Expression and Significance of MicroRNA-21 and P-gp in Colon Cancer Cells
Xiaoli YAN, Yanfang FAN, Peng YAN, Jing XUE, Zhenhong LIU, Jining ZHENG
Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China
Abstract [Objectives] To investigate the expression and significance of miR-21 and P-gp in colon cancer cell line HCT-15. [Methods] RT-qPCR was used to detect the miR-21 and ABCB1 mRNA expression level of P-gp coding genes in normal colon mucosal cell NCM460 and colon cancer cell HCT-15, and Western Blot was used to detect the expression of P-gp in these two cell lines. [Results] The results of RT-qPCR showed that the expression level of miR-21 and ABCB1 mRNA in colon cancer cell HCT-15 was significantly higher than that in normal colon cell NCM460, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Western Blot results showed that the expression level of P-gp in HCT-15 was significantly higher than that in NCM460, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). [Conclusions] The expression level of miR-21 and ABCB1 mRNA/P-gp in colon cancer cell HCT-15 was higher than that in normal colonic mucosal cell NCM460, and the relationship between miR-21 and multidrug resistance in colon cancer might be related to P-gp.
Key words Colorectal cancer, miR-21, ABCB1, P-gp
1 Introduction
Cancer is now the leading cause of death in countries around the world. According to the2018GlobalCancerStatisticscompiled by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, the number of new cases of colorectal cancer ranked fourth in the world, and the number of deaths ranked fifth in the world[1]. China’s 2016 cancer statistics show that the incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer ranked fifth[2]. At present, the screening strategy and plan of colon cancer in China are not perfect, most patients are in the middle and late stage of cancer when they are first diagnosed, and the rate of recurrence and metastasis is high. Adjuvant therapy has been proved to have good clinical value[3]. Systemic chemotherapy plays a more and more important role in resectable colorectal cancer[4]. However, some patients with advanced colorectal cancer are resistant to chemotherapeutic drugs, so that the effect of chemotherapy is significantly reduced, and even chemotherapy fails. By searching the database PharmGKB, we found thatABCB1 is involved in the metabolism of many antineoplastic drugs[5-6], and high expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expressed byABCB1 gene can easily lead to drug resistance in tumor cells. Therefore, it is expected to reverse the multidrug resistance of tumor cells by inhibiting the expression of P-gp.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a kind of non-coding small molecule RNA (about 18 to 24 nucleotides), which can bind to the corresponding target mRNA 3′-non-coding region, and regulate the expression of target genes at the post-transcriptional level. It participates in many biological processes of cells[7], and is also related to the MDR of tumors[8]. Therefore, it is very important to find miRNAs with high sensitivity and specificity for basic research and clinical application of tumor. In this study, we detected the expression levels of miR-21 andABCB1 mRNA (P-gp) in normal colon mucosal cell NCM460 and colon cancer cell HCT-15, to explore the relationship between them, and to verify the previous tissue level results.
2 Materials and methods
2.1MaterialsNCM460 and HCT-15 were purchased from Guangzhou Jiniou Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) was purchased from BI Company, and RPMI-1640 medium and trypsin were purchased from Gibco Company.Hairpin-itTMmicroRNA and U6 snRNA standardized RT-PCR quantitative kits were purchased from Suzhou GenePharma Biotechnology Company. RT-qPCR kit was purchased from Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd.ABCB1 and GAPDH primers were designed and synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. Western Blot P-gp rabbit anti-human monoclonal antibody purchased from Cell Signaling Technology Co., Ltd and internal reference β-actin rabbit anti-human monoclonal antibody was purchased from ABclonal Company. Western Blot sheep anti-rabbit secondary antibody was purchased from Beyotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
2.2Methods
2.2.1RNA extraction and reverse transcription real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). RNA extraction: NCM460 and HCT-15 cells were cultured in complete RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2incubator. Cells were washed three times with PBS when the cell coverage rate reached 80% to 90% and TRIZOL reagent was used to extract the total RNA of the cell. The concentration of RNA was detected by Nanodrop 2000 spectrophotometer, and the sample purity was in accordance with the standard when A260/A280ratio of the sample was in the range of 1.8 to 2.1.
RT-qPCR experiment: miR-21 was reversely transcribed and amplified by SYBR dye Hairpin-it miRNAs RT-qPCR quantitative kit. With U6 snRNA as the internal reference, the program was operated according to the instructions.ABCB1 took GAPDH as the internal reference, and the program was operated strictly according to the instructions of RT-qPCR the kit. miR-21 primer: forward TCGCCCGTAGCTTATCAGACT, reverse CAGAGCAGG GTCCGAGGTA;U6 snRNA primer: forward ATTGGAACGATACAGAGAAGATT, reverse GGAACGCTTC ACGAATTTG;ABCB1 primer: forward GGAGCCTACTTGGTGGCA CATAA, reverse TGGTAGCTCATCATCTGGGACA;GAPDHprimer: forward GCACCGTCAAGGCT GAGAAC,reverse TGGTGAAGACGCC AGTGGA. Two duplicate holes were made in each sample, and the difference ofCtvalue between the duplicate holes was less than 1. The experiment was repeated 3 times.
2.2.2Western blot experiment. The logarithmic growth phase cells of each group were taken, and the total protein was extracted by cleavage of each group, and the protein concentration was determined by enzyme labeling instrument. The protein with loading amount of 30 μg was taken for SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. PVDF membrane was transferred at 200 mA constant current and sealed with 5% skim milk powder. It was treated with P-gp first antibody (1∶1 000) and β-actin first antibody (1∶100 000) overnight at 4 ℃. The membrane was washed with TBST, incubated with secondary antibody (1∶1 000) and then washed with TBST. SuperEnhanced chemiluminescence(ECL) detection reagents were used to develop and then take pictures. The experiment was repeated 3 times.
2.3Resultdetermination
2.3.1RT-qPCR result determination. 2-△△Ctwas used to determine the change multiple of target gene expression in the experimental group compared with the control group, where △△Ct=(Cttarget gene-Ctinternal reference gene)experimental group-(Cttarget gene-Ctinternal reference gene)control group.
2.3.2Western Blot result determination. The images were analyzed by Quantity One software. The ratio of P-gp band gray value to β-actin band gray value was used as the relative expression of P-gp.
2.4StatisticalanalysisSPSS 19.0 software was used for statistical analysis, and independent samplet-test was used for measurement data. The difference was statistically significant whenP<0.05.
3 Results and analysis
3.1RelativeexpressionlevelsofmiR-21andABCB1mRNAinNCM460andHCT-15cellsThe expression level of miR-21 andABCB1 mRNA in colon cancer cell HCT-15 was significantly higher than that in normal colon cell NCM460, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05) (see Table 1 for details).
Table 1 Relative expression levels of miR-21 andABCB1 mRNA in NCM460 and HCT-15 cells (n=3)
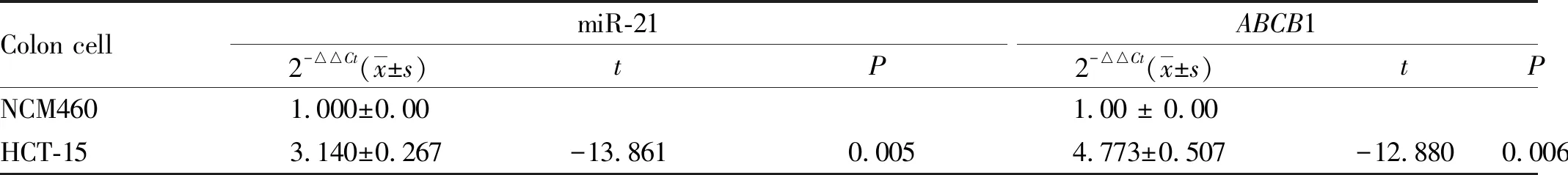
Colon cellmiR-212-△△Ct(x±s)tPABCB12-△△Ct(x±s)tPNCM4601.000±0.001.00 ± 0.00HCT-153.140±0.267-13.8610.0054.773±0.507-12.8800.006
3.2RelativeexpressionlevelofP-gpinNCM460andHCT-15cellsFrom Fig.1 and Table 2, it can be seen that the expression level of P-gp in colon cancer cell HCT-15 was significantly higher than that in normal colon cell NCM460, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).

Fig.1 Expression level of P-gp in normal colon cell NCM460 and colon cancer cell line HCT-15
Table 2 Relative expression level of P-gp in NCM460 cell and HCT-15 cell (n=3)

Colon cellP-gpx±stPNCM4600.297± 0.022HCT-150.486 ± 0.014-12.5000.000
4 Discussion
Multidrug resistance (MDR) refers to the resistance of tumor cells to a variety of other antineoplastic drugs with different structures and mechanisms after exposure to one antineoplastic drug. The cause and mechanism are very complex, among which the high expression of P-gp expressed byABCB1 gene is one of the main reasons. P-gp can rely on ATP to mediate drug efflux pump, reduce intracellular drug concentration and cause drug resistance in cancer cells. At present, it has been confirmed thatABCB1 gene is involved in the metabolism of many antineoplastic drugs. Although a large number of clinical studies intend to inhibit tumor MDR by inhibiting the function of P-gp, P-gp antagonists have not been fully used in clinic because of their low affinity to substrate, high dose and high toxicity.
Some studies have proved that miRNAs are related to tumor MDR. The study of Sabry Detal.[9]showed that the expression of miR-21 was increased in colorectal cancer, which was consistent with the experimental results at the tissue level in the early stage of this study. Lopes-Ramos CMetal.[10]found that the overall sensitivity and specificity of miR-21-5p in predicting the response of
colorectal cancer patients to chemotherapy were 78% and 86%, respectively. The study of Zhaoetal.[8]showed that the expression level of miR-21 in drug-resistant cell lines was higher than that in parent cell lines, and inhibition of miR-21 expression in drug-resistant cell lines could enhance the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic drugs; increasing the expression of miR-21 in parent cell lines could enhance the resistance of cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. All these prove that miR-21 is related to chemotherapy resistance of colorectal cancer. In this study, we detected the expression of related genes and proteins at the cellular level, and found that the expression level of miR-21 andABCB1 mRNA (P-gp) in colon cancer cells was higher than that in normal colon cells. This suggested that the increased expression of miR-21 in colorectal cancer cells might be related to the high expression of P-gp.
By searching the database RNA 22 tool, it was found that there were complementary base sequences between miR-21 andABCB1. Therefore, it was speculated that miR-21 was probably the regulatory gene ofABCB1, and might participate in tumor MDR by regulating P-gp. Therefore, targeted down-regulation of miR-21 expression may be of certain significance in reversing tumor chemotherapy resistance. However, it is not clear how miR-21 andABCB1 mRNA (P-gp) interact and participate in colorectal cancer MDR. Therefore, further experiments are needed to explore the specific regulation of miR-21 on the targeting regulation of P-gp and the detailed mechanism of their involvement in chemotherapy resistance of colorectal cancer.
- Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Application of Chaihu plus Longgu Muli Decoction in Treatment of Physical and Mental Diseases
- Study on Pharmacological Effects of Calycosin in Astragali Radix
- Advances in Research on Treatment of Heart Failure with Yangxinshi Tablet
- Advances in Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activity of Pholidota spp.
- Treatment of Arthralgia Syndrome from Zang and Fu
- Effects of Zingber mioga Aqueous Extract on Hepatic Anti-alcoholism in Mice

