Prokaryotic Expression of IBV N Protein and Development of Indirect IBV N Protein-mediated ELISA
Li Wei-qun,Wang Xin,Zhong Ming,Sun Xiao-qi,Zhao Lei,Huang Xiao-dan,Zhang Rui-li,and Li Guang-xing*
1 Key Laboratory for Laboratory Animals and Comparative Medicine of Heilongjiang Province,College of Veterinary Medicine,Northeast Agricultural University,Harbin 150030,China
2 College of Pharmaceutical Engineering,Jilin Agriculture Science and Technology College,Jilin 132101,China
Abstract: Avian infectious bronchitis (IB) is an acute and highly contagious disease caused by infectious bronchitis virus(IBV). In the study,according to IBV gene sequences published in GenBank,specific primers were designed to clone N gene by RT-PCR,and this gene was inserted into pET-30a (+) vector resulting in a prokaryotic expression plasma pET-30a-N. The results of SDS-PAGE and Western Blot analysis showed that the recombinant protein was expressed successfully and had good reactivity with IBV positive serum. Using purified recombinant N protein as a coating antigen,the indirect ELISA protocol was established and optimized,in which N protein was 2.5 μg · mL-1 of concentration,sample serum of 1 : 40 dilution. For clinical specimen,the IBV antibodies could be detected by this method efficiently and got nearly the same results as those of IBV-mediated ELISA. It would provide a good tool for rapid diagnosis and epidemiological study of avian infectious bronchitis.
Key words: infectious bronchitis virus,N protein,prokaryotic expression,indirect ELISA
Introduction
Avian infectious bronchitis (IB) is an acute,highly contagious respiratory disease caused by infectious bronchitis virus (IBV). IBV belongs to the genusGammacoronavirusin the familyCoronaviridaeof the orderNidovirales(Cavanagh,2007). The genome is a non-segmented single-positive-stranded RNA with a length of 27.6 kb (Brierleyet al.,1987; Bandeet al.,2016),and the virion carries a capsule and a fiber. The IBV genome has 10 distinct open reading frames,which mainly encode four structural proteins of the virus,namely S protein,M protein,N protein,E protein and some non-structural proteins. Currently,the IBV gene localization sequence is 5' 1a-1b-S-3a-3b-E-M-5a-5b-N-PolyA 3'.
In 1930,IB was first discovered in North Dakota,USA. In 1972,the disease was first discovered in Guangdong by Qi Ronglu. More than 30 serotypes have been isolated in the world. Due to the continuous emergence of new serotypes,it has brought certain difficulties to the prevention and treatment of IB(Thiel,2007; Jones,2010). Agustina and Maria (2009)analyzed the nucleotide and amino acid sequences of 20 strains of proteins isolated fromArgentinafrom 2001 to 2008. Only five isolates belong toMassachusettsorConnecticut,and other strains are divided into three groups and generated groups. There is no correlation and geographic pattern,and these results may explain the reasons for the failure of the mass serotype vaccine immunization program to control IB (Awadet al.,2015).
At present,the research on IBV mainly focuses on the study of viral genetic variation and pathogenesis(Toroet al.,2016). Among them,the interaction of S protein in virus and host cells and its molecular characteristics are most active,but due to the high variation of S protein,it makes rapid and accurate diagnosis of the disease. Restrictedly,IBV N protein is a viral core capsid protein and a phosphorylated protein that cannot be glycosylated. It consists of 409 amino acids with a molecular mass of 46 ku,which is the most evolutionarily conserved. In the process of IBV infection,N protein stimulates the body to produce the earliest ELISA antibody,the highest titer,and can also cause cell-mediated immune response.Therefore,N protein is a stable immunogen for the diagnosis and treatment of IB and novel genetic engineering vaccine research (Worthingtonet al.,2008; Zhanget al.,2010).
In this study,theNgene of IBV isolate HH06 was cloned into the prokaryotic expression vector pET-30a (+) for expression,and the purified recombinant protein was used as a coating antigen to establish an indirect ELISA assay for IBV antibody. It laid the foundation for epidemiological research.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial strain and vector
The cloning vector pMD18-T was purchased from Dalian Bao Biological Engineering Company; pET-30a (+) was stored in our laboratoryE. coli JM109 andRossettacompetent cells were prepared and preserved by our laboratory.
Viruses and serum
IBV HH06 strain was isolated,identified and stored by our laboratory.E. colipositive serum andSalmonellapositive serum were received by researcher Liu Siguo of Harbin Veterinary Research Institute; AIV positive serum was received by researcher Wang Xiurong of Harbin Veterinary Research Institute; IBV positive chicken serum and NDV positive serum was given by researcher Liu Shengwang of Harbin Veterinary Research Institute; ALV positive serum was kept by the laboratory; IBV serum clinical samples were provided by Heilongjiang Animal Health Supervision Institute.
Enzymes and reagents
EcoRⅠandXhoⅠ,T4DNA ligase,ExTaqenzyme,DNA Marker and low protein Marker were purchased from Dalian Bao Bioengineering Company.HRP conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG was purchased from Solarbio. The DNA gel extraction kit was purchased from Beijing Solabio Technology Company.The DNA recovery kit was purchased from Biowest Company.
Cloning of N gene of IBV HH06 stain
The IBV HH06 strain was inoculated into 9-11-dayold SPF chicken embryos. The inoculation dose was 0.1 mL per embryo and the dead embryos were discarded within 24 h. Allantoic fluid was collected 72 h later. Virus genomic RNA was extracted by the Trizol method and reverse transcribed to obtain cDNA. Using HH06-N up and HH06-N down as primers,cDNA was used as a template for PCR amplification ofNgene. Based on the gene sequences of NCBI (GenBank accession No.SC021202),the primer sequences were as the followings: HH06-N-up(5'-CGCTCAATCGCTGGTATG-3'); HH06-N-down(5'-CGGCACTGGCGTCTTTAT-3'). Then purified and recovered the PCR product with the DNA recovery kit and connected it with the pMD18-T vector. The recombinant plasmid was conversed into theE. coliJM109 competent cells and identified by bacterial liquid PCR and enzyme digestion. The correct positive plasmid was sent to Harbin Bo Shi Biotechnology Company for sequencing.
Prokaryotic expression of N protein of IBV HH06 stain
The recombinant plasmid which was identified correctly was extracted according to the DNA gel extraction kit. Using S and P as primers,the recombinant plasmid was used as a template for PCR amplification ofNgene. The forward and reversed primers were designed withEcoRⅠandXhoⅠrestriction sites at the 5' terminus. The primer sequences were as the followings: S (5'-CCGGAATTCATGG CAAGCAGTAAGGCA-3'); P (5'-CCGCTCGAGT CAAAGTTCATTTTCACC-3'). Then purified and recovered the PCR product with the DNA recovery kit and connected it with the pET-30a vector. The recombinant plasmid was conversed into theE. coliJM109 competent cells and identified by bacterial liquid PCR and enzyme digestion. The correct pET-30a-N was induced expression using IPTG in theRossettacompetent cells to harvest the N protein.
Purification and Western Blot
Recombinant proteins were purified using a Ni-NTA agarose protein purification kit according to the manufacturer's instructions (Qiagen). The recombinant protein was isolated by SDS-PAGE,transferred to nitrocellulose membrane and incubated with IBV multi-antibody (1 : 500 dilution) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG(1 : 4 000).
Preparation for polyclonal antibody of N protein of IBV HH06 strain
New Zealand white rabbits were immunized with the purified recombinant N protein mixed with Freund's complete adjuvant on the back to harvest polyclonal antibody of the N protein of IBV HH06 strain. The antibody titers of the serum were determined using the indirect ELISA.
Indirect ELISA for N protein of IBV HH06 strain
Experiments to explore the most suitable conditions of the indirect ELISA were made. At the meantime,specific and repetitive experiments were taken to test and verify the validity of this method. Finally,indirect ELISA was used to detect serum clinical samples provided by Heilongjiang Animal Health Supervision Institute for evaluating the IBV antibodies.
Results
Cloning and identification of N gene of IBV HH06 strain
The total RNA of the extracted IBV HH06 strain was used for RT-PCR amplification of theNgene containing the complete open reading frame,which was 1 750 bp in size,and the recombinant plasmid pMD18-T-N was synthesized. The positive recombinant bacterial liquid was sent to Harbin Boss Biotechnology Company for sequence determination,and the results of sequencing were sequenced and analyzed using biological software,such as NCBIBLAST and DNAStar. The nucleosides of HH06 strain and reference strain (SC021202) were used. The acid sequence alignment homology was 95.9%,the homology with the vaccine strains H52 and H120 was 85.9%,and the nucleotide homology with the standard strain Massachusetts was 87.1%,which was the same as the classical strains Beaudette and Con46. The source values were 87% and 87.3%,respectively,and the homology was 86.5%-99.7% compared with other domestic isolates (Table 1).
The pMD18-T-N plasmid was used as a template,and S and P were used as primers to amplify the target geneN,and a 1 230 bp target band was successfully amplified. The recombinant liquid pET-30a-N was used as template to identify the bacterial liquid. The PCR was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis,and the specificNgene target band with the same size was amplified (Fig. 1A). The recombinant expression plasmid pET-30a-N was identified byEcoRⅠsingle digestion and identified byEcoRⅠandXhoⅠ. The size of single restriction enzyme was about 6 650 bp.Double digestion could digest about 1 230 bp of theNgene and 5 422 bp of pET-30a (+) vector fragment was identical to the expected result. The recombinant expression plasmid pET-30a-N was successfully constructed (Fig. 1B).
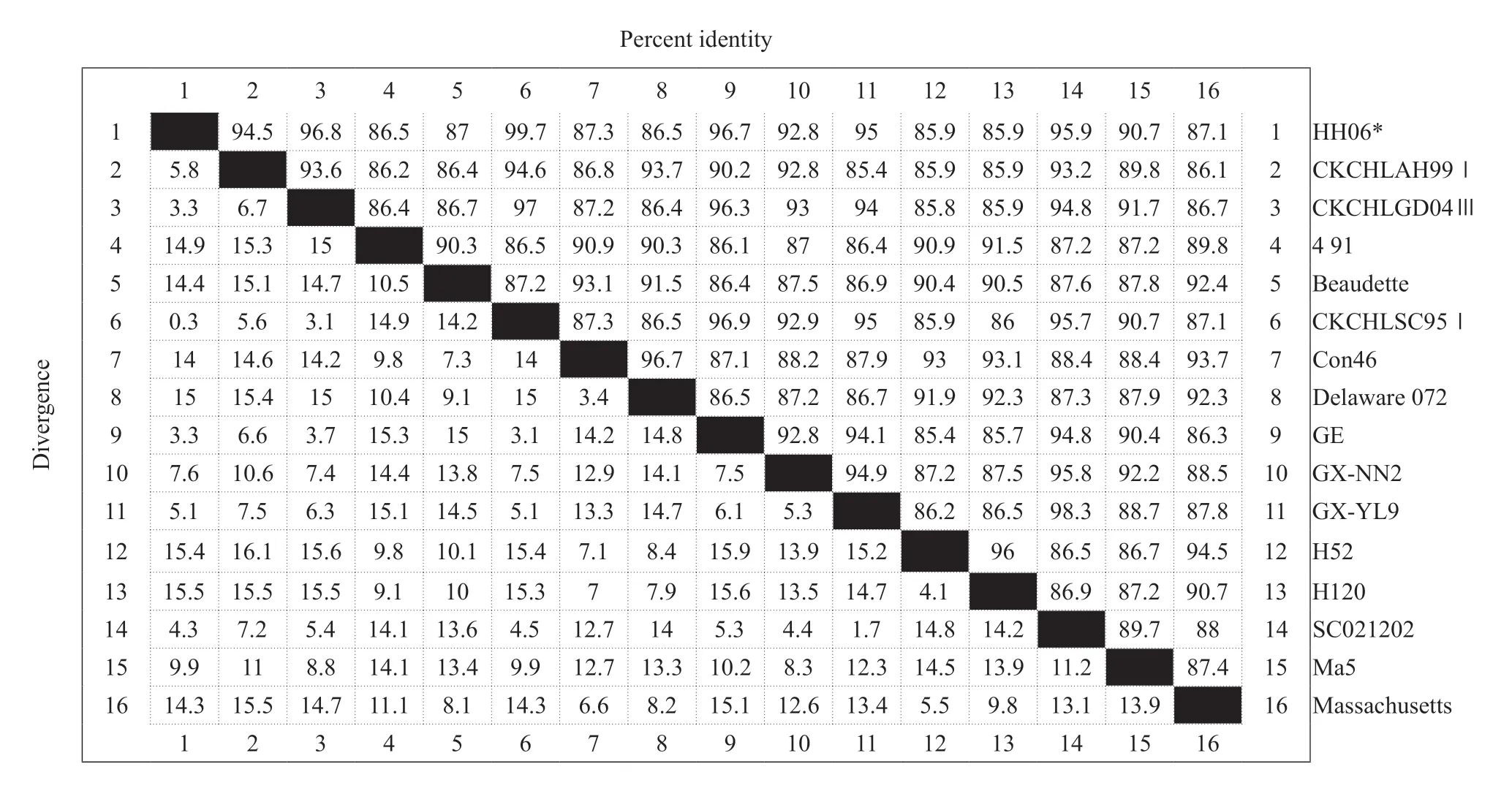
Table 1 Comparison of HH06 sequences among avian infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) isolates

Fig. 1 Construction and identification of prokaryotic expression plasmid(A) HH06 gene N with 1 230 bp is successfully amplified. Lane 1,DL-2000 DNA Marker; Lane 2,Product of N gene; Lane 3,Water control.(B) Identification of recombinant plasmid pET-30a-N by restriction endonucleases digestion. Lane 1,DL-10000 DNA Marker; Lane 2,Identification of recombinant pET-30a-N digested by EcoRⅠand XhoⅠ; Lane 3,Identification of recombinant pET-30a-N digested by EcoRⅠ.
ldentification of recombinant protein
After the recombinant plasmid pET-30a-N was transferred into the competent cells of the expressing bacteria,a single colony was picked and added to the liquid LB medium,and cultured overnight at 37℃,and the positive bacterial liquid was selected for induction expression,followed by electrophoresis analysis. The results showed a significant band at the 51 ku position,whereas the control group showed no band expression at the corresponding position (Fig. 2A). The cells which would induce expression would be subjected to 12% electrophoresis analysis after sonication and supernatant. It could be seen from the figure that the band appeared in the supernatant,indicating that the protein existed in a soluble form.
After the expression product was transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane,the N fusion protein was subjected to Western Blot detection using IBV whole virus polyclonal antibody. The N fusion protein specifically reacted with the corresponding IBV whole virus polyclonal antibody (Fig. 2B).
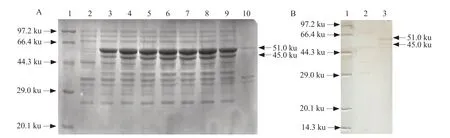
Fig. 2 Expression of Escherichia coli-expressed recombinant IBV N protein with 51 ku and truncated-expressed 45 ku(A) SDS-PAGE of recombinant IBV N protein. Lane 1,Protein Marker; Lane 2,pET-30a-N (non-induced); Lane 3-8,pET-30a-N (induced 1-6 h); Lane 9,pET-30a-N (supernatant of induced); Lane 10,pET-30a-N (sediment of induced). (B) Western Blot of recombinant IBV N protein. Lane 1,Protein molecular weight; Lane 2,pET-30a-N (non-induced); Lane 3,pET-30a-N (induced supernatant).
Preparation and identification of polyclonal antibody against N protein of IBV HH06 strain
The recombinant N protein was purified and immunized to New Zealand white rabbits to prepare rabbit anti-N polyclonal serum. The ELISA results showed that the prepared antiserum had a titer of 1 : 218,and the reactivity with the IBV HH06 strain was good,and the titer was 1 : 215. Western Blot analysis showed that rabbit anti-N polyclonal antibody serum and unpurified recombinant N protein formed a specific reaction band at 51 ku (Fig. 3A),indicating that rabbit anti-N polyclonal serum had good reactivity. Indirect immunofluorescence assay showed that BHK-21 cells transfected with eukaryotic plasmid PVAX-N could detect specific fluorescence,while control cells and transfected PVAX1 empty vector cells showed no specific fluorescence (Fig. 3B).
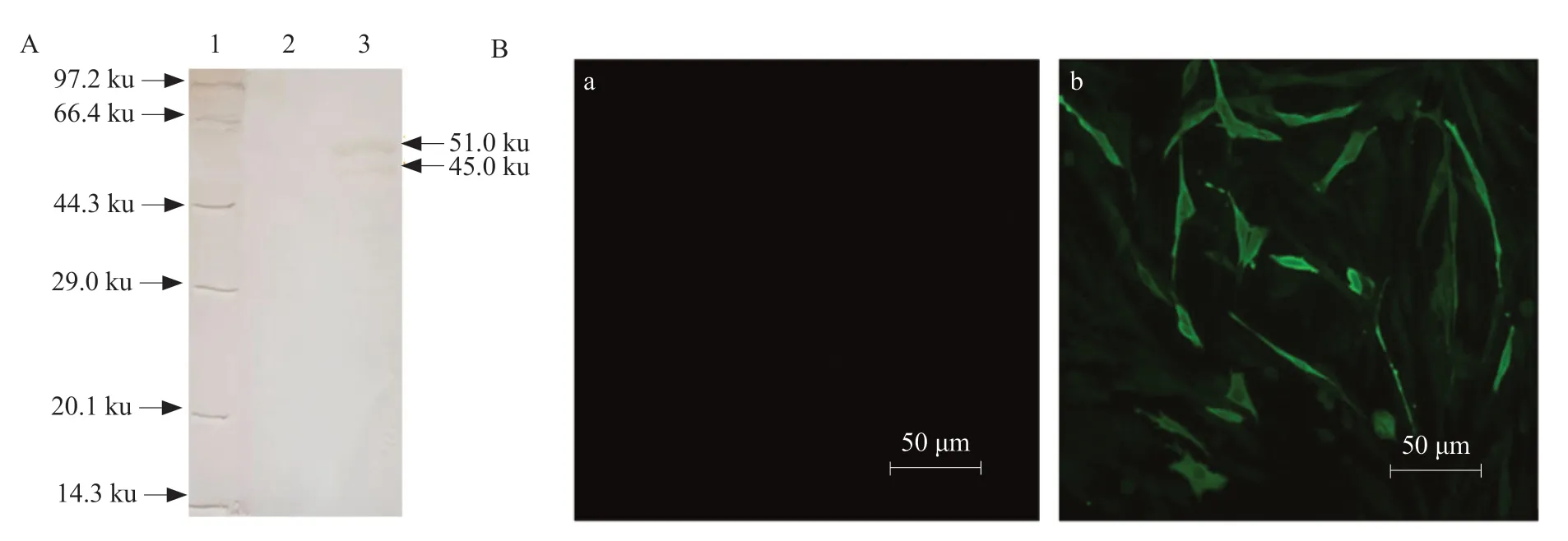
Fig. 3 Identification of biological activity of polyclonal antibody IBV N protein(A) Western Blot of polyclonal antibody. Lane 1,Protein Marker; Lane 2,pET-30a (+); Lane 3,pET-30a-N induced protein.(B) Polyclonal antibodies are specifically fluorescent with eukaryotic plasmids. (a) Cell transfection of PVAX1 empty vector; (b) Cell transfection of PVAX-N recombinant plasmid.
Establishment of an indirect ELISA method
According to the analysis of the data,the optimal coating concentration of antigen was 2.5 μg · mL-1and the optimal dilution of serum was 1 : 40 (Table 2).Under this situation,the OD490nmwas close to 1.0 and theP/Nvalue was the largest. Meanwhile,when the 1%BSA was used as a blocking solution,the closed time was 120 min,the serum was used for 1 h,the working concentration of the secondary antibody was 1 : 1 000 for 1 h and the substrate coloration time was 10 min,thePvalue was close to 1 and theP/Nvalue was the largest (Fig. 4). Ninety-six samples of SPF chickennegative sera were used to measure the OD490nm. According to the calculation,the mean OD490nmof the 96 negative sera was 0.180 and the standard deviation was 0.016. According to the critical value calculation method,the critical value was 0.180+3×0.016=0.2286. Thus,when the OD490nmvalue of the sample was ≥0.2286,it could be judged as positive with 99.9% confidence,otherwise,it was negative. The minimum intraplateCVof 30 sera was 0.6%,the maximum was 6.5%;the minimumCVamong plates was 1.6%,and the maximum was 12.3%,both less than 15%,indicating that the established indirect ELISA assay had good repeatability.

Table 2 Optimization of serum concentration and antigen concentration
Avian leukosis virus,bird flu virus,Newcastle disease virus,Escherichia coli,Salmonellapositive serum,IBV positive serum and negative serum were used to establish indirect ELISA assays. Data analysis showed that the OD490nmvalues of the positive serum of the virus ofavian leukosis virus,bird flu virus Newcastle disease virus,Escherichia coliandSalmonellawere all lower than the critical value of 0.2286 for the determination of IBV positivity and there was no cross reaction with IBV positive serum. The OD490nmvalue of IBV positive serum was significantly different from that of other positive serum OD490nm,indicating that the method had good specificity (Fig. 5A).
The IBV positive serum was serially diluted in eight stages and the indirect ELISA method was used to determine the OD490nm. Fig. 5B showed that when the positive serum was diluted 1 : 500,the result was positive,indicating that the method had good sensitivity.
Serum samples from two chicken farms were tested for IBV antibodies using an indirect ELISA method.A total of 75 chicken egg samples from chicken farms were tested. A total of 71 samples were positive,the positive rate was 94.7%,and the OD490nmvalue was 0.351 to 1.738. The coincidence rate between the virus and the virus as the coating antigen was 94.7%; in the chicken farm 2,there were 60 broiler chicken serum samples,50 were positive,the positive rate was 83.3%,and the OD490nmvalue was between 0.347 and 1.684.The compliance rate of the coating antigen ELISA test was 84.7% (Table 3). The results showed that the two chicken farms produced high IBV antibody levels after three IB vaccine immunizations.
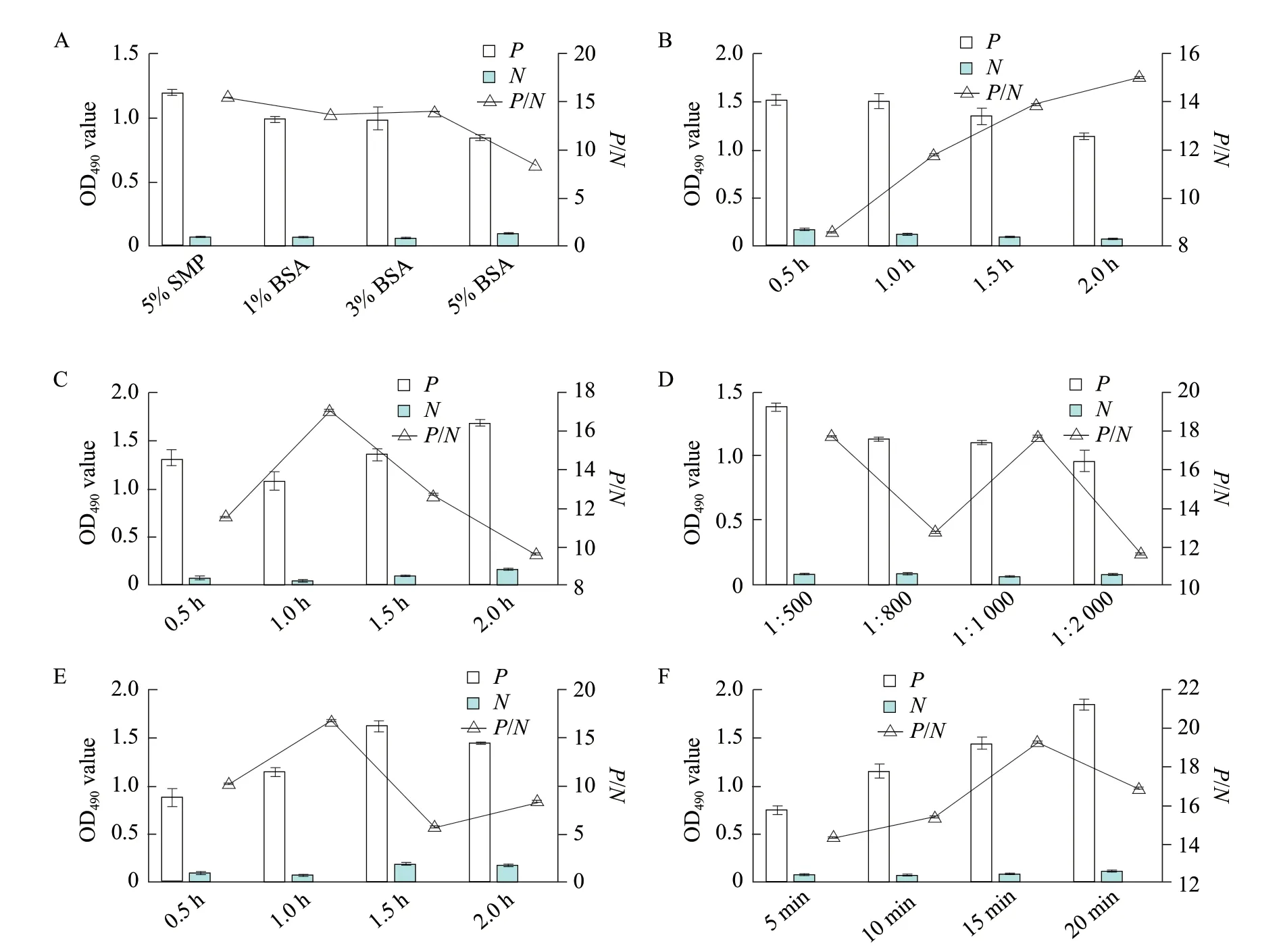
Fig. 4 Optimization of indirect ELISA detection methodThe best blocking solution is 1% BSA and the best blocking time is 2 h; the best optimal time of conjugate is 1 h; the best serum incubation time is 1 h;the best secondary antibody dilution is 1 : 1 000; the best optimal incubation time of enzyme labeled antibody is 1 h and the best optimal reaction time of substrate is 10 min.

Fig. 5 Specificity and sensitivity of ELISA method(A) Result of specificity test of other avian viruses. OD490nm value of IBV positive serum is significant different from other positive sera and has good specificity. (B) Results of sensitivity test. When positive serum is diluted 1 : 500,result is positive and method has good sensitivity.

Table 3 Results of clinical test
Discussion
Cloning and sequence analysis of N gene of IBV HH06 strain
In this study,a pair of primers was designed based on IBV SC021202 strain published on NCBI. The complete open reading frame containingNgene of 1 750 bp was successfully amplified from the total RNA of IBV HH06 strain by RT-PCR. The fragment of interest was ligated into the pMD18-T cloning vector. Since the cloning vector had a strong selfreplication function and was highly replicated in the bacterium,the target fragment was ligated into the pMD18-T cloning vector. It was beneficial to obtain enough target genes. Since the low temperature and long time during the ligation process were more favorable for the connection of the target fragment to the cloning vector,in the experiment,16℃ was selected and the conditions were connected overnight(12 h). According to the sequencing results,a pair of subcloning primers was designed,andEcoRⅠandXhoⅠrestriction sites were inserted upstream and downstream,and the recombinant plasmid was used as a template for PCR amplification. During the PCR process,the gradient was set and the temperature was changed. Explored the reaction conditions of the system and finally obtained the target gene with a size of 1 230 bp.
The cloned target fragment was sequenced. The sequencing results showed that theNgene of IBV HH06 strain had the highest nucleotide homology with CK/CH/LSC/95I (GenBank: DQ287915.1)Ngene.The homology of HH06 strain and vaccine strain H52,H120 was 85.9%,the nucleotide homology with the IBV standard strain Massachusetts was 87.1%,and the homology with the classical strains Beauudette and Con46 was 87% and 87.3%,respectively.
Induced expression of N protein of IBV HH06 strain
The prokaryotic expression system and the eukaryotic expression system are two expression systems for expressing foreign genes commonly used in genetic engineering. In the experiment,E. coliexpression system was the most widely used,because it had the advantages of time and labor saving,convenient operation,high target gene expression level,high protein expression concentration,strong anti-pollution ability,short culture period and easy to protein purification (Johnsonet al.,2003).
The pET-30a (+) expression vector contains a histone tag consisting of six histidines,contains a T7 lac promoter,and has a restriction enzyme site for enterokinase protein and thrombin. The expressed protein can be pro-expressed. The purification and the sensitivity of the fusion label can also be quantitatively detected. Therefore,this experiment used pET-30a (+)expression vector to express recombinant N protein,which provided a basis for the differential diagnosis of IBV in the future.
In this experiment,IPTG was used to induce the expression of N protein. Because IPTG exerted certain toxic effects on the cells during protein-induced expression,the expression of protein was not increased with the induction time and the concentration of IPTG. The expression product might be degraded by proteases as the induction time prolongs,and the expression level was related to the toxic effect of the expression product on the cells. In addition,the temperature also played a decisive role in the process of expressing foreign genes inE. coli(Birdet al.,2004). Therefore,the induced expression condition of N protein in this experiment was 37℃,1 mmol · L-1IPTG induction for 6 h,and finally a fusion protein with a size of 51 ku was expressed,and this protein was a soluble protein.
According to the amino acid sequence of the HH06 strain of IBV,the relative molecular mass of the N protein is about 45 ku,and the fusion protein of the pET-30a (+) vector itself is about 6 ku,so the actual molecular weight of the expressed protein is about 51 ku. In the SDS-PAGE test,two bands were found,one of which was about 51 ku,which was the same size as expected,the other band had a molecular weight of about 47 ku,and the same result was obtained by Western Blot. In IBV (Sternet al.,1982) and turkey coronavirus (Breslinet al.,2001),the similar phenomenon had been reported,and this experiment had similar results,so it was speculated that the protein of 47 ku might be the cleavage of 51 ku protein product.
Establishment of an indirect ELISA method
Compared with other serological detection methods,ELISA has the advantages of high sensitivity,high speed,high safety,time and labor saving,accurate results,etc. It is suitable for laboratory examination and clinical detection. Chenet al. (2003) expressed theNgene inE. coliand insect cells,and purified the N protein as a coating antigen to establish an ELISA method for detecting IBV antibodies. Since there were no virions,the safety of detection was improved,suggesting a good application prospect.
IBV has four major structural proteins. Although S protein is the main protein that determines the antigenicity of IBV,it is active in evolution and is prone to mutations such as mutation and recombination. At
the same time,S protein also has shortcomings such as difficulty in expressionin vitroand high glycosylation modification to determine its antigenicity,which limits its application prospects. However,theNgene is the most conserved in genetic evolution,and the homology can be as high as 94%-99%. The nucleotide and amino acid sequences of theNgene were sequenced in this study (GenBank: KC256943.1) on NCBI. Other IBV representative strains (including typical respiratory and nephrotic strains) were aligned,nucleotide homology was over 88%,amino acid homology was over 91%,and the inheritance of IBV N protein was also demonstrated stability. In addition,during the replication of the virus,the expression of N protein was higher than that of other structural proteins,and the ELISA antibody produced by the body was the earliest,and the titer was also the highest (Ignjatovic and Galli,1993). The N protein plays a role in cellular immunity and virus assembly,so N protein is a good diagnostic antigen for IBV antibody detection. Therefore,in this study,theNgene of IBV HH06 strain was cloned,and it was ligated into the expression vector and transformed intoE. colifor expression,which provided reference value for the future researches of N protein.
The choice of coating solution,the concentration of antigen coating,the choice of blocking solution,the concentration of serum and enzyme-labeled secondary antibody,incubation time and color development time are closely related to the establishment of ELISA method. The pH of the coating solution has a certain relationship with the adsorption performance of the solid phase carrier. When the pH of the coating buffer is 9.0-9.6,the adsorption capacity of the antigen and the solid phase carrier is the strongest. Therefore,the coating buffer used in this study was Carbonate buffer pH 9.6. Due to the mutual interaction between protein molecules,if the concentration of the coated antigen is higher,the corresponding force will be enhanced,resulting in the antigen and the solid phase carrier being weakly bound and easily eluted;and the coating antigen concentration is too low. In addition,the antigen and the solid phase carrier are not sufficiently combined. If the antigen concentration is too high or too low,it will affect the accuracy of the experimental results. Therefore,in order to make the experimental results highly accurate,it is necessary to determine the coating concentration of the antigen.Therefore,the experiment had been explored through the cross method several times. The optimal coating concentration of the antigen was determined to be 2.5 μg · mL-1,and the optimal serum dilution was 1 : 40,which ensured the accuracy of the experiment.
One of the main reasons for the non-specific results in the experiment was that the space on the surface of the solid phase carrier that adsorbed the unadsorbed antigen adsorbed other substances,so in the experiment,the antigen was efficiently blocked by selecting the optimal blocking solution,thereby reducing the specificity combination in the experiment.When Virginia and other human antibodies were tested for influenza virus,0.5% BSA was used as a blocking solution,and good results were obtained (Hinshaw and Larsen,1990). Therefore,bovine serum albumin(BSA) is better than skim milk as a blocking solution.In this experiment,three different concentrations of BSA and skim milk were selected for comparison. The experimental results showed that the results of 1% and 3% of BSA were not different. Significantly,in order to save the cost of the experiment,1% of BSA was finally selected as the blocking solution.
At 37℃,different gradients were set for the incubation time of each step in the experiment,the concentration of the enzyme-labeled secondary antibody,and the color-developing time to ensure that only one variable was present,the incubation time,the concentration of the enzyme-labeled secondary antibody,and the color development. The time was optimized,and the optimal incubation time,the optimal concentration of the secondary antibody and the optimal color development time were determined,which made the detection method more clinically practical.
In this experiment,avian influenza virus (AIV),Newcastle disease virus (NDV),avian leukosis virus(ALV),Escherichia coli,Salmonellapositive serum,IBV positive serum,and negative serum were detected by an indirect ELISA method established by experiments. The OD490nmvalues were all smaller than the IBV negative positive threshold,indicating that the indirect ELISA assay established in this study had good specificity. The results of intraplate and interplate repeatability tests showed that the difference in OD490nmvalues detected by different serum samples at different times was not significant,indicating that the established ELISA method had good repeatability and stability. The positive detection rate was slightly lower than the commercial kit,and the coincidence rate was 85%. In this study,the clinical samples were tested by the established indirect ELISA method.The average positive detection rate was 89%,and the average coincidence rate with the virus as the coating antigen ELISA was 89.7%,indicating that the N protein obtained in this experiment could be replaced.IBV virus to detect IBV antibody had good application value and could be used as an important tool for rapid diagnosis and immune monitoring of clinical IBV.
Conclusions
In conclusion,this study successfully cloned the IBVNgene into the pET-30a (+) and named pET-30a-N.The recombinant protein was expressed successfully and had good reactivity with IBV positive serum.Using purified recombinant N protein as a coating antigen,the indirect ELISA protocol was established and optimized. It would provide a good tool for rapid diagnosis and epidemiological study of avian infectious bronchitis.
 Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2020年1期
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2020年1期
- Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Spatiotemporal Change of Agrometeorological Flood Disasters in Heilongjiang Province
- Technical Parameter Optimization for Straw Fibre Mulching Film Raw Material from Corn Stalk
- Effect of Zinc Acetate on Broiler Nutrient Metabolism and Skeleton Characteristic
- Effects of Facultative Anaerobic Cellulolytic Bacteria and Nitrogen-fixing Bacteria Isolated from Cow Rumen Fluid on Rumen Fermentation and Dry Matter Degradation in Vitro
- Effects of Different Feeding Methods on Behaviors,Immunities and Growth Performances of Suckling Calves
- Visualizing Patterns and Differences in Fine Particulate Matter(PM2.5) Research Between the USA and China over Last 25 Years: A Bibliometric Analysis
