Successful ex vivo expansion of mouse hematopoietic stem cells
Hideo Ema
State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, National Clinical Research Center for Hematological Disorders, Institute of Hematology and Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Tianjin,China
Abstract
Keywords:Ex vivo expansion, Hematopoietic stem cells, Polyvinylalcohol, Self-renewal
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) have been used for stem cell transplantation to treat patients with leukemia and other diseases for several decades.1However,HLA-matched donors are often unavailable, and the proportion of HSCs in donor cell sources is limited.Thus, methods enabling ex vivo expansion of HSCs have long been sought.HSCs easily differentiate in vitro, and it is difficult to induce their selfrenewal while preventing differentiation.A number of culture systems designed to expand mouse HSCs in vitro have been reported.2However, it is sometimes difficult to reproduce published data, mostly because culture conditions are unstable, and in vivo assays used to determine the number of expanded HSCs are not precise.
Yamazaki et al.performed a series of experiments in an effort to establish stable and reproducible culture conditions.3-5First they found that recombinant albumin can replace bovine serum albumin (BSA) in serum-free culture of HSCs.3They then extensively optimized serum-free culture conditions,5and finally showed that polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) can replace recombinant albumin.4
Several decades ago PVA was suggested to serve as a replacement for BSA in embryology experiments,6but investigators have continued to use BSA in many types of tissue cultures.Now, Yamazaki's team has tested PVA and found it superior to albumin for use in HSC expansion.4Their serum-free and albumin-free media consists of 0.1% PVA in Ham's F-12 medium with a mixture of insulin, transferrin,selenium, and ethanolamine from Gibco.It was previously known that HSCs efficiently divide in the presence of stem cell factor (SCF) and thrombopoietin (TPO).7Yamazaki's team retitrated concentrations of these cytokines and reported that in their system a combination of 10ng/mL SCF and 100ng/mL TPO produced optimal expansion.4They also reported that HSCs undergo more efficient expansion in fibronectin-coated dishes.4
Competitive repopulation has been used as the most reliable assay to detect HSC activity.For such analysis, test donor and competitor cells are usually cotransplanted into myeloablated mice.Researchers have recently become aware that competitive repopulation can be undertaken in normal mice also.8-10In that case,endogenous HSCs in the host mouse simply complete with transplanted test donor-derived HSCs.The percent chimerism in peripheral blood is reflected by the ratio of the number of donor HSCs to the number of host HSCs.
In vivo limiting dilution type assays have been used to measure the number of HSCs in culture, as the frequency of HSCs in cultured cells is usually very low.A large number of samples at three or more appropriate cell doses should be analyzed to determine HSC frequency with reliability.11However, a very small number of mice per cell dose are often used for practical reasons, making it difficult to estimate HSC frequency with precision.Yamasaki's team estimated HSC frequency in their culture after a month by in vivo limiting dilution and calculated the fold-increase as 236-899.4
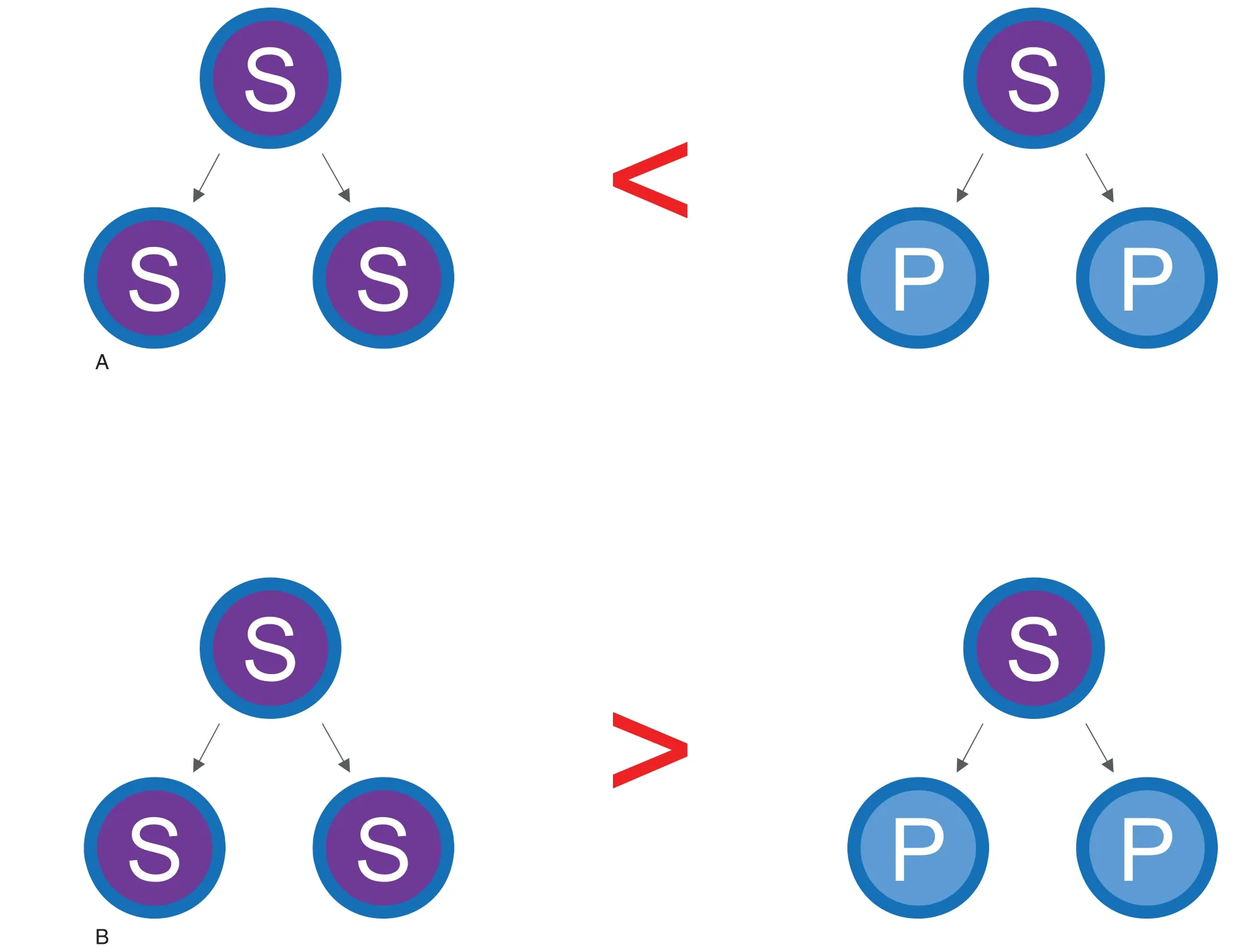
Figure 1.Symmetrical HSC self-renewal takes place in the presence of PVA.In this model,PVA increases the probability of symmetrical self-renewal of HSCs.Symmetrical differentiation: an HSC (S) gives rise to two progenitor cells (P).Symmetrical self-renewal: an HSC gives rise to two HSCs.(A) The probability of symmetrical differentiation exceeds that of symmetrical self-renewal in the presence of SCF and TPO.(B)The probability of symmetrical self-renewal exceeds that of symmetrical differentiation in the presence of SCF, TPO, and PVA.
Here, I have calculated the fold-increase in a different way using their data.4It is estimated that a C57BL/6 mouse has~4.5×108bone marrow cells in its entire body.12Given that CD150+CD34-c-Kit+Sca-1+Lin-(CD150+34-KSL) cells account for ~0.001% bone marrow cells,13a mouse harbors~4500 CD150+34-KSL cells.After transplantation with cultured cells into normal mice, on average, 10% chimerism was obtained,as reported in Yamazaki's study.4Assuming that transplanted HSCs are functionally equivalent to host HSCs and all transplanted HSCs engraft, the number of HSCs (N) in cultured cells can be calculated as:N/(4500+N)=0.1.Thus,in this case, N=500.Yamazaki's team used 50 CD150+34-KSL cells to initiate the culture.Thus, the fold-increase of CD150+34-KSL cells in culture appeared to be 10 by my calculation.The percentage of CD150+34-KSL cells in bone marrow varies, depending on how sorting gates, particularly the CD150 gate,are set.13If that gate is relatively wide,as was the one used by Yamazaki et al.,4the fold-increase could be up to 40.Nevertheless, their data clearly show significant ex vivo expansion of functional HSCs.
An important question to be addressed now is how PVA acts to support HSC self-renewal,as PVA may function differently from recombinant albumin.Currently,we assume that PVA reversibly antagonizes HSC differentiation,enabling more symmetrical selfrenewal than symmetrical differentiation (see Fig.1).Once we clarify the mechanism,we should be able to apply this protocol to achieve safe and efficient expansion of human HSCs expansion in the near future.
- 血液科学的其它文章
- A chemotaxis model to explain WHIM neutrophil accumulation in the bone marrow of WHIM mouse model
- Interleukin-12 supports in vitro self-renewal of long-term hematopoietic stem cells
- The disruption of hematopoiesis in tumor progression
- Progress of cGVHD pathogenesis from the perspective of B cells
- Molecular mechanisms for stemness maintenance of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells
- Tumor heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia:insights from single-cell sequencing