研究并探讨64排螺旋CT低剂量扫描技术在肺结节诊断中的应用效果
王勇敢

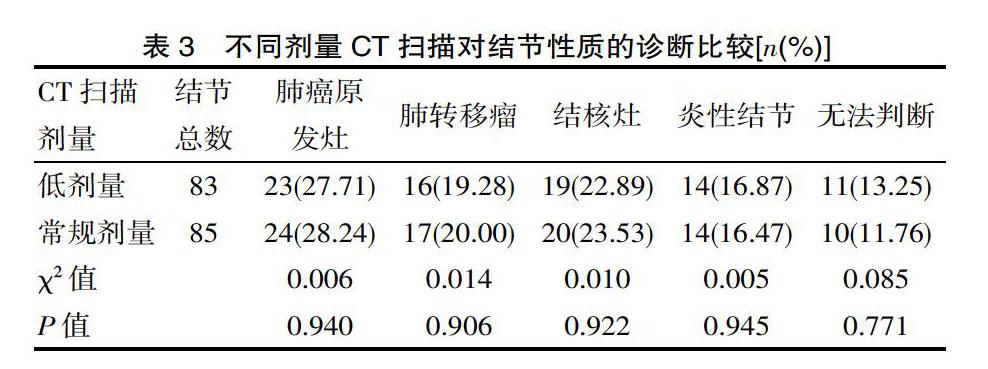

[摘要] 目的 探讨64排螺旋CT低剂量扫描技术诊断肺结节的临床价值。方法 方便选取该院自2018年1月—2019年1月诊治的52例肺部结节患者为观察对象,采用64排螺旋CT常规剂量(200 mA)与低剂量(40 mA)进行扫描,比较常规剂量和低剂量检查结果。结果 低剂量CT扫描微结节、小结节、大结节个数、总个数分别为12个、41个、30个、83个,常规剂量CT扫描分别为14个、41个、30个、85个,两者比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.130、0.023、0.013、P=0.718、0.880、0.908)。低剂量与常规剂量下肺部结节分叶征、毛刺征、血管集束征、胸膜凹陷征、钙化、空洞、支气管征比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);低剂量CT扫描对结节性质诊断中,肺癌原发灶、肺转移瘤、结核灶、炎性结节、无法判断结节个数分别为23个、16个、19个、14个、11个,常规剂量CT扫描分别为24个、17个、20个、14个、10个,两者比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.006、0.014、0.010、0.005,0.085,P=0.940、0.906、0.922、0.945、0.771)。结论 64排螺旋CT进行40 mA低剂量扫描对肺结节检出率、影像学特征、结节性质诊断与常规剂量相当,而射线剂量显著低于常规剂量,安全系数更高,有望成为筛查和诊断肺结节的有效手段。
[关键词] 肺结节;64排螺旋CT;低剂量;影像特征;结节性质;诊断
[Abstract] Objective To explore the clinical value of 64-slice spiral CT low-dose scanning technology in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules. Methods Convenient select a total of 52 patients with pulmonary nodules in the hospital from January 2018 to January 2019 were selected as observation objects, and the 64-slice spiral CT conventional dose (200 mA) and low dose (40 mA) were scanned to compare test results of the conventional dose and the low dose. Results The number and total number of micronodules, small nodules, and large nodules in low-dose CT scans were 12, 41, 30, and 83, and conventional dose CT scans were 14, 41, and 30, 85, there is no statistically significant difference between the two (χ2=0.130, 0.023, 0.013, P=0.718, 0.880, 0.908). There was no significant difference between low-dose and regular-dose lung nodule sign, burr sign, vascular bundle sign, pleural depression sign, calcification, cavity, and bronchus sign (P>0.05). In the diagnosis of nodular properties, the number of primary lung cancer, lung metastases, tuberculosis, inflammatory nodules, and nodules that cannot be judged were 23, 16, 19, 14, and 11, respectively. Conventional-dose CT scans were 24, 17, 20, 14, 10, and there was no significant difference between the two(χ2=0.006, 0.014, 0.010, 0.005, 0.085, P=0.940, 0.906, 0.922, 0.945, 0.771). Conclusion The 64-slice spiral CT with 40mA low-dose scan has the same detection rate, imaging characteristics, and nodular diagnosis of pulmonary nodules as conventional doses, but the radiation dose is significantly lower than conventional doses, and the safety factor is higher. It is expected to become a screening and effective means for diagnosis of pulmonary nodules.
[Key words] Pulmonary nodules; 64-slice spiral CT; Low dose; Imaging characteristics; Nodular properties; Diagnosis
随着医学技术的发作,CT扫描技术不断成熟,在临床中得到广泛应用,当前CT扫描已成为肺结节筛查和诊断的重要方法。相關研究显示,肺癌高危人群每年肺结节发现率达1.3%左右,而结节为恶性的比例高达43%左右[1]。64排螺旋CT具有空间分辨率高、成像质量高的特点,能够发现微小病变。然而64排螺旋CT常规扫描剂量较大,人们接受度不高,在人群筛查中应用受限[2]。既往研究表明低剂量CT扫描在普通人群健康体检中亦能够较好地检出肺结节[3]。为进一步探讨64排螺旋CT低剂量扫描在肺结节检出、影像学特点、结节性质判断中的应用价值,该研究方便选取2018年1月—2019年1月52例CT常规扫描证实存在肺结节的患者,进行200 mA常规剂量扫描、40 mA低剂量扫描,并进行比较,现报道如下。

