Quantitative Evaluation Method of Amylase Performance in Detergents for Hand Dishwashing
Ye Xiao, Shi Rongying
Shanghai Hutchison Whitecat Co., Ltd., China
Abstract
Key words
detergents for hand dishwashing; amylase; performance evaluation
There are many kinds of detergent enzymes, including protease, lipase, amylase, cellulase, mannanase, etc., in which amylase is more commonly added to the detergents for hand dishwashing due to the particularity of dirt in food production.Decomposing starch dirt into soluble dextrin or oligosaccharide, amylase solves the problem of starch dirt removal difficulty through its application in dishwashing detergent.
There is currently no standard method for the performance evaluation of amylase in detergents for hand dishwashing in China.Evaluation is usually achieved based on the soaking experiment of a series of standard stain board approved by CFT (Center for Testmaterials), such as DM-71, DM-76, DM-77 and so on.
To better evaluate the application performance of amylase in detergents for hand dishwashing, referring to B1 degreasing rate method[1]in Detergents for Hand Dishwashing (GB/T9985-2000), the author designed and verified an experimental testing method.
Experiment
Instruments and reagents
RHLQ-Ⅱvertical detergency testing machine is from China Research Institute of Daily Chemical Industry, RW20 digital overhead stirrer and C-MAG HS7 heating plate are from IKA, amylase samples are from DuPont, Novozymes and KDN; AES (70%), while cocamidopropyl betaine (30%) and other conventional detergent raw materials are all commercially available.
Preparation of detergents for hand dishwashing containing amylase
1 000 g base material of detergent for hand dishwashing was prepared in advance (the amylase stability has been verified), three kinds of amylase were added into 100 g base material respectively according to the designed different amount to obtain the detergents for hand dishwashing containing amylase for testing.
Preparation of starch solution and slide with line
250 g deionized water was added into the 250 g standing beaker and mixed with the overhead stirrer at the speed of 450 r/min, 10 g potato starch was weighed and slowly added into the beaker, and the heater was turned on at the same time with the heating temperature set as 350 ℃.The potato solution was kept boiled for 2 minutes, after which the beaker was moved to the experiment table and cooled down naturally to 40~45 ℃ for use.
1 cm line was marked on the upper edge of slide and the detergency was controlled below such line.
Preparation of stain slides
The four clean slides were put on the weighing frame and accurately weighed with an analytical balance (accurate to 1 mg) asm0.The slides were immersed in the starch solution one by one with the 1 cm line as the upper control edge, taken out slowly and hung to the slide holder and left in the air overnight (about 18 hours) at room temperature, and then the dried slides were moved to the corresponding weighing frame to be accurately weighed with an analytical balance asm1.The amount of starch stain in each group of slides was controlled between 0.18 to 0.25 g.
Test procedure
The slide with known starch stain amount was inserted into the corresponding washing stand for washing.
The detergency testing machine was powered on, the washing temperature was set as required, the rotation speed was set as 160 r/min, and the washing time was set as 3 min.
250 mg/L hard water was prepared in advance for use.Two groups of stained slides were prepared for each sample.4.00 g detergent samples were weighed and put into each wash bucket respectively.When the temperature of test solution reached the set temperature, stained slides with known mass together with the washing stand were put into the corresponding wash bucket.When the last washing stand was put into the wash bucket, soaking time calculation began.At the same time, the mixing paddle was installed.When the set soaking time expired, the detergency testing machine was started for washing.3 minutes later, the detergency testing machine stopped automatically, the mixing paddle was removed and the washing stand was taken out, the washed stained slides were clamped and hung on the slide drying rack one by one for 4 hours, and then placed on the corresponding weighing frame and weighed asm2.The starch stain removal rate is calculated as follows:
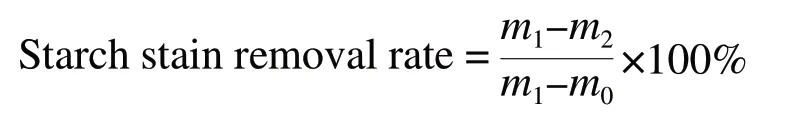
Results and discussion
In the experiment, several factors that may affect the performance of amylase in detergents for hand dishwashing were compared and tested.Besides, the evaluation method was also verified (the mean value was taken as the test data).
Effect of amylase addition on the performance of detergents for hand dishwashing in removing starch stains
In the experiment, whether the method can test the function of amylase was verified, for which two kinds of detergents (with the same detergent base material) without amylase and with amylase were tested, and amylase 1 was taken as the test object.The test conditions included the enzyme addition of 0.4%, the temperature of 30 ℃ and the soaking time of 10 min.The test results show that, within experimental error, the detergent for hand dishwashing without amylase basically has no effect on the removal of starch stains under the experimental conditions (the removal rate is 0.85%), but after adding amylase, the performance of removing starch stains has been improved significantly (the removal rate is 30.92%), demonstrating the efficiency of this method in testing the effect of amylase.
Effect of the addictive amount of amylase on the performance of detergents for hand dishwashing in removing starch stains
The addictive amount of amylase more or less affects the performance of starch stain removal.Generally, to the extent of conventional addition range, the higher the addictive amount of amylase, the better the effect of starch stain removal.Amylase 1 was used as the test object, the washing temperature was 30 ℃, the soaking time was 10 minutes, and the enzyme content was set as 0.2%, 0.3% and 0.4%, respectively.On the premise that other experimental conditions remain unchanged, the test results reveal that the corresponding removal rates of 0.2%, 0.3% and 0.4% enzyme addition are 23.61%, 29.61% and 31.38%, respectively, proving that the starch stain removal effect is significantly improved with the increase of amylase additive amount.
Effect of washing temperature on the performance of detergents for hand dishwashing in removing starch stains
Enzyme is significantly characterized by temperature sensitivity.The enzyme activity increases with the increment of temperature at a low temperature.Enzyme reaction velocity is maximum at the appropriate temperature.The enzyme begins to inactivate and the activity decreases[2]after reaching a certain temperature.Therefore, different washing temperature will affect the performance of starch stain removal.Four washing temperatures were designed in the experiment, amylase 1 was used as the test object, the test conditions included the enzyme content of 0.4% and soaking time of 10 minutes.
The experimental results show that the catalytic activity of the enzyme is greatly affected by the temperature.In the conventional washing temperature range, the removal effect of starch stains is enhanced significantly with the increase of temperature.The corresponding removal rates at 10℃, 20℃, 30℃ and 40℃ were 3.33%, 11.97%, 32.11% and 69.3%, respectively.At low temperature, the enzyme played little role; at 40℃, the removal effect was maximum and reached 69.3%.Most of the enzymes can play the largest role in removing stains at 30 ℃~40 ℃, provided that the washing temperature is not too high.Enzyme is protein in chemical nature, which will be destroyed and irreversibly denatured at too high temperature, and thus lose the catalytic effect.[2]
Effect of soaking time on the performance of detergents for hand dishwashing in removing starch stains
Generally speaking, the bound starch stain can also be removed by the detergents for hand dishwashing without amylase, but it requires soaking for a long time or strong external force; the addition of amylase can greatly save the soaking time, making washing time and labor-saving.However, considering the characteristics of enzyme, it takes a certain time for enzyme to function, so the soaking time during washing will also affect the performance of starch stain removal.Three soaking times were designed, amylase 1 was used as the test object.The test conditions included the enzyme content of 0.4% and the washing temperature of 30 ℃ .According to the experimental results, the removal rates corresponding to the soaking time of 10, 15 and 20 min were 35.12%, 53.81% and 66.21%, respectively, showing that the longer the soaking time, the more sufficient the action time of enzyme, the better the starch stain removal effect.
Effect of pH value on the performance of detergents for hand dishwashing in removing starch stains
Enzyme showed the strongest activity in the optimal pH range, which would be decreased if it was greater than or less than the optimal pH.In the conventional pH range for detergents for hand dishwashing, three pH values were designed and adjusted to investigate the effect of pH, and amylase 1 was used as the test object.The test conditions included the enzyme content of 0.4%, the temperature of 30 ℃ and the soaking time of 10 min.According to the experimental results, when the pH is 5.0, 7.0 and 9.0, the corresponding removal rates are 5.47%, 20.12% and 30.6%, respectively.In the conventional pH range for detergents for hand dishwashing, the lower the pH, the worse the starch stain removal effect.Therefore, from the perspective of starch stain removal performance, the higher the pH, the better the effect.However, considering the mildness of detergent, it is better to control neutral pH for detergents for hand dishwashing with enzyme.
Effect of different amylases on the performance of detergents for hand dishwashing in removing starch stains
Influenced by source, production strain, host and preparation method, the amylase performance varies with the kind.Three different kinds of amylase were determined under the conditions of 0.4% as enzyme content, 30 ℃ as temperature and 10 minutes as soaking time.It can be seen from the experimental results that amylase 2 has the best effect of removing starch stains with the same additive amount, but amylase 2 is not necessarily the best choice from the perspective of product application, the stability, price and other factors of the enzyme should also be taken into account, that is to say, the cost performance of amylase needs to be considered comprehensively.
Conclusion
The experiment test data above fully verifies the validity of the test method.The method allows effective evaluation of the effect of various factors on the starch stain removal performance, including the additive amount of enzyme, washing temperature, soaking time, pH of the product and the kind of amylase.
However, we should not neglect the limitations of the method, that is, it can effectively evaluate the differences in the tests in the same batch, but the parallelism of test results is not very good between different batches, so the method needs to be improved and perfected to minimize the differences in test results between different batches.
 China Detergent & Cosmetics2019年4期
China Detergent & Cosmetics2019年4期
- China Detergent & Cosmetics的其它文章
- Fluorinated Surfactants and Fluorinated Polymer Materials (IV):Strategy for Solving PFOS Problems
- Research and Safety Evaluation of Thallium in Cosmetic Products
- A Study on the Whitening Efficacy of Flavones in Lotus Leaf
- Refutation of Cosmetics Rumors
- Flight Inspection Analysis on National Cosmetics in 2018
- Standard Explanation of the Instruction for Use of Consumer Products—Labelling for Detergents
