小剂量多巴胺治疗新生儿窒息后肾损害的效果
刘志杜
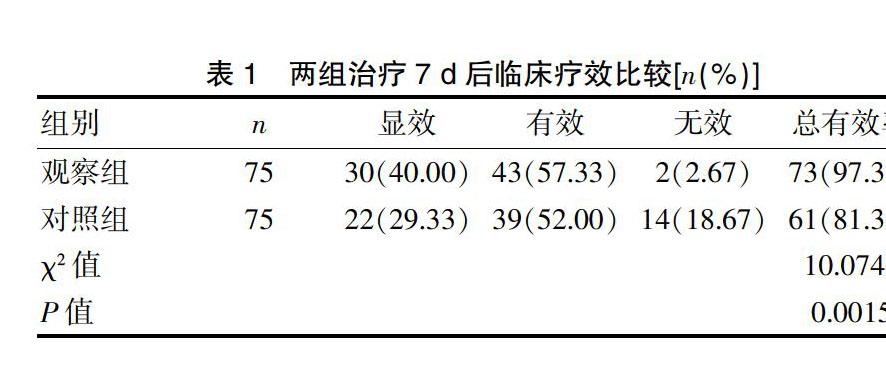
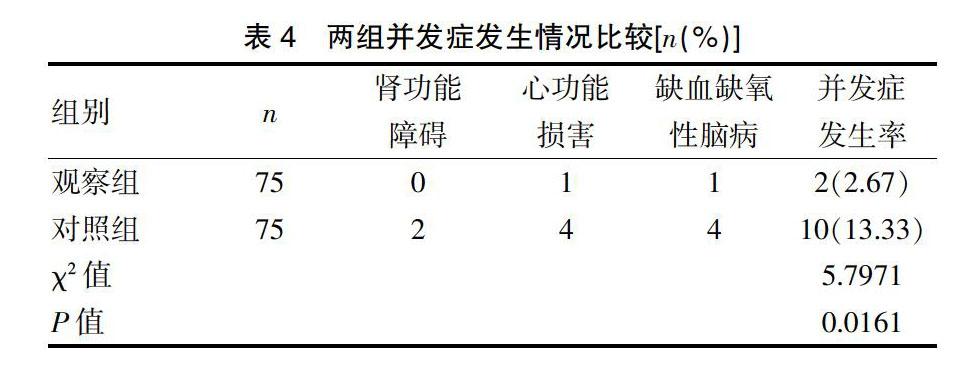
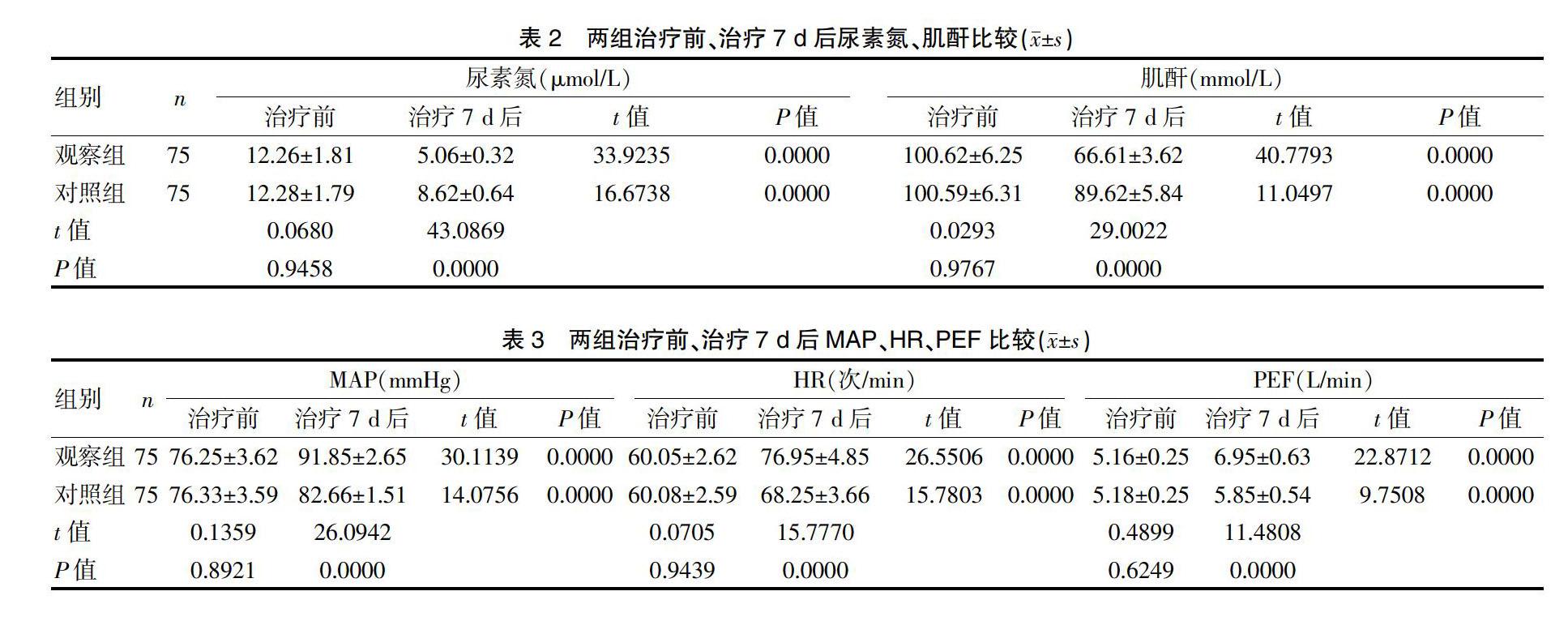
[摘要] 目的 分析小劑量多巴胺治疗新生儿窒息后肾损害的临床疗效。 方法 选取我院2017年4月~2019年4月收治的新生儿窒息后肾损害患儿150例为研究对象,依入院顺序奇偶性平均分为对照组和观察组,各75例。对照组采用临床常规治疗,观察组在对照组基础上予以小剂量多巴胺治疗,两组均治疗7 d。比较两组临床疗效,治疗前、治疗7 d后尿素氮、肌酐水平、MAP、HR、PEF、并发症发生率。 结果 治疗7 d后,观察组临床总有效率(97.33%)高于对照组(81.33%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组治疗前尿素氮、肌酐组间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),治疗7 d后观察组显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗7 d后两组尿素氮、肌酐组内比较均显著低于治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组治疗前MAP、HR、PEF组间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),治疗7 d后观察组显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗7 d后两组MAP、HR、PEF组内比较均显著高于治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组并发症发生率(2.67%)低于对照组(13.33%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 小剂量多巴胺可有效缓解新生儿窒息后肾损害患儿病情,促进尿素氮、肌酐等指标复常,有效预防肾功能障碍等并发症发生,疗效显著,值得借鉴。
[关键词] 小剂量;多巴胺;新生儿窒息;肾损害
[中图分类号] R722.1 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2019)30-0093-03
Effect of low-dose dopamine in treatment of neonatal asphyxia induced renal damage
LIU Zhidu
Department of Pharmacy, Huadu District Maternal and Child Health Hospital(Huzhong Hospital) of Guangzhou City, Guangzhou 510800, China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the clinical efficacy of low-dose dopamine in the treatment of neonatal asphyxia induced renal damage. Methods A total of 150 children with neonatal asphyxia induced renal damage admitted to our hospital from April 2017 to April 2019 were enrolled in the study and evenly divided into the control group and the observation group according to the parity of admission sequence, with 75 children in each group. The control group was treated with routine clinical treatment while the observation group was treated with low-dose dopamine on the basis of the control group. Both groups were treated for 7 days. The clinical efficacy, the urea nitrogen and creatinine levels, MAP, HR and PEF before treatment and after 7 days of treatment, and the incidences of complications of the two groups were compared. Results After 7 days of treatment, the total effective rate of the observation group(97.33%) was higher than that of the control group(81.33%), with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). Before treatment, the differences in urea nitrogen and creatinine levels between the two groups were not statistically significant(P>0.05), but after 7 days of treatment, the urea nitrogen and creatinine levels of the observation group were significantly lower than those of the control group, with statistically significant differences(P<0.05). The urea nitrogen and creatinine levels after 7 days of treatment were significantly lower than those before treatment in both groups, with statistically significant differences(P<0.05). Before treatment, the differences in MAP, HR and PEF between the two groups were not statistically significant(P>0.05), but after 7 days of treatment, the MAP, HR and PEF of the observation group were significantly higher than those of the control group, with statistically significant differences(P<0.05). The MAP, HR and PEF after 7 days of treatment were significantly higher than those before treatment in both groups, with statistically significant differences(P<0.05). The incidence of complications in the observation group(2.67%) was lower than that in the control group(13.33%), with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). Conclusion Low-dose dopamine can effectively alleviate the conditions of children with neonatal asphyxia induced renal damage, promote the returning of indexes such as urea nitrogen and creatinine, and effectively prevent complications such as renal dysfunction, which shows remarkable efficacy and is worth learning.
本研究结果显示,观察组临床总有效率、MAP、HR、PEF明显比对照组高,观察组治疗后7 d后尿素氮、肌酐水平、并发症发生率显著比对照组低(P<0.05)。与贾焕奇[11]研究结果接近,其研究结果发现研究组治疗后血尿素氮、血肌酐水平均显著比对照组低(P<0.05),提示小剂量多巴胺在新生儿窒息后肾损害治疗中安全、有效。分析原因如下:多巴胺属于内源性儿茶酚胺药物,可刺激心脏β受体产生作用,提高心脏β受体兴奋性,加快心率,促进血压、心率等生命体征复常[12-13]。另外,多巴胺可增加心输出量,具有扩张肠系膜血管、兴奋血管中受体等作用,在低心排出量伴随肾功能损伤等疾病治疗中取得了显著效果[14-15]。多巴胺也是人体重要的一种神经传导物质,主要由人体脑细胞分泌而来,多巴胺通过静脉泵注,结合多巴胺受体,可有效增加肾血管流量,扩大肾脏血管,增强肾小球的滤过率,促进钠离子以尿量排泄,可有效预防肾脏缺血现象发生,降低肾脏功能障碍发生率[16]。由于新生儿年龄较小,因此选择小剂量的多巴胺,可缓解患儿临床症状,改善肾脏功能的同时降低不良反应,安全性更高,可作为新生儿窒息后肾损害的首选药物。本研究创新之处在于研究小剂量多巴胺治疗新生儿窒息后肾功能损害患儿,可促进心率、血压、气道峰压复常,为研究小剂量多巴胺在新生儿窒息后肾损害治疗中的临床疗效提供更加科学的参考依据。
综上所述,新生儿窒息后肾损害患儿采用小剂量多巴胺治疗,可有效缓解患儿紫绀等症状,促进血压、心率升高,降低尿素氮、肌酐水平,有效预防肾功能障碍等并发症发生,取得良好的治疗效果,值得进一步推广。
[参考文献]
[1] 简秋萍,苏丽君,姜世成,等. NO吸入联合小剂量多巴胺、多巴酚丁胺静脉滴注治疗新生儿持续肺动脉高压效果观察[J]. 山东医药,2018,58(6):69-71.
[2] 许朝颖. 小剂量多巴胺治疗新生儿窒息后肾损害的疗效观察[J]. 中国现代药物应用,2016,10(14):141-142.
[3] 符媛. 小剂量多巴胺应用于重度窒息新生儿肾功能损害的临床疗效[J]. 云南医药,2017,38(6):618-619.
[4] 张靖,梁新蕾. 多巴胺联合多巴酚丁胺治疗新生儿窒息后肾损害的效果及其对肾功能指标的影响[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2019,4(2):70-71.
[5] 王博雄,张子友,吉张艳. 小剂量多巴胺治疗窒息后肾损害临床疗效及对新生儿呼气峰流速值、心率、平均动脉压水平影响[J]. 陕西医学杂志,2019,48(1):105-107.
[6] Rakesh K, Vishnu Bhat B, Adhisivam B, et al. Effect of therapeutic hypothermia on myocardial dysfunction in term neonates with perinatal asphyxia-a randomized controlled trial[J]. J Matem Fetal Neonatal Med,2018,31(18):2418-2423.
[7] 周世林,胡朝辉,丁宇星.动脉血乳酸检测在新生儿窒息后器官损害程度及预后判断中的价值[J].现代医院,2018,18(9):1382-1384.
[8] 郝玉贵.小剂量多巴胺在治疗新生儿窒息后肾损害的临床疗效观察[J]. 北方药学,2017,14(9):64-65.
[9] 张丽丽. 小剂量多巴胺用于治疗重度窒息新生儿肾功能损害的疗效分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健,2015,30(30):5192-5194.
[10] 张海珠. 小剂量多巴胺治疗重度窒息新生儿肾功能损害的疗效观察[J]. 现代临床医学,2015,(1):41-42.
[11] 贾焕奇. 小剂量多巴胺在治疗新生儿窒息后肾损害的临床疗效观察[J]. 中国现代药物应用,2016,10(2):164-165.
[12] 陈红梅,曾峰. 小剂量多巴胺治疗新生儿窒息后肾损害的临床疗效[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2017,21(7):155-156.
[13] Tapia-Bustos A,Perez-Lobos R,Vio V,et al. Modulation of postnatal neurogenesis by perinatal asphyxia:Effect of D1 and D2 dopamine receptor agonists[J]. Neurotox Res,2017,31(1):109-121.
[14] 张毓娴,蔺婧,齐薛浩. 小剂量盐酸多巴胺联合高频振荡通气治疗新生儿持续性肺动脉高压的应用疗效及安全性研究[J]. 中国药物警戒,2018,15(8):452-455, 461.
[15] 李程远. 多巴胺联合多巴酚丁胺对窒息后肾损害新生儿靶器官功能指标及分子指标的影响[J]. 海南医学院学报,2016,22(18):2112-2114.
[16] 彭磊,樂功芳,龚益明. 小剂量多巴胺治疗重度窒息新生儿肾功能损害的临床疗效[J]. 检验医学与临床,2014, 11(23):3340-3341.
(收稿日期:2019-07-17)

