Antioxidative effect of peroxiredoxin-3 in the rat myocardium exposed to renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
Xue-Bo Li,Xin Jin,Long Xu,Bo Hu,Guang-Tao Xu,De-Qing Chen*
1Key Laboratory of Evidence Identification in Universities of Shandong Province,Shandong University of Political Science and Law,Jinan 250014,China.2Forensic and Pathology Laboratory,Jiaxing University Medical College,Jiaxing 314001,China.3Department of Pathology,Molecular Medicine Center,Jiaxing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,Jiaxing 314001,China.
Abstract
Keywords:Peroxiredoxin-3,Antioxidation,Renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury
Introduction
The kidney is an important excretory and secretory organ of the human body and plays a crucial role in maintaining the relative stability of the internal environment [1].Studies have shown that renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is often one of the dangerous complications during the kidney surgery because it may cause distant organ injury such as myocardial injury,wherein oxidative stress is one of the important mechanisms [2-5].When renal I/R occurs,the excess oxygen free radicals and other harmful substances produced by the reperfusion kidney will traffic into remote organs such as the heart,and then cause different degrees of the oxidative stress injury in myocardial tissues.The heart is an organ that requires plenty of oxygen and is vulnerable to oxidative stress attacks [6-8].Potent antioxidant defenses could be activated to protected the cardiac fibroblasts against oxidative stress triggered by inflammation after myocardial injury[9].
Peroxiredoxins has been proposed to protect cells against oxidative stress-induced damage [10].Several cellular processes are known to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) under physiological and pathophysiological conditions [11].Prx-3,a member of the peroxiredoxins family,is a mitochondrial antioxidant protein capable of catalyzing hydrogen peroxide reduction and regulating various metabolisms.It is induced by oxidants in the cardiovascular and urinary systems.It has well reported that Prx-3 plays a role in the antioxidant defense system and homeostasis within mitochondria[12,13].It has been demonstrated that clearance of cellular hydrogen peroxide is closely related to Prx-3,which plays a remarkable antioxidant role in the myocardium and protects the myocardial tissue against oxidative stress [14,15].Prx-3 is able to up-regulate mitochondrial ROS levels and control cell growth,proliferation,and other cellular properties by regulating sulfhydryl-dithiobase exchange reactions of cysteine.
Our previous study demonstrated that the heart may suffer a certain degree of damage from oxidative stress after renal I/R [16].However,the role of Prx-3 in protecting the myocardial tissue against renal I/R-induced myocardial injury (RI/RMI) remains unclear.The present study was to investigate the Prx-3 expression in a rat RI/RMI model in an attempt to find a new approach to the prevention and treatment of myocardial injury induced by renal I/R.
Materials and methods
Compliance with ethical standards
Sprague Dawley male rats weighing (200 ± 10) g(Zhejiang Academy of Medical Sciences,China) were housed at the Laboratory Animal Centre of Jiaxing University Medical College,China.All experimental protocols and the care of Sprague Dawley rats were approved by the Ethics Committee for the use of animal subjects of Jiaxing University Medical College(JUMC-20183013).
Rat model establishment
Sprague Dawley male rats weighing (200±10)g were generally anesthetized by isoflurane using an anesthetic mask connecting a Small Animal Anesthesia-Ventilator Station (RWD Life Science,China).Twenty-four Sprague Dawley rats were equally randomized into three groups: (1) normal group,wherein rats were not treated with the surgical operation; (2) control group,wherein rats were executed with right nephrectomy and simple separation of the left renal artery after celiotomy; (3) I/R group,wherein I/R was achieved by clamping the left renal artery for 45 min,followed by 24 hour reperfusion based on the control group.Approximately 5 mL blood was drawn from the rat common carotid artery and centrifuged (Centrifuge 5804 R,Eppendorf,Germany)at 4 °C 3,500 rpm for 15 min to collect the serum.Finally,rats were sacrificed by deep anesthesia.All rat left kidneys were removed and fixed in 4% neutral PBS/paraformaldehyde for subsequent histopathological experiments.The rat myocardial tissue was homogenized and centrifuged at 4 °C 3,500 rpm for 30 min,and stored at -80 °C for molecular biological detection.
Histopathological evaluation of renal damage
The kidney tissue was fixed in 4% neutral PBS/paraformaldehyde,paraffin-embedded,sliced into 4-μm sections and hematoxylin and eosin stained according to conventional protocols.The histopathological changes were examined by pathologists under the microscope and imaging system(DM3000 Led,Leica,Germany).Injury quantification was graded from 10 areas corresponding to the kidney tissue using the following parameters: tubular cell necrosis,apoptosis,cytoplasmic vacuole formation,hemorrhage,and tubular dilatation based on a five-score system (1,histopathological change ≤10%;2,=11%-25%;3,=26%-50%;4,=51%-75%;and 5,≥76%) [17-19].The mean score for each parameter was calculated and analyzed.
Detection of biochemical indicators
The renal function was assessed by measuring the concentrations of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (Scr) using a kit (Lot.181444-01,Roche Diagnostics,Germany) [20,21].Oxygen free radicals are used for lipid peroxidation in vivo,and the end product of oxidation is malondialdehyde (MDA),which can cause cross-linking polymerization of proteins,nucleic acids,and other living macromolecules,and has cytotoxicity.MDA content is an important parameter to reflect the potential antioxidant capacity of the body,which can reflect the rate and intensity of lipid peroxidation in the body,and also indirectly reflect the degree of tissue peroxidation damage.The level of MDA in the rat myocardial tissue was detected using the thiobarbituric acid kit (Lot.A600941-0025,Sangon,China),knowing that it is a reflection of whether the myocardium is damaged by oxidative stress.
Real-time polymerase chain reaction(PCR)
To assess the Prx-3 mRNA expression level,total RNA was isolated from the myocardial tissue using Trizol reagent (Lot.10296010,Invitrogen,China).Transcription to cDNA was conducted with the M5 Super qPCR RT kit(Lot.MF166,Mei5 Biotech,China)[20].Primer sequences were Prx-3 (F:5’-GGTTTGGGCCACATGAACAT-3’,R:5’-AAGCCCATGGAGCAGTACTT-3’),GAPDH (F:5’-TCGTGGAGTCTACTGGCGTCTT-3’,R:5’-CATTGCTGACAATCTTGAGGGAG-3’).Real-time PCR was performed using QuantStudio 3(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Singapore),with a total volume of 20 μL containing 2 × PCR SuperMix,primers,cDNA,and sdH2O.The PCR cycling conditions were as follows:20s at 95°C,30s at 60°C,and 60s at 72°C (40 cycles).Relative gene expression was calculated by the 2ΔΔCTmethod and normalized to GAPDH.
Western blotting analysis
Western blot analysis was performed as previously described [22,23].The rat myocardial tissue homogenate was electrophoretically separated in 10%sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels and transferred to the nitrocellulose membrane.Specific binding of antibody was blocked using 5% skimmed milk in Tris-buffered saline with 0.1% Tween-20 for 1 hour.The membrane was immunoblotted with primary anti-Prx-3 antibody (Lot.D621157-0100,Sangon,China) overnight at 4 °C,and subsequently with the alkaline phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibody.The antigen-antibody product was measured by an automatic chemiluminescence/fluorescence image analysis system(5200 Multi,Tanon,China).
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation(SD).All experiments were repeated in triplicate.Microsoft Excel 2010 database and SPSS version 19.0 were used to record and analyze the data.The mean comparisons between multiple groups were performed by single-factor analysis of variance with posthoc Dunn’s multiple comparison tests.A value of less than 0.05(P<0.05)was considered statistically significant.
Results
Function and pathological changes of the rat renal tissue
Compared with the normal and control groups,the serum level of BUN and Scr was significantly increased in the I/R group (P <0.05) (Figure 1).Histopathological changes in the kidneys were also more obvious,including glomerular cystic and renal interstitial hemorrhage,renal tubular epithelial cell edema,and tubular type formation as compared with the normal and control groups (Figure 2).These abnormalities indicate that the renal I/R surgery was successful.
MDA level and the expression of Prx-3 mRNA and protein in the rat myocardial tissue
The levels of MDA and the expression of Prx-3 mRNA and protein in the I/R group were significantly increased in comparison with those in the normal and control groups (P <0.05 for all) (Figure 3),indicating that the self-regulatory ability of the myocardium against oxidation was enhanced markedly after RI/MRI.
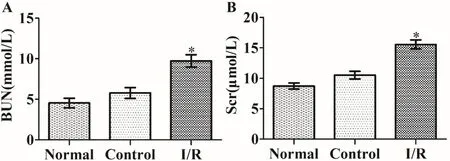
Figure 1 Renal function.
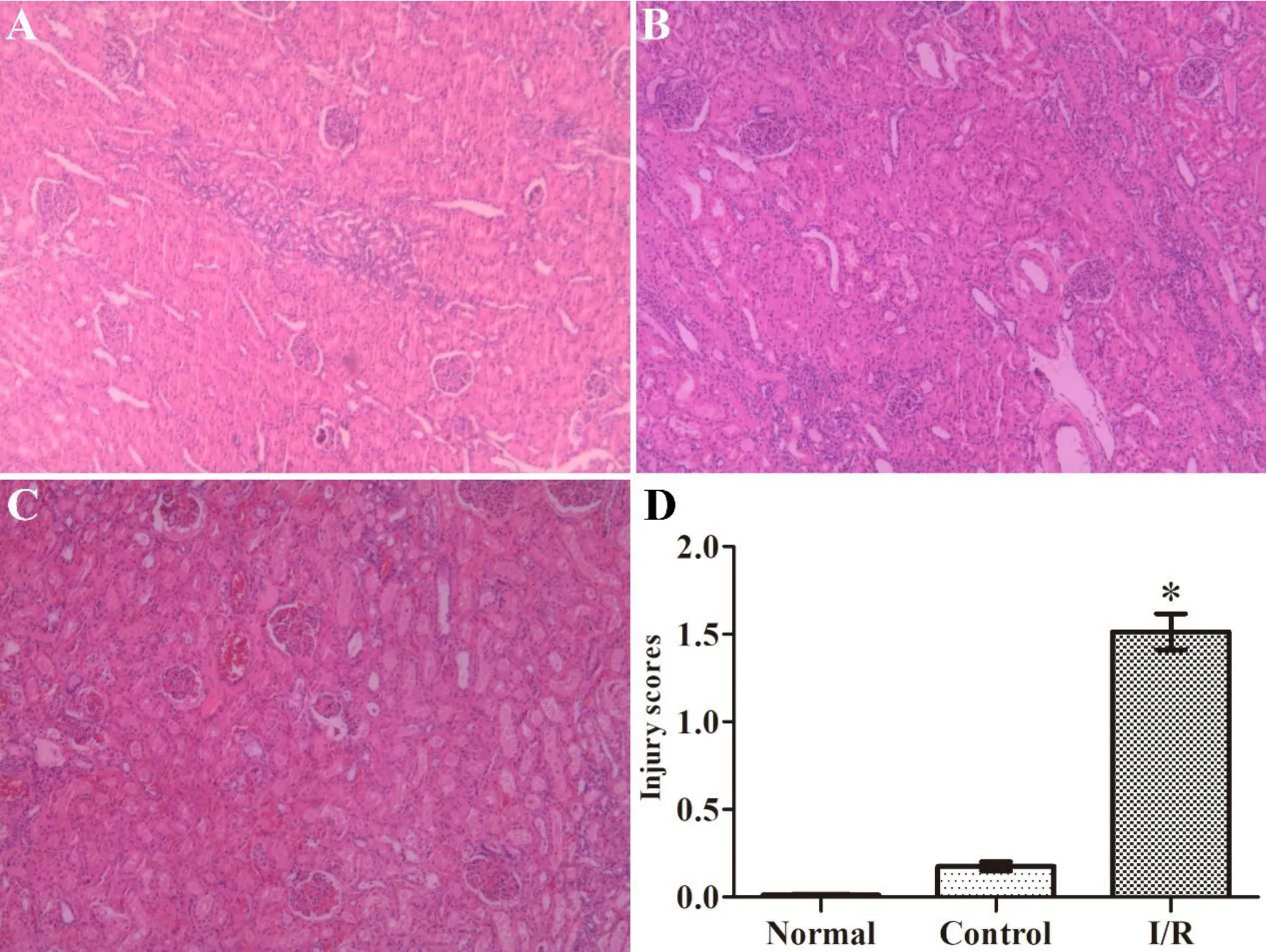
Figure 2 Renal histopathological alternations.
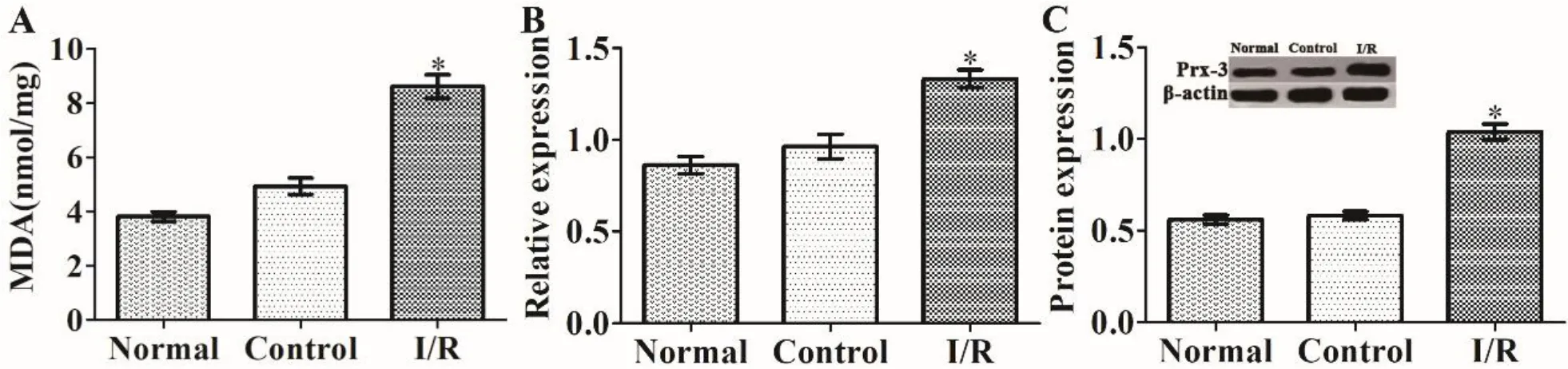
Figure 3 MDA level and the expressions of Prx-3 mRNA and protein in the rat myocardial tissue.
Discussion
In this study,we successfully established an RI/RMI rat model and demonstrated the effect of Prx-3 in enhancing the self-regulatory ability of the myocardium against oxidation in RI/RMI.Previous studies have shown that oxidative stress is involved in the pathophysiological processes in I/R-insulted organs[24],wherein mitochondrial ROS is released into the cytoplasm and reacts with lipids,resulting in accumulation of MDA and other peroxide products[25,26].It was found in the present study that the myocardial MDA level was significantly increased after renal I/R surgery,suggesting that the rat myocardial tissue was assaulted by oxidative stress products carried by blood flow.
As a member of the peroxiredoxins family,Prx-3 plays an important role in free radical scavenging in oxidative stress events [27].The body eliminates excess free radicals by upregulating the Prx-3 expression to protect myocardial tissue against oxidative damage in the myocardial I/R injury.In the current RI/RMI model,the expression of Prx-3 mRNA and protein were both upregulated,indicating that Prx-3 participated in the self-regulatory process of the myocardial tissue against oxidative stress.It is conceivable that pretreatment with certain antioxidants such as Prx-3 to enhance the self-regulatory ability of the myocardial tissue against oxidative damage may prove to be a promising strategy for the clinical management of RI/RMI.
In conclusion,we successfully established an RI/RMI rat model and demonstrated the existence of oxidative stress damage to the remote myocardium after renal I/R surgery.More importantly,Prx-3 was demonstrated to enhance the self-regulatory ability of the myocardial tissue against oxidative stress damage in RI/RMI rats and could attenuate the symptoms of myocardial injury during the perioperative period of renal I/R surgery.Since myocardial injury in renal I/R process could be attributable to multiple factors,further studies are needed to better clarify the underlying mechanisms.
