Study on the Biological Basis of Qi, Blood, and Vessel in Immune Thrombocytopenia Patients With Syndrome of Qi Failing to Govern Blood Based on the Theory of Qi and Blood
WANG Ming-jing (王明镜), CHEN Zhuo (陈 卓), ZHU Shi-rong (朱世荣),3, DING Xiao-qing (丁晓庆),CHEN Hai-yan (谌海燕),QUAN Ri-cheng (全日城), XU Yong-gang (许勇钢),ZHAO Pan (赵 攀), JIANG Yun-yao (姜云耀), HU Xiaomei (胡晓梅)
1. Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, 100091, China;
2. Graduate School, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, 100700, China;
3. Graduate School, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, 100029, China; 4. Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, 100078, China
ABSTRACTObjective:To investigate the biological basis of qi, blood and vessel in immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) patients with syndrome of qi failing to govern blood (SQFGB) based on traditional Chinese medicine. Methods:A total of 52 ITP patients with SQFCB were enrolled and divided into bleeding group (38 cases) and non-bleeding group (14 cases). Bleeding group was further divided into mild qi deficiency group (25 cases) and moderate/severe qi deficiency group (13 cases) based on Chinese Medicine syndrome score. 20 healthy volunteer were recruited as control group. The count of platelet (PLT)was taken as the blood related indicator. The expressions of cytokines including IL-1β, IL-17A, TNF-α,CD40L, and TGF-β, detected by Aim Plex Multiple Immunoassays for Flow, were taken as the qi related indicators. The expressions of VEGF-A, detected by Aim Plex Multiple Immunoassays for Flow and NO,NOS, and ET-1 detected by ELISA, were taken as the vessel related indicators. Results: As compared to the control group, the count of PLT, taken as the blood related indicator, was significantly lower in ITP group patients with SQFCB (P<0.05). The expression levels of IL-17A and TNF-α, taken as the qi related indicators, were significantly higher, while those of CD40L, IL-1β, and TGF-β, also taken as the qi related indicators, were significantly lower in ITP patients with SQFCB, respectively (P<0.05). The expression levels of NO and ET-1, taken as the vessel related indicators, were significantly higher, while the expression levels of NOS and VEGF-A also taken as the vessel related indicators, were significantly lower in ITP patients with SQFCB, respectively (P<0.05). The count of PLT, taken as the blood related indicator,was significantly lower in moderate/severe group than those in mild group (P<0.05). The expression levels of CD40L and TGF-β, taken as the qi related indicators, were also significantly lower in moderate/severe group than those in mild group, respectively (P<0.05). Conclusion:The count of PLT might be the biological basis of blood. The expressions of NO, NOS, ET-1 and VEGF-A might be the biological basis of vessel. The expressions of IL-1β, IL-17A, TNF-α, TGF-β, and CD40L may be the biological basis of qi.The expressions of CD40L and TGF-β could reflect the degree of qi deficiency in ITP patients based on the theory of qi and blood.
KEYWORDS Syndrome of qi failing to govern blood; Immune thrombocytopenia; Theory of qi and blood;Chinese medicine
INTRODUCTION
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an acquired autoimmune disorder disease characterized by thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage of skin mucous membrane or organs[1,2]. It was recorded as "bleeding syndrome" or "purpura" in Chinese medicine. Syndrome of qi failing to govern blood (SQFCB) is one of the common syndromes of ITP[3].
According to the theory of Chinese medicine[4], vessel is the place where qi and blood meet, and the path of qi and blood running.The running of qi and blood in the human body is governed by the vessel, while the relaxation and contraction of vessel is regulated by the qi,and the govern function of qi helps the vessel to restrict the running of blood. Therefore, the normal running of blood in the vessel is based on the abundant qi, the intact and unobstructed vessel. If the qi is imaginary, then it is difficult to govern the blood, leading to abnormal regulation of the vessel, further affecting the physiological function of the vessel. If the physiological function of the vessel is abnormal, the blood will overflow the vessel, the qi will be lost accompanying with the blood, then qi deficiency and bleeding will be more serious. The qi, blood and vessel are closely connected, and they together form a blood circulation system[5].
The intuitive manifestation of patients with ITP is that the blood can not be governed by the vessel,then the blood flow out of the vessel. Whileas the cause of this phenomenon is qi deficiency. The qi will be unable to help the vessel govern the blood because of the qi deficiency, which result in the blood flowing out of the vessel. While the qi deficiency will be further aggravated since the qi will lost along with the blood overflowing the vessel based on the theory of "the blood carries the qi" in Chinese medicine. Such cycles and reciprocations will lead to the loss of function of vessel, the weakness of qi and blood, and then result in the disease prolongation and difficult treatment.
The concepts of qi and vessel in Chinese medicine theory are too broad. The biological basis of qi and vessel involved in this pathological process are unknown. At the same time, the essence of pathological changes from qi deficiency to syndrome of qi failing to govern blood based on Chinese medicine needs to be studied in depth.
This study aims to explore the biological basis of qi, blood and vessel, in order to know how the interactions of qi, blood and vessel play a role in the pathogenesis of ITP patients with SQFCB and the essence of SQFCB which provide the objective evidence for the diagnosis and efficacy evaluation of ITP with SQFCB, based on the theory of qi and blood in Chinese medicine.
METHODS
Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnosis of ITP: Chinese consensus report on diagnosis and treatment of adult primary immune thrombocytopenia (version 2016)[6]. Newly diagnosed ITP describes patients within 3 months of diagnosis. Persistent ITP describes patients with ITP lasting between 3 and 12 months from diagnosis. This category includes patients not achieving spontaneous remission or those unable to maintain a response after stopping treatment between 3 and 12 months from diagnosis. Chronic ITP describes patients with ITP lasting for more than 12 months. Severe ITP describes patients with a platelet count less than 10×109/L and with bleeding symptoms at presentation suffcient to mandate treatment, or occurrence of new bleeding symptoms requiring additional therapeutic intervention, such as a different platelet-enhancing agent or an increased dose. Refractory ITP describes patients who fulfll 2 criteria (1) failed splenectomy or subsequent relapse and (2)reassessed diagnosis.
The diagnosis of ITP with SQFCB and the score of qi deficiency: the program of diagnosis and treatment of purpura (immune thrombocytopenia)of Chinese medicine published by the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 2010[7]. The main symptom is the skin purpura with a light and sparse appearance. The secondary symptoms include: a. nosebleed, bleeding teeth,more menstrual flow; b. longer course of disease,and bleeding after exertion; c. fatigue, dizziness,shortness of breath; d. face color sallow; e. less food intake, loose stools or constipation; f. pale tongue thin white; g. fine or deep pulse. It can be diagnosed by having main symptom plus with one of the secondary symptoms of a to c and with 2 of the secondary symptoms of d to g.
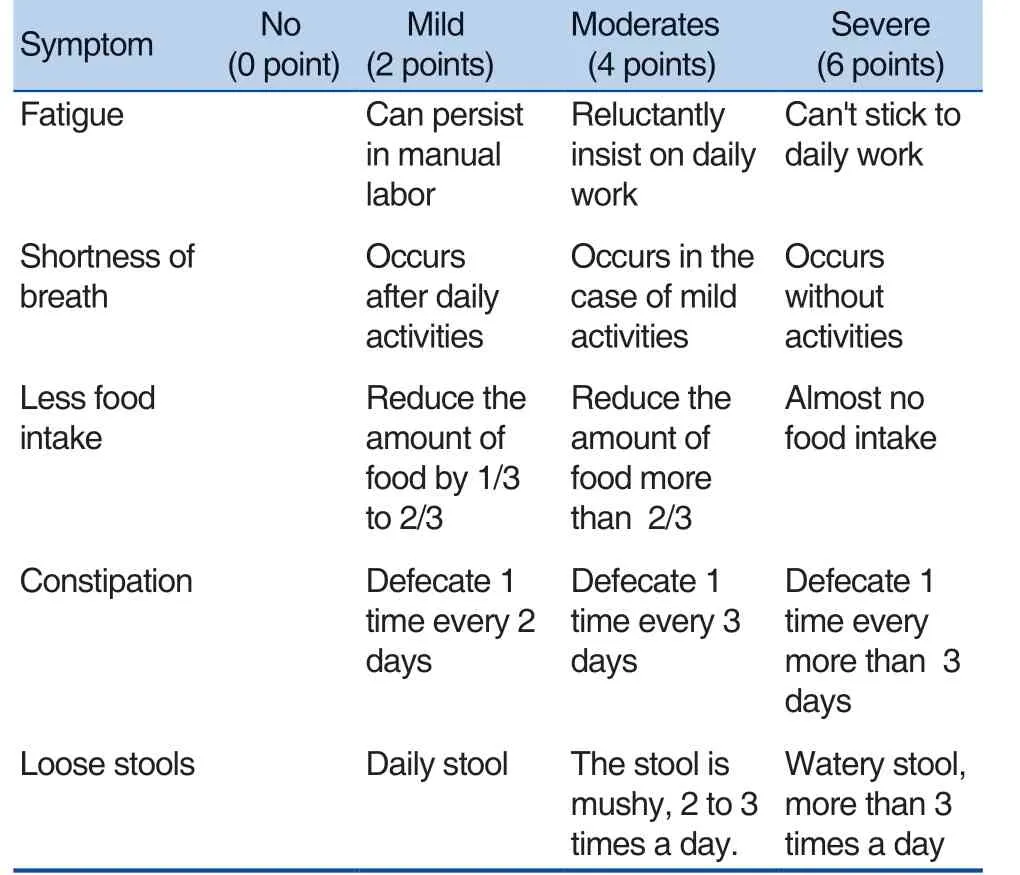
The scores of qi deficienc
Patients
This study involved 52 ITP patients with SQFCB who were admitted to Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences or Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,between January 2016 to June 2018. Among this 52 patients, there were 27 males and 25 females, aged from 18 to 63 years old (median age at 45 years old).Study protocol was approved by Ethics Committee of Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (2015XLA108-2). Participants were provided informed consent before being enrolled.The methods were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines. This study was registered on Chinese Clinical Trial Registry. The registration number was ChiCTR-IOR-17014236.
Main Reagents
Nitric oxide (NO)/ nitric oxide synthase (NOS)kit and endothelin 1 (ET-1) kit were provided by Beijing Roche Inspection Institute co., LTD., Beijing,China. Cytokines Interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) kit, IL-17A kit, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) kit, and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A)kit,Aimplex®Human custom 15-plex kit (T1C156701)and Aimplex®TGF beta1 1-plex kit(B111206)were provided by Beijing kuang bo biological co.,LTD., Beijing, China.
Measurement of Serum Level of Key Indicators
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell was separated by density gradient centrifugation. The detections of cytokines IL-1β, IL-17A, TNF-α, and VEGF-A were performed according to the AimPlex test instructions. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect NO/NOS and ET-1 in peripheral blood.
Statistics
Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 21.0 software (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL,USA). All data were presented as mean±standard deviation (mean±SD). Independent sample T test was used. A value of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Changes of the Blood Related Indecator in ITP Patients with SQFCB
The count of platelet (PLT) was taken as the blood related indicator. As compared with the control the group [177 (166, 194)×109/L], the count of PLT of ITP group was significantly reduced [25(17, 36)×109/ L] (P<0.05) (Figure 1A). There was no significant change of count of PLT between the bleeding group and the non-bleeding group[24 (18, 30)×109/L, 32.5 (14.75, 46.5)×109/L](P>0.05) (Figure 1B). The count of PLT of moderate/severe qi deficiency group was significantly decreased compared with that of mild group [21 (16,36)×109/L,39 (14,76)×109/L] (P<0.05) (Figure 1C). These results suggested that the count of PLT can be taken as the blood related indecator of ITP patients with SQFCB. Since the count of PLT was significantly reduced in ITP patients with SQFCB and reduced more significantly in the moderate/severe qi deficiency group.
Changes of the Qi Related Indecators in ITP Patients with SQFCB
The expressions of cytokines including IL-1β,IL-17A, TNF-α, CD40L, and TGF-β, were taken as the qi related indicators. As compared with the control group, the expressions of CD40L,IL-1β, and TGF-β were significantly decreased in the ITP group, respectively (P<0.05), whileas the expressions of TNF-α and IL-17A were significantly increased in the ITP group, respectively (P<0.05),as shown in Table 1 and Figure 2.

Figure 1. The count of PLT in ITP patients with SQFCB.

Figure 2. Comparison of cytokines of the ITP group and the control group.
Table 1. Comparison of the expressions of cytokines between the ITP group and the control group

Table 1. Comparison of the expressions of cytokines between the ITP group and the control group
Note: Compared with the control group, P<0.05.
n CD40L IL-1β TGF-β TNF-α IL-17A Control group 20 24.14±7.08 5.15±1.74 61169.72±19099.77 2.64±0.66 157.35±30.18 ITP group 52 7.69±2.94 3±1.12 14778.95±10060.56 23.12±6.39 194.32±85.44
Table 2. Comparison of Expressions of the cytokines of the bleeding group and the non-bleeding group

Table 2. Comparison of Expressions of the cytokines of the bleeding group and the non-bleeding group
n CD40L IL-1β TGF-β TNF-α IL-17A Non-bleeding group 14 6.78±1.27 2.54±1.02 14108.59±7036.21 17.93±3.39 202.52±63.44 Bleeding group 38 8.03±3.3 3.17±1.23 15025.93±10917.82 19.82±4.09 191.22±93.31
There was no significant difference of the levels of CD40L, IL-1β, TGF-β, TNF-α and IL-17A between the bleeding group and the non-bleeding group (P>0.05), as shown in Table 2, Figure 3.
The expressions of CD40L and TGF-β were significantly decreased in the moderate/severe qi deficiency group compared with the mild qi deficiency group (P<0.05). There was no significant change of expression of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-17A between the moderate/severe qi deficiency group and the mild qi deficiency group (P>0.05), as shown in Table 3, Figure 4.
Changes of the Vessel Related Indicators in ITP Patients with SQFCB
The expressions of VEGF-A, NO, NOS, and ET-1 were taken as the vessel related indicators.As compared with control group, the expressions of NO and ET-1 of the ITP group were significantly increased respectively (P<0.05), whileas that of NOS and VEGF-A were significantly decreased,respectively (P<0.05), as shown in Table 4. There was no significant difference of the expressions of NO, NOS, ET-1 and VEGF-A between the nonbleeding group and the bleeding group (P>0.05),as shown in Table 5. There was no significant difference of the expressions of NO, NOS, ET-1 and VEGF-A between the mild qi deficiency group and the moderate/severe qi deficiency group (P>0.05),as shown in Table 6.
Table 3. Comparison of the expressions of cytokines between the mild qi deficiency group and the moderate/severe qi deficiency group

Table 3. Comparison of the expressions of cytokines between the mild qi deficiency group and the moderate/severe qi deficiency group
Note: Compared with the mild qi deficiency group, P<0.05.
n CD40L IL-1β TGF-β TNF-α IL-17A Mild qi deficiency group 25 11.32±2.65 3.25±1.53 20521.13±5218.19 21.33±2.37 232.24±46.54 Moderate/ severe qi deficiency group 13 7.83±2.96 3.41±1.27 10751.24±4181.54 22.14±1.38 265.17±91.32
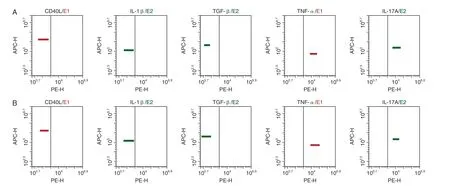
Figure 3. Expressions of cytokines of the bleeding group and the non-bleeding group.

Figure 4. Expressions of cytokines of mild qi deficiency group and the moderate/severe qi deficiency group.
DISCUSSION
ITP is a common hematological diseasecharacterized by hemorrhage or high-risk bleeding tendency caused by platelet reduction, and belongs to the "bleeding syndrome" in Chinese medicine.Syndrome of qi failing to govern blood (SQFCB)is one of the common syndrome of ITP, based on Chinese medicine[3].
Table 4. Comparison of the expressions of vessel related indicators between the ITP group and the control group

Table 4. Comparison of the expressions of vessel related indicators between the ITP group and the control group
Note: Compared with the control group, P<0.05
n NO NOS ET-1 VEGF-A Control group 20 58.06±17.39 26.23±1.88 0.94±0.09 36.78±12.65 ITP group 52 81.65±33.01 21.73±3.22 1.22±0.38 19.07±7.39
Table 5. Comparison of the expressions of vessel related indicators between the non-bleeding group and the bleeding group

Table 5. Comparison of the expressions of vessel related indicators between the non-bleeding group and the bleeding group
NO NOS ET-1 VEGF-A Non-bleeding group 14 83.23±19.62 21.68±4.75 1.32±0.21 16.67±7.84 Bleeding group 38 76.62±33.22 22.44±6.57 1.27±0.32 21.2±3.13 n
Table 6. Comparison of the expressions of vessel related indicators between the mild qi deficiency group and the moderate/severe qi deficiency group

Table 6. Comparison of the expressions of vessel related indicators between the mild qi deficiency group and the moderate/severe qi deficiency group
NO NOS ET-1 VEGF-A Mild group 25 76.63±34.56 24.23±4.55 1.06±0.63 19.56±5.74 Moderate/severe group 13 61.43±27.45 23.14±3.23 1.18±0.47 21.42±4.35 n
Previous studies have found that some inflammatory factors have a regulatory effect on the growth and relaxation of vascular endothelium.For example, IL-1β promotes vascular growth by influencing various vascular growth factors[8].TGF-β can regulate the differentiation, proliferation,migration, apoptosis and extracellular matrix of endothelial cells, regulate the permeability of blood vessels, and then interfere with the development and reconstruction of blood vessels[9,10]. TNF-α is a promoter-inducing factor for inflammatory response.The production and release of TNF-α do harm to the body's immune balance and cause damage to the body[11,12]. IL-17A promotes the release of inflammatory factors and adhesion molecules,which cause infiltration of tissue inflammatory cell[13,14]. CD40L is widely distributed in activated CD4+ T cells, endothelial cells, platelets, etc.CD40L enhances the adhesion of platelets and then promote the repair of vascular endothelium[15].It is found that the expressions of TNF-α and IL-17A in ITP patients were significantly higher than those in the control group, which may be one of the reasons of venation injury in patients with ITP, while,the expressions of IL-1β, TGF-β and CD40L in the ITP group were lower than those in the control group. We speculated that the ITP patients had a high bleeding risk because the damaged vascular endothelium could not be repaired in time[16,17].We also found that the expressions of CD40L and TGF-β were lower in the moderate/severe group compared with the mild group, and it was speculated that the levels of CD40L and TGF-β could reflect the degree of qi deficiency in ITP patients with SQFGB. The expressions of CD40L, IL-1β, TGF-β,TNF-α, and IL-17A might represent qi in Chinese medicine.
Recent research suggests that ET-1 activates monocytes in plasma and promotes the production of inflammatory factors, and the upregulation of inflammatory factor secretion leads to increased level of ET, resulting in the increase of inflammatory response and damage of vascular endothelial cells in a vicious circle[18,19]. NO,catalyzed by NOS, can dilate blood vessels and inhibit activation of platelets, while NO participates in destruction of platelets[20]. We found that the expression of NO in the ITP group was higher than that in the control group and the expression of NOS in the ITP group was lower than that in the control group. It was speculated that the large amounts of NOS in the ITP patients were consumed to synthesize excessive NO, which caused damage to the vascular endothelium and thus aggravated the tendency of bleeding. In addition, high expression of TNF-α can significantly down-regulate the expression of NOS, which also leads the low expression of NOS in this study[21]. VEGF-A is an important factor in promoting angiogenesis. The body produces a large amount of VEGF-A when blood vessels are damaged, which accelerates endothelial cell migration to repair damaged tissues by increasing vascular permeability[22,23].It was found that the expression of VEGF-A in ITP patients was significantly lower than that in the control group, suggesting that the damaged vessels of ITP patients could not be repaired in time. The abnormal expressions of the above indicators reflect that the patient's vessel is in a state of injury, resulting in a high risk of bleeding.However, there was no significant difference in the expression of the above indicators between the mild group and the moderate/severe group.These results suggested that ET-1, NO, NOS,and VEGF-A can not be used as indicators for differenting the degree of choroidal damage. The mentioned qi and vessel related indicators were not significantly different between the bleeding group and the non-bleeding group, indicating that such patients had dysregulation of qi and vessel since got sick.
To sum up, abnormalities of expressions of IL-1β, IL-17A, TNF-α, TGF-β, and CD40L reflect the state of qi deficiency in patients with ITP, and levels of ET-1, NO, NOS, and VEGF-A reflect the state of vessel. PLT count reflects the state of blood.This provides an idea for ITP treatment and also plays a positive role in revealing the mechanism of Chinese medicine treatment in ITP.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict.
 World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2020年1期
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2020年1期
- World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies Center for Translation
- New Year's Message
- INSTRUCTION FOR AUTHORS
- Professor YANG Yu-fei's Experience on the Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine Treatment Strategy for Advanced Colorectal Cancer
- Two Definitions of Life Will Highlight on Physiological Understanding of Six Meridians
- Effects of Shenmai Injection (参麦注射液) Combined with Meglumine Adenosine Cyclophosphate Injection on Cardiac Function and Peripheral Serum Levels of TNF-α,TGF-β1 and IFN-γ in Patients with Viral Myocarditis
