超声弹性成像弹性比值与桥本甲状腺炎的 相关性研究
王晓雪 孙颖 曲博


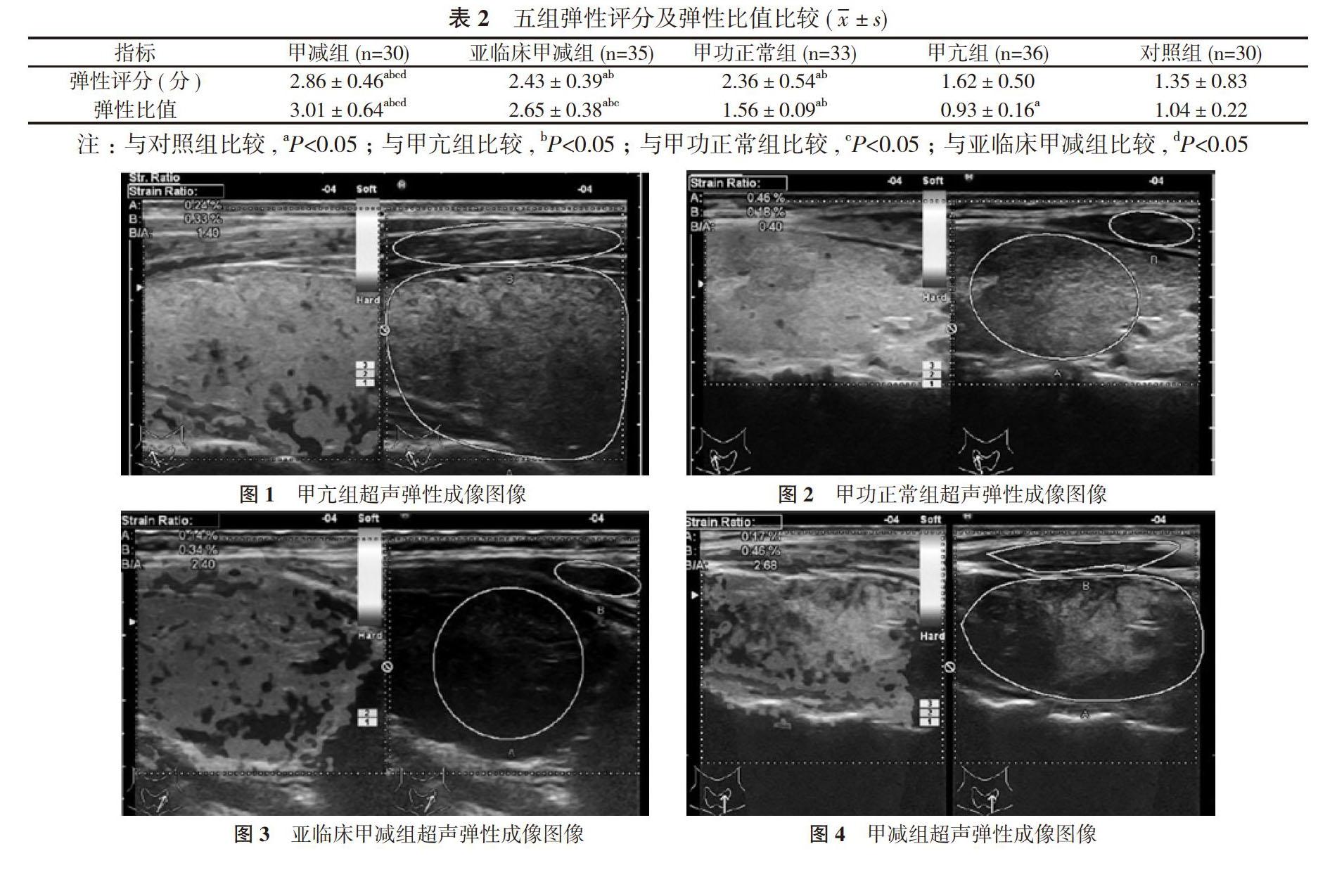
【摘要】 目的 探讨超声弹性成像评价桥本甲状腺炎(HT)的临床应用价值。方法 172例HT
患者, 排除甲状腺结节38例, 依据患者甲状腺功能不同分为甲减组(30例)、亚临床甲减组(35例)、甲功正常组(33例)、甲亢组(36例), 对HT患者进行超声弹性成像检查, 分析HT弹性评分、甲状腺与胸锁乳突肌的弹性比值(B/A)与患者促甲状激素(TSH)相关性。另选同期进行健康体检的30例健康人作为对照组, 比较五组弹性评分及弹性比值。结果 甲减组弹性评分高于亚临床甲减组、甲功正常组、甲亢组及对照组, 差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05);亚临床甲减组弹性评分高于甲亢组及对照组, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);甲功正常组弹性评分(2.36±0.54)分高于甲亢組的(1.62±0.50)分、对照组的(1.35±0.83)分, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);甲亢组与对照组弹性评分比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。五组弹性比值比较, 差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05), 即甲减组>亚临床甲减组>甲功正常组>对照组>甲亢组。经Pearson相关分析, 超声弹性图像弹性评分与血清TSH不具有相关性(P>0.05);超声弹性图像弹性比值与血清TSH呈正相关(r=0.412, P<0.01)。结论 超声弹性成像技术评价桥本甲状腺炎腺体弹性比值与桥本甲状腺炎病程发展相关, 为临床提供更有价值的信息。
【关键词】 桥本甲状腺炎;血清促甲状腺激素;超声弹性成像技术
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2019.34.008
Study on the correlation between the elastic ratio of ultrasound elastography and Hashimotos thyroiditis WANG Xiao-xue, SUN Ying, QU Bo. Department of Ultrasonography, Jinzhou Kangning Hospital, Jinzhou 121000, China
【Abstract】 Objective To discuss the clinical value of ultrasound elastography in evaluation of Hashimotos thyroiditis (HT). Methods A total of 172 HT patients, excluding 38 cases of thyroid nodule, were divided into hypothyroidism group (30 cases), subclinical hypothyroidism group (35 cases), thyroid function normal group (33 cases), hyperthyroidism group (36 cases) according to different thyroid function. Ultrasound elastography was performed in HT patients, and the correlation between HT elastic score, thyroid and sternocleidomastoid muscle elastic ratio (B/A) and thyrotropin (TSH) was analyzed. Another 30 healthy people with physical examination in the same period were selected as the control group. The elastic score and elastic ratio was compared in five groups. Results The elastic score in hypothyroidism group was higher than those in subclinical hypothyroidism group, TSH normal group, hyperthyroidism group and control group, and their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The elastic score in subclinical hypothyroidism group was higher than those in hyperthyroidism group and control group, and their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The elastic score (2.36±0.54) points in TSH normal group was higher than those (1.62±0.50) and (1.35±0.83) points in hyperthyroidism group and control group, and their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in elastic score in hyperthyroidism group and control group (P>0.05). There was statistically significant difference in elastic ratio in five groups (P<0.05), that was hypothyroidism group > subclinical hypothyroidism group > TSH normal group > control group > hyperthyroidism group. According to Pearson correlation analysis, there was no correlation between the elastic score of ultrasound elastography and serum TSH in each group (P>0.05), and there was a positive correlation between the elastic ratio of ultrasound elastography and serum TSH in each group (r=0.412, P<0.01). Conclusion The elastic ratio of Hashimotos thyroiditis is correlated with the course of Hashimotos thyroiditis by ultrasonic elastography, which provided more valuable information for the clinic.
本研究结果显示, HT甲亢组弹性比值低于对照组, 可能是由于:HT初期, 只有少量淋巴细胞及浆细胞浸润, 甲状腺组织弹性反而升高, 直至HT中期, 嗜酸性细胞浸润, 甲状腺组织弹性才降低。
HT疾病是一个缓慢发展的过程, 随着疾病的发展, 甲状腺的硬度逐渐增加, 常规超声只能显示组织形态及血流变化, 超声弹性成像初步判定甲状腺硬度, 亦可通过甲状腺弹性评分定量评价甲状腺硬度, 降低主观误差。超声弹性比值B/A与患者血清TSH呈显著正相关, 可见超声弹性成像可定量评价HT疾病进展。然而血清TSH可药物干预, 而甲状腺组织硬度反映的是甲状腺病理变化, 比血清TSH更具有临床参考价值。
超声弹性成像从图像及弹性评分双重分析甲状腺硬度, 为临床无创性判定HT疾病进展提供新的方法。随着科技的不断进步, 超声弹性成像技术将进一步发展, 为临床医生提供更有价值的信息。
参考文献
[1] 张倩倩, 王学梅. 剪切波弹性成像在乳腺良恶性病变鉴别诊断中的价值. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2012, 23(6):385-388.
[2] 张艳, 唐杰, 李艳密, 等. 实时组织弹性成像应变指数在前列腺周围区病灶的鉴别诊断价值. 中国医学科学院学报, 2010, 32(5):499-502.
[3] 巩海燕, 胡彧, 叶新华. 实时组织弹性成像对肝纤维化的诊断效能分析. 南京醫科大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 33(1):131-134.
[4] Luo S, Kim EH, Dighe M, et al. Thyroid nodule classification using ultrasound elastography via linear discriminant analysis. Ultrasonics, 2011, 51(4):425-431.
[5] 尚旭, 周琦, 姜珏, 等. 常规超声及实时超声弹性成像在桥本氏甲状腺炎诊断中的价值. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2011, 20(5):406-409.
[6] Miyagawa T, Tsutsumi M, Matsumura T, et al. Real-time Elastography for the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer: Evaluation of Elastographic Moving Images. Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2009, 39(6):394-398.
[7] Taylor LS, Porter BC, Rubens DJ, et a1. Three-dimensional sonoelastography: principles and practices. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2000, 45(6):1477-1494.
[8] Bhatia KSS, Rasalkar DP , Lee YP, et al. Cystic change in thyroid nodules: A confounding factor for real-time qualitative thyroid ultrasound elastography. Clinical Radiology, 2011, 66(9):799-807.
[9] 宁春平, 姜双全, 孙立涛. 弹性成像技术鉴别诊断甲状腺实性肿块的价值. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2010, 19(11):966-969.
[收稿日期:2019-06-20]

