Long-term efficacy of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin chemotherapy on stage III colon cancer:A meta-analysis
Hong-Tao Fu,Ying-Ying Xu,Jing-Jing Tian,Jia-Xin Fu,Shao-Ling Nie,Yan-Yan Tang,Ping Chen,Liang Zong
Abstract
BACKGROUND
Many clinical studies for the long-term survival or efficacy of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin(XELOX)in colon cancer have already been studied,but its clinical benefit is controversial.
AIM
To evaluate the long-term efficacy of XELOX regimen in comparison with other adjuvant chemotherapy protocols in colon cancer.
METHODS
By searching the PubMed,EMBASE and Cochrane databases,a total of 12 randomized controlled trials involving 6698 stage III colon cancer cases(XELOX protocol:n=3298 cases;other adjuvant chemotherapy protocol:n=3268 cases)were included.The parameter outcomes included the overall survival and the disease-free survival.The quality control of selected literature was based on the Jadad scale and the GRADE system.
RESULTS
In comparison to other adjuvant chemotherapy regimen,XELOX regimen showed a better overall survival(odds ratio=1.29,95% confidence interval:1.15-1.44,P < 0.0001)and a better disease-free survival(odds ratio=1.32,95%confidence interval:1.18-1.46,P < 0.0001)for colon cancer patients,suggesting the XELOX regimen can be a good option for postoperative treatment of stage III colon cancer.
CONCLUSION
The XELOX regimen can be a preferred option for adjuvant treatment of stage III colon cancer after surgery.
Key words:Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin chemotherapy;Colon cancer;Meta-analysis;Long-term effect
INTRODUCTION
Colorectal cancer(CRC)accounts for 9% of all cancers worldwide.It is the second most common cancer in women and the third most frequent cancer in men.More than 70% of the deaths associated with CRC are caused by metastasis to the liver.Although surgery may be potentially curable,less than 25% of cases can be managed with a recurrence rate of up to 70%[1].The purpose of colon cancer treatment is to cure locally and to prevent metastasis and recurrence.Therefore,in the local excision of colon cancer at the same time,the treatment should be according to individual condition,and chemotherapy is an important method that is based on the patient’s condition,surgical situation and clinical stage of appropriate postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy.
Many clinical studies for the long-term survival benefit or efficacy of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin(XELOX)in colon cancer have already been studied[2-4],but its clinical benefit is controversial[5].Since the 1990s,the introduction of irinotecan or oxaliplatin has extended the spectrum of therapeutic options.The combination of oxaliplatin or irinotecan with 5-fluorouracil(5-FU)plus leucovorin(LV or FA)has been considered the standard regimen for first-line treatment of metastatic CRC.However,this is an inconvenient therapeutic option due to the requirement for continuous vascular infusion of 5-FU.A retrospective study on XELOX plus bevacizumabvsLV plus 5-FU plus irinotecan(also known as FOLFIRI)plus bevacizumab treatment for metastatic colon cancer reported that XELOX plus bevacizumab was more effective in response rate and overall survival(OS)compared with LV plus 5-FU plus irinotecan plus bevacizumab[6].
Capecitabine is an orally administered fluoropyrimidine that was rationally designed to generate 5-FU preferentially at the tumor site.Capecitabine demonstrated a safety profile superior to that of 5-FU/LV,with a significantly lower incidence of diarrhea,stomatitis,nausea,alopecia and grade 3/4 neutropenia.Also,oral administration of capecitabine simplifies chemotherapy and provides convenient outpatient therapy.Because capecitabine has been adopted as a substitute for infused 5-FU/LV to overcome the inconvenience of 5-FU,subsequent data have found XELOX(also known as CAPOX)to be a comparable therapeutic regimen to infused 5-FU/LV plus oxaliplatin(known as FOLFOX-4 or FUOX).In the Loreeet al[7]study,XELOX and FOLFOX were compared in the treatment of colon cancer.The results showed that XELOX may be associated with improved disease-free survival(DFS)despite greater toxicities and reduced adjuvant chemotherapy duration to 3 mo.In a safety analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III colon cancer after radical resection of stage III colon cancer,mFOLFOX6/XELOX regimens are acceptable[8].
Randomized phase III trials demonstrated that outcomes using first-line XELOX are comparable with those achieved using continuous infusion of 5-FU and FOLFOX.There are many chemotherapy options for advanced CRC,and the long-term benefit is uncertain.Combining XELOX is advantageous for the reasons as follows:Synergistic effects,no overlapping toxicities,easy to administer and outpatient management[9-12].XELOX has been studied extensively in rectal cancer where the standard therapy is XELOX plus radiation therapy.To determine the efficacy of XELOX in colon cancer,the long-term efficacy of capecitabine combined with oxaliplatin(XELOX regimen)in comparison with other adjuvant chemotherapy protocols was evaluated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This meta-analysis is in terms of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses(PRISMA)2009 declaration.
Search strategy
Two researchers independently retrieved randomized controlled trials(RCT)articles involved in oxaliplatin combined with capecitabine in CRC published in PubMed,EMBASE,Cochrane,web of science,clinical trial and China National Knowledge Infrastructure databases from 1991 to August 2017.The retrieval languages were Chinese and English.The retrieval was performed using the following keywords.English search terms for:(PubMed):Search(((Colonic Neoplasms [MeSH Terms])OR((((((((((Colonic Neoplasm [Title/Abstract])OR Colon Neoplasm* [Title/Abstract])OR Neoplasm*,Colonic)OR Neoplasm*,Colon [Title/Abstract])OR Cancer of Colon[Title/Abstract])OR Cancer of the Colon [Title/Abstract])OR Colonic Cancer*[Title/Abstract])OR Cancer*,Colonic [Title/Abstract])OR Colon Cancer*[Title/Abstract])OR Cancer*,Colon [Title/Abstract])))AND(((((((((((ECX)[Title/Abstract] OR XELOX)[Title/Abstract] OR Xeloda)[Title/Abstract] OR Capecitabine [Title/Abstract]))ORN(4)- pentyloxycarbonyl – 5’ - deoxy- 5-fluorocytidine [Title/Abstract])OR Capecitabine))OR Capecitabine [MeSH Terms])AND(((oxaliplatin [MeSH Terms])OR oxaliplatin [Title/Abstract])OR((((((((((((((((1,2 - diamminocyclohexane(trans-1)oxolatoplatinum(II)[Title/Abstract])OR oxalato-(1,2-cyclohexanediamine)platinum II [Title/Abstract])OR L-OHPcpd[Title/Abstract])OR oxaliplatine [Title/Abstract])OR1,2-diaminocyclohexane platinum oxalate [Title/Abstract])OR platinum(II)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine oxalate[Title/Abstract])OR cis-oxalato-(trans-l)-1,2-diaminocyclohexane - platinum(II)[Title/Abstract])ORoxaliplatin,(SP-4-3-(cis))-isomer [Title/Abstract])OR oxaliplatin,(SP-4-2-(1R-trans))- isomer [Title/Abstract])OR oxaliplatin,(SP - 4 - 2 -(1S-trans))-isomer [Title/Abstract])OR ACT-078 [Title/Abstract])OR ACT-078 [Title/Abstract])OR Eloxatine [Title/Abstract])OR Sanofi Synthelabo brand of oxaliplatin[Title/Abstract])OR Sanofi brand of oxaliplatin [Title/Abstract])OR Eloxatin[Title/Abstract])))).Chinese search terms for:Capecitabine,oxaliplatin,XELOX,colon cancer.
Selection criteria
Literature was retrieved and screened in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines.Two reviewers independently screened literature and abstracts based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria and screened the full text if necessary.In the literature that met the inclusion criteria,two reviewers used a unified data extraction table to independently extract data.Disagreements were resolved through consultation or by a third researcher.
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria was:(1)Experimental design for RCT;(2)The research object for the pathological diagnosis of patients with CRC;(3)The experimental group intervention for capecitabine combined with oxaliplatin,the control group for other chemotherapeutic drugs;(4)Observation results for patients with long-term efficacy:OS and DFS;(5)If the study included many cases,then only select the required part;and(6)The selected patients were stage III colon cancer patients and had undergone surgery without neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Exclusion criteria
Studies were excluded if:(1)Non-RCT;(2)Subjects included rectal cancer;(3)DFS or OS was not compared with two chemotherapy regimens in the same trial;(4)No specific data were provided;and/or(5)Repeated publication.
Data extraction
Data for each article was extracted,including the first author and title of the RCT,sample size,follow-up time,publication time,medication regimen,DFS and OS.
Methodological quality and statistical analysis of the RCTs were evaluated with the following criteria.The offset assessment of a single study was evaluated by two independent researchers.Any disagreements were evaluated by a third researcher.Quality evaluation mainly included random sequence generation,randomization concealment,blindness,withdrawal and withdrawal,and the Jadad scale was used to evaluate the score.We defined 1-3 points as low quality and 4-7 points as high quality.At the same time,the meta-analysis software Review Manager Version 5.3 recommended by the Cochrane library was used to test the heterogeneity and calculate the combination of odds ratio(OR)value and 95% confidence interval(CI).
Statistical detection ofPvalues less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.The heterogeneity of the study was determined by thettest and theI2test.The unified random effect model was used for consolidation.I2< 50% were considered as no statistical heterogeneity among the studies,and a random effect model was used to merge effects.Conversely,the random effect model was used to combine the effects.The output combined the OR value and the 95%CI and tests the merging statistic.TheZtest was used.The test level was α=0.05.
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis included a sensitivity analysis performed in subgroup analyses.If a document was excluded and the impact on the overall outcome was greater,then the literature was reread and the quality was evaluated.Then it was determined whether it was eventually incorporated.
Methodological quality
The literature was included and the GRADE system was used to assess methodological quality.In order to thoroughly reveal the source of heterogeneity,we also conducted meta regression and subgroup analysis.In addition,the funnel plot and application of shear reinforcing method(if the funnel plot was asymmetric or incomplete,then there was publication bias,and shear reinforcing method was applied;symmetry indicates that the publication bias is less likely without using the shear reinforcing method).Begg’s funnel plots and Egger’s tests were conducted to assess potential publication bias.Data analysis was performed using Stata 12.0 edition.
RESULTS
After searching the database,360 documents were selected.Eighteen repetitive documents were excluded.After reading the title and abstract,285 papers were excluded from the study of capecitabine combined with oxaliplatin compared with other drugs that affect colon cancer.After reading the full text,41 articles were excluded because they did not involve relevant outcome indicators.Two articles were excluded because there were no relevant data,and two articles in the control group did not meet the inclusion criteria.Finally,12 articles met the requirements[13-24](Figure 1).
Data and quality evaluation were included in a clinical controlled trial(Table 1).
Statistical analysis
OS:The meta-analysis obtained OS data from 11 articles.Finally,ten papers were included.The combined analysis showed that the XELOX group had longer OS compared with other chemotherapy groups(Figure 2A).The study has statistical significance(OR=1.29,95%CI:1.15-1.44,P< 0.0001).There was no heterogeneity among the study sites(P=0.46,I2=0%).
Results of the OS subgroup analysis(subgroup analysis of different follow-up visits)(Figure 3):Annual survival was statistically significant:(OR=1.70,95%CI:1.13-2.56,P=0.01).There was no heterogeneity in the study(P=0.66,I2=0%).The 2-year survival rate was statistically significant:(OR=3.30,95%CI:1.37-7.97,P=0.01).There was no heterogeneity in the study(P=0.99,I2=0%).The 3-year survival rate was not statistically significant:(OR=0.97,95%CI:0.56-1.69,P=0.93).There was no heterogeneity in the study(P=0.93,I2=0%).The 7-year survival rate was statistically significant(OR=1.30,95%CI:1.13-1.50,P=0.0003).There was no heterogeneity in the study(P=0.75,I2=0%).
Results of the OS subgroup analysis(XELOXvsother chemotherapy groups)(Figure 4A):XELOXvsFU/FA:The study was statistically significant:(OR=1.24,95%CI:1.07-1.44,P=0.005).There was no heterogeneity in the study(P=0.73,I2=0%).XELOXvsFOLFOX:The study was statistically significant:(OR=1.29,95%CI:1.07-1.55,P=0.008).There was no heterogeneity in the study(P=0.32,I2=0%).XELOXvscapecitabine:The study was statistically significant:(OR=1.28,95%CI:1.14-1.44,P=0.008).There was no heterogeneity in the study(P=0.99,I2=0%).
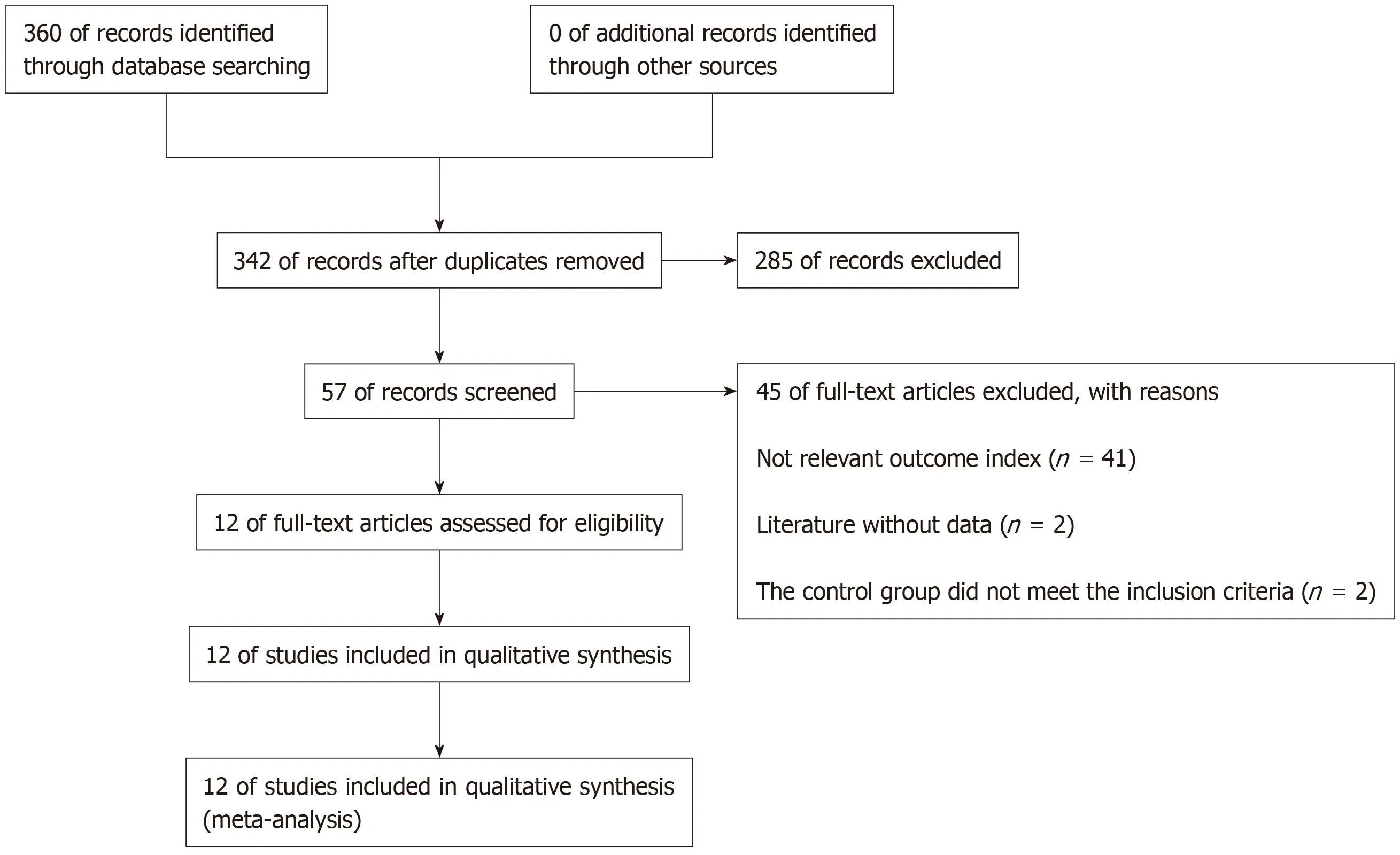
Figure 1 Flow chart of the 12 articles that met the inclusion criteria.
DFS:In this meta-analysis,DFS data were obtained in five articles,and four articles were finally included.The combined analysis showed that the XELOX group had longer DFS compared with other chemotherapy groups(Figure 2B).The study had significant statistical significance(OR=1.32,95%CI:1.18-1.46,P< 0.0001).There was no heterogeneity in the study(P=0.68,I2=0%).
Results of the DFS subgroup analysis(XELOX and other chemotherapy drug groups(Figure 4B):XELOXvsFU/FA:DFS had significant statistical significance:(OR=1.34,95%CI:1.17-1.53,P< 0.0001).There was no heterogeneity among the study sites(P=0.94,I2=0%).XELOXvsFOLFOX:DFS had statistical significance:(OR=1.28,95%CI:1.08-1.53,P=0.004).There was low heterogeneity among the studies(P=0.24,I2=27%).
Process of deflection analysis
Included 11 articles from OS meta-analysis:There was statistical significance(P=0.004)with moderate heterogeneity in this meta-analysis(P=0.007,I2=59%)(Figure 5A).
Articles were included in the DFS meta-analysis:There was statistical significance(OR=1.24,95%CI:1.04-1.46,P=0.01)with moderate heterogeneity in this metaanalysis(P=0.09,I2=51%)(Figure 5B).In its subgroup analysis,there was statistical significance(P=0.02)with high heterogeneity in this meta-analysis(P=0.02,I2=73%)(Figure 5C).
The sources of heterogeneity
Sensibility analysis 1:There was heterogeneity in the article published by Zhanget al[15](Figure 2A).After evaluating the article,the quality was low and samples were excluded.After exclusion(OR=1.29,95%CI:1.15-1.44,P< 0.0001),there was no heterogeneity among the studies(P=0.46,I2=0%).
Sensibility analysis 2:The sensitivity analysis(Figure 2B)showed heterogeneity in the article from Diaoet al[13].After evaluating the article,the quality was low and samples were excluded.After exclusion(OR=1.32,95%CI:1.18-1.46,P< 0.0001),there was no heterogeneity among the studies(P=0.68,I2=0%).After completely excluding Diaoet al[13],the study remained statistically significant(P=0.004),and the heterogeneity of the study was greatly reduced(P=0.24,I2=27%)(Figure 4B).
Bias detection of OS:The funnel plot was conducted to evaluate the publication bias.However,we did not observe clear asymmetry suggesting the results from this study are reliable(data not shown).
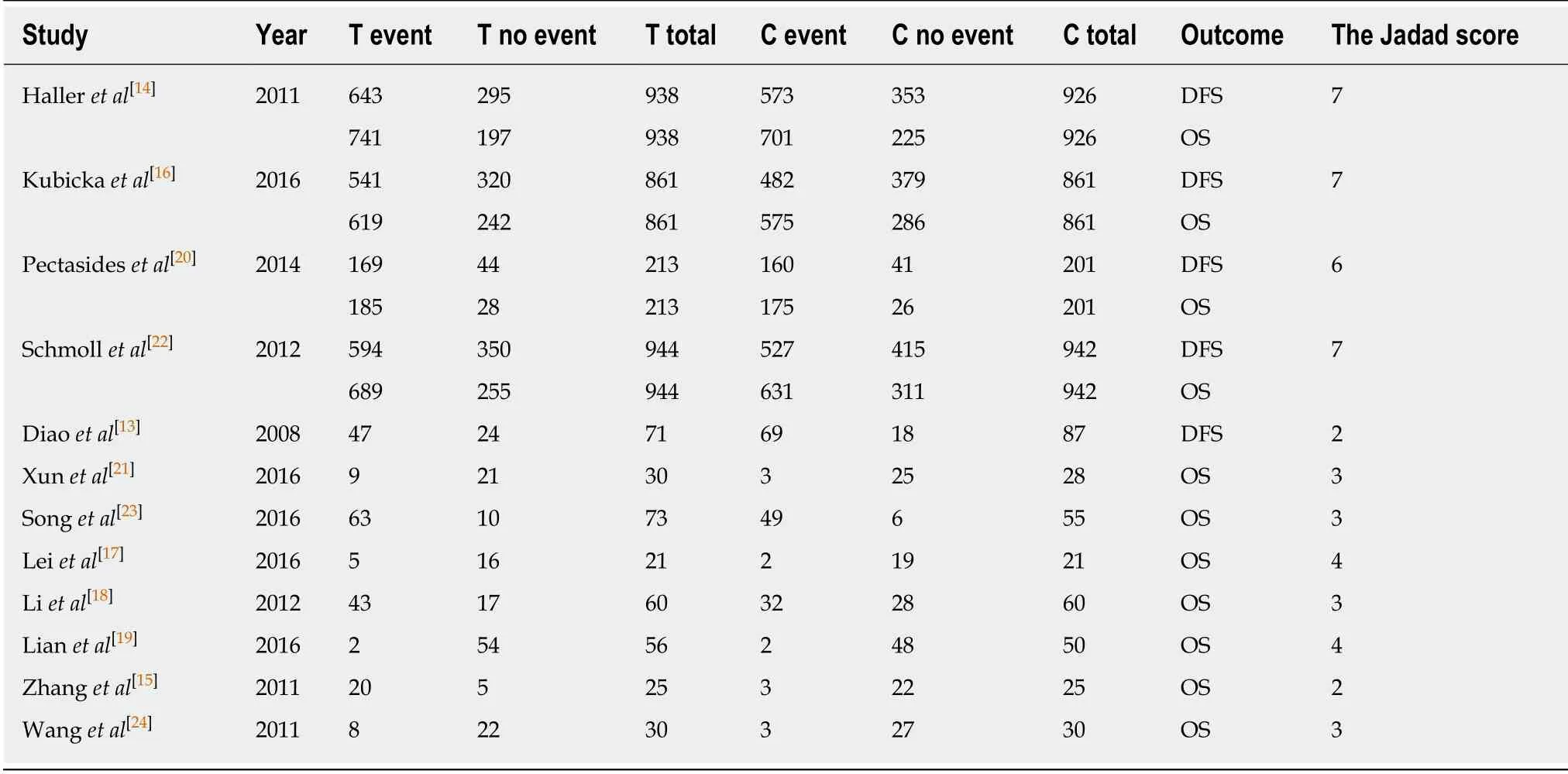
Table 1 Data and quality evaluation of clinical controlled trials
DISCUSSION
Liet al[18]reported that in elderly CRC patients(age above 70-years-old),a reduction in chemotherapy dose did not decrease the DFS with a benefit of less mortality.But,elderly patients receiving 50% of planned cycles had shorter DFS and higher CRC mortality than elderly patients receiving the full planned cycles[25].Therefore,a reduced dose but full cycles should be considered for elderly CRC patients.Our results are consistent with Kimet al[26]who found that OS was better in patients receiving at least 75% of expected cycles,but a dose reduction did not affect OS.These results suggest that a primary dose reduction in elderly patients may reduce the side effects of chemotherapeutics and help them finish the full planned cycles.The choice between mFOLFOX6 and XELOX should be discussed based on the gene subtypes of colon cancer[27-36].
It is well known that the prognosis of CRC patients has significant association with gene mutations.It is generally accepted that dMMR confers favorable prognosis in patients with resected colon cancer[10,11].Sinicropeet al[12,37]found thatKRASmutations were associated with adverse prognosis specifically in pMMR tumors,while Blonset al[38]showed thatKRASmutations conferred shorter DFS in patients with left colon primaries.
Patients with poor compliance may affect the accuracy of the results[39].Cancer patients are generally expected to have higher adherence to treatment than other patients because they are highly motivated by the gravity of their disease[40,41].However,studies have shown cancer patients to have similar adherence rates to patients with other diseases[42-45].Treatment duration plays a role in adherence to the regimen:when medication is continued over a longer period of time,patients become less adherent[46].
For oral cytotoxic agents,which require close monitoring of side effects and regular patient visits.There is no gold-standard measurement,and all methods have limitations[42,47].Previous studies of oral cytotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs have mainly used self-reported questionnaires[48],which tend to overestimate adherence because patients are inclined to over-report to please their doctors.
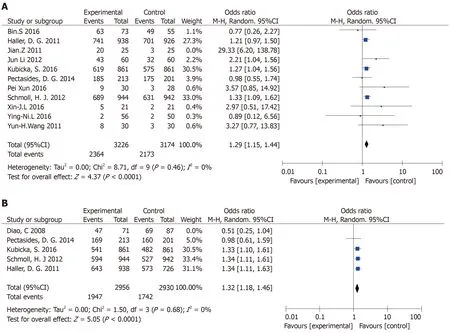
Figure 2 The combined analysis.A:The capecitabine plus oxaliplatin(XELOX)group had longer overall survival compared with other chemotherapy groups;B:The XELOX group had longer disease-free survival compared with other chemotherapy groups.
The side effects of commonly used adjuvant chemotherapy regimens FOLFOX is more serious[49].The annoying neurotoxicity side effect of FOLFOX appears at the 8-10thcycle of administration.This time period is the critical time to gain or lose survival benefits.Although treatment series of fewer cycles showed some potential to ameliorate this neurotoxicity[50,51],recent studies failed to show any convincing benefit[52-55],even on a molecular basis[56].It is still a challenge to be solved.Any “wait and go” policy to reduce side effects needs to be evaluated in a larger cohort of patients[57].
To our knowledge,many studies have indicated that monocyte count is associated with poor survival in patients with many types of cancer,but the potential mechanisms remain unknown[58].Low monocyte to lymphocyte ratio(MLR)level may help improve the demographic and clinicopathological characteristics[59].We found that low MLR,low monocyte and high lymphocyte were all associated with better prognosis in advanced gastric cancer patients.Meanwhile,our study indicated that low level MLR and low level neutrophil or high level lymphocyte correlated with better median DFS and OS for all patients.The 5-year DFS and OS rates of patients with low level MLR were higher than those with high level MLR[58,60-67].We speculate that there may be similar mechanisms in CRC.
Nowadays,tumor molecular pathology assessment serves as a regular part of clinical practice.Treatment effect is unlikely uniform across different molecular subtypes.Molecular pathological epidemiology is an integrative science to determine the molecular pathology in relation to clinical features and outcome in patients and populations.Molecular pathological epidemiology will be a future direction for personal treatment[68,69].
In this study,some of the non-English articles were not included because of the low assessed quality.Secondly,a limited number of RCT trials and small number of included patients may limit the conclusion of this study.Finally,a diversity in genetics,tumor staging and XELOX dose may also influence the results.Therefore,our conclusion needs to be further validated by a large RCT trial in the future.
In conclusion,the XELOX regimen is recommended for stage III colon cancer after surgery.
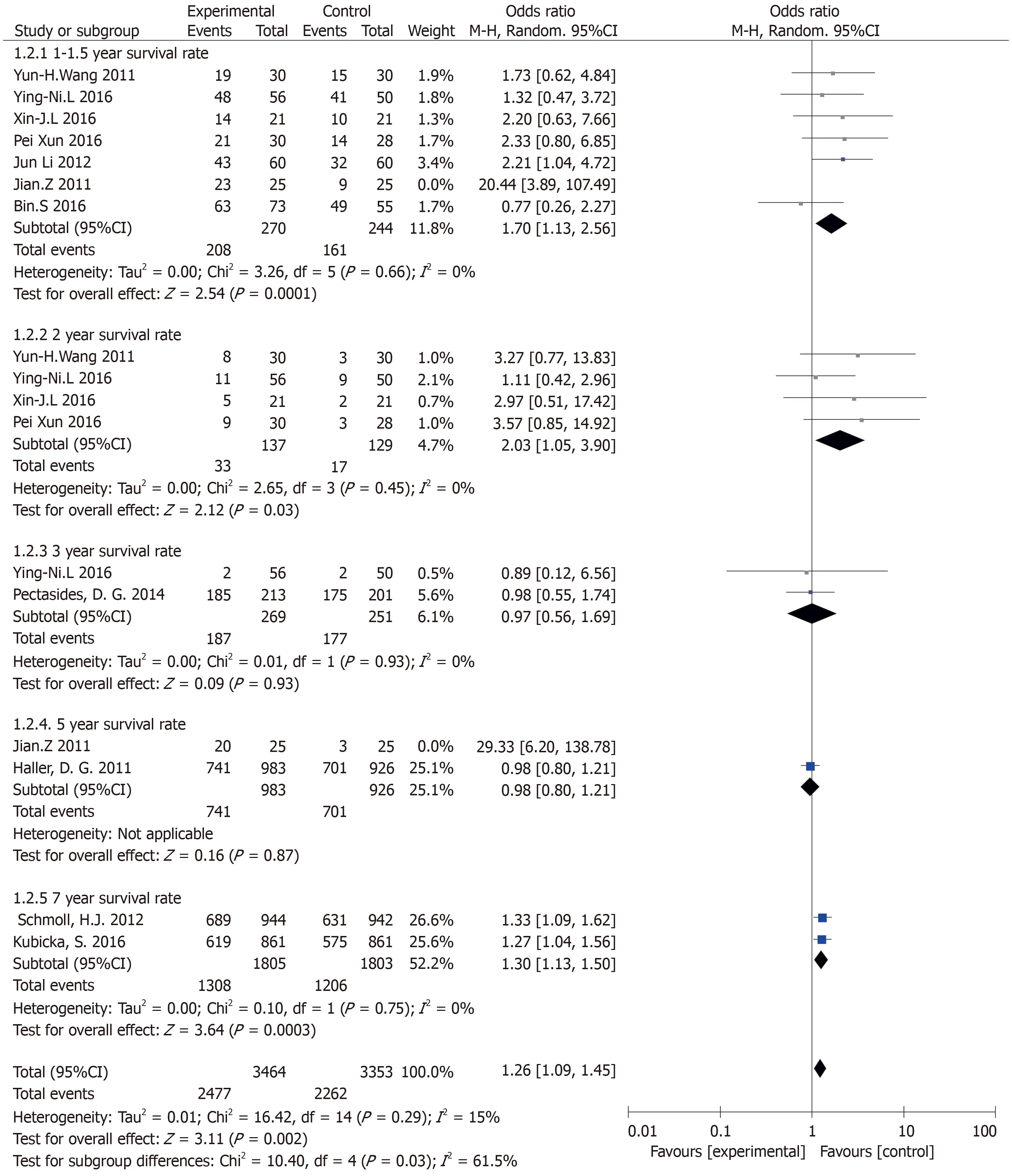
Figure 3 Results of the overall survival subgroup analysis(subgroup analysis of different follow-up visits).
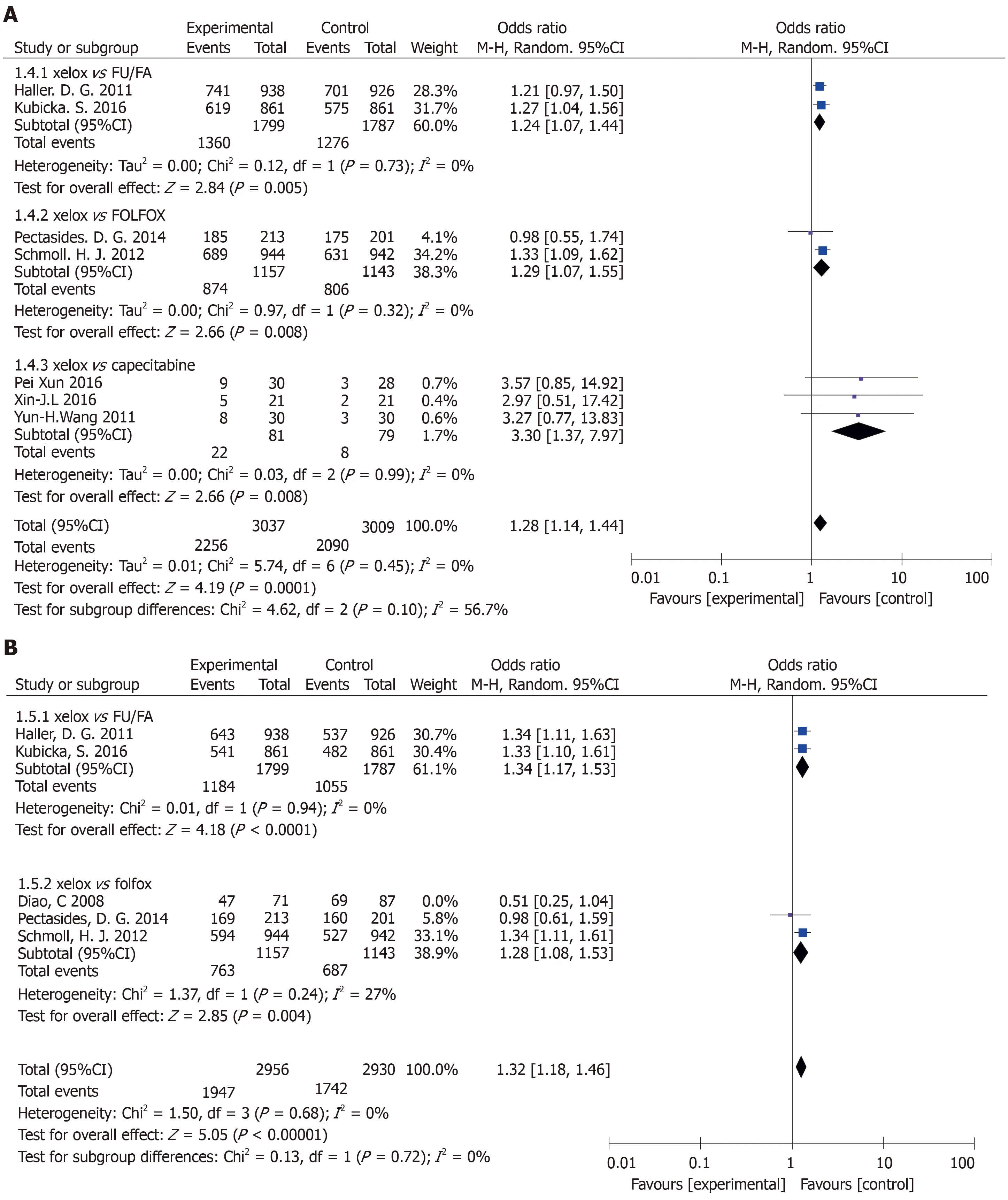
Figure 4 Subgroup analysis of overall survival and disease-free survival [capecitabine plus oxaliplatin(XELOX)vs other chemotherapy groups].A:The capecitabine plus oxaliplatin(XELOX)group had longer overall survival compared with other chemotherapy groups;B:The XELOX group had longer disease-free survival compared with other chemotherapy groups.
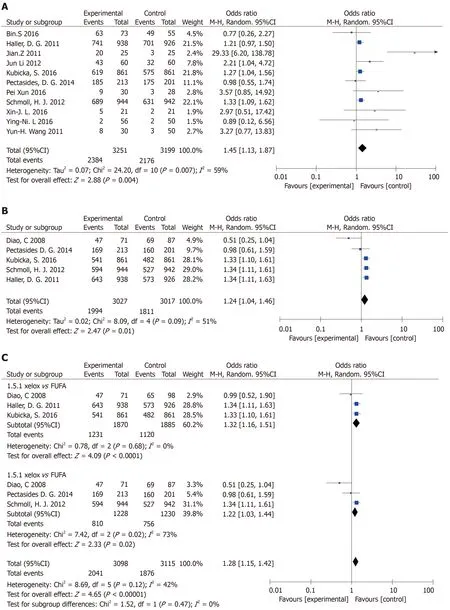
Figure 5 Process of deflection analysis.A:Overall survival(The capecitabine plus oxaliplatin(XELOX)group vs other chemotherapy groups);B:Disease-free survival(The XELOX group vs other chemotherapy groups);C:Subgroup analysis of disease-free survival(The XELOX group vs other chemotherapy groups).
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Colorectal cancer(CRC)accounts for 9% of all cancers in the world.In the last decade,it is the third most common malignant tumor in Europe and the United States.There is an urgent need to establish an effective standard treatment for CRC.In addition,more than 70% of CRC-related deaths are associated with the liver metastasis.A recurrence rate and poor overall survival make CRC a serious public health problem.
Research motivation
The aim of treatment for CRC is to cure locally and prevent metastasis and recurrence.Generally,comprehensive treatment is the focus of CRC,and chemotherapy is one of the important treatment methods.Reasonable and effective chemotherapy can prolong the life span and improve the quality of life of patients.Therefore,local resection of colon cancer should be combined with individual treatment.For patients with CRC,the choice of chemotherapy is very important for their prognosis.In patients with CRC,the purpose of adjuvant chemotherapy is to eliminate the occult micrometastasis during surgery,so as to improve the overall survival.
Research objectives
The purpose of this study was to explore the efficacy of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin(XELOX)regimen over other chemotherapy regimens,specifically XELOXvs5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin,XELOXvs5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin plus oxaliplatin,XELOXvscapecitabine and XELOXvsoxaliplatin plus 5-fluorouracil.
Research methods
By searching the PubMed,EMBASE and Cochrane databases,a total of 12 randomized controlled trials involving 6698 stage III colon cancer cases(XELOX protocol:n=3298 cases;other adjuvant chemotherapy protocol:n=3268 cases)were included.The parameter outcomes included the overall survival and the disease-free survival.The quality control of selected literature was based on the Jadad scale and the GRADE system.
Research results
In comparison to other adjuvant chemotherapy regimen,the XELOX regimen showed a better overall survival and a better disease-free survival for colon cancer patients.
Research conclusions
In clinical application,XELOX and 5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin plus oxaliplatin showed similar efficacy,but different types of patients may have different benefits from treatment.According to our data,in comparison to other adjuvant chemotherapy regimen,XELOX regimen showed a better overall survival and a better disease-free survival for colon cancer patients,suggesting the XELOX regimen can be a good option for postoperative treatment of stage III colon cancer.
Research perspectives
The XELOX regimen is recommended for stage III colon cancer after surgery.In addition,our conclusion needs to be further validated by a large RCT trial in future.

