Modulation of various enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation by Schima wallichii(DC.)Korth in mice bearing Dalton's ascitic lymphoma
Ganesh Chandra Jagetia,K.Lalhminghlui
110 Maharana Pratap Colony,Sector 13,Hiran Magri,Udaipur,313002,India.2Department of Zoology,Mizoram University,Aizawl-796004,India
Abstract
Key words:Mice,Schima wallichii,Dalton's lymphoma,Glutathione,Antioxidant enzymes,Lipid dilapidation.
Introduction
In 2018,approximately 18.1 million new cases were diagnosed out of which 9.6 million patients died of the disease throughout the world.Despite several advances made in the cancer treatment strategies,the complete cure of cancer,especially in advance stages is elusive[1-3].This makes invasive cancer the leading cause of death in the developed world and the second leading cause of death in the developing world[4].To tackle the serious threat posed to humans due to cancer,biologists and chemists have been using the medicinal properties of plants to develop new molecules,which may tame cancer one day.Medicinal plants have been identified and used throughout the human history for healthcare and treatment of numerous human diseases.A number of different species of plants have been reported to be useful in treating various diseases including cancer and in fact many of the modern cancer chemotherapy drugs were isolated from plants before they were synthesized by combinatorial chemistry[5,6].Cancer research is the intense scientific effort to understand disease processes and discover possible therapies.
Schimawallichii(SW),Chilauni(Family:Theaceae)grows in warm temperate to subtropical climates across southern and south eastern Asia.It is distributed among the eastern Himalaya of eastern India and Nepal,Indochina,Ryukyu Islands,Southern China,and Taiwan[7].SW possess numerous medicinal properties.The bark is used as an antiseptic for cuts and wounds,vermicide,mechanical irritant and anti-gonorrheal drug[8,9].Decoction of the bark is good for fever and is said to be effective againsthead lice [10].Fruit decoction is used against snakebite[11].The young plants,leaves and roots are indicated against the fever and the bark is rubefacient and act as an anthelmintic agent[8,9].The stem bark decoction of SW helps to treat fever and head lice infection and bark juice is able to disinfest the animals from liver flukes[12].The leaves and fruits of SW possess antitumor,antimutagenic and antibacterial properties[13-15].The anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activity of hydroalcoholic extract of stembark of SW has been also reported[17].The stem bark extract has been found to be anti-pyretic,anti-inflammatory and analgesic [18].Various extracts of SW have been reported to scavenge various free radicals[19].GSH,GST,CAT,SOD,and lipid peroxidation had close relation with radicals scavenging,which is important in cancer therapy.Therefore,present study was designed to study the effects of SW on the activities of these enzymes and lipid peroxidation in the Swiss albino mice bearing Dalton's ascitic lymphoma.
Materials and methods
Chemicals
Doxorubicin hydrochloride(DOX)was procured from Getwell Pharmaceuticals,Gurgaon,India.1-chloro-2,4-dinitro-benzene(CDNB),5,5-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid)(DTNB),diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid(DETAPAC)ethylenediaminetertaacetic acid(EDTA),glutathione,nitro blue tetrazolium(NBT),phenazine methosulphate,sodium azide,2-thiobarbituric acid(TBA),sodium dodecyl sulphate,reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide(NADH),nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate(NADPH)tetraethoxypropane,and 5-thio-(2-nitrobenzoic acid)(TNB)were purchased from Sigma Chemicals Co.St.Louis,USA.Other routine chemicals were procured from Merck India,Mumbai.
Collection and preparation of the plant extract
The non-infected stem bark of SW also known as Chilauni,or Makusal,Kanak in Hindi and khiang in Mizo language was collected from Bazar veng,Lunglei,Mizoram,India during the months of April and May.The SW was identified and authenticated by the BotanicalSurvey ofIndia,Shillong,Meghalaya(BSI/ERC/Tech/Identification/2017/570).The washed stem bark was shade dried atroom temperature in clean and hygienic conditions.The dried bark was ground to powder in an electrical grinder and the dried powder of SW stem bark was extracted sequentially with petroleum ether,chloroform,ethanol and distilled water in order of increasing polarity using a Soxhlet apparatus.The ethanol extract was concentrated and evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure and stored at-80°C until use.
Animal care/handling
The guidelinesissued by the World Health Organization(WHO),Geneva,Switzerland and the INSA(Indian National Science Academy,New Delhi,India)were strictly followed for handling and caring of animals.Swiss albino mice purchased from Pasteur Institute(Shillong)were bred and maintained in a controlled environment of temperature(24-25°C),50%humidity and a light and dark cycle of 12 h each.About five animals were housed in a sterile polypropylene cage which contained sawdust(procured locally)as bedding material.For experiment,normally six to eight weeks old Swiss albino mice of both genders weighing around 25-30 g were selected.The animals were fed with commercially available food pellets and allowed free access to water.The animal experiments were carried out according to NIH and Indian National Science Academy,New Delhi,India guidelines.The Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of Mizoram University,approved the entire study vide letter No.MZU/IAEC/14-15/10 Aizawl,India.
Tumor model
TheDAL bearingmicewereprocuredfrom North-Eastern Hills University(NEHU),Shillong,India and the tumor was maintained in 4-6 weeks old Swiss albino mice by serial intraperitoneal transplantation.One million viable DAL cells were inoculated intraperitoneally into each animal under aseptic conditions and the day of inoculation was taken as day 0.
Experimental design
The changes in the enzyme activity,GSH and lipid peroxidation by the ethanol extract of SW(SWE)was determined in DAL bearing mice divided into the following groups.
SPS groups:The tumorized mice of this group were given 0.01 ml/g body weight of sterile physiological saline and served as the negative control group.
SWE groups:This group of animals was intraperitoneally injected with 10 mg/kg body weight of the ethanol extract of SW[9].
DOX groups:This group ofanimals was intraperitoneally injected with 0.5 mg/kg body weight of doxorubicin,a standard anticancer drug and served as positive control.
Biochemical assays
The animals were sacrificed after nine days of drug/s treatment at an interval of 2,4,8,12 and 24 hours.The animals were perfused with isotonic cold saline transcardially.Both the treated and untreated livers of the animals were removed under aseptic conditions.The livers were weighed and 10%homogenate was prepared in cold sterile PBS(pH 7.4)and used for the estimation of GSH,GST,CAT,SOD and lipid peroxidation.
Total proteins
The proteins were estimated by standard procedure of Bradford[20].
Estimation of GSH
GSH was estimated as described earlier[21].GSH was measured by its reaction with DTNB(Ellman's reaction)to give a compound that absorbs light at 412 nm.In brief,1.8 ml of 0.2 M Na2HPO4was mixed with 40µl of 10 mM DTNB and 160µl of tissue homogenate and allowed to stand for 2 minutes.The absorbance was read against the blank at 412 nm in Eppendorf UV/VIS Spectrophotometer(Eppendorf India Ltd,Kolkata).The blank consisted of distilled water instead of tissue homogenate.
Estimation of GST
GST was determined by the method of Habiget al[22].Usually,0.5 ml of 0.1M phosphate buffer(pH 6.5),0.1 ml of 20 mM CDNB,and 8.8 ml distilled water were incubated at 37°C for 10 min followed by the addition of 0.5 ml of 20 mM GSH and 0.1 ml of tissue homogenate.The absorbance was read at 340 nm with a UV-VIS double beam spectrophotometer at 1 min interval for 6 minutes.Distilled water was used as a blank.
CAT assay
CAT was assayed according to technique described by Aebi[23].In a 3 ml cuvette,20µl of tissue homogenate was mixed with 1.98 ml of 50 mM phosphate buffer(pH 7.0).The reaction(maintained at 20°C)was started by adding 1 ml of 30 mM H2O2and the decrease in absorbance was monitored at 240 nm for 60 seconds.
SOD assay
SOD is an enzyme that catalyzes the dismutation of two superoxide anions into hydrogen peroxide and molecular oxygen and the activity of SOD was estimated as described earlier[24].100µl of tissue homogenate,100 µl of 186 µM phenazine methosulfate,300 µl of 3.0 m Mnitro blue tetrazolium,200 µl of 780 µM NADH were incubated for 90 seconds at 30°C.The reaction was terminated by adding 1000 µl of acetic acid followed by the addition of 4 ml n-butanol.The absorbance was recorded at 560 nm using UV/VIS double beam spectrophotometer.The percent inhibition was calculated by measuring the absorbance of blank without SOD enzyme.The SOD activity was calculated using the formula(Blank-Sample)/Blank×100.
Lipid peroxidation assay
Malondialdehyde(MDA)formed from the breakdown of polyunsaturated fatty acids,serves as a convenient index for determining the extent of peroxidation reaction of lipids.MDA has been identified as the product of lipid peroxidation that reacts with thiobarbituric acid to give a red species absorbing at 535 nm.Lipid peroxidation assay was carried out following the method of Buege and Aust[25].1 ml of tissue homogenate was thoroughly mixed with 2 ml of TCA-TBA-HCl reagent,heated in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes,cooled immediately at room temperature and centrifuged at 1000rpm for10min.The supernatant was collected and its absorbance was read at 535 nm against blank in a UV-VIS double beam spectrophotometer.The blank contained all the reagents minus the tissue homogenate substituted with distilled water.The MDA concentration of the sample was calculated using the extinction coefficient of 1.56×106M-1cm-1.
Determination of liver toxicity
For the estimation of the toxicity of SWE in the liver of tumorized mice,the tumor bearing mice were injected with 10 mg/kg body weight of ethanol extract one day after transplantation of Dalton's lymphoma for nine days subsequently.After the treatment was over,the mice were sacrificed,perfused with cold isotonic saline transcardially and the livers were collected at different post treatment times.The livers were weighed and 10%homogenate was prepared in cold sterile PBS(pH 7.4)and used for the estimation of AST,ALT,creatinine and uric acid at 2,4,8,12 and 24 h after the last administration of the extract.Commercially available response Kits using a Response 910 auto analyzer(Diagnostic Systems GmbH¸Holzheim,Germany)were used to measure AST,ALT,creatinine and uric acid according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Statistical analyses
The statistical difference between the different groups was tested by Studentsttest using Origin Pro 8 SRO v8.0724(B724),Northampton,MA,USA.The one-way ANOVA was used for multiple comparison with the application of Tukey's post-hoc test.The results were confirmed by repetition of the experiments.Test of homogeneity was applied to determine any statistical differences between the repeat experiments.The data of all experiments were combined and expressed as mean±standard error of the mean(SEM).APvalue of<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
GSH content
The GSH content of Dalton's lymphoma tumor cells was 14.92±0.01.The treatment of DAL tumorized mice with 10 mg/kg body weight SWE caused a significant decrease in the GSH contents when compared to untreated tumorized mice.This decline was 1.5 folds lower at all the assay times except 2 h where it was 1.3 folds.The analyses between different post-SWE treatment assay times also revealed a time dependent but significant decline in the GSH contents up to 24 h post SWE treatment.The maximum reduction in GSH concentration was observed at 24 h(P<0.0001).Treatment of DAL mice with 0.5 mg/kg body weight of DOX also caused a time dependent decline in the GSH contents.The SWE treatment reduced the GSH contents comparable to DOX treatment.However,this decline was significantly lower(P<0.01)when compared to SWE treatment.The data are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.
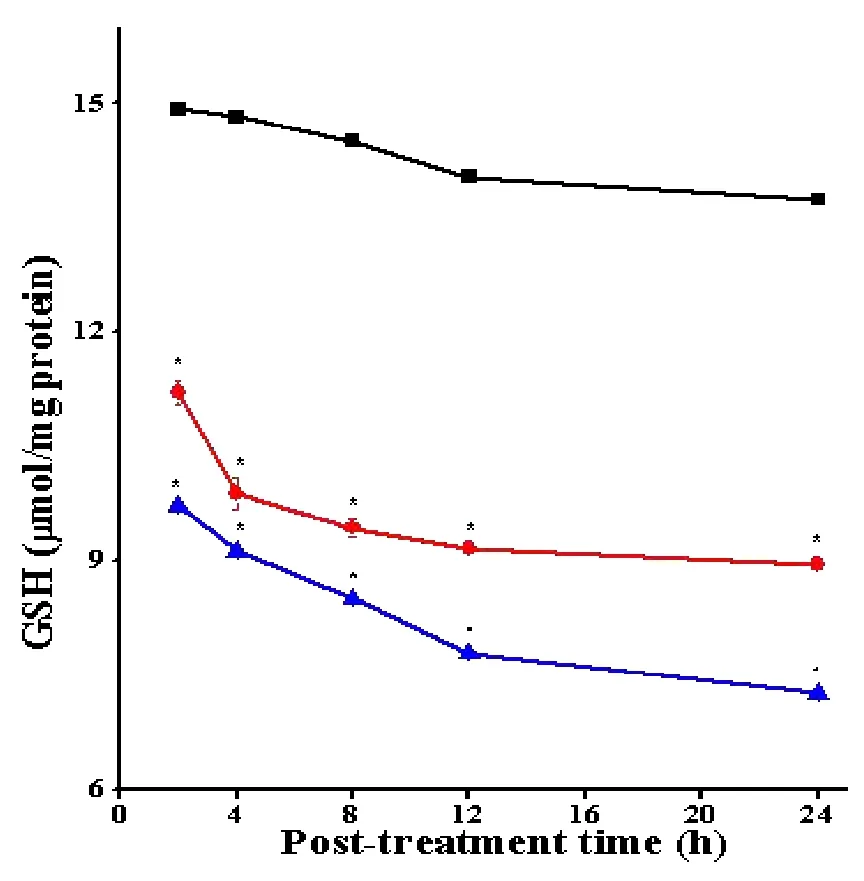
Figure 1 Alteration in the GSH contents in the DAL cells treated with SWE.
The activity of GST
The activity of GST in the DAL cells of tumorized mice was 0.082±0.002.The administration of SWE led to a significantdecline ateach post-SWE-treatment assay time when compared to SPS treatment.The GST activity declined in a time dependent manner and the highest decrease in GST activity was observed at 24 h post treatment.However,theGST activity did notshow a significant decline with post-SWE-treatment assay time.The pattern of GST activity in the DOX treated tumorized mice was similar to that of SWE treatment.DOX resulted in a significant(P<0.05)reduction in the GST activity at all the post treatment times.The data are shown in Table 2 and Figure 2.
The activity of CAT
The CAT activity in the DAL cells of tumorized mice was 19.79±0.11.The treatment of DAL tumorized mice with 10 mg/kg body weight of SWE led to a significant decline in the CAT activity.The analysis of CAT activity with time showed that SWE treatment led to a significant decline with each assay time and the lowest CAT activity was observed at 24 h post-treatment assay time,where this reduction was 1.7 folds when compared to SPS group.The pattern of decline in CAT activity in DOX group was almost similar except that it was marginally lower than SWE treatment.The DOX treatmentofDAL tumorized miceled to a significant attrition(P<0.05)in the CAT activity until 24 h post treatment.The data are shown in Table 3 and Figure 3.
The activity of SOD
The spontaneous SOD activity in the DAL cells of tumorized mice is 1.81±0.05.Treatment of tumorized mice with 10 mg/kg body weight SWE resulted in a significant reduction in the SOD activity at each post-SWE-treatment time.The SOD activity declined in a time dependent manner after SWE until 24 h post treatment,where it was 2.2 folds lower than SPS treatment.The decline in the SOD activity in tumorized mice treated with DOX showed a pattern similar to SWE treatment except that it was lower than the SWE treatment.The DOX treatment also caused a significant decline in the SOD activity at each post-assay time when compared to SPS group.The data are shown in Table 4 and Figure 4.
Lipid peroxidation
The lipid peroxidation in the DAL cells has been 0.32±0.01 MDA at 2 h which increased with assay time.The treatment of DAL mice with 10 mg/kg body weight SWE caused a significant(P<0.05)rise in the lipid peroxidation as early as 2 h post treatment.The lipid peroxidation increased with time in SWE treated group.The pattern of lipid peroxidation after DOX treatment was almost similar to that of SWE treatment except that the rise was greater than SWE treatment.The data are shown in Table 5 and Figure 5.
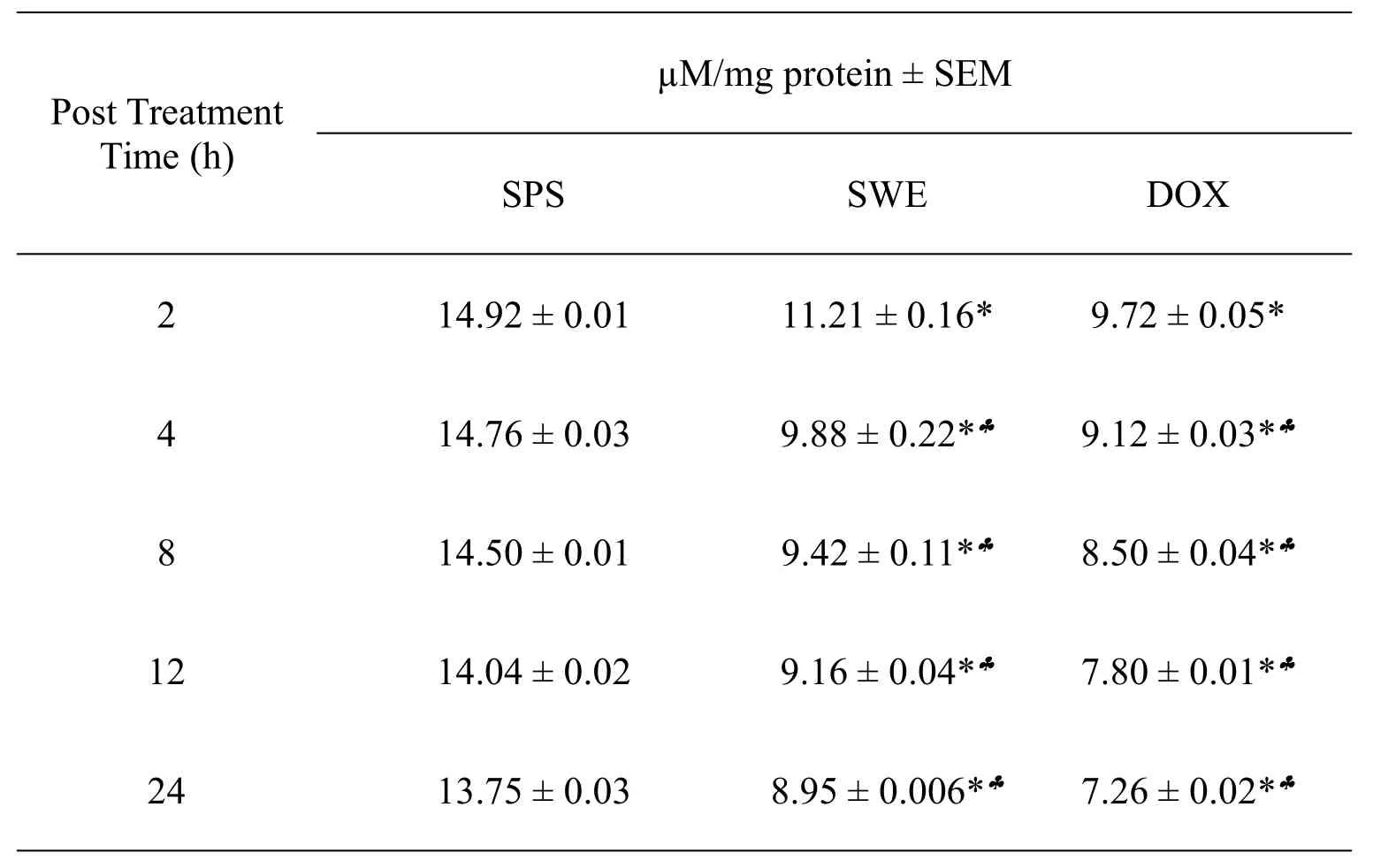
Table 1 The GSH contents of mice bearing DAL treated with 10 mg/kg SWE or DOX
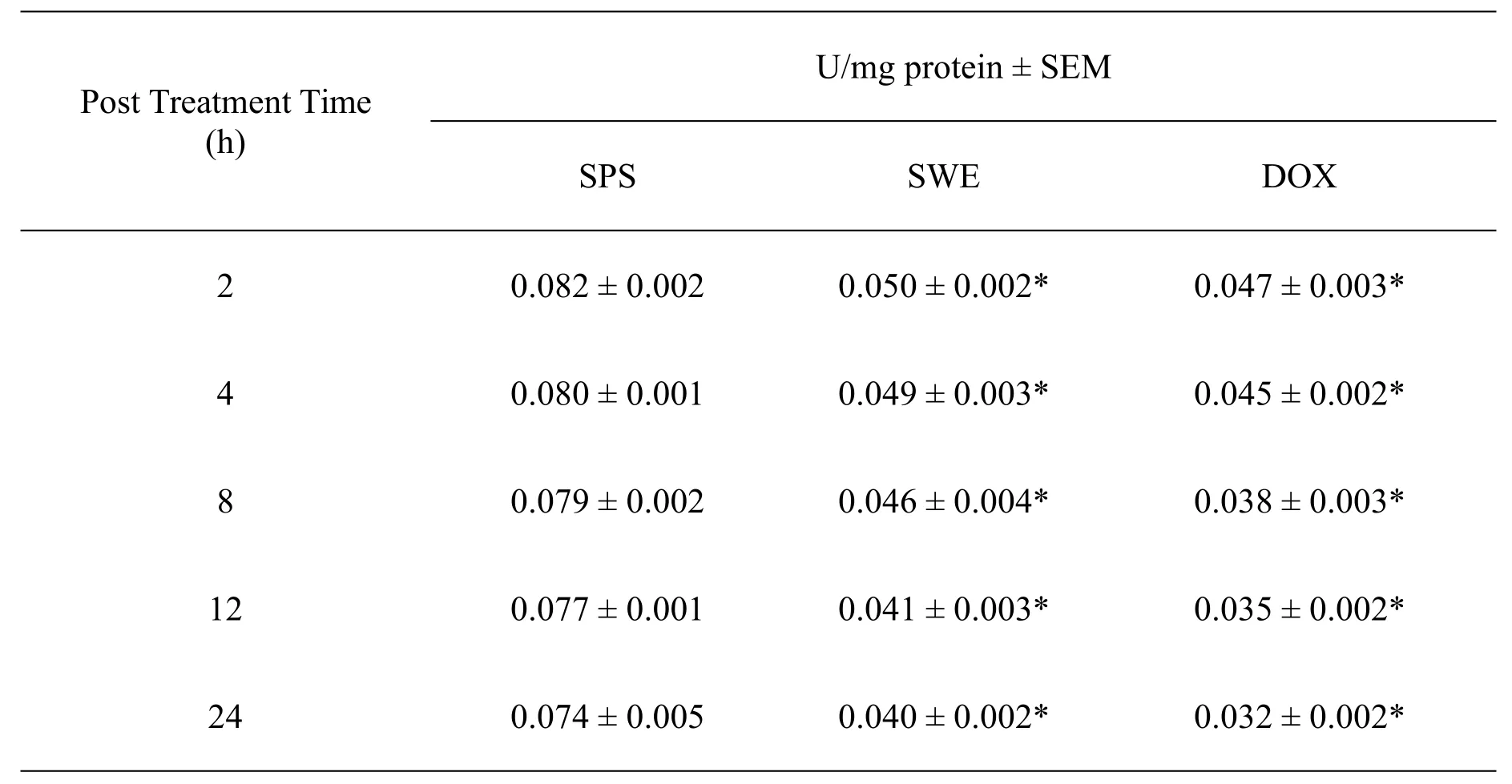
Table 2 The activity of GST in mice bearing DAL treated with 10 mg/kg body weight SWE or DOX
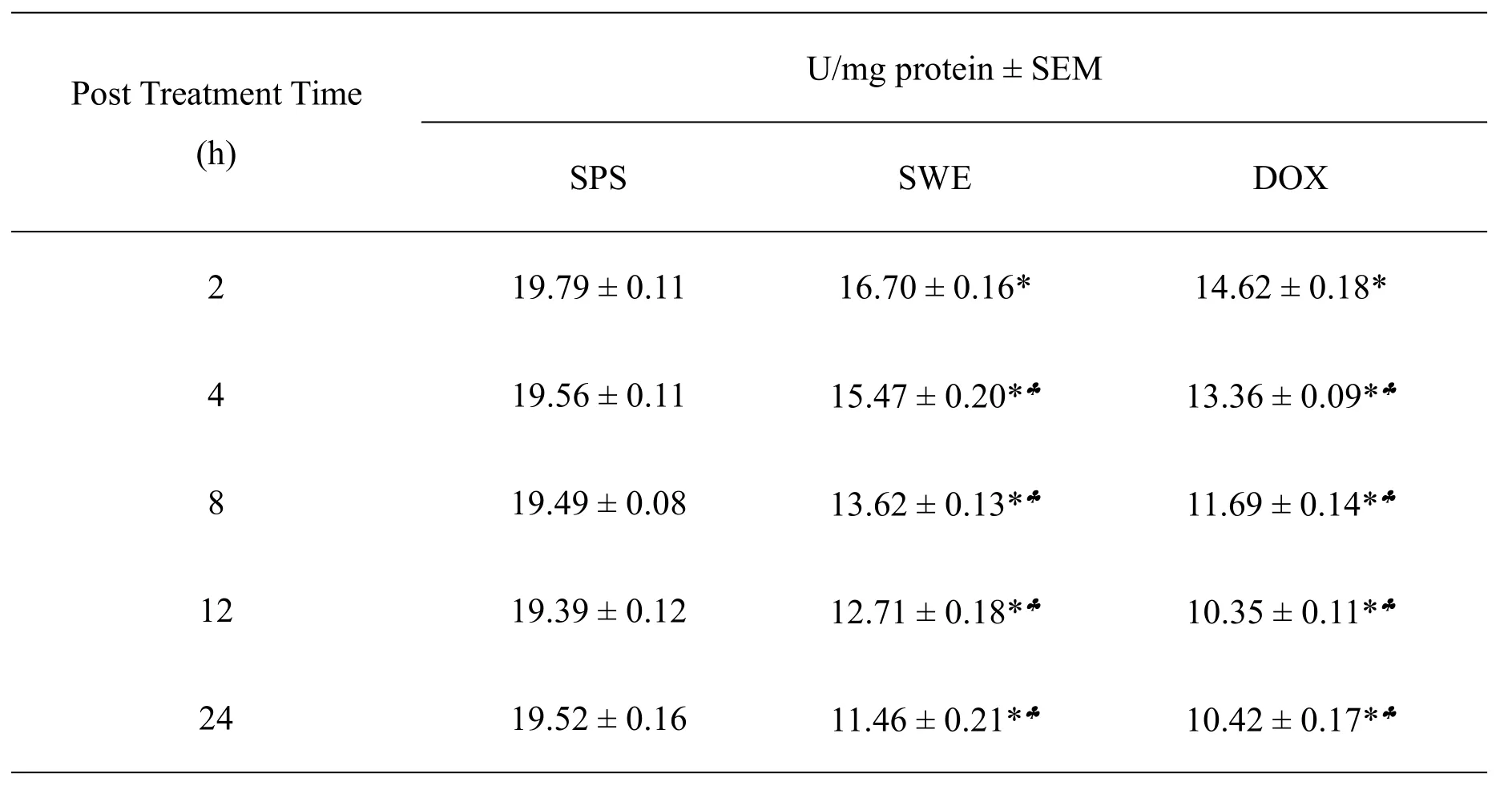
Table 3 The CAT activity of mice bearing DAL treated with 10 mg/kg body weight SWE or DOX
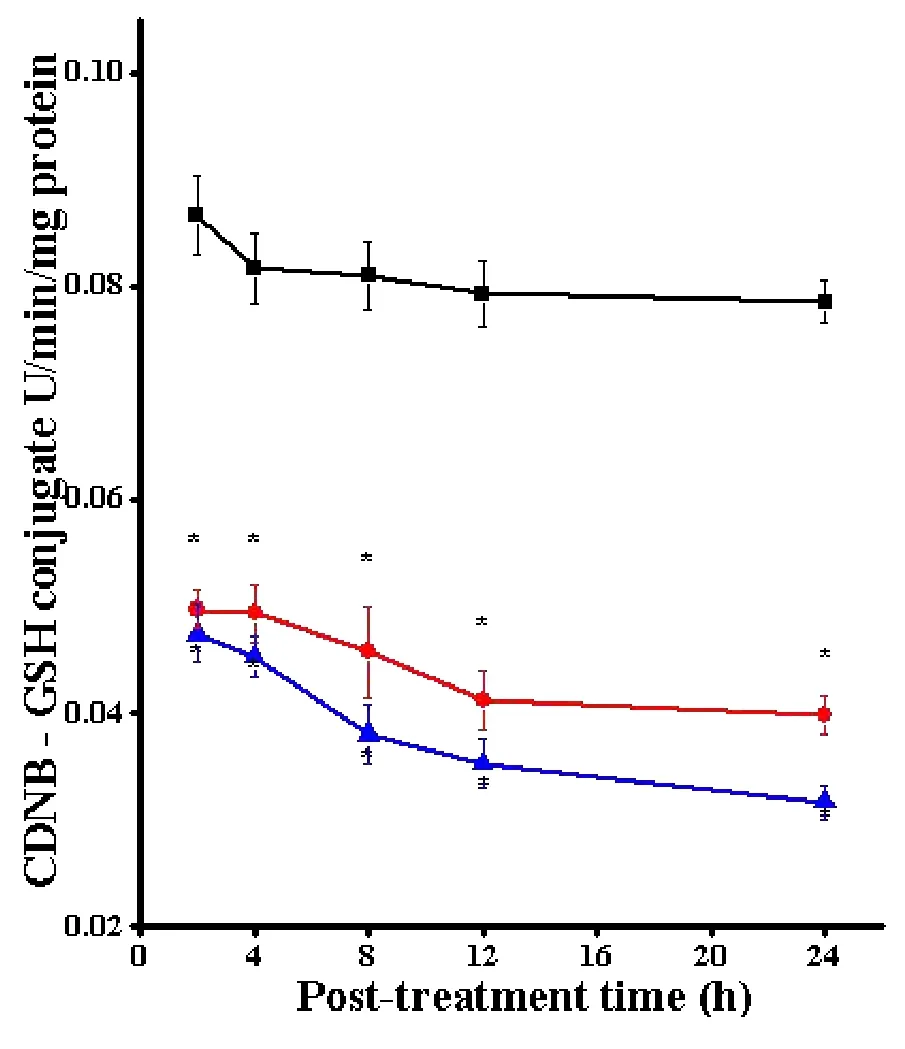
Figure 2 Alteration in the GST activity in the DAL cells treated with SWE.
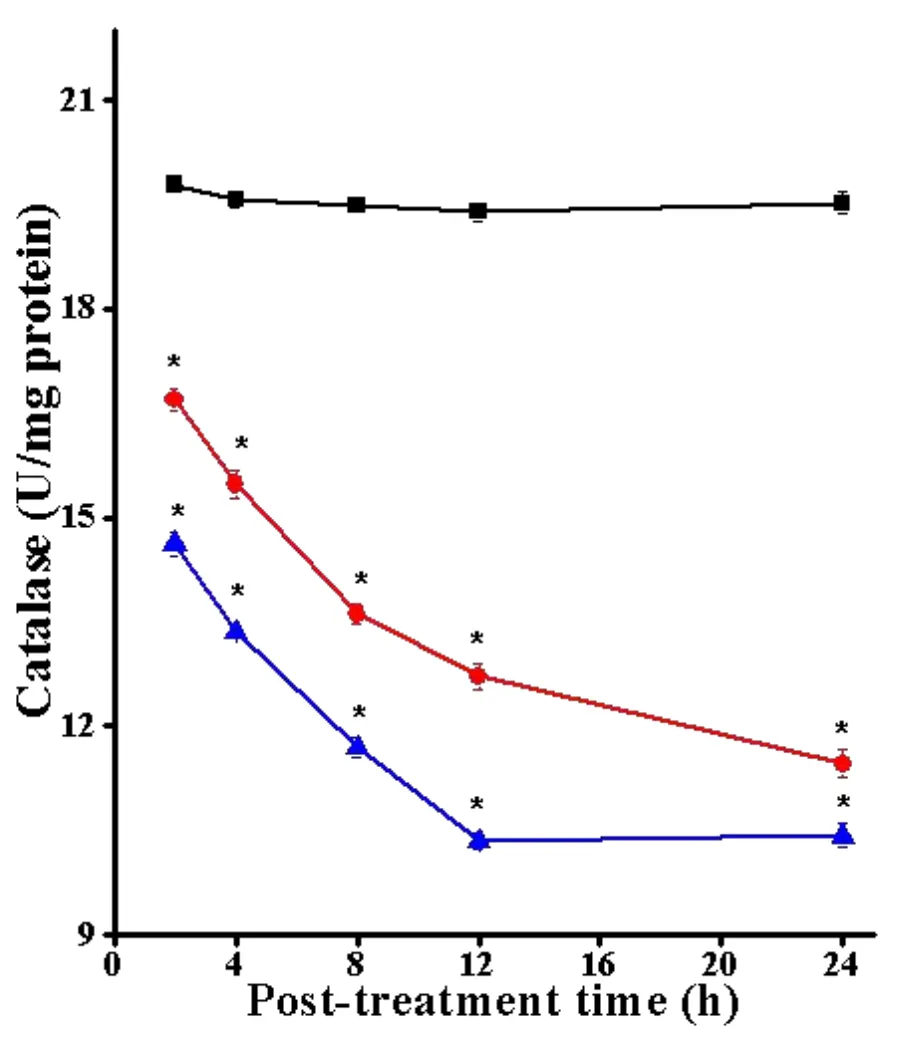
Figure 3 Alteration in the CAT activity in the DAL cells treated with SWE.
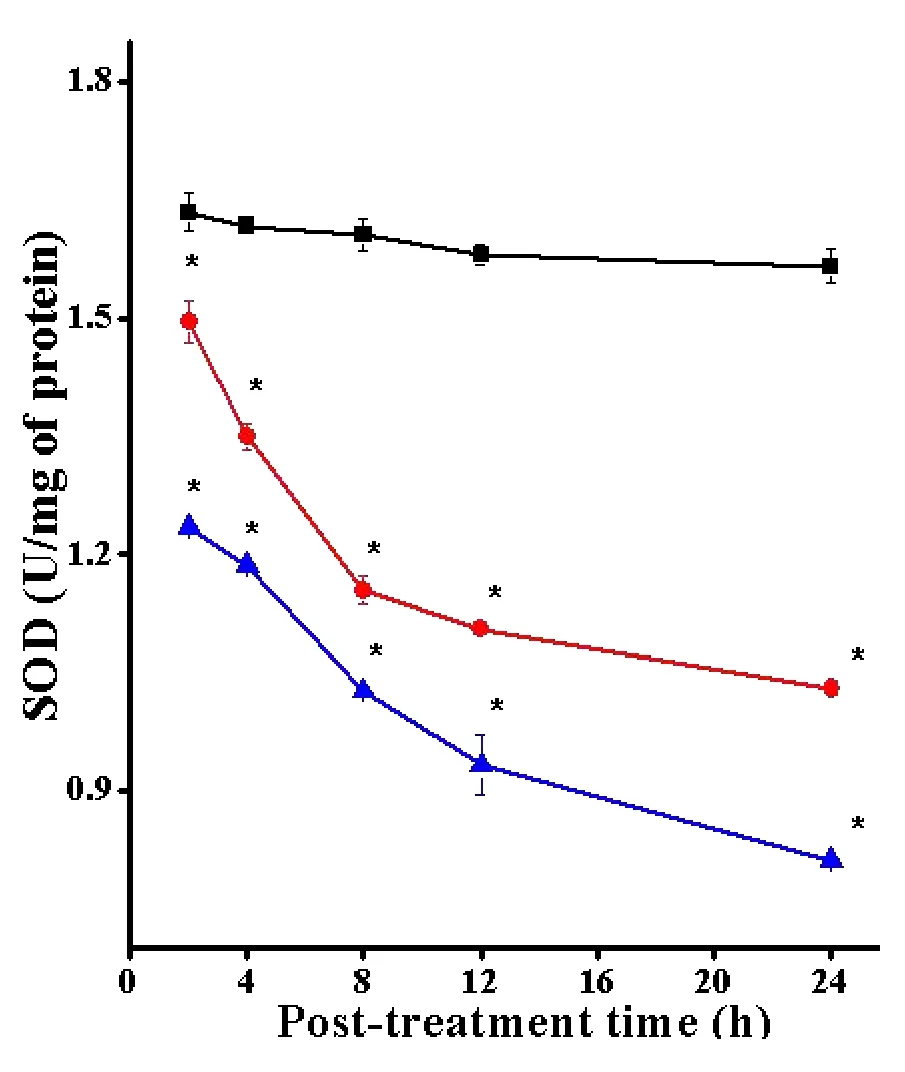
Figure 4 Alteration in the SOD activity in the DAL cells treated with SWE.
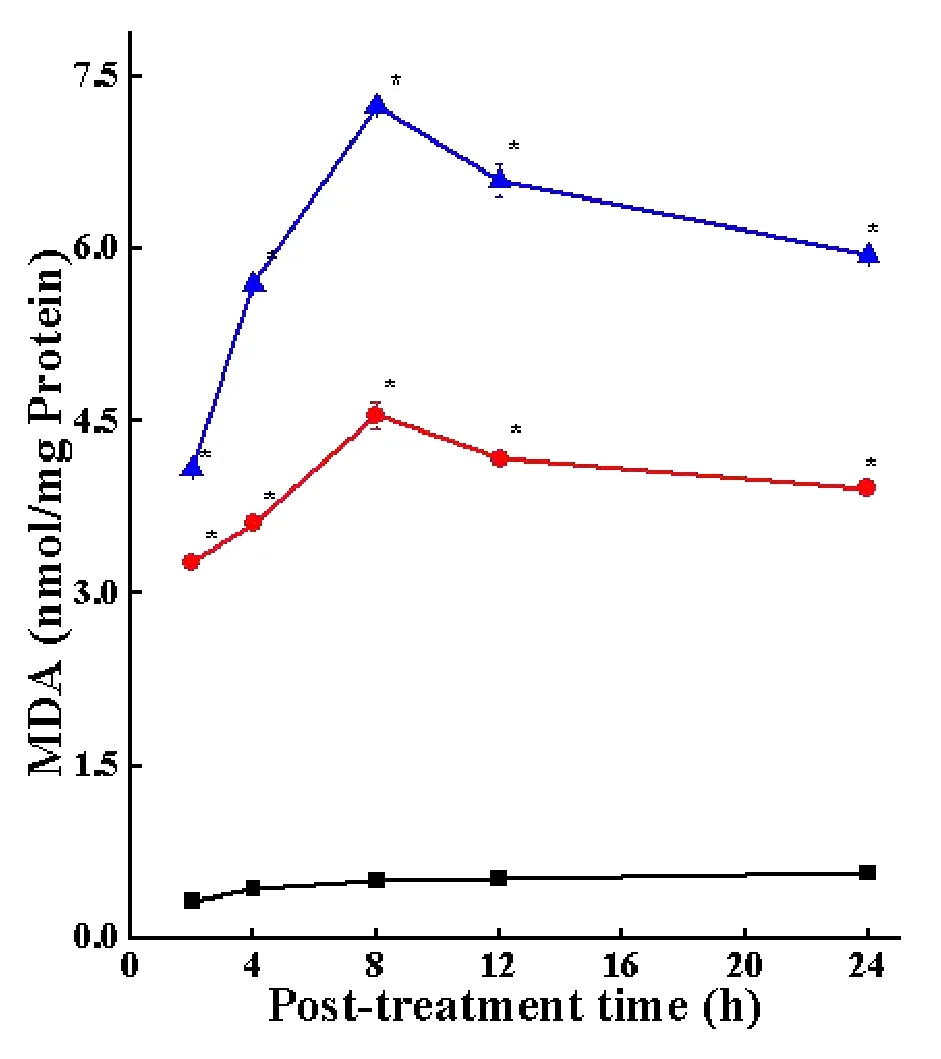
Figure 5 Alteration in the lipid peroxidation in the DAL cells treated with SWE.
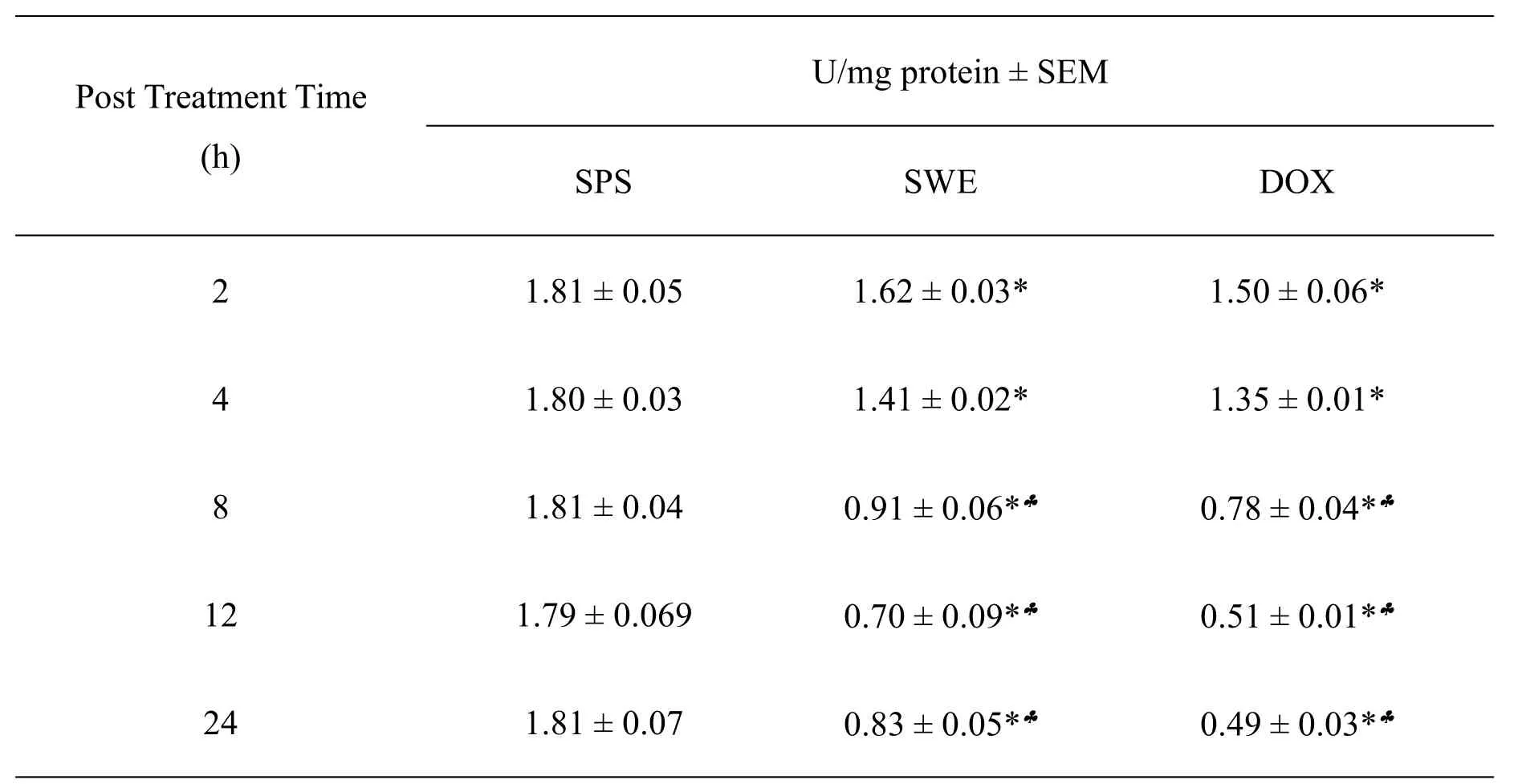
Table 4 The SOD activity of mice bearing DAL treated with 10 mg/kg body weight SWE or DOX
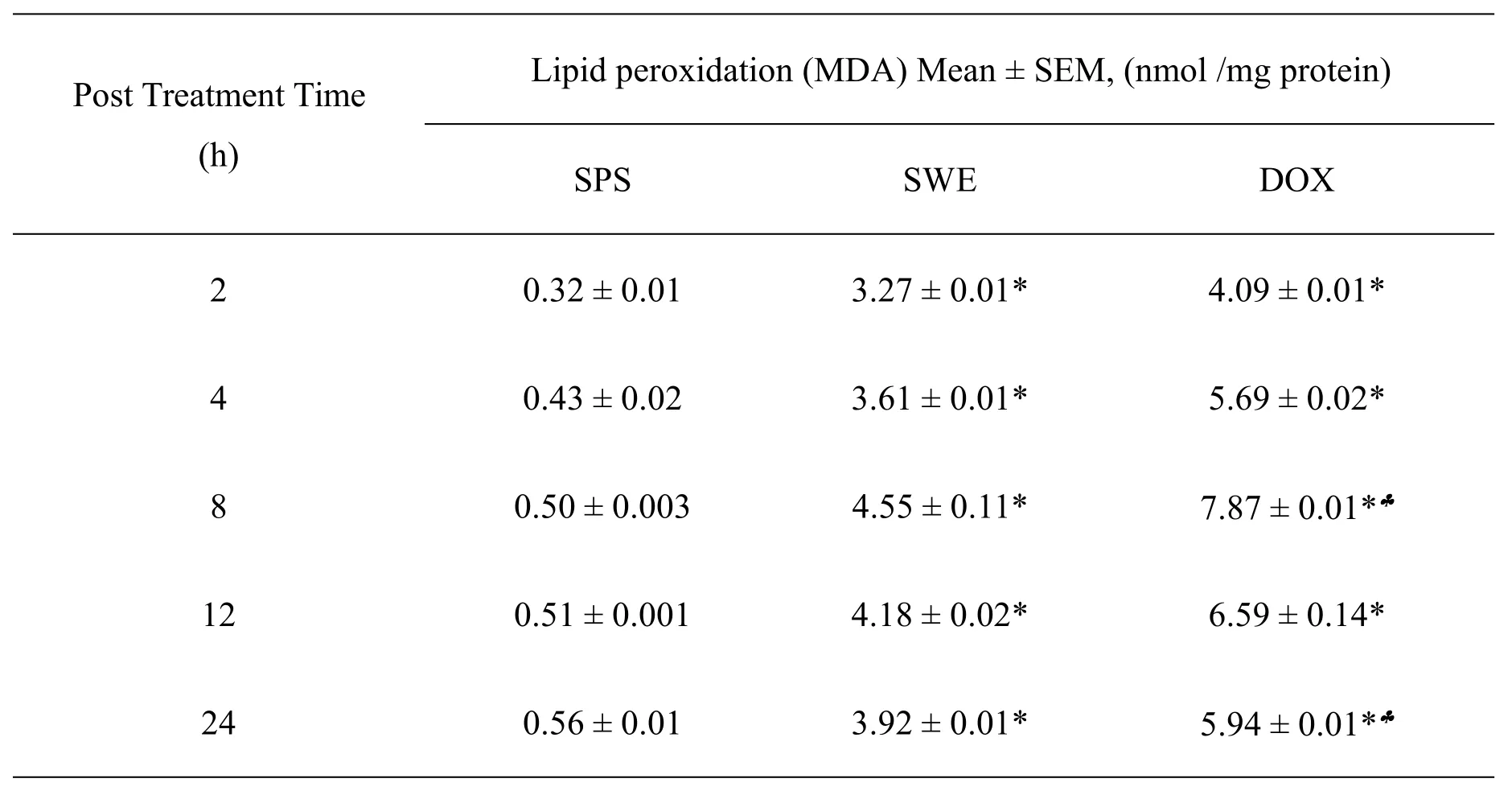
Table 5 The lipid peroxidation in mice bearing DAL treated with 10 mg/kg body weight SWE or DOX
Liver function test
The intraperitoneal administration of 10 mg/kg body weight SWE and DOX for consecutive 9 days did not significantly alter AST,when compared to SPS controlin mouse liver.However,the activities of ALT were significantly(P<0.05)higher in the liver of tumorized mice.Despite this marginal rise the activities of AST and ALT were within normal range(Figure 6,7).The administration of SWE resulted in an elevation in creatinine and uric acid,especially at 12 and 24 h post treatment.However,the differences were not statistically significant.The changes in creatinine and uric acid did not cross the normal level i.e.0.6-1.2 mg/dl and 3.4-7 mg/dl for creatinine and uric acid,respectively(Figure 8,9);indicating the safety of SWE for the kidney.The special data are shown in Table 6.
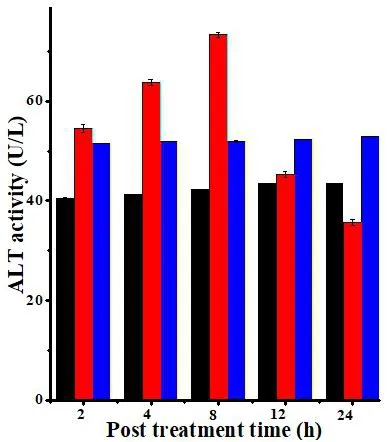
Figure 6 The ALT activity in the DAL bearing mice treated with SWE
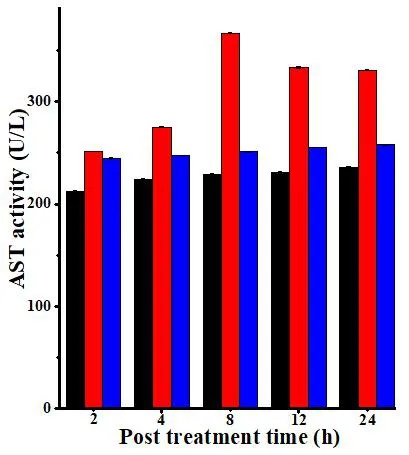
Figure 7 The AST activity in the DAL bearing mice treated with SWE.
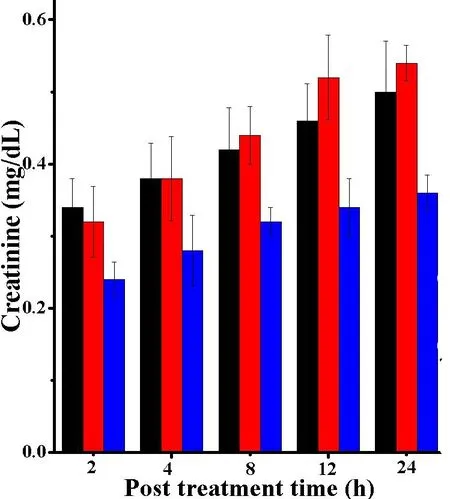
Figure 8 The creatinine contents in the DAL bearing mice treated with SWE.
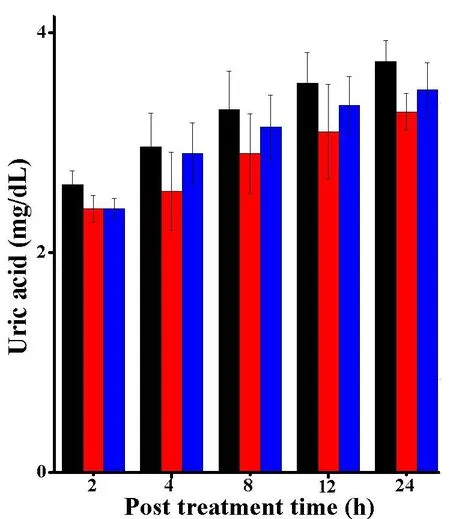
Figure 9 The uric acid contents in the DAL bearing mice treated with SWE
Discussion
The GSH is an important biomolecule which is indispensable in the elimination and detoxification of toxins¸cell differentiation,proliferation and apoptosis.The reduced GSH levels leads to oxidative stress[27-29].However,the elevated level of glutathione is responsible for cancer progression,chemoresistance and treatment failure in cancer patients[30-32],whereas alleviation in GSH causes enhanced oxidative stress that make tumor cells more amenable to chemotherapy or radiotherapy[33-36].ThetreatmentofSWE decreased the glutathione contents in the DAL cells in a time dependent manner,and this reduction in GSH concentration may have elevated the oxidative stress and killed the DAL cells leading to tumor regression.The ethanol extract ofColocasia giganteahas been reported to deplete the GSH contents in DAL cells[37].
GSTs belong to phase II detoxification enzyme family.The GSTs play crucial roles in the protection of cells from the reactive electrophilic attack.They also catalyze the detoxification of numerous endogenous and exogenous electrophilic substances [38].The overexpression ofGSTsislinked to tumor resistance to chemo-and radio-therapy[39-41].Treatment of DAL cells with SWE had a negative effect on the activities of GST.Similarly,ethanol extract ofColocasia giganteahas been found to reduce the GST activity and kill DAL cells[37].Phenethyl isothiocyanate present in various cruciferous vegetables has been reported to reduce GST activity in cholangiocarcinoma cellsin vitro[42].
CAT isoneoftheimportantdetoxifying enzymes which is involved in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide and convert it into molecular oxygen and water[43].The tumor cells express low CAT than normal tissues due to the higher oxidative stress in tumor cells[44].Despite this fact CAT is involved in the protection of tumor cells and resistance to chemotherapy.
SODs are ubiquitously present in the organisms utilizing oxygen for their energy requirements.The SODs detoxify the superoxide anion free radicals generated during aerobic respiration and they convert this free radical into oxygen and less toxic hydrogen peroxide [46-48].SODsare involved in resistance to chemotherapy[49-51].Augmented levels of SODs are correlated with cancer cell survival[51].The DAL cells showed higher SOD activity,whereas treatment of DAL tumorized mice with SWE caused a time dependent depletion in their activities,which may have killed tumor cells effectively in our earlier study[8,9].The ethanol extract ofColocasiagiganteahas been reported to reduce the SOD activity in DAL cells earlier[37].
The lipid peroxides are produced by cells and serve as signaling molecule through post translational modification of proteins[52].Lipid peroxides exert cytotoxic effect[53].The lipid peroxidation is involved in the non-apoptotic form of cell death and its role in triggering cell death is now well understood[53,54].The SWE treatment has increased lipid peroxidation in a time dependent manner and this increase in the lipid peroxidation may have contributed in its own way to the death of DAL cells in our earlier study[8,9].The ethanol extract ofColocasia giganteaalso killed DAL cells by increasing the lipid peroxidation[37].TheAlstonia scholarishas been reported to kill Ehrlich ascites tumor cells by increasing lipid peroxidation earlier[55].
The liver is the main metabolic organ,which synthesizes AST,ALT,creatinine and uric acid.Determination of the activity of transaminase enzyme can provide valuable information on liver toxicity[56].The intraperitoneal administration of SWE(10 mg/kg body weight)for consecutive 9 days was safe as it did not significantly alter AST and ALT,creatinine and uric acid in the mice.Thoughthere was aminorchangeinboth creatinine and uric acid levels,these changes did not cross the normal level i.e.0.6-1.2 mg/dl[57]and 3.4-7 mg/dl[58]for creatinine and uric acid,respectively,indicating the safety of SWE administration.
The exact mechanism of decline in the activities of GST,CAT and SOD,and the GSH contents by administration of SWE in the tumorized mice is not known.It is plausible that SWE treatment may have reduced the upregulated expression of Nrf2 signaling leading to down-regulation of GSH contentsand GST,CAT and SOD activities followed by increased lipid peroxidation.The Nrf2 has been reported to be overexpressed in the tumor cells[59,60],which increases the amount of GSH,GST,CAT and SOD in the tumors.
Conclusion
In our study,we found that tumor cells had higher amount of GSH,GST,CAT,SOD;the treatment of DAL cells with SWE reduced the level of GSH and the activities of GST,CAT,SOD and increased the lipid peroxidation,which may be responsible for its tumor cell killing effects.
