Squamous Cell Carcinoma Secondary to Mutilating Palmoplantar Keratoderma
He-Dan Yang,Juan Jiang,∗,Xiu-Lian Xu
1Department of Scientific Research and Education,2Department of Pathology,Hospital of Skin Diseases(Institute of Dermatology),Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College,Nanjing,Jiangsu 210042,China.
Introduction
Mutilating palmoplantar keratoderma (MPK), also known as Vohwinkel syndrome(VS),is a rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis. It is manifested by diffuse honeycomb-like keratotic thickening in the skin of the palms and soles,starfish-shaped keratotic plaques on the dorsum of the hands and feet,and fibrous constricting bands(pseudoainhum)at the interphalangeal joints of the hands and feet,which may compromise neurovascular function and mobility and even result in autoamputation.1This condition usually occurs on the fifth digits;it often manifests in early childhood but becomes more evident in adulthood.Some features have been noted to be associated with MPK, such as alopecia, hearing loss, spastic paraplegia, myopathy, ichthyosiform dermatoses, and nail abnormalities.1
Currently,there is no specific and satisfactory therapy for MPK. The most common complications of the disease are autoamputations of the fingers and toes,and MPK can also cause significant disability. Squamous cell carcinoma has been reported as a complication of MPK only once previously.1Here, we present the unusual case of squamous cell carcinoma secondary to MPK.
Case report
Our patient was a 34-year-old woman,who had initially presented with hyperkeratotic lesions on both her heel and the tip of her index finger when she was 5 years old.Her lesions had subsequently developed as several punctate hyperkeratotic plaques,gradually extending to the entire palmoplantar surface;she was diagnosed as palmoplantar keratoderma by Hospital of Skin Diseases(Institute of Dermatology),Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College.Her symptoms did not improve significantly after intermittent therapy with oral acitretin (10mg/day), and constricting fibrous bands developed over her fifth fingers and fifth toes,leading to progressive strangulation at the age of 15 years.In the following year,similar lesions were noted on her other fingers and toes,and autoamputation was noted on the fifth fingers of both her hands.On the basis of her clinical features,the patient was diagnosed as having MPK,and she began her currently ongoing treatment with oral acitretin capsules(10-20mg/day).Shortly thereafter,the symptoms of a chronic ulceration and bleeding occurred on her left sole;her left lower limb was subsequently amputated below the knee due to the serious bleeding when she was 16 year old.Three years ago,the patient presented with complaints of persistent ulceration and bleeding from the original lesion for a year.Consequently,she underwent another amputation,this time of her right foot.At that time,she was also suffering from significant pain in her right hand.During the year prior to the amputation of her right foot,she had been receiving several treatments in local hospitals,such as antibiotics,debridement,and medication.However,all these treatments were ineffective.Notably,the patient was born of non-consanguineous healthy parents,and there was no family history of similar conditions.
A dermatological examination of the patient showed diffuse hyperkeratotic plaques with ulceration and scabbing,an erythematous rim in the skin of the dorsum of her hands,an enlargement of the distal ends of all her fingers,the presence of constricting bands affecting the interphalangeal joints of all her fingers,and the absence of the fifth fingers on both her hands;there was also a marked flexion deformity in her right wrist joint(Fig.1A and 1B).The patient was otherwise generally well;she displayed standard physical,mental,and hearing development,and her hair,teeth,and mucous membranes were all normal.She did not have any symptoms of deafness or ichthyotic skin.There was no evidence of an associated systemic disease.
Routine laboratory tests revealed no obvious abnormalities.A skin biopsy from the dorsum of the patient’s right hand revealed a keratinizing tumor infiltrating deep into the reticular dermis.Marked nuclear pleomorphism and mitosis accompanying mixed chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate were observed(Fig.2A and 2B).The immunohistochemistry results show that the tumor cells were immunopositive for CK5/6,P63,and ki-67(40%of cells were ki-67-positive)(Fig.2C-2E).Unfortunately,the patient and her family refused to undergo genetic analyses,so we were unable to identify a causative mutation of gene.
On the basis of these findings, the patient was diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma secondary to her MPK.
Discussion
MPK is a rare genodermatosis that may result in disability or even carcinogenesis.Currently,there are two known genetic variants of MPK.The first subtype,known as classical VS,is associated with deafness.It is caused by a mutation of connexin 26,encoded by the GJB2 gene on chromosome 13q11-12.This subtype usually presents with starfish-shaped hyperkeratoses on the dorsal aspects of the hands and feet,2which typically occurs in white women and usually first manifests in early childhood.The second subtype,called loricrin keratoderma or Camisa syndrome(variant VS)and first reported by Camisa and Rossana,3is associated with ichthyosis instead of deafness.It is linked to a mutation in loricrin gene(LOR)on chromosome 1q21.This subtype sometimes,but not always,presents with starfish-shaped hyperkeratosis.No consistent extracutaneous characteristics have been reported.Additionally,a new variant of VS that occurs without deafness or ichthyosis was recently reported.4
We made a literature search on PubMed and the Wanfang Database and found a total of 143 VS cases from 69 relevant reports were identified from 1975 to 2017.Most of these reported cases were sporadic,although familial cases with different modes of inheritance were also described.Among these cases,there were 41 cases of classical VS,60 cases with loricrin keratoderma or Camisa syndrome,and 42 cases with the new VS variant that presents without deafness or ichthyosis;additionally,there was only one reported case of carcinogenesis.3Gene mutations have been identified as a cause of MPK,and summarized in Table 1.
The diagnosis of MPK relies mainly on the clinical features and must be differentiated from other types of keratoderma that can also be associated with autoamputation of the digits,including Olmsted syndrome,acral keratoderma,congenital pachyonychia,Sybert’s palmoplantar keratoderma, Meleda disease, and Gamborg-Nielsen palmar and plantar keratoderma.The diagnosis of VS in our patient was made based on the characteristic clinical appearance of palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and the constriction rings bilaterally affecting the patient’s fingers and toes.Our patient did not display the typical symptoms of VS,neither deafness nor ichthyosis,and she lacked any family history of this condition.Therefore,we consider that this case might belong to the new phenotype.Unfortunately,our patient refused to undergo a genetic analysis, so it was not possible to investigate the underlying genetic cause of her condition.
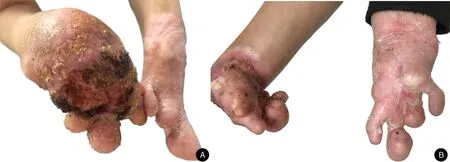
Figure 1.Clinical manifestations of the patient.(A)There were diffuse hyperkeratotic plaques with ulceration and scabbing over the erythema bases in the skin of the dorsum of the patient’s right hand.(B)There were diffuse hyperkeratotic erythema and scaling on her left hand,and her right wrist joint showed a flexion deformity.Constricting bands affecting the interphalangeal joints of all fingers and the absence of the fifth fingers were observed on both hands.
Squamous cell carcinoma usually arises in skin that has been damaged by thermal burns or chronic inflammation or ulcers.On the basis of clinical features and pathological results,our patient was definitely diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma.Besides,we considered it secondary to MPK due to the long history of the chronic ulcers in the areas of skin lesions.
Presently,there are no specific and satisfactory therapies for MPK. Some doctors have successfully treated patients with MPK by oral acitretin and topical application of adapalene(0.1%).23It was also reported that low-dose isotretinoin therapy is effective in terms of relieving constriction and preventing amputation;additionally,a small dose increase was shown to lead to the partial improvement of ichthyosis and palmoplantar keratoderma.24However,there has been no consistent result concerning whether these treatments relieve symptoms only temporarily. Reconstructive surgery has been used to treat pseudoainhum,but the recurrence of MPK is possible after Z-plasty.Additionally,excision of the constricting bands and the use of grafts and flaps have been alternative means of preventing hyperkeratosis and autoamputation of the digits.In one study,a case of VS presented with constriction bands at the fifth digit on the right hand that were reconstructed using a distant abdominal skin flap; thereafter, satisfying postoperative effects were observed at the 18-month follow-up.25However, the duration of treatment for preventing keratoderma recurrence and the steps to be taken in the case of a recurrence are not yet clear.Hence,it is crucial to continue exploring the disease mechanisms in MPK and studying new therapeutic options.
The lesions on our patient did not improve despite the long-term administration of an oral acitretin capsule(10-20mg daily)and a topical emollient.Consequently,she suffered disability and canceration,so she was finally recommended to undergo orthopedic surgery.
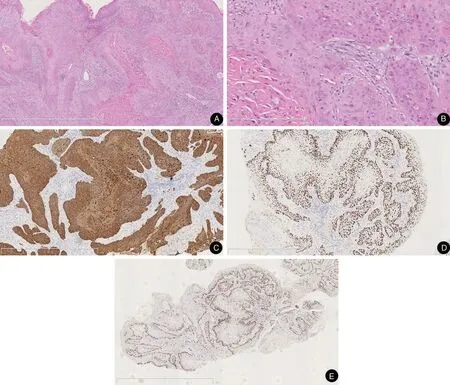
Figure 2.Pathological results of the patient’s lesions.(A and B)Histopathological results of a keratinizing tumor infiltrating deep into the reticular dermis.A marked nuclear pleomorphism and mitosis accompanying mixed chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate are visible.(A)H&E,×50.(B)H&E,×200.(C-E)Immunohistochemistry images of the patient’s lesions.(C)CK5/6,×50.(D)P63,×50.(E)ki67,×25.
Acknowledgement
The work was supported by CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences(No.CIFMS-2017-I2M-1-017).
Table 1
Correlation between the genotype and phenotype of MPK
VS:Vohwinkel syndrome.
Pseudoainhum Familyand/orPalmoplantarHearing Gene with mutation Country Sexhistoryautoamputationkeratodermaimpairment Ichthyosis Diagnosis References G c G p..J J3 D B B5 6 2 28 6-H3 60delGAG T Cu hr i n ki a s h F F /M + + ++ ++ -- V V S S 5 6 G c G c G c G L c...O.J J J J 1 1 1 6 B B B B R 9 9 7 4 2 2 2 2 3 6 5 6 T G G_p>6> >.G 4 C A l 7 C y.(1 i D n(p 3 6 s p.0 G.6 G T V C H l y y a A)r 5 l 6 G 9 5 C S H A e is r G)GTC Z S S E Bg i p w r m a y a e zp b i dn it l a e b n w ea n F F M F F / /M M ++-++ +++++ +N+++o t m entioned ++++- --+-+ V V V V L o S S S S r icr in keratoderma 7 8 9 1 1 0 1 c.798_799dupT L gO.1R 53234085_153234086del,UK F/M + - + - + Loricrin keratoderma 12 c.660_661delGC L 7 L 7 O O3 3 R 0 R 0 i i n n s s G G I C G U ta K h e l i r y n ma a ny F M F F ++++ ++ -+ ++++ --n- o t m entioned++++ L V o S r icri n keratoderma 1 1 3 6-15 L 2 L 2 L 2 O O O 3 3 0 R 0 R 0 R 9--i n 2 2 s 3 3 T 1 1 in in s s GG J J U a a K p p a a n n F F F/ /M M +-+ +++ +++ -+- +++ L V V o S o r h i c w r i i n n k k e e l’r s a t k o e d r e a r t m od a e rm a 1 1 1 7 8 9 L L 5 L 1 L c O O O O A 7 0 7 R R 8 R 1 R 9 i- n 61s G G 0 2(c in.5 s 4 G5 G-T5 G4 G6 Ci nsG)I C C C n h h h d i i i i n n n a a a a F F F M / M +++- +-++ ++++ ---+ -+++ V L V V oS S S r icr i n keratoderma 4 2 2 2 0 1 2
[20]Song S,Shen C,Song G,et al.A novel c.545-546insG mutation in the loricrin gene correlates with a heterogeneous phenotype of loricrin keratoderma.Br J Dermatol 2008;159(3):714-719.doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08657.x.
[21]Fu LQ.Study of gene mutation of loricrin in a Chinese patient with Vohwinkel syndrome and a patient with Olmsted syndrome.Peking Union Medical College and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,Tsinghua University of Medicine;2006:21-39.
[22]Liu YM,Gao XJ,Tian X,et al.Mutation analysis for GJB2 and LOR genes in two patients with Vohwinkel syndrome.Chin J Med Genet 2013;5(2):203-206.doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-940 6.2013.04.018.
[23]Wang B,Zhang Z,Huang X,et al.Successful treatment of mutilating palmoplantar keratoderma with acitretin capsule and adapalene gel:a case report with review of the literature.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2016;30(1):169-172.doi:10.1111/jdv.12672.
[24]Nico M, Fernandes JD. Low-dose isotretinoin prevents digital amputation in loricrin keratoderma (Vohwinkel syndrome with ichthyosis).J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2017;15(6):665-667.doi:10.1111/jdv.12672.
[25]Zhang M,Song K,Ding N,et al.Using a distant abdominal skin flap to treat digital constriction bands:a case report for Vohwinkel syndrome.Medicine(Baltimore)2016;95(6):e2762.doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000002762.
- 国际皮肤性病学杂志的其它文章
- Instructions for Authors
- Deep Penetrating Nevus
- Apocrine Sweat Gland Adenocarcinoma in the Left Retroauricular Area:A Rare Case Report
- Actinic Granuloma:A Case Report
- Cutaneous Metastasis of Uterine Cervical Carcinoma with a Cellulitis-Like Presentation
- Toxic Shock Syndrome Due to Streptococcus pyogenes Presenting with Purpura Fulminans in an Older Adult

