一种基于电学特性的沥青混凝土吸水状况推测方法
郭庆林,鄂丰铭,刘强,高颖


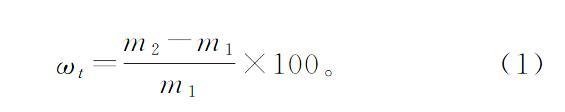
摘要:沥青路面在使用过程中不可避免会受到自然降水和地下水的影响,水分交替作用最终将导致沥青路面的水损害,而以往室内测定沥青混凝土含水率的方法无法对沥青路面的干湿状态进行快速评定。为了快速评定沥青路面的干湿状态,采用电学方法推测沥青混凝土的含水率。以密实型沥青混凝土电阻特性为依据,测量浸水前后沥青混凝土电阻率的变化,进而建立沥青混凝土吸水率与其电阻率的数学关系,以电阻率来推测沥青混凝土内部的含水率。结果表明,沥青混凝土含水率与电阻率对数值具有良好的线性相关性,沥青混凝土吸水率越大,电阻越小。所提方法可为不同沥青混凝土面层的干湿状况评定提供一定的借鉴。
关键词:路基工程;沥青混凝土;电阻率;吸水率;推测方法
中图分类号:U416.217文献标识码:Adoi: 10.7535/hbgykj.2020yx01001
An estimation method for the absorbed moisture of asphalt
concrete based on electrical resistance
GUO Qinglin, E Fengming, LIU Qiang, GAO Ying
(School of Civil Engineering, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, Hebei 056038, China)
Abstract:Asphalt pavement is inevitably affected by the natural precipitation and groundwater in the service stage. Hydrologic cycle will eventually lead to the moisture damage of asphalt pavement. However, the existing indoor method for moisture measurement of asphalt concrete cannot quickly assess the pavement wetting state. Therefore, in order to evaluate the wet and dry state of asphalt pavement quickly, an electrical method is proposed to estimate the moisture content in the asphalt concrete in this paper. And, the electrical resistance of dense asphalt concrete is measured before and after soaking. Then, the mathematical relationship between absorbed moisture and electrical resistance of asphalt concrete is established. The absorbed moisture can be estimated using the electrical resistance of asphalt concrete. Results show that a linear relationship exists between the content of absorbed moisture and the logarithm of electrical resistance. The more the absorbed moisture is, the smaller the electrical resistance is. This method can be used to evaluate the dry/wet condition of asphalt pavement.
Keywords:road engineering; asphalt concrete; electrical resistance; moisture uptake; estimation method
暴露在自然環境中的沥青路面由于经受降雨的长期反复作用,雨水会逐渐扩散到沥青混凝土内部,久而久之会造成沥青路面的松散、剥落等病害[16]。研究表明,水在沥青混凝土内部的运动过程一般分为2个阶段:第1阶段,自由水填充大孔隙,吸水率快速增大;第2阶段,水分向微孔隙扩散并在胶结料扩散中达到上限,长期作用下沥青胶结内聚力与集料沥青膜间粘结力下降,飞散质量损失率增大[711]。因此,对沥青路面干湿状况的研究有助于评价降雨对沥青路面的影响程度。一直以来,主要采用称重法对沥青混凝土含水状态进行测定[12],而对于沥青路面干湿状态的评价仍缺乏有效的测试方法。2017年,马晓霞等[13]对沥青混凝土的含水介电性能进行研究,指出沥青混凝土介电常数会随着含水率增加而上升,利用介电常数与含水率相关性模型可以估计沥青路面的干湿状态。郭庆林等[14]提出一种沥青混凝土电阻测量装置,通过分析马歇尔试件的电阻率与含水率的关系来预估沥青路面的含水率。宋杰等[15]指出非饱和土电阻率随含水率增加呈幂指数减小的规律,建立了电阻率与含水率、压实度的关系模型,运用电阻率方法评价了非饱和土的压实状况。文献[16—18]也指出沥青混凝土含水率增加会引起其电阻的变化。因此,通过沥青混凝土电阻特性的变化推测其含水率具有一定的可行性。本文以马歇尔试件为对象,研究沥青混凝土在不同浸水时间下的电阻特性变化规律,进而以此推测沥青混凝土含水率。
1试验测试方案
1.1试验材料与级配
本文采用AH70#沥青,主要性能指标如表1所示。采用的级配类型为AC13型密实型级配,级配曲线如图1所示。经马歇尔试验确定最佳油石比为50%。试验采用尺寸为Φ101.6 mm×63.5 mm标准马歇尔试件,沥青混凝土表观密度为2.39 g/cm3,理论相对最大密度为2.53 g/cm3,孔隙率为5.6%。
第1期郭庆林,等:一种基于电学特性的沥青混凝土吸水状况推测方法河北工业科技第37卷表1AH70#沥青技术性能指标
Tab1Properties of asphalt AH70#
指标测试值针入度(25 ℃,100 g,5 s,0.1 mm)68延度/cm(15 ℃)>100软化点/℃48密度/(g·cm-3)1.034闪点/℃285黏度/(Pa·s)(135 ℃)0.468
1.2含水率测定方法
采用称重法测定沥青混凝土含水率。测量出的马歇尔试件浸水前、后的质量分别记为m1,m2,则浸水一定时间后的试件含水率ωt可通过式(1)计算得到。
ωt=m2-m1m1×100。 (1)
1.3电阻特性测试方法
为了使测试结果更具代表性,试件浸水温度分别采用5,30,60 ℃,为提高自由水的导电性,在水中加入少许NaCl,配置成质量分数为005%的盐溶液进行浸水。浸水时间分别为0,6,12,24,48 h;浸水完成后,称量好2份7 g粉状石墨作为导电连接电极平铺于马歇爾试件上下表面;同时在平铺石墨粉上放置长8 cm、宽1.5 cm的铜片。为避免电极极化效应,在铜片上方施加一重物,从而保证各电极的良好接触。马歇尔试件电阻测量装置如图2所示。
测量完成后,计算电阻特性值。为避免试件厚度差异的影响,选用单位长度的电阻率作为考察指标,探讨电阻值与含水率的相关性。为降低离散性,保证测试精度,每组试验条件分别制备6个平行试件,总计15组试件,参与测试的试件总数为90个。
2结果分析
2.1沥青混凝土含水率随浸水时间的变化规律
由图3可以看出,沥青混凝土试件的含水率在初期浸水(12 h以内)时增长较快,后期增长速度减慢。浸水初期水分快速进入试件表面空隙,后期由于密级配沥青混凝土空隙较少,水分向沥青混凝土内部的运动转为扩散形式,故而含水率增长速度减慢。从图3中还可以看出,当浸水时间较短时,温度对水扩散的影响不显著。当浸水超过20 h后,水温越高水分向沥青混凝土内部扩散的速度越快,说明水温对水扩散的速率具有显著影响。
2.2沥青混凝土电阻率随浸水时间的变化规律
由图4可以看出,电阻率随浸水时间的延长呈现非线性减小的趋势,且随浸水时间延长呈现对数递减趋势。说明水分扩散进入沥青混凝土后形成了导电通道,随着水分扩散的不断加剧,导电通道逐渐增多,进而导致了沥青混凝土电阻率的快速减小。从图4还可以看出,温度对沥青混凝土的电阻率的影响不显著,这主要是由于沥青混凝土内部的随机结构差异所造成的。
2.3沥青混凝土电阻率与含水率的关系
由图3及图4可以看出,含水率随浸水时间延长而增大,而电阻率随浸水时间延长而减小,为了建立由电阻率推测沥青混凝土内部含水率的数学关系,对含水率及电阻率进行了回归分析,结果如图5所示。
由图5可以看出,马歇尔试件电阻率与含水率之间存在对数函数关系。二者相关性系数为0.847 3,具有良好的相关性,说明沥青混凝土含水率与电阻率对数值呈线性相关关系,采用电阻率推测沥青混凝土内部的含水率具有一定的可行性。电阻率越大,沥青混凝土含水率越小。
3结论
1)密级配沥青混凝土含水率随浸水时间的延长而逐渐增大,初期增长较快,后期水分扩散速率减慢。温度对水扩散速率具有显著影响,水扩散速率随着温度的升高而增大。
2)沥青混凝土电阻率随浸水时间的延长而降低,呈现对数递减趋势。
3)沥青混凝土含水率与电阻率对数值存在良好的线性相关性,未来可以利用沥青混凝土电阻率测试结果快速评定沥青混凝土面层的干湿状况。本文只对AH70#沥青混凝土进行了研究,还需要对其他类型的沥青混凝土作进一步试验验证。
参考文献/References:
[1]王聪,马飞. 不同空气压力下沥青混凝土的透水性[J]. 公路交通科技,2014,31(4):5256.
WANG Cong, MA Fei. Research on permeability performance of asphalt concrete under different air pressures [J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2014, 31(4):5256.
[2]罗蓉,柳子尧,黄婷婷,等. 冻融循环对沥青混合料内水气扩散的影响[J]. 中国公路学报, 2018,31(9):2026.
LUO Rong, LIU Ziyao, HUANG Tingting, et al. Effects of freezingthawing cycles on water vapor diffusion in asphalt mixtures[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31 (9):2026.
[3]何中南. 长期浸水对沥青和集料沥青界面性能损伤的实验研究[J].中外公路, 2012, 32(4): 261263.
HE Zhongnan. Experimental study on damage of asphalt and aggregateasphalt interface by longterm immersion[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2012, 32 (4): 261263.
[4]高颖,郭庆林,王可意,等. 不同形状假设下沥青混凝土级配快速识别效果对比[J].铁道科学与工程学报, 2018, 15(9): 22522257.
GAO Ying, GUO Qinglin, WANG Keyi, et al. Comparative analysis on the fast recognized gradation of asphalt concrete under different shape assumptions [J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(9): 22522257.
[5]郭庆林,程永春,陶敬林. 沥青混凝土数字图像集料粘连效应分割方法研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2015, 31(3): 3236.
GUO Qinglin, CHENG Yongchun, TAO Jinglin. Research of aggregate adhesion effect segmentation method in asphalt concrete digital image [J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2015, 31 (3): 3236.
[6]郭庆林. 沥青混合料内部应力分布及其对粘弹性能的影響研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2013.
GUO Qinglin. Research on Internal Stress Distribution of Asphalt Mixture and Its Impact on Viscoelastic Performance[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2013.
[7]ABUAWAD I M A, AlQADI I L, TREPANIER J S. Mitigation of moisture damage in asphalt concrete: Testing techniques and additives/modifiers effectiveness[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 84: 437443.
[8]MA T, GENG L, DING X, et al. Experimental study of deicing asphalt mixture with antiicing additives[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 127: 653662.
[9]WANG W, WANG L, XIONG H, et al. A review and perspective for research on moisture damage in asphalt pavement induced by dynamic pore water pressure[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 204:631642.
[10]BOZORGZAD A, KAZEMI S F, MOGHADAS N F. Evaporationinduced moisture damage of asphalt mixtures: Microscale model and laboratory validation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 171:697707.
[11]XU H, XING C, ZHANG H, et al. Moisture seepage in asphalt mixture using Xray imaging technology[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 131:375384.
[12]刘丹. 干湿交替作用下沥青混凝土高温性能变化规律研究[D].邯郸:河北工程大学,2018.
LIU Dan. Study on High Temperature Performance of Asphalt Concrete under Drywet Alternation[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2018.
[13]马晓霞,张鹏,钟静. PAC件含水量与介电常数的相关性研究[J].公路工程, 2017,42(1): 253256.
MA Xiaoxia, ZHANG Peng, ZHONG Jing. Study on the relationship between PAC specimen moisture content and dielectric constant [J]. Highway Engineering, 2017, 42 (1):253256.
[14]郭庆林,刘富春,张鹏,等.快速检测沥青路面材料含水率用的电阻测量装置[P].中国:ZL201821994146.2, 20190701.
[15]宋杰,李术才,刘斌,等.基于电阻率特性的非饱和土压实度定量评价方法[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 35(6): 3341.
SONG Jie, LI Shucai, LIU Bin, et al. Quantitative assessment method of unsaturated soil compaction degree based on resistivity property[J]. Journal of Changan University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 35(6):3341.
[16]赵蕾.沥青混凝土导电性的影响分析[J].山西建筑, 2017,43(9):129131.
ZHAO Lei. Discussion on silica powder performance in concrete [J].Shanxi Architecture, 2017,43(9): 129131.
[17]LIU X, WANG C, DENG Y, et al. Computation of fractal dimension on conductive path of conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 115:699704.
[18]何永佳,敖灶鑫,吕林女,等.融雪化冰用钢渣导电沥青混凝土的电阻稳定性[J].北京工业大学学报, 2011, 37(1): 8084.
HE Yongjia, AO Zaoxin, L Linnü, et al. Electrical resistance stability on conductive asphalt concrete using steel slag as aggregate for deicing and snowmelting [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2011, 37 (1): 8084.
收稿日期:20190805;修回日期:20190916;责任编辑:冯民
基金項目:国家自然科学基金(51508150);国家重点研发计划(2018YFF0300201);河北省自然科学基金(E2018402206); 河北省教育厅青年拔尖人才计划(BJ2017034)
第一作者简介:郭庆林(1984—),男,山东肥城人,副教授,博士,主要从事沥青混凝土细观损伤理论方面的研究。
Email:guoql@hebeu.edu.cn
郭庆林,鄂丰铭,刘强,等.一种基于电学特性的沥青混凝土吸水状况推测方法[J].河北工业科技,2020,37(1):14.GUO Qinglin,E Fengming,LIU Qiang,et al.An estimation method for the absorbed moisture of asphalt concrete based on electrical resistance[J].Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology,2020,37(1):14.

