplopia, soft neck without resistance, bilateral nasolabial sulcus symmetrical, tongue extended and centered, normal pharyngeal reflexes, right upper limb muscle strength was grade III, right lower limb muscle strength was grade IV, left upper and lower limb muscle strength was grade V, right upper limb muscle tone was increased, limb tendon reflexes were normal, and bilateral pathological signs were negative.
Cranial CT showed left basal ganglia hemorrhagic foci absorbed.
The patient had a history of hypertensive disease and cerebral hemorrhage, and took oral amlodipine for blood pressure control and mecobalamin for neuroprotection(regular dose).
The treatment of BTX-A (Institute of Biological products, Lanzhou, China) was injected in different upper limb muscles (Figure 1A).Detail as follows:Biceps brachii (100 unit), Brachioradialis (60 unit),Pronator teres (40 unit), Flexor digitorum superficialis(40 unit), Flexor digitorum profundus (60 unit).Robot-assisted training started the day after the BTX-A injection and continued for twice a day(30 minutes per time),5 times a week for a total period of 3 weeks.The robot (Hocoma Inc, Switzerland.Figure 1B) is a 3-dimensional (3D), multi-joint rehabilitation training and evaluation system that can provide accurate gravity compensation, its training program is 3D motion execution based on virtual reality, include movements of shoulder, elbow and wrist joints, and hand grasping, which are similar to real activity of daily living(ADL)action.
Assessment of the patients response to therapy was monitored by the use of the following assessment methods: the modified Ashworth scale (MAS) to measure spasticity grade [12, 13], Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) to measure pain intensity [14, 15], the Fugl-Meyer assessment in upper limb (FMA-UL) to measure motor function [16], and the modified barthel index [17] (MBI) to measure ADL.Evaluations were performed before the BTX-A injection combined with robot-assisted training, after combined treatment and follow-up data were taken 3 months after discharge,the results of evaluations showed that the combined therapy had greatly clinical improvement in the MAS,NRS, FMA-UL, MBI of this stroke patient (Table 1).In concrete terms, there was decreased in pain and spasticity, increased in motor function and ADL that were maintained up to three-month follow-up after discharge.
Discussion
In this case report,we observed the improvements of a post-stroke patient after 3 weeks of robot-assisted in combination with BTX-A therapy.In previous study,Botulinum toxin type A was found to be safe and efficacious for the treatment of poststroke limb spasticity [18–21].In addition, it had reported the effectiveness of BTX-A on the upper limb pain[22–24].These outcomes on spasticity and pain are similar to this case report.Robot-assisted training can promote the recovery of the upper limb motor function and ADL in this study.We considered that robot-assisted training system can provide upper limb support and increase sensory information input based on virtual reality, thus patient can easily carry out independent movement, and effectively improve the upper limb motor ability and ADL through active training, some similar studies have the same viewpoint [25, 26].About the effects of robot-assisted training on spasticity, the improvements may be due to counteracting the influence of gravity on the upper limb active training, reducing the requirements of the patients' active muscle movement function and physical strength, making the active muscle and the antagonistic muscle repeatedly balance training,inhibiting the excessive increase of muscle tension and the occurrence of abnormal movement mode [27].However, further studies are necessary to demonstrate this theory for robot-assisted training.After 3 months of follow-up period, it was considered to have reached a platform period of upper limb function at discharge.As this is a case report, the study results are universal,but they can expand the number of cases and select the control group to further test the combined treatment method in clinical trials.
Conclusion
The combined BTX-A and robot-assisted training treatment had an obvious improvement in upper limb spasticity, pain, motor function and ADL.Therefore,the combination therapy is worthy of further application in patients with spastic stroke.
